-
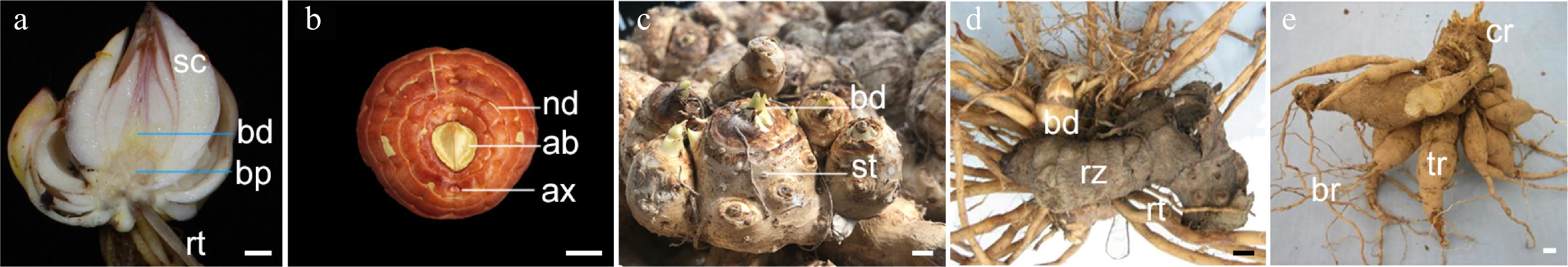

Figure 1.
Photos to document the classification and morphological diversity of geophytes. (a) Dormant lily bulbs, (b) gladiolus corms, (c) Zantedeschia aethiopica tuber, (d) Canna indica rhizome, (e) Dahlia tuberous root. ab: apical bud; ax: axillary bud; bd: bud; bp: basal plate; br: branch root; cr: root crown; nd: node; rt: root; rz: rhizome; sc: scale; st: stem root; tr: tuberous root. The scale bar represents 1 cm.
-
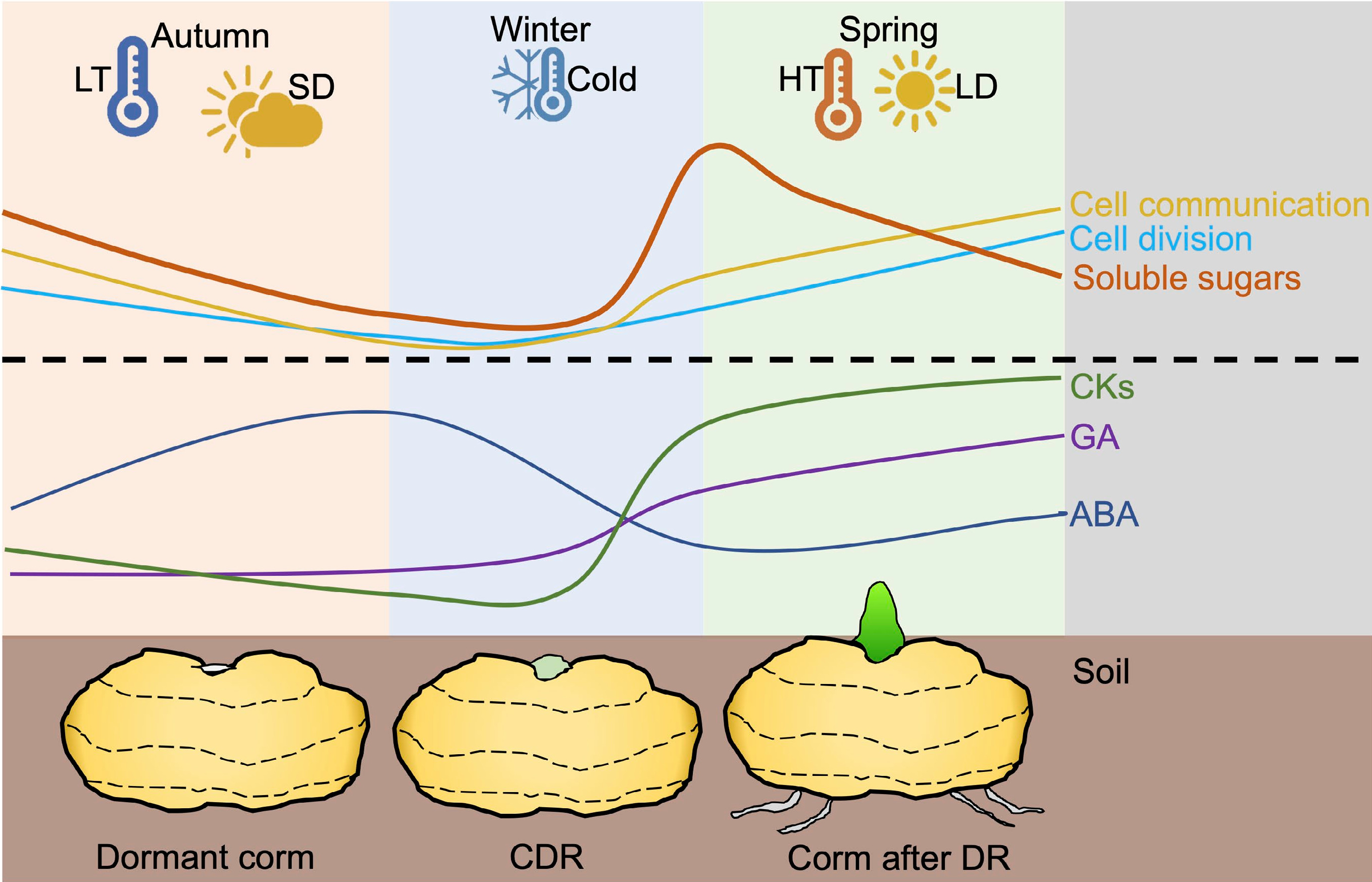
Figure 2.
