-
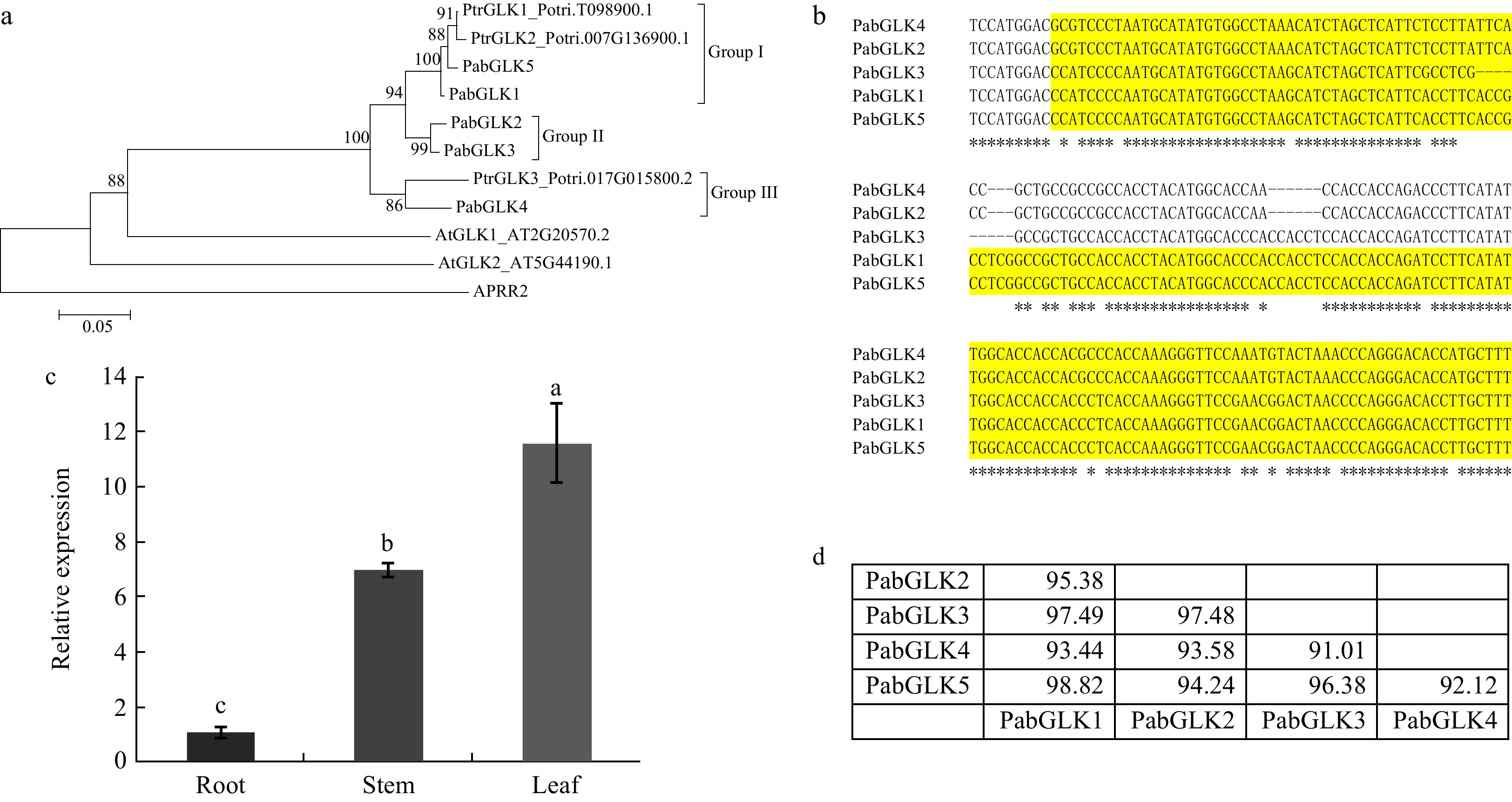
Figure 1. Identification of GLKs that are expressed in P. alba × P. berolinensis. (a): Phylogenetic relationship among GLKs from P. alba × P. berolinensis, P. trichocarpa, and Arabidopsis. (b): A multiple sequence alignment of the identified PabGLKs. The colored region was used for RNAi. (c): Tissue specific expression levels of the PabGLKs in P. alba ×
