-
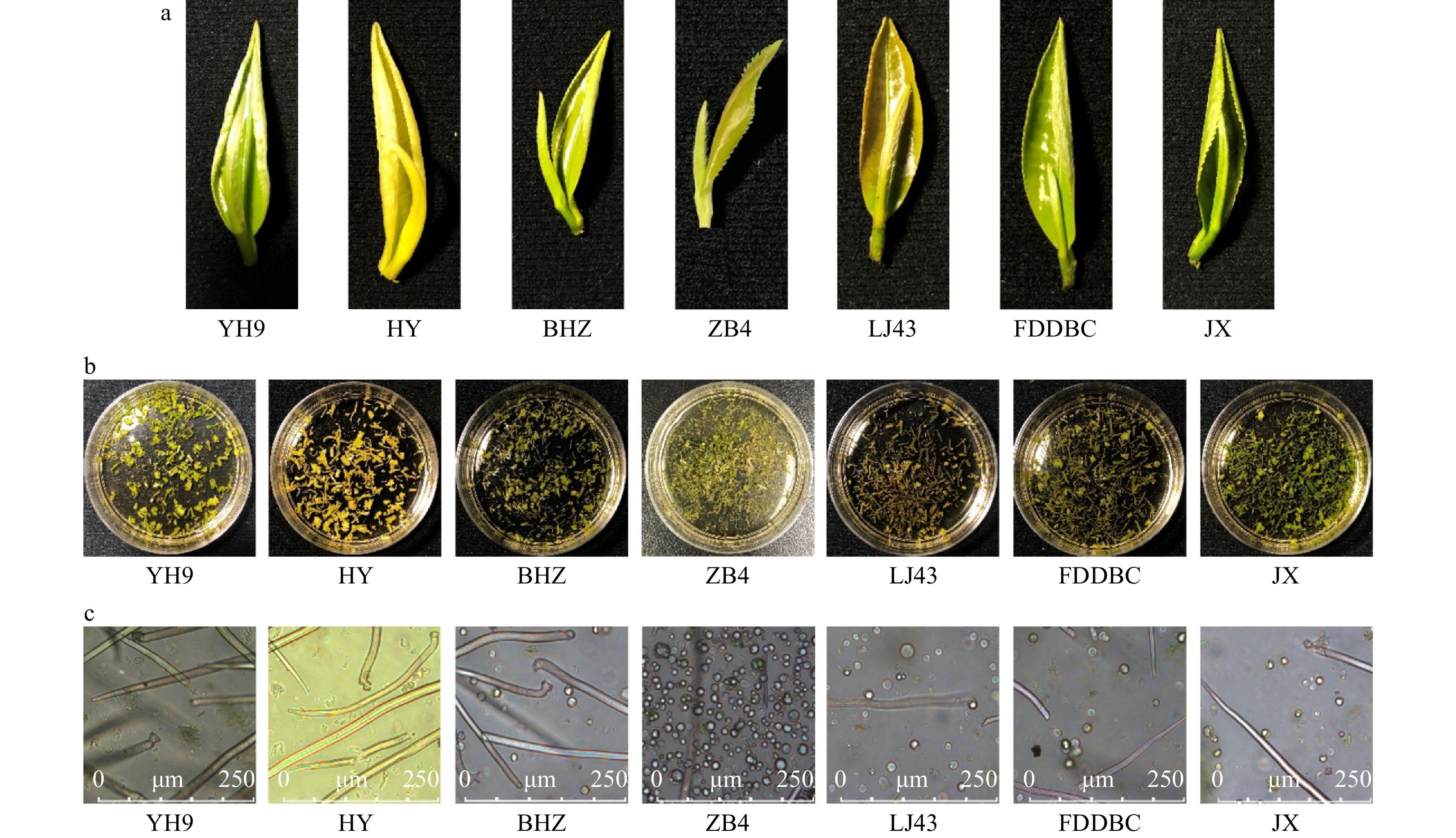
Figure 1. Protoplasts isolated from different tea plant cultivars. (a) Materials used for protoplast isolation. (b) Leaf strips in enzyme solution before enzyme digestion. (c) Isolated protoplast in enzyme solution. YH9, Yinghong 9; HY, Huangyu; BHZ, Baihaozao; ZB4, Zhongbai 4; LJ43, Longjin 43; FDDBC, Fuding Dabaicha; JX, Jinxuan.
