-

Figure 1.
Plant architecture and fruit phenotype of three F. vesca accessions Yellow Wonder (YW), Hawaii 4 (H4), and Rügen (Rü). (a)−(c) Photographs of YW, H4, and Rü plants. Note the absence of runners in YW and Rü, but prolific runners (arrows) in H4. (d) Both YW and H4 develop yellow color fruits as shown, but Rü develops red color fruit. Plants are pictured in 4 in × 4 in pots.
-
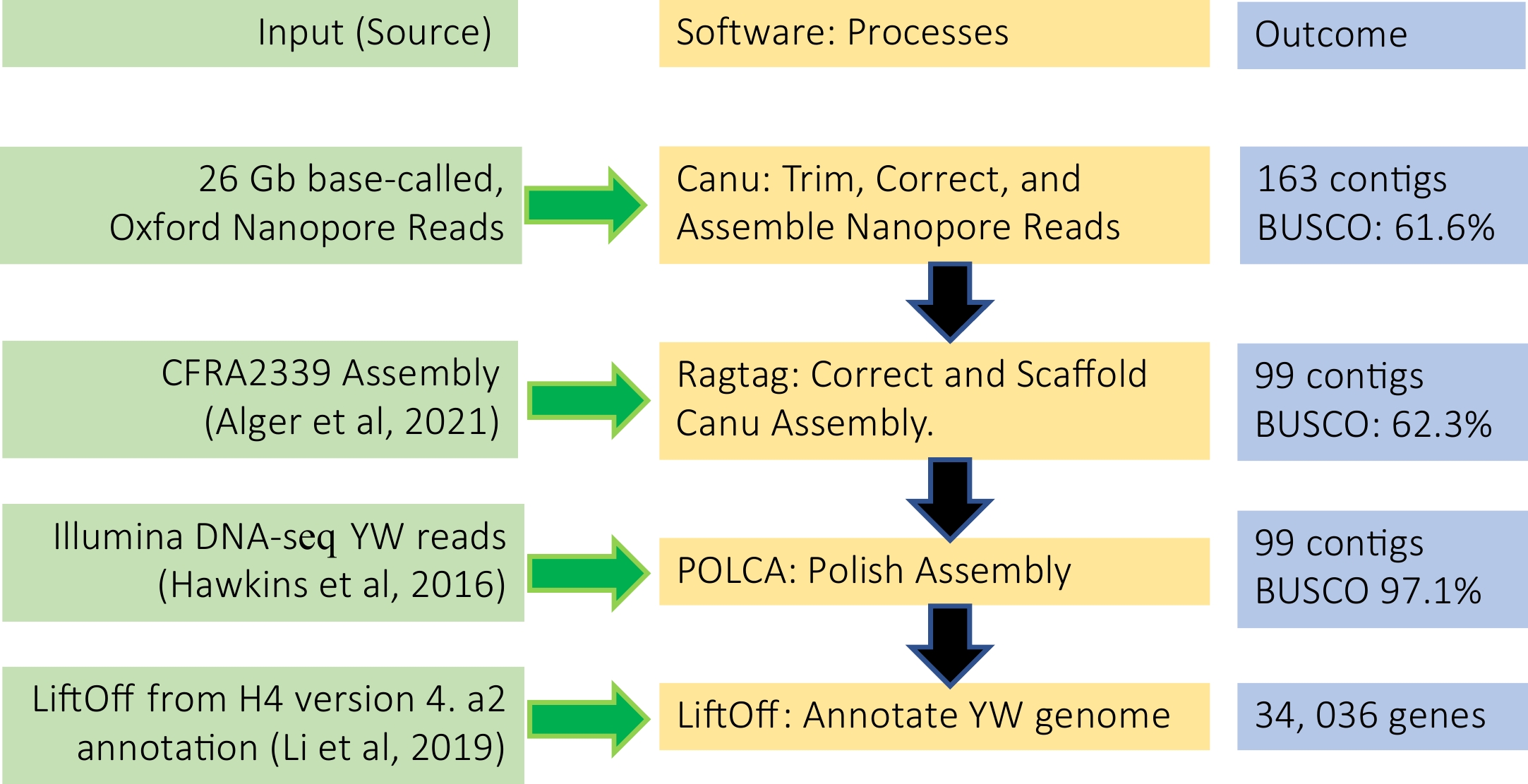
Figure 2.
