-
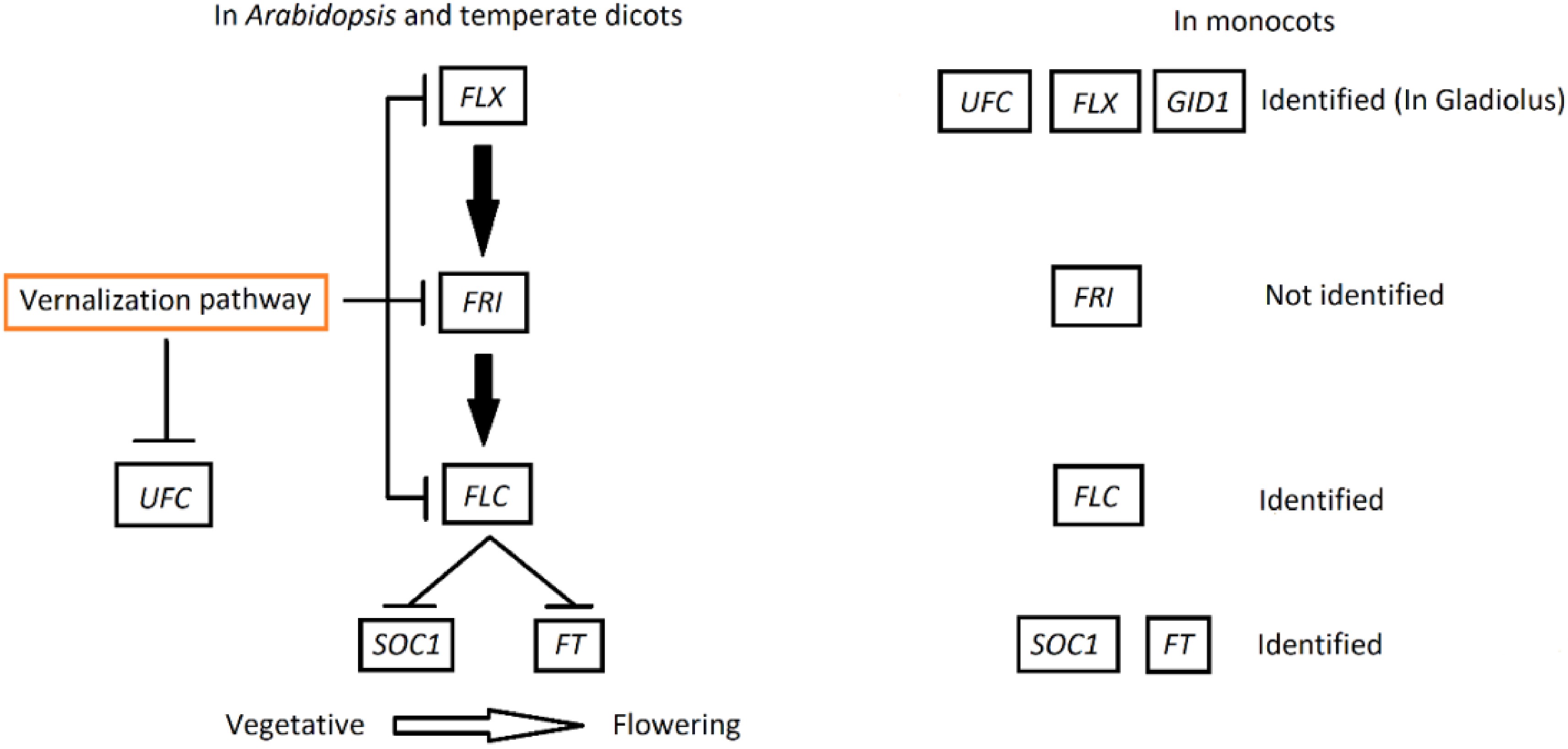
Figure 1.
Model represents portion of flowering pathway regarding the role of the FLX gene in flowering along with the UFC gene in Arabidopsis and temperate dicots. FLX upregulates FRI which also upregulates the expression of the FLC protein and suppresses flowering by repressing the expression of the floral integrator SOC1 and FT. The vernalization pathway downregulates the expression of FLX, FRI and FLC genes, allowing the floral integrators to initiate flowering in vegetative state of dicots, while the vernalization pathway also downregulates the UFC gene[37]. In monocots, FLX, FLC, GID1, SOC1 and FT have been identified[22,35,51], while UFC and FLX have just been identified in gladiolus (in the current study). GIBBERELLIN-INSENSITIVE DWARF1 (GID1) regulates GA synthesis. However, FRI was not identified either by lacking the presence of these repressor genes or monocots relying on other options of the flowering pathway genes.