P. berolinensis quantified with qRT-PCR. 18S rRNA and α-Tubulin were used as endogenous control. (d): Nucleotide sequence similarities among differnt PabGLKs in P. alba × P. berolinensis. -
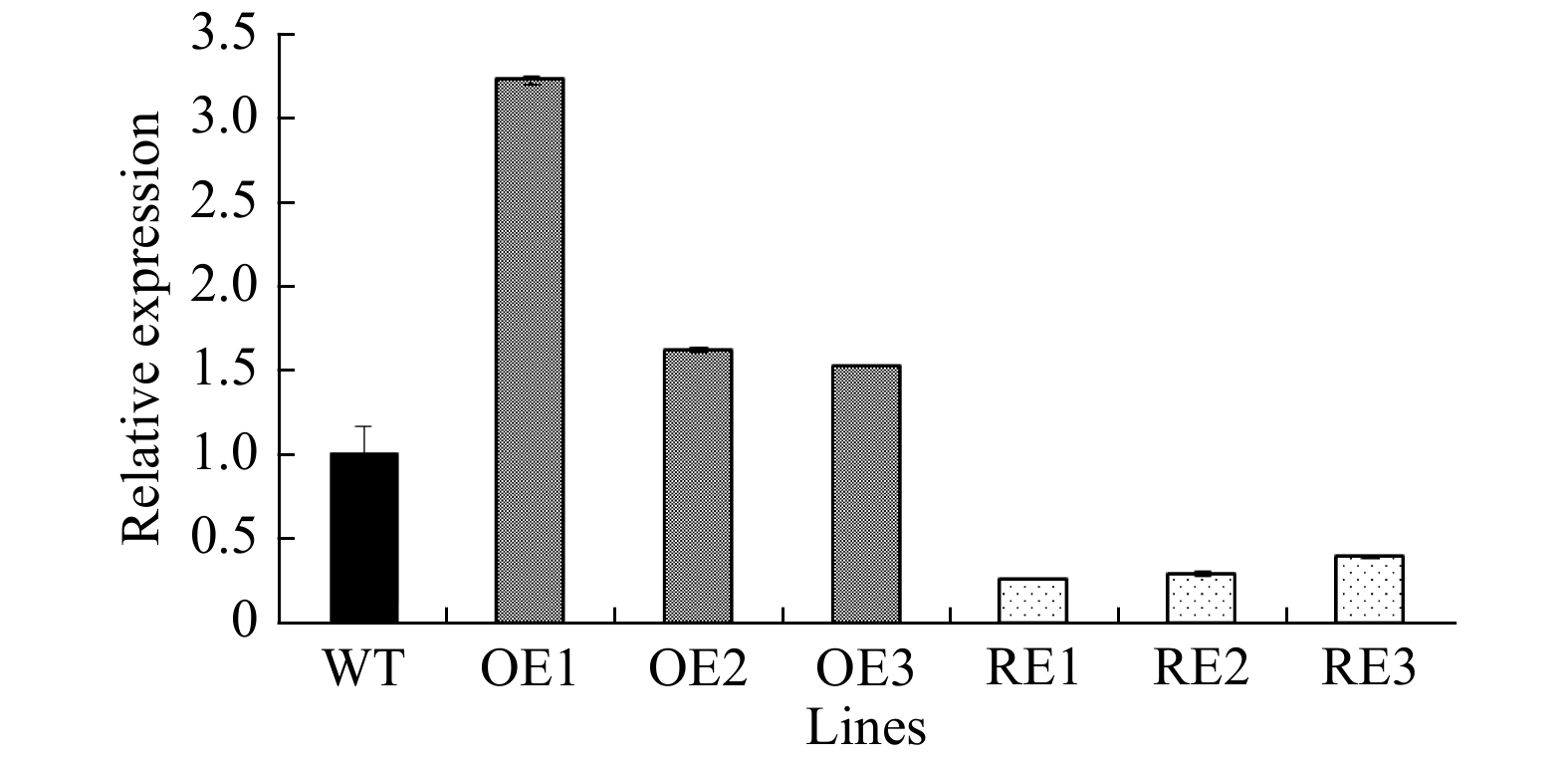
Figure 2. Relative PabGLK5 transcript levels in PabGLK5 overexpression lines and the total transcript levels of all five PabGLKs in PabGLK RNAi lines. OE, overexpression lines of PabGLK5; RE, repression lines of PabGLKs; WT, wildtype.