De novo genome assembly and annotation pipeline used in this study.
-
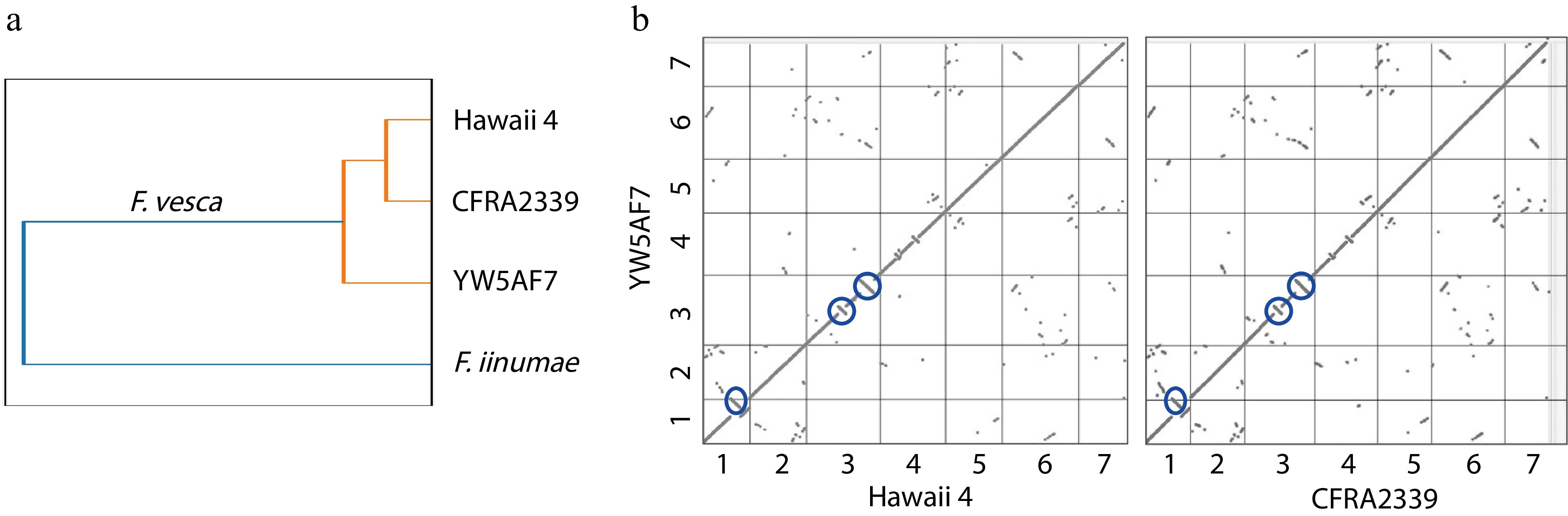
Figure 3.
YW5AF7 genome structure shows consistent differences from previously-published genomes of Fragaria vesca accessions. (a) YW5AF7 genome clusters are distinct from previously published F. vesca genomes, Hawaii 4 and CFRA2339, as well as Fragaria iinumae. This is indicated by Jaccard similarity coefficient calculated by Sourmash. (b) Inversions are observed in Chr 1, 3, and 4 between YW5AF7 and the other two F. vesca accessions (highlighted in blue circles). Y and X axis show seven chromosomes. Synteny plots generated on COGE.
-
Fragaria vesca
accessionsHawaii-4
(FvH4_v4.0)CFRA2339 Yellow Wonder
(FvYW_v1.0)Assembly length (MB) 220 244 220 Total contigs 29 402 96 auN (MB) 32 31 32 N50 (MB) 34 31 34 L90 (MB) 7 7 7 Number of annotated genes 34,008 30,349 34,007 BUSCO 0.947 0.967 0.961 Table 1.
Quality metrics for FvYW_v1.0 and previously published F. vesca genomes.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)