-
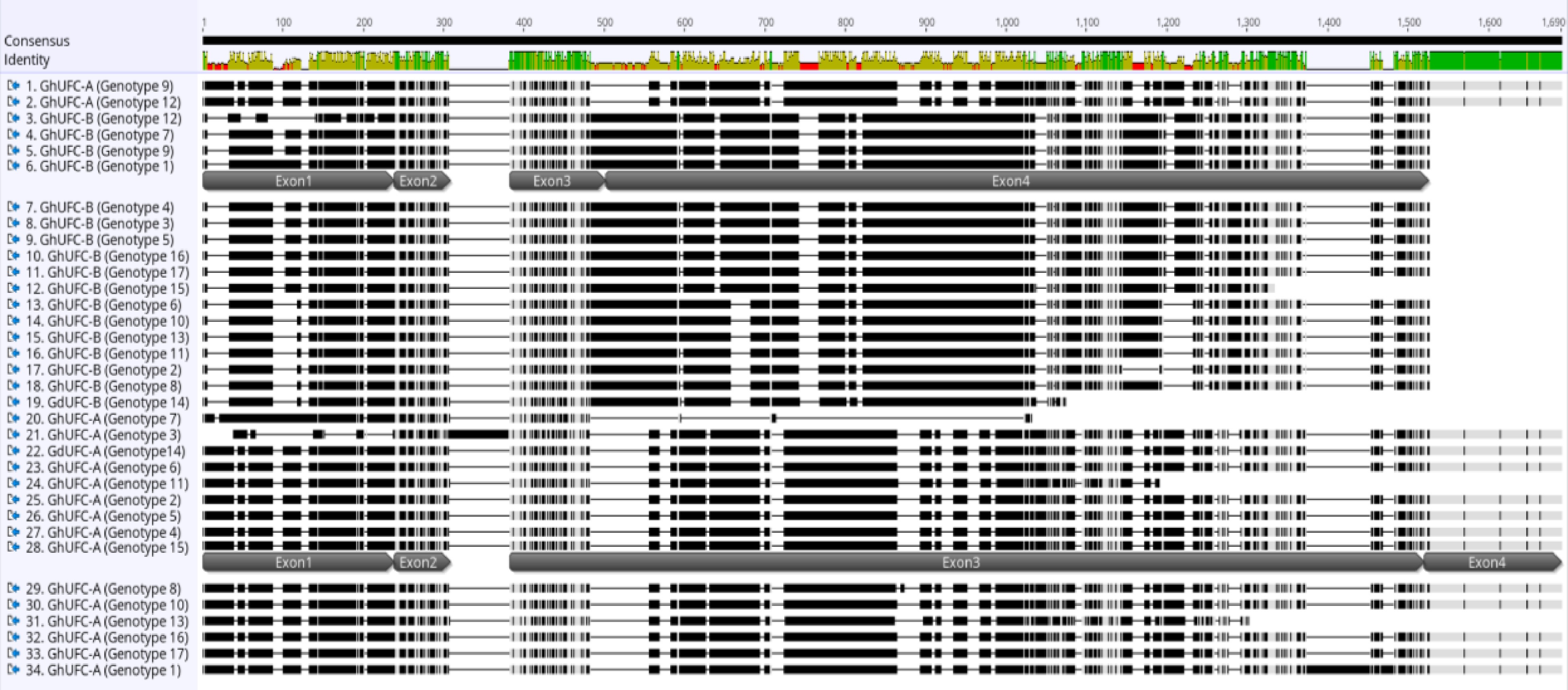
Figure 2.
