-
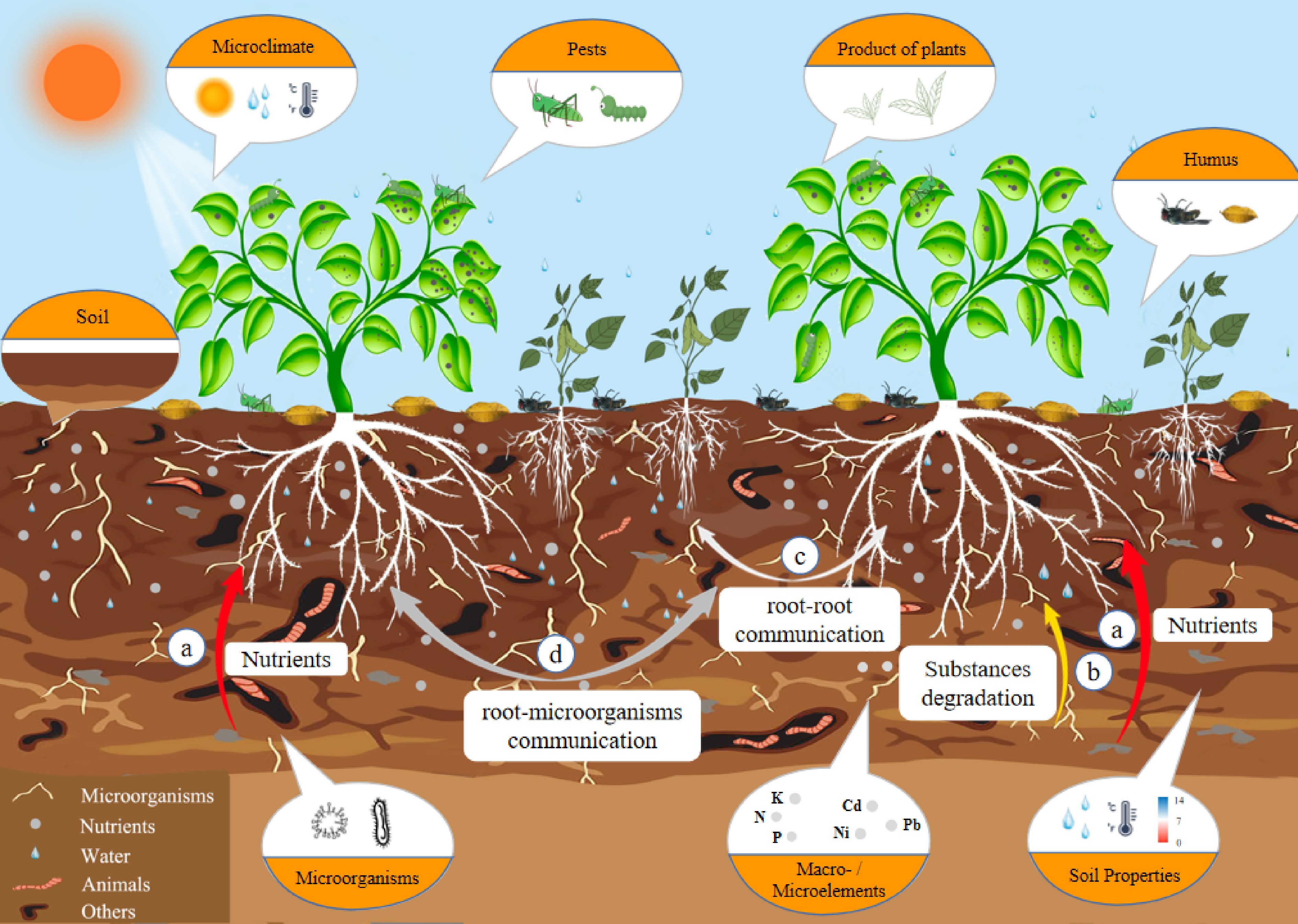
Figure 1.
Interactions between intercropping and host plants. The influence of intercropping on the host plants mainly includes two factors. 1 Above-ground factors: pests and microclimate, such as temperature, humidity and light intensity. 2 Below-ground factors: soil nutrients, enzymes and microorganisms. There are complex material exchanges between host plants, intercropping plants and soil microorganisms. (a) Host plants absorb nutrients from the soil. (b) Soil microorganisms degrade humus in soil. (c) Signal communication between the roots of intercropping plants and the host plants. (d) Signal communication between the roots of host plants and soil microorganisms.
-
Tea plantation
intercropping plant(s)Pest(s) and effect Volatiles/predators Reference(s) Flemingia macrophylla Leafhoppers are attracted Volatiles (cis-3-hexen-1-ol, cis-3-hexenyl acetate, nonanal and alpha-farnesene) [54] Lavandula pinnata L., Corymbia citriodora (Hook.), Tagetes erecta, Leonurus Artemisia Leafhoppers are repelled Volatiles (alpha-pinene, 1,8-cineole, thymol anisole, thymol, p-cymene, limonene and camphor) [52−54] Rosmarinus officinalis L., Catsia tora and Paspalum notatum Leafhoppers are controlled predators (spiders, ladybirds, coccinellids, and lacewings, Anystis baccarum) [17, 52, 55] Chamaecrista rotundifolia Herbivorous beetles, Thysanoptera or Geometridae are controlled Predators (Serangium japonicum, Pharoscymnus taoi, Cryptogonus postimedialis or parasitoids) [11, 56] Mentha haplocalyx Green plant bugs are repelled Volatiles (unknown) [53] Red bean Leafhoppers and thrips are controlled Predators (Orius sauteri) [57] Rosmarinus officinalis Ectropis obliqua are repelled Volatiles (Beta-myrcene, Gamma-terpinene,
(R)-(−)- linalool, (S)-(−)-cis-verbenol,
(R)-(+)-camphor, and (S)-(−)-Verbenone)[59] Maize Leafhoppers and Trialeurodes vaporariorum are controlled Volatiles (unknown) [58] Acacia confusa Merr. trees Hemiptera, Lepidoptera, and Coleoptera are controlled Predators (Araneida, Hymenoptera, Hemiptera) [60] Table 1.
Effects of different intercropping patterns on pests in tea plantations.
-
Tea plantation intercropping plant(s) Nutrients increased in intercropping patterns Reference(s) Soybean Ammonium N, Nitrate N, AP, OM, AK (flowering–podding or mature period of soybean) [13] Chestnut SOM, N, P and K [18] Stropharia rugosoannulata SOM, TN and AN [68] Osmanthus and Michelia TN, TK, AN, AP and SOM [14] Loquat or citrus or waxberry AN, AP, AK and SOM (loquat) and AP, AK and SOM (waxberry) and AN, AP and AK (citrus) in top-, sub- and bottom-soil [16] Peanut TP, TK, AP and AK in top-, sub- and bottom-soil [9] Walnut AN, AP, AK and SOM [69] Vulpia myuros SOM, TN, alkali-hydrolyzed N, AP and AK [15] Table 2.
Effects of different intercropping patterns on soil nutrients.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(2)