-
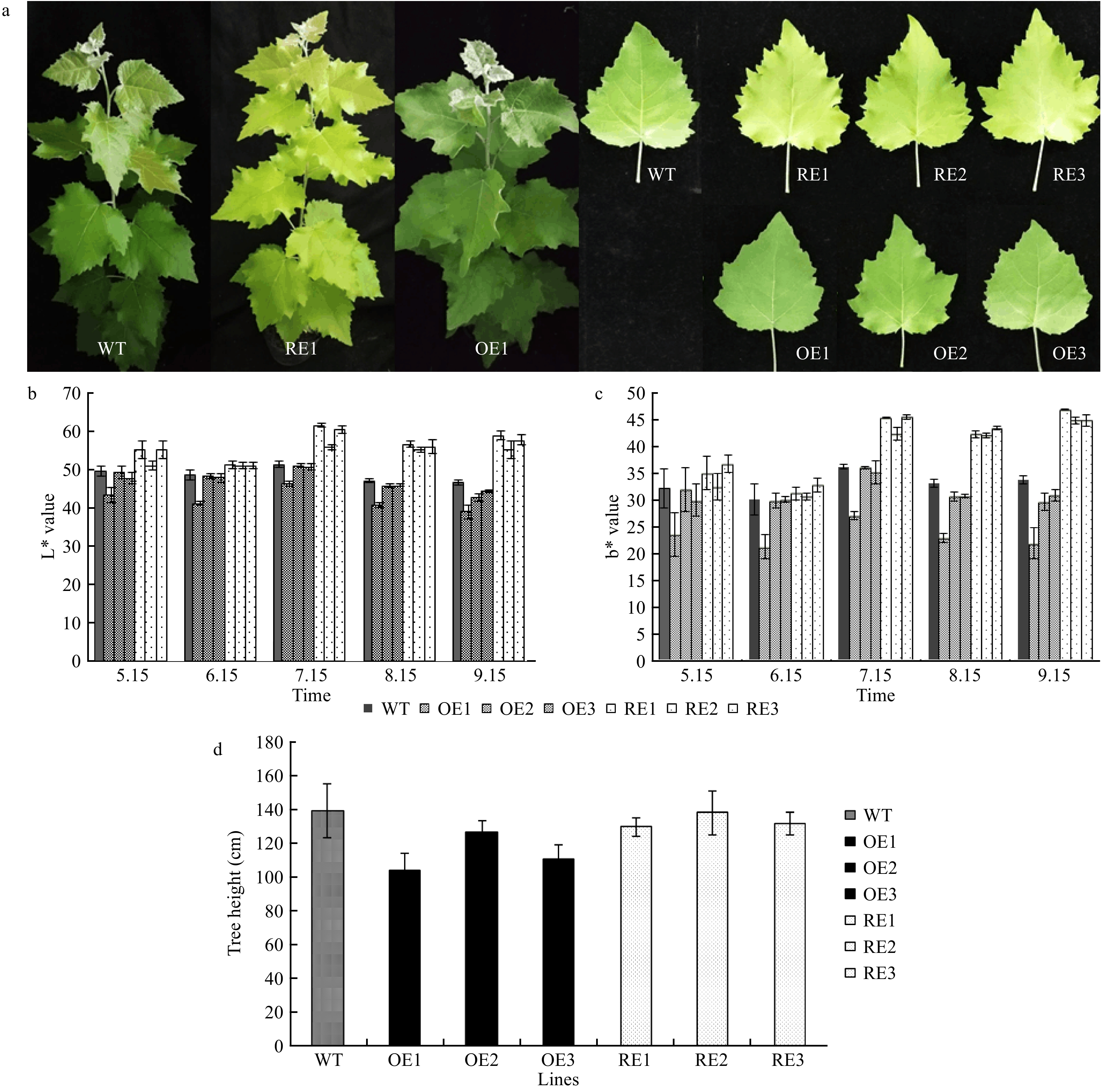
Figure 3. Phenotypic characterization of the PabGLK transgenic lines. (a): The yellow-green leaf phenotype of the PabGLK RNAi lines. (b) and (c): L* and b* values of the transgenic lines and WT measured by the CIELab color system. (d): Plant heights of one-year-old WT and transgenic lines. OE, overexpression lines of PabGLK5; RE, repression lines of PabGLKs; WT, wildtype.