Multi-alignment of UFC coding sequence in G. ×hybridus (GhUFC) and Gladiolus dalenii (GdUFC), the alignment is for the 17 genotypes, each genotype has 2 alleles, allele A and allele B: GhUFC-A, GdUFC-A, GhUFC-B, GdUFC-B. Both alleles has 4 exons but allele A size is larger in coding sequence than allele B. The alignment shows insertion and missing coding sequences in some genotypes. The multi-alignment is done in MUSCLE pair-alignment using neighbor joining cluster method and CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
-
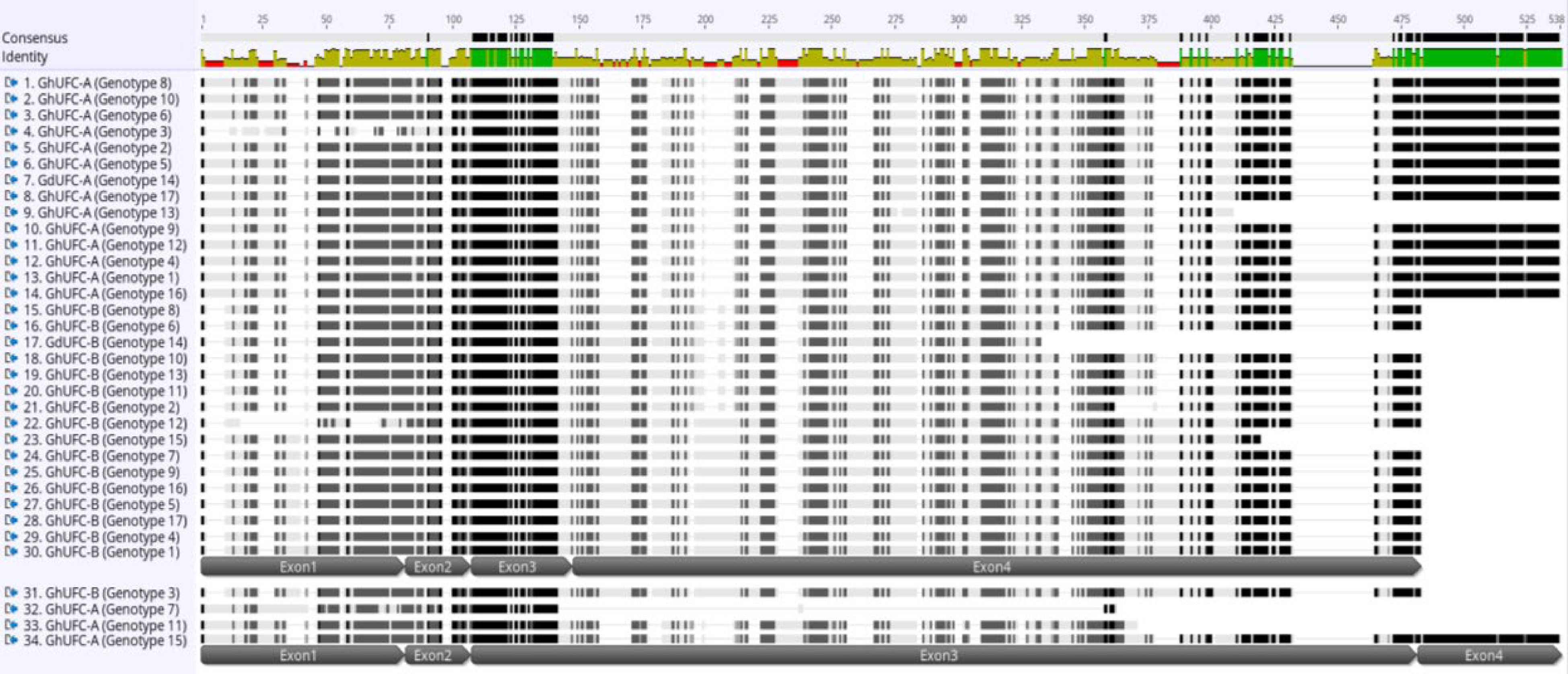
Figure 3.