-
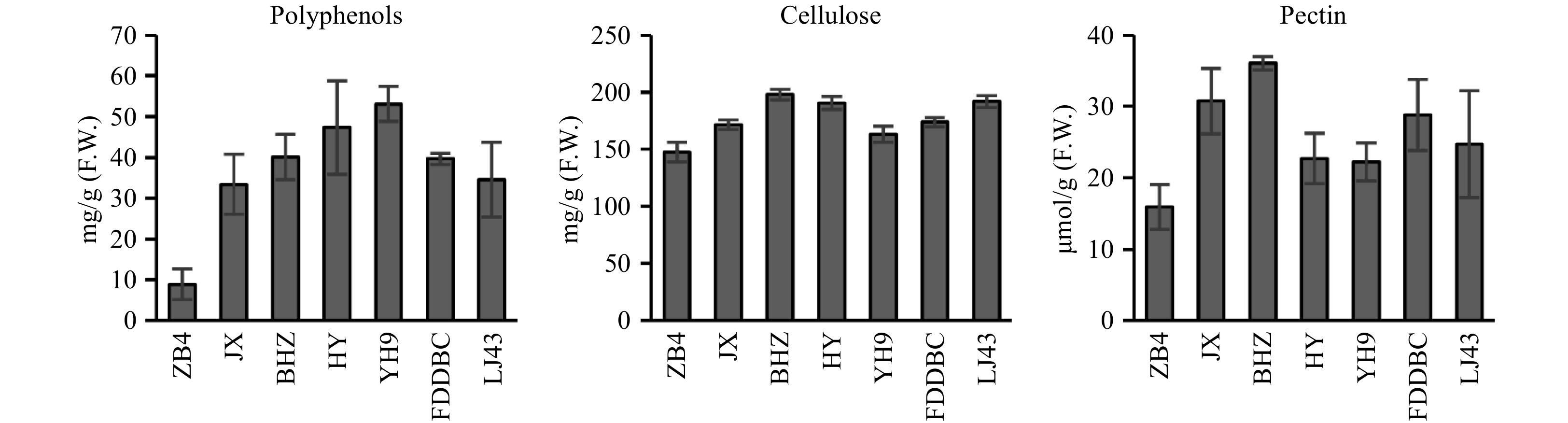
Figure 2. Polyphenols, cellulose and pectin content analysis of different tea plant cultivars. YH9, Yinghong 9; HY, Huangyu; BHZ, Baihaozao; ZB4, Zhongbai 4; LJ43, Longjin 43; FDDBC, Fuding Dabaicha; JX, Jinxuan.
-
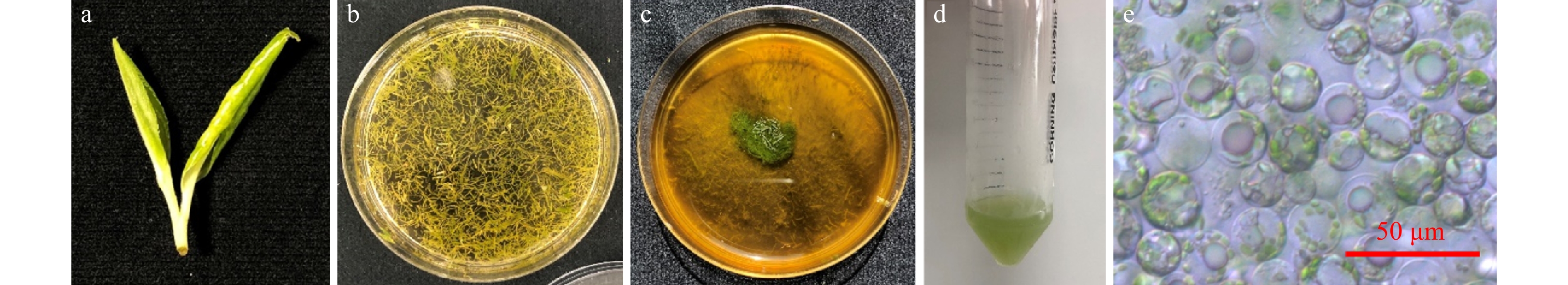

Figure 3. Isolate protoplasts from ‘ZB4’. (a) Leaves used for protoplasts isolation. (b) Leaf strips before enzyme digestion. (c) Leaf strips after enzyme digestion (3% cellulase R-10 and 0.3% macerozyme R-10) for 12 h. (d) Purified protoplasts solution. (e) Purified protoplasts. Bar: 50 μm.