Biochemical and physiological processes occur during the whole process of dormancy in geophytes. In autumn, low temperature and short days induce endogenous ABA and inhibit CKs and GA. Besides, soluble sugars are decreased in shoots along with blocked PD and slow cell division. During the winter, long-term cold treatment contributes to decreasing ABA content in dormant organs and promoting GA, CKs, and soluble sugars. Meanwhile, callose around the PD is degraded which helps to active cell communication and cell division in buds. When the temperature and light are suitable for corm sprouting, ABA is continuously decreased and soluble sugars are used for plant growth. CDR: corm dormancy release; DR: Dormancy release; LD: Long day; LT: low temperature; SD: short day.
-
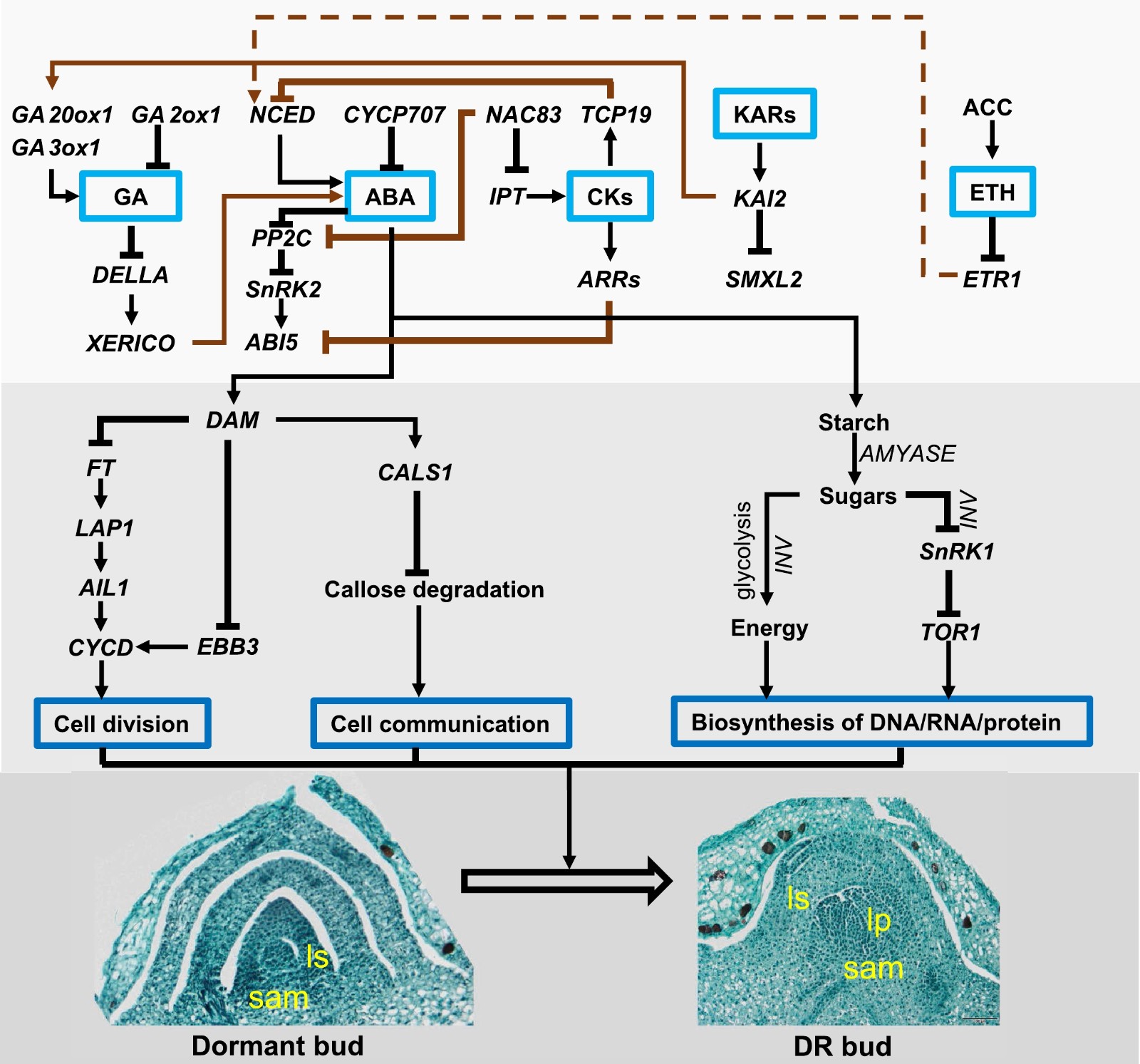
Figure 3.