Multi-alignment of UFC amino acid sequence in Gladiolus ×hybridus (GhUFC) and G. dalenii (GdUFC), the alignment is for the 17 genotypes, each genotype has 2 alleles, allele A and allele B: GhUFC-A, GdUFC-A, GhUFC-B, GdUFC-B. Both alleles has 4 exons but allele A size is larger in amino acid sequence than allele B. The alignment shows insertion and missing amino acid sequences in some genotypes. The alignment identify conserved amino acid sequences (green color). The multi-alignment is done in MUSCLE pair-alignment using neighbor joining cluster method and CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
-
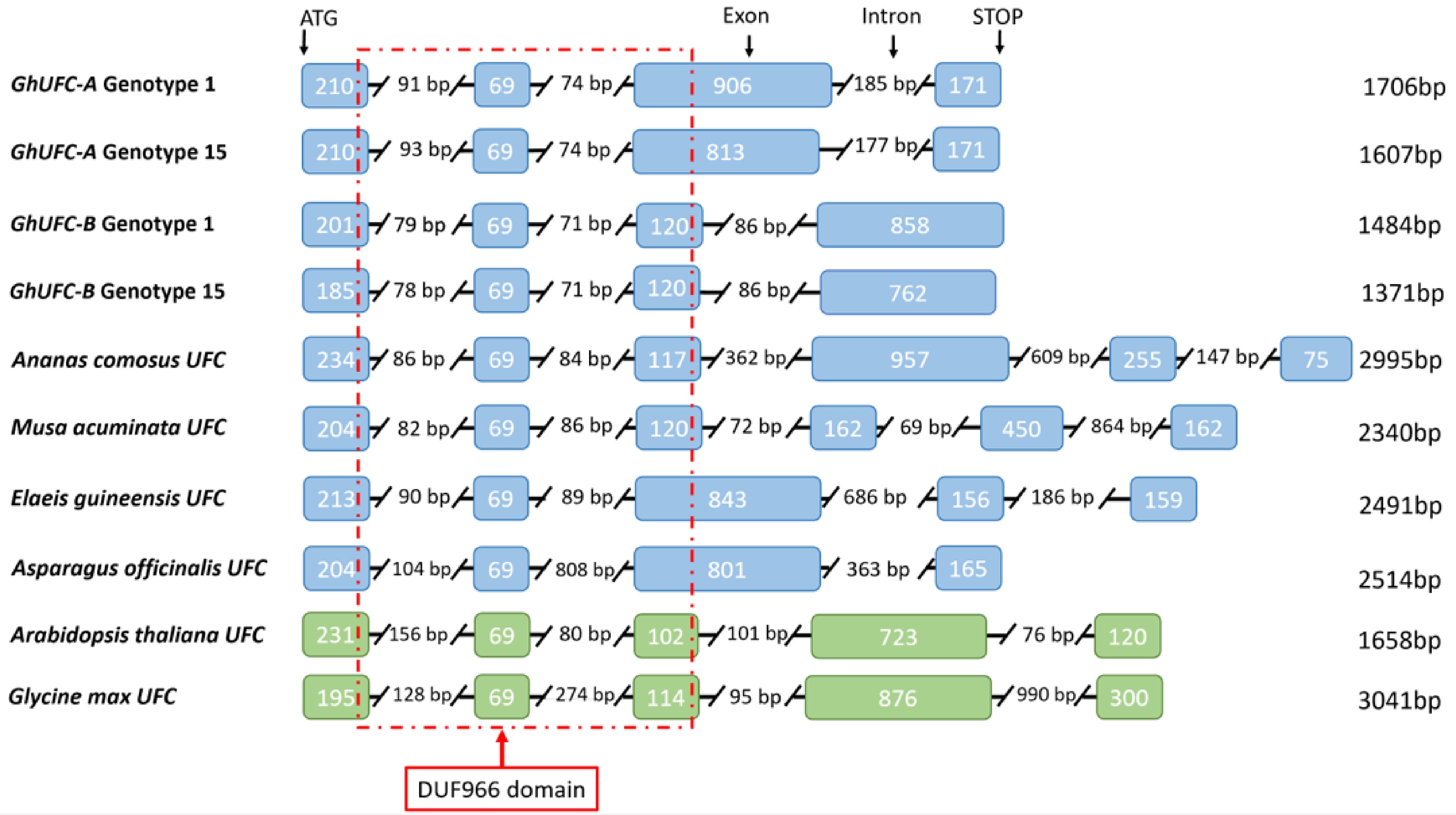
Figure 4.