-
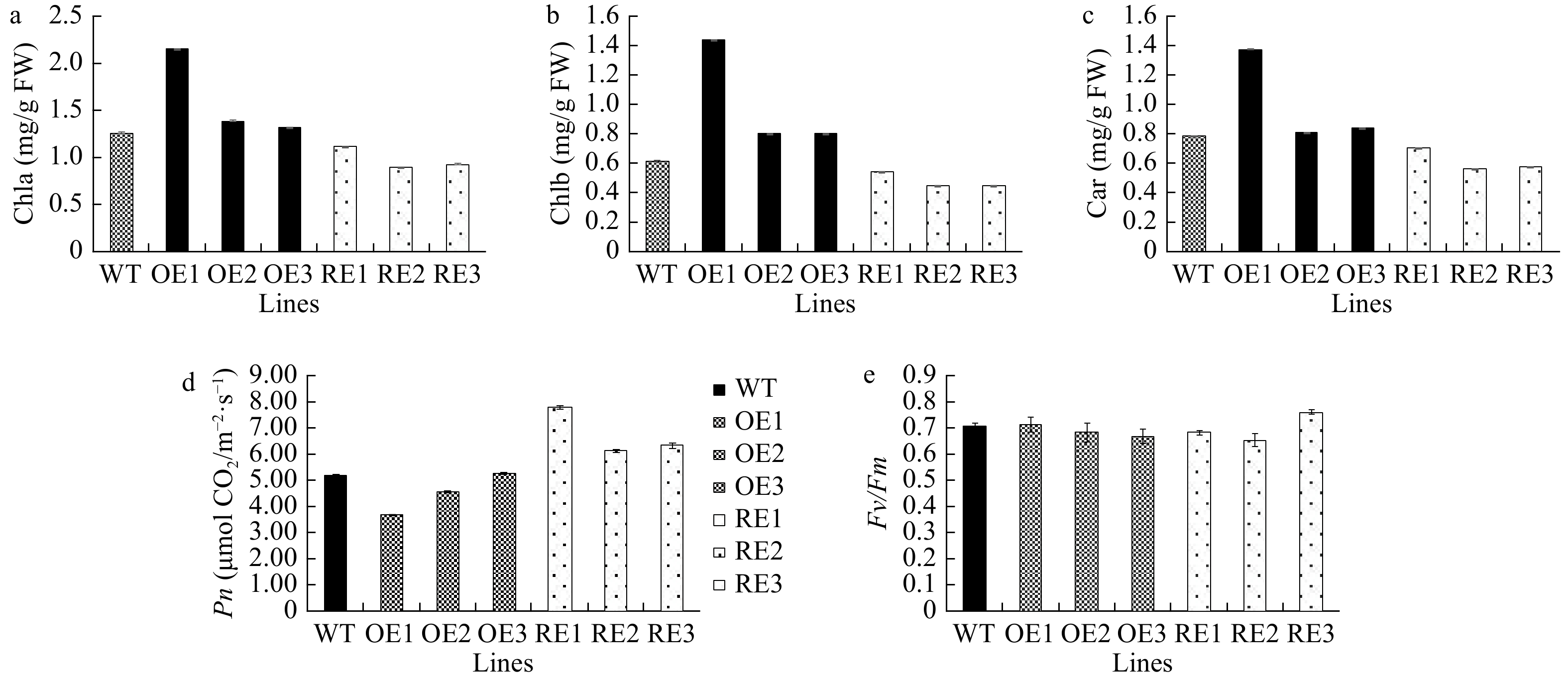
Figure 4. Pigment contents and photosynthetic and fluorescence parameters of the WT and transgenic lines. OE, overexpression lines of PabGLK5; RE, repression lines of PabGLKs; WT, wildtype. (a), (b) and (c) show the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid in the WT and transgenic lines, respectively. (d) and (e) show photosynthetic parameters Pn and Fv/Fm, respectively.