The interplay among hormones and carbohydrates in regulating GDR. During GDR, ABA is the master hormone that could delay dormancy release by repressing cell division, blocking cell communication via callose, and inhibiting the biosynthesis of DNA, RNA, and protein by releasing SnRK1. Other hormones like GA, CKs, KARs, and ETH could interplay with ABA via transcription factors. A solid line represents the direct effect, and a dashed line represents the indirect effect. The interplay is summarized from different species. ABA: abscisic acid; ABI5: ABA INSENSITIVE 5; ACC: 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid; AIL1: AINTEGUMENTA-like 1; ARR: RESPONSE REGULATOR 1; CALS1: CALLOSE SYNTHASE 1; CKs: cytokinins; CYP707A: CYTOCHROME P450, FAMILY 707, SUBFAMILY A; CYCD: D type CYCLINS; DAM: Dormancy-Associated MADS-Box; DELLA: aspartic acid–glutamic acid–leucine–leucine–alanine; EBB3: EARLY BUD-BREAK 3; ETH: ethylene; ETR1: Ethylene Receptor 1; FT: FLOWER LOCUS T; GA: Gibberellic acid; GA2ox1: Gibberellin 2-Oxidase 1; GA20ox1: Gibberellin 20-Oxidase 1; GA3ox1: Gibberellin 3-Oxidase 1; IPT: ISOPENTENYL TRANSFERASE; KARs: Karrikins; KAI2: KARRIKIN-INSENSITIVE 2; LAP1: Like- APETALA 1; NAC: NAM, ATAF, CUC; NCED: 9-CIS-EPOXYCAROTENOID DIOXYGENASE; PP2C: Protein phosphatase 2C; SnRK1/2: SNF1-related protein kinase 1; TCP: Teosinte Branched Cyldoeia/PCF; TOR1: Target of Rapamycin; SMXL2: SMAX1-LIKE.
-
Modification type Regulation factors* Functional class* Target genes* References Chromatin remodeling complexes BRM SWI2/SNF2-like FT, CO, SOC1 [91] Chromatin remodeling complexes EBS BAH and PHD domain-containing protein FT [93] Heterochromatin LHP1 HP1 homologue FT [91] Histone deacetylation FLD Homologous to a subunit of histone deacetylase complexes FLC [91] Histone deacetylation FVE Putative subunit of histone deacetylase complex FLC [91] Histone monoubiquitination HUB1/2 E3 homologs FLC [94] Histone methylation MRG1/2 H3K36me3 FT [95] Histone methylation VRN1/2 H3k27me3 FLC, FT [91,96] Histone demethylation JMJ30 Histone demethylase SnRK2.8 [97] DNA methylation MET1 Maintenance CpNpG methyltransferase FLC [91] * BAH: bromo-adjacent homology; BRM: BRAHMA; CO: CONSTANS; EBS: EARLY BOLTING IN SHORT DAYS; FLC: FLOWER LOCUS C; FLD: FLOWER LOCUS D; FT: FLOWER LOCUS T; FVE: FLOWER LOCUS VE; HUB: HISTONE MONO-UBIQUITINATION; JMJ30: JUMONJI C DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 30; LHP1: LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN; MET1: METHYLTRANSFERASE 1; MRG: MORF RELATED GENE 1; PHD: Plant homeodomain; SnRK: SNF1-related protein kinase 1; SOC1: SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CO 1; SWI2/SNF2: SWITCHING2/ SUCROSE NONFERMENTING; VRN: VERNALIZATION. Table 1.
Dormancy associated genes regulated by epigenetics.
-
miRNA Targets* Species Function Reference miR156 SPL Paeonia suffruticosa Bud dormancy release [105] miR159 MdMYB33 and MdMYB65 Malus domestica ABA homeostasis [102] miR159 MYB/TCP Lilium pumilum Bulb dormancy release [90] miR160 ARF Lilium pumilum Bulb dormancy release [90] miR169 HAP2 Populus tremuloides Vegetative bud dormancy [106] miR169 NF-YA Prunus mume Bud dormancy release [101] miR172 AP2 Paeonia suffruticosa Bud dormancy release [105] miR319c TCP2 Camellia sinensis Apical bud burst [107] miR390 TAS3 Pyrus pyrifolia Endodormancy release [108] miR390 CDPK1 Solanum tuberosum Tuber dormancy [104] miR6390 DAM Pyrus pyrifolia Dormancy
transition[103] * AP: APETALA; ARF: AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR; CDPK: CALCIUM-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE; DAM: DORMANCY-ASSOCIATED MADS-BOX; HAP: HAPLESS; MYB: MYELOBLASTOSIS; NF-YA: Nuclear Transcription Factor Y Subunit Alpha; SPL: SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE; TAS: TRANS-ACTING SIRNA3; TCP: TEOSINTE BRANCHED1/CYCLOIDEA/PCF. Table 2.
miRNA related to bud dormancy.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(2)