-
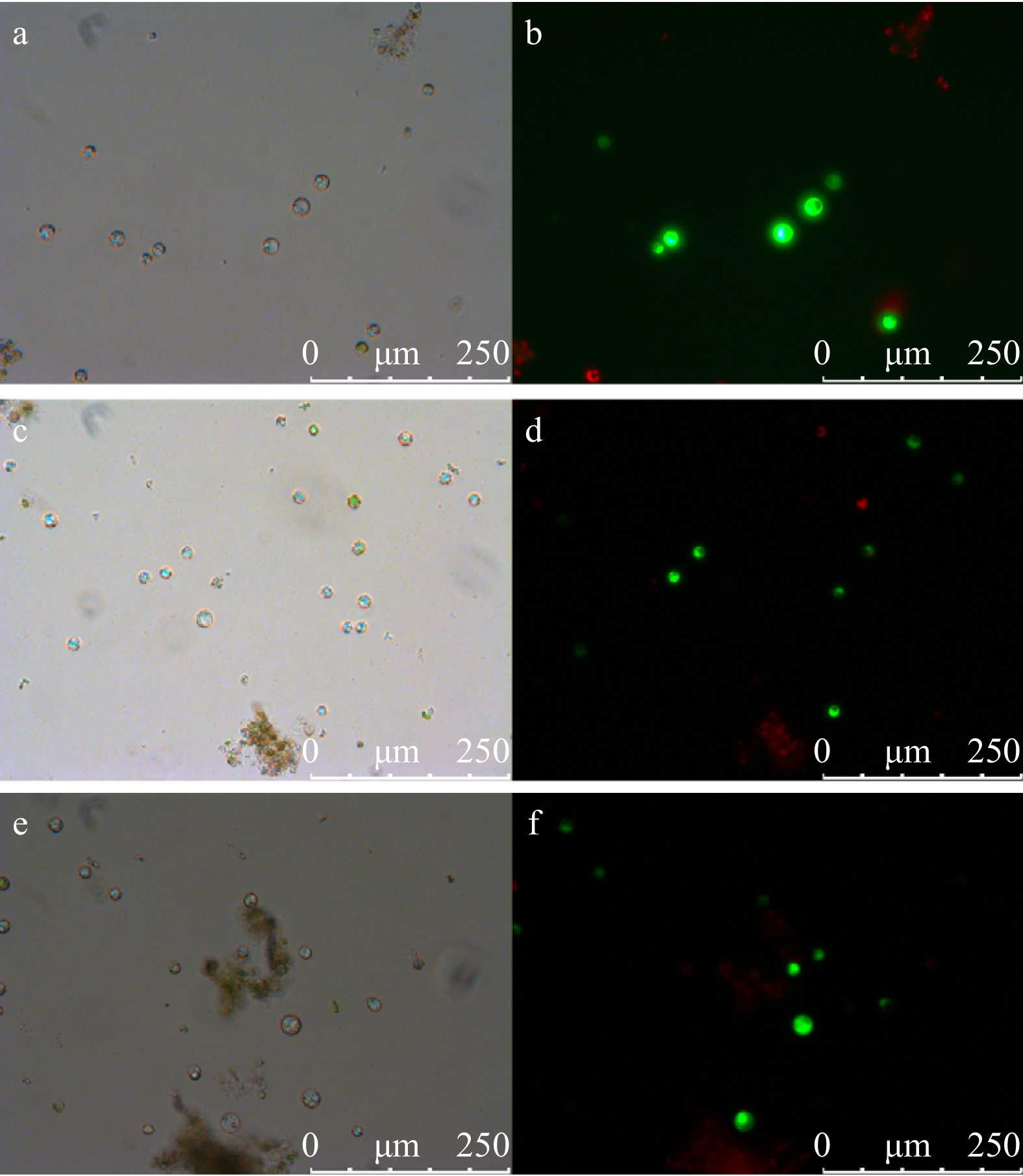
Figure 4. Transfection of tea plant mesophyll protoplast with 35S::YFP construct (pSAT6-EYFP-N1 4.6 kb). (a, c, e) Tea plant mesophyll protoplasts in bright field. (b, d, f) YFP expressed in tea plant mesophyll protoplasts.