Intron-exon configuration of the UFC genes in Gladiolus ×hybridus of genotypes 1 and 15 in relation to several species. Monocot species are highlighted in blue: Ananas comosus, Musa acuminata, Elaeis guineensis and Asparagus officinalis. Dicot species highlighted in green for Arabidopsis thaliana and Glycine max. Sequences were aligned based on first exon sequences. Total length of the gene’s coding region is listed on the right of each respected species. The red line represents the conserved domain DUF966 in relation to the location of the domain with exon configuration.
-
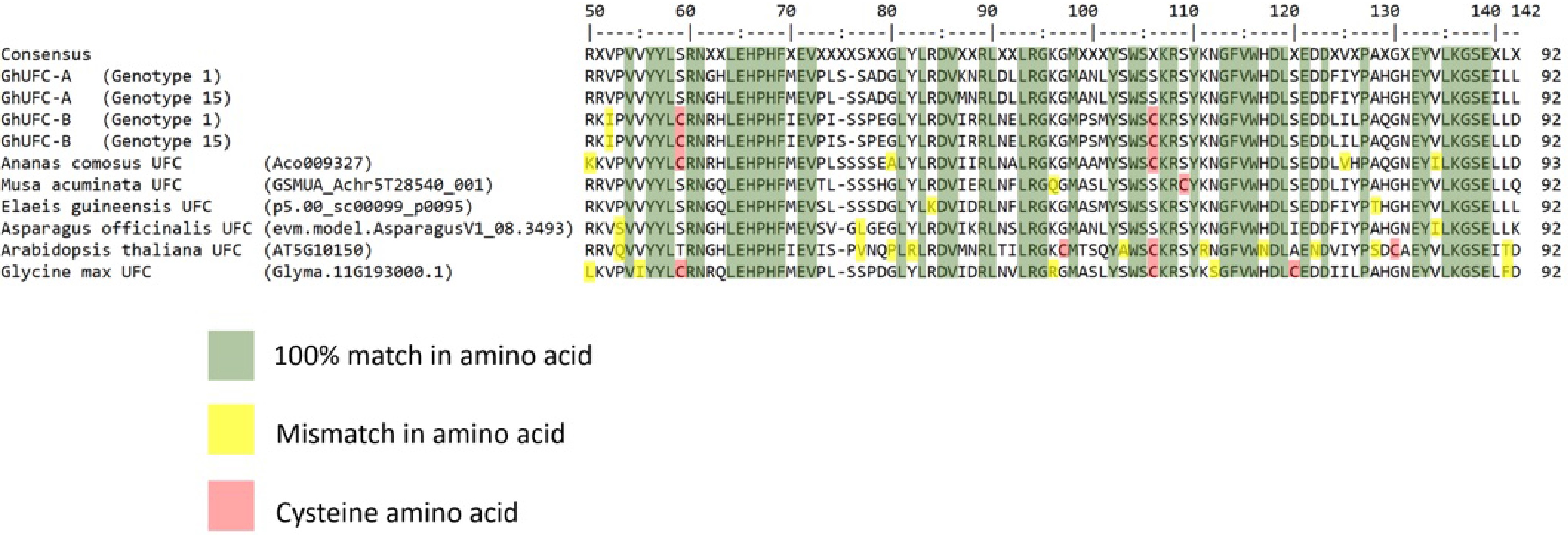
Figure 5.
Alignment of the globular region containing DUF966 domain of UFC proteins from Gladiolus ×hybridus of genotypes 1 and 15, Ananas comosus, Musa acuminata, Elaeis guineensis, Asparagus officinalis, Arabidopsis thaliana and Glycine max. Green coloration shows identical amino acid sequence; yellow color highlights the polymorphisms while red color shows the cytosine amino acid. The conserved domain DUF966 is 92 amino acids.