-
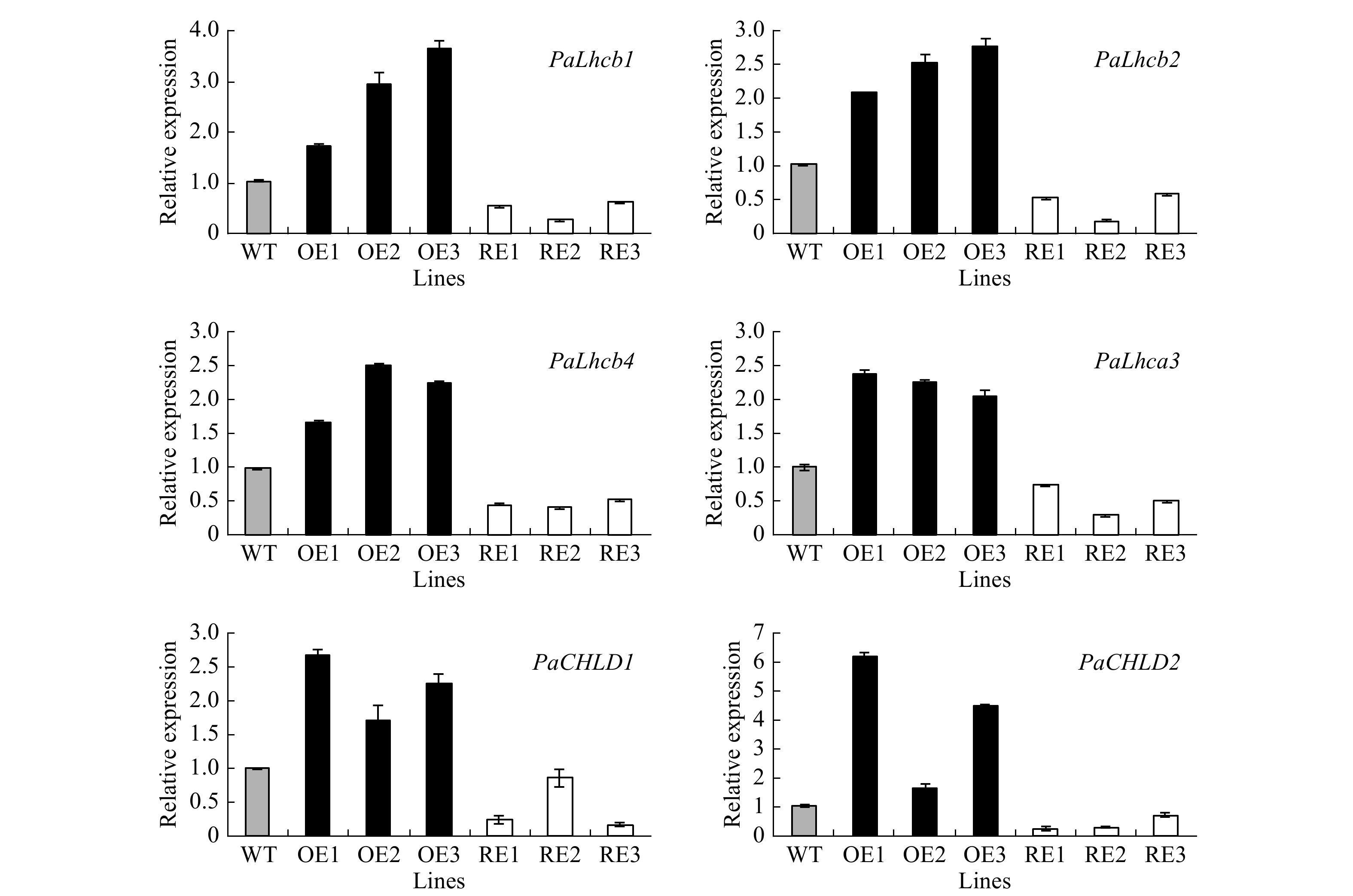
Figure 5. Expression profiles of photosynthesis-related genes in transgenic poplar. OE, overexpression lines of PabGLK5; RE, repression lines of PabGLKs; WT, wildtype.
-
Primers Sequences (5'-3') PaGLK-RNAi-Cis-NcoI CATGCCATGGCCATCCCCAATGCATATGTG PaGLK-RNAi-Cis-AscI TTGGCGCGCCGCAGGAAATCTAGTTGCCAGT PaGLK-RNAi-Anti- XbaI GCTCTAGACCATCCCCAATGCATATGTG PaGLK-RNAi-Anti-BamHI CGCGGATCCGCAGGAAATCTAGTTGCCAGT Table 1. Primers used for RNAi vector construction.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(1)