-
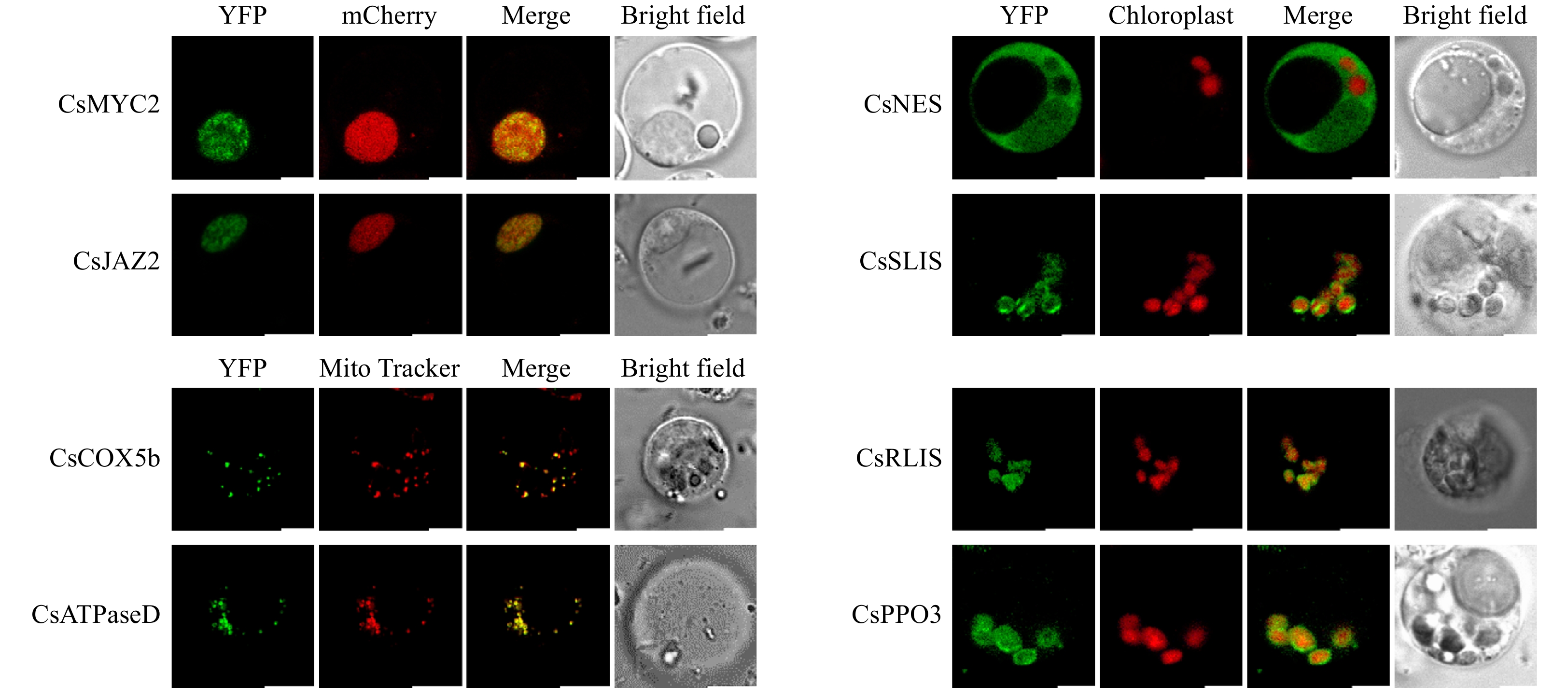
Figure 5. Subcellular localization analysis of different tea plant proteins. Bar: 5 μm.