-
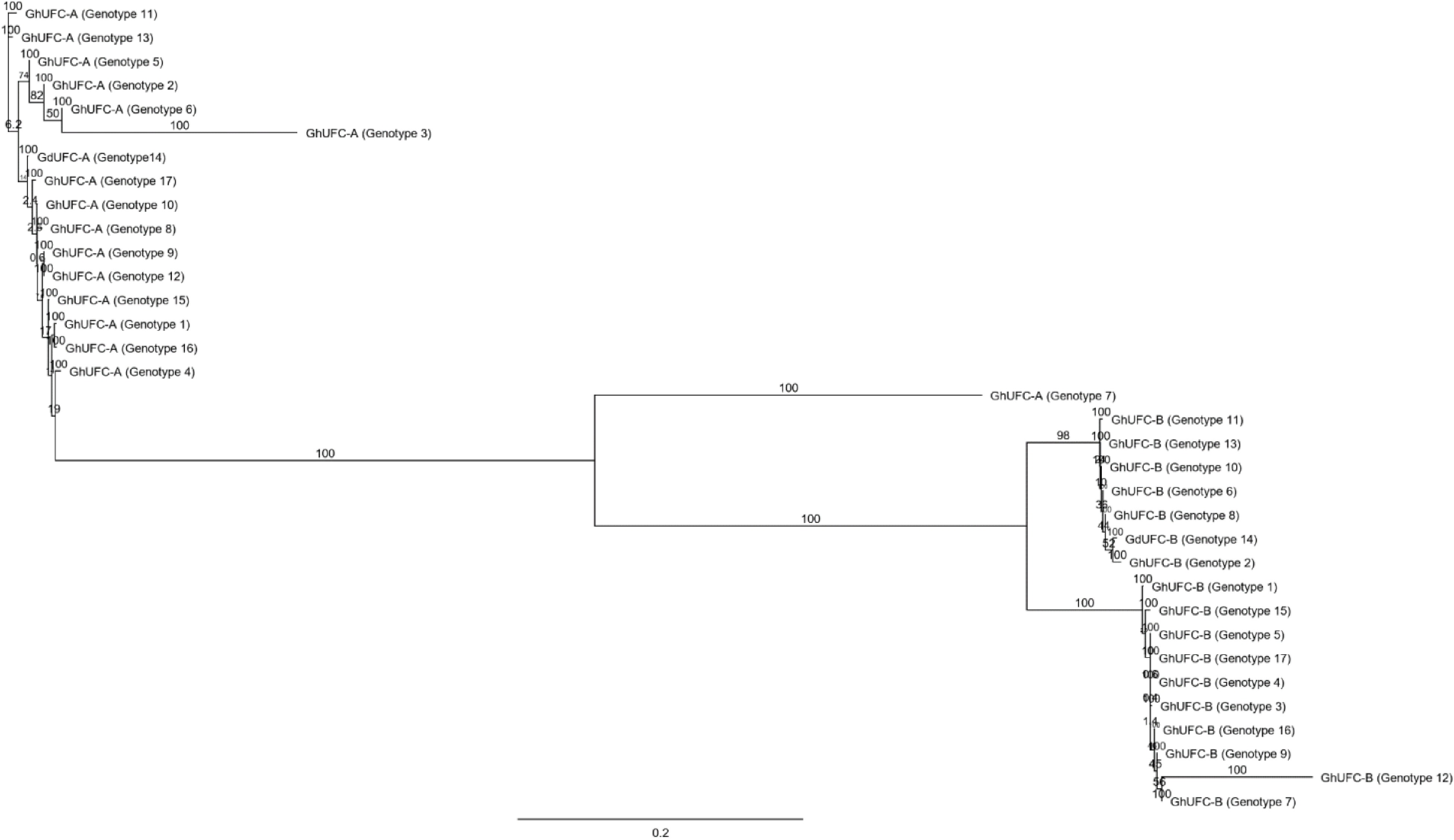
Figure 6.
The phylogenetic tree of all UFC genotypes in Gladiolus; genetic distances were computed using the Tamura-Nei method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The tree build using the Neighbor-Joining method and the bootstrap test was performed for each tree (500 replicates) and the tree format is organized and ordered with a scale bar of 0.2 (Geneious®).
-

Figure 7.