-
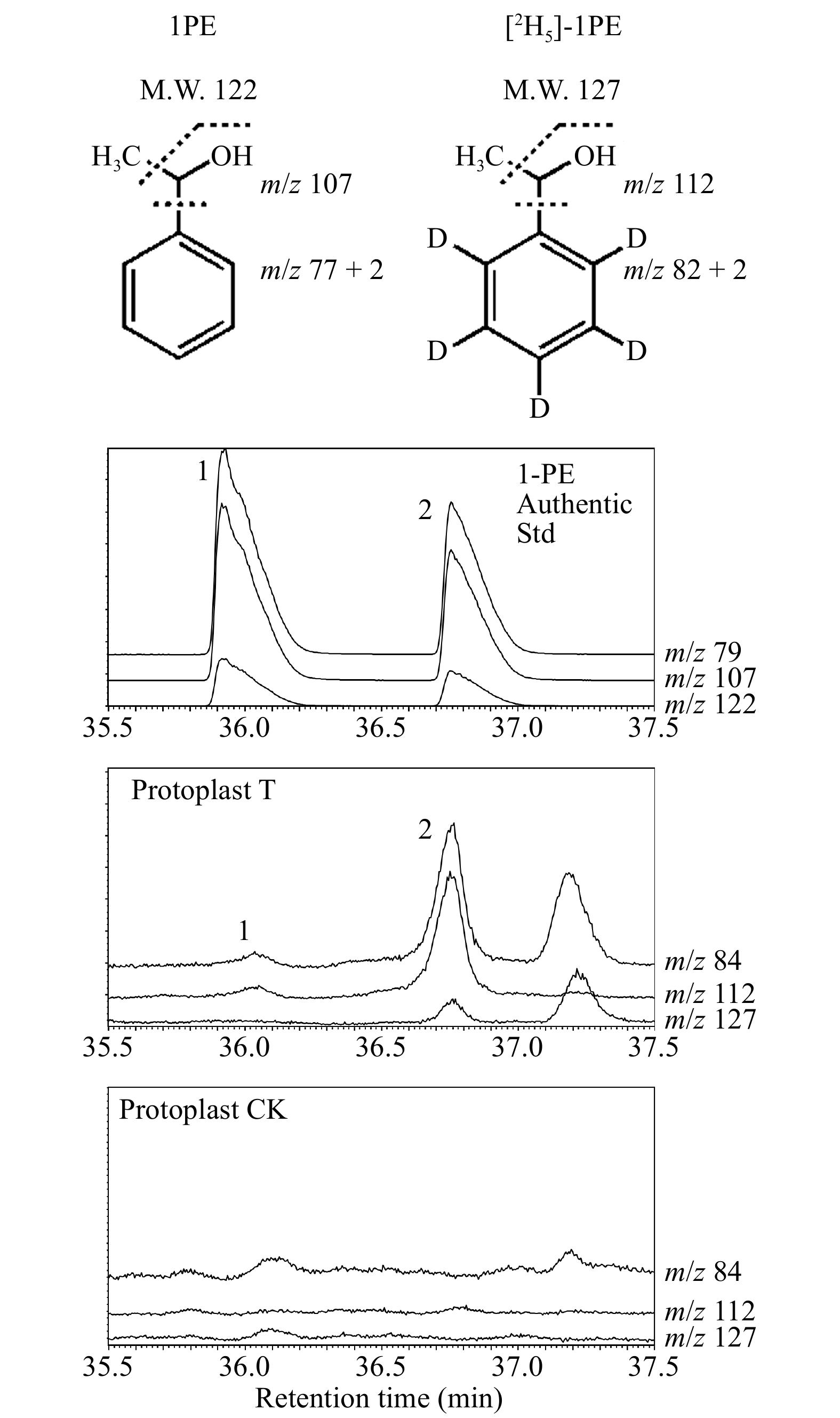
Figure 6. Stable isotopic tracing using tea mesophyll protoplasts.
-
Cellulase
R-10Macerozyme
R-10Pectolase
Y-23Protoplast
(No./g F.W.)1.50% 0.10% 0.50% (4.64 ± 1.32) × 106 3.00% 0.30% (3.49 ± 0.46) × 107 1.50% 0.30% (1.18 ± 0.02) × 107 1.50% 0.60% (7.32 ± 1.49) × 106 3.00% 0.60% (3.02 ± 0.40) × 107 Table 1. Protoplast yield in different enzyme solutions.
-
Isolation time Protoplast (No./g F.W.) 6 h (1.73 ± 0.32) × 107 9 h (2.27 ± 0.09) × 107 12 h (2.75 ± 0.49) × 107 15 h (2.05 ± 0.08) × 107 18 h (1.85 ± 0.14) × 107 Table 2. Protoplast yield over different digestion times.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(2)