Multi-alignment of FLX amino acid sequence in Gladiolus ×hybridus (GhFLX) with other species; Arabidopsis thaliana, Ananas comosus, Elaeis guineensis, Musa acuminata and Glycine max. The alignment is for the three gladiolus genotypes (3, 6 and 16) each genotype has 3 exons. The alignment shows missing amino acid sequences in gladiolus genotypes 3, 6 and 16 as amino acid sequences does not have a stop codon. The alignment identifies conserved amino acid sequences (green color). Note: Arabidopsis thaliana – FLL4 is a functional protein which has two exons only (Lee and Amasino, 2013). The multi-alignment is done in MUSCLE pair-alignment using neighbor joining cluster method and CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
-
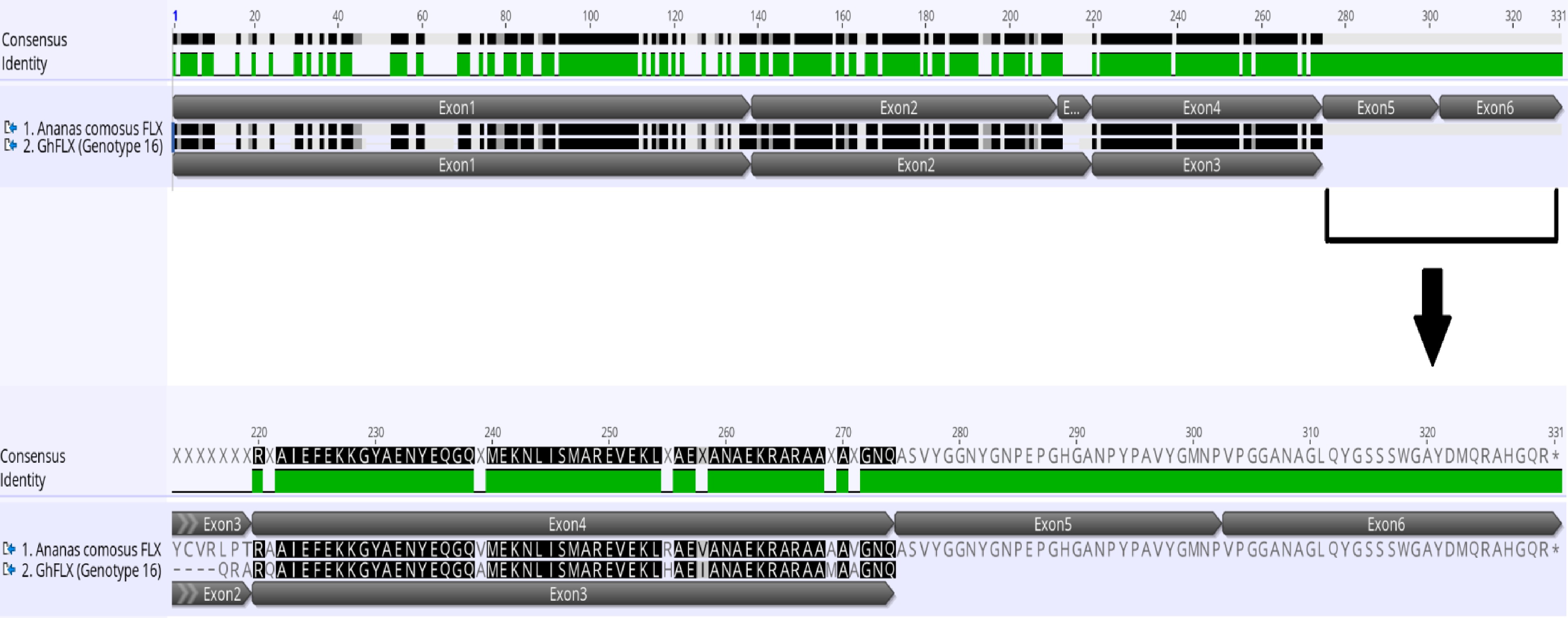
Figure 8.
Pair alignment of FLX protein in Ananas comosus and Gladiolus ×hybridus genotype 16 showing the complete FLX protein in Ananas comosus with five exons while incomplete FLX protein in Gladiolus ×hybridus (GhFLX) which lacks the remaining two exons and stop codon. The alignment is done in MUSCLE pair-alignment using neighbor joining cluster method and CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
-
Genotype Code RGC Gladiolus ×hybridus 21213 1 + Gladiolus × hybridus 2220 2 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 2231 3 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 2337 4 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 35314 5 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 3923 6 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 3931 7 + Gladiolus × hybridus 74210 8 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 7736 9 + Gladiolus ×hybridus 28236 10 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 15531 11 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 20732 12 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 60314 13 − Gladiolus dalenii 'arolina Primrose' 14 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 'Beatrice' 15 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 'Glamini'® 16 − Gladiolus ×hybridus 'Vista' 17 − Table 1.
Gladiolus genotypes used in this study, their codes and whether they are Rapid Generation Cycling (RGC): + is for RGC genotypes and – for Non-RGC genotypes. All gladiolus genotypes were tested for the presence of UFC, FLX and FRI genes.
-
Species (Gene locus/ID) Gladiolus ×hybridus genotype Genotype 1 Genotype 15 GhUFC-A (%) GhUFC-B (%) GhUFC-A (%) GhUFC-B (%) Ananas comosus (Aco009327) 189 (33.51) 249 (53.21) 191 (34.35) 231 (52.98) Musa acuminata (GSMUA_Achr5T28540_001) 251 (54.09) 170 (39.35) 250 (57.74) 148 (31.36) Elaeis guineensis (p5.00_sc00099_p0095) 254 (52.05) 172 (40.86) 250 (51.23) 155 (39.85) Asparagus officinalis (evm.model.AsparagusV1_08.3493) 213 (46.61) 148 (35.58) 213 (50.0) 135 (29.87) Arabidopsis thaliana (AT5G10150) 137 (28.54) 129 (29.79) 138 (31.72) 117 (29.32) Glycine max (Glyma.11G193000.1) 181 (33.64) 226 (52.19) 188 (35.67) 207 (52.01) Table 2.
The identity of amino acid sequences and number (%) of two UFC proteins (GhUFC-A, GhUFC-B) in two Gladiolus (genotypes 1 and 15) in relation to other species (Gene locus/ID) through pair alignment, using MUSCLE alignment for the neighbor joining clustering method and the CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
-
Species (Gene locus/ID) Gladiolus × hybridus genotype Genotype 1 Genotype 15 GhUFC-A (%) GhUFC-B (%) GhUFC-A (%) GhUFC-B (%) Ananas comosus (Aco009327) 70 (76.09) 79 (84.95) 79 (84.95) 79 (84.95) Musa acuminata (GSMUA_Achr5T28540_001) 78 (84.78) 71 (78.02) 78 (84.78) 71 (78.02) Elaeis guineensis (p5.00_sc00099_p0095) 79 (85.87) 72 (79.12) 79 (85.87) 72 (79.12) Asparagus officinalis (evm.model.AsparagusV1_08.3493) 75 (82.42) 70 (76.09) 75 (82.42) 70 (76.09) Arabidopsis thaliana (AT5G10150) 61 (66.30) 61 (64.89) 62 (67.39) 61 (64.89) Glycine max (Glyma.11G193000.1) 70 (76.92) 75 (82.42) 70 (76.92) 75 (81.52) Table 3.
Identity of amino acid sequences, number (%) of UFC proteins in the conserved domain DUF966 in Gladiolus genotypes 1 and 15 in relation to other species (Gene locus/ID) through pair alignment.
-
Species (Accession no.) Gladiolus × hybridus genotype GhFLX Genotype 3 (%) GhFLX Genotype 6 and 16 (%) Ananas comosus (XP_020095672.1) 180 (64.98%) 177 (64.60%) Musa acuminata (XP_009420070.1) 122 (48.03%) 122 (48.03%) Elaeis guineensis (XP_010922618.1) 132 (50.00%) 131 (49.62%) Arabidopsis thaliana – FLX (NP_001154541.1) 82 (30.48%) 82 (30.48%) Arabidopsis thaliana – FLL1 (NP_566492.1) 135 (50.00%) 135 (50.00%) Arabidopsis thaliana – FLL2 (NP_001320766.1) 96 (36.09%) 94 (35.34%) Arabidopsis thaliana – FLL3 (NP_564678.1) 104 (34.67%) 104 (34.67%) Arabidopsis thaliana – FLL4 (NP_001119474.1) 67 (26.38%) 68 (26.77%) Glycine max (Glyma.15g269300) 156 (57.14%) 155 (56.78%) Table 4.
Number (%) of amino acid sequences of GhFLX protein in Gladiolus genotypes 3 and 6 (genotype 16 is identical to genotype 6) in relation to the other species through pair alignment; similarities of sequences in identity of gladiolus genotypes ranged from ~26% to ~65% across all investigated species of the whole FLX protein; alignment is done in MUSCLE, using the neighbor joining clustering method and the CLUSTALW sequencing scheme (Geneious®).
Figures
(8)
Tables
(4)