-
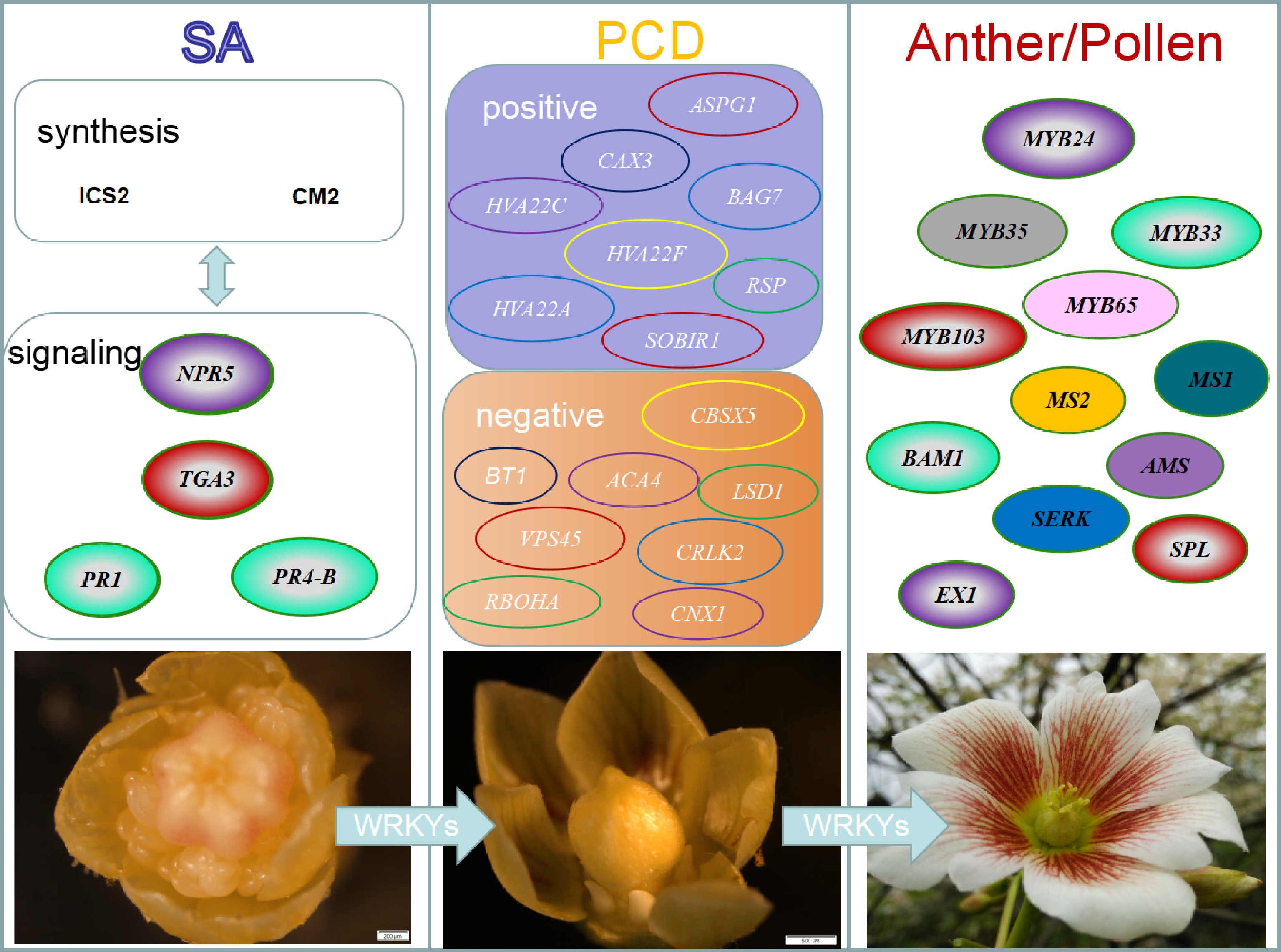
Figure 1.
Hypothetical model for development of female flowers in Vernicia fordii. The SA triggers PCD in tapetum cells, leading to stamen abortion and female flower formation. Transcriptome analysis and co-expression networks suggest that SA accumulation may trigger PCD and inhibit stamen development in female flowers. ICS2: Isochorismate synthase 2; CM2: Chorimate mutase 2; NPR5: Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related genes 5; TGA3: TGA1A-RELATED gene3; PR1: Pathogenesis- related 1; PR4-B: Pathogenesis-related 4-B; ASPG1: Aspartic protease in guard cell 1; CAX3: Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3; BAG7: BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 7; HVA22C: HVA22-like C; HVA22F: HVA22-like protein F; HVA22A: HVA22-like protein A; SOBIR1: Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase; RSP: CO(2)-response secreted protease; CBSX5: CBS domain-containing protein CBSX5; BT1: Adenine nucleotide transporter BT1; ACA4: Alpha carbonic anhydrase 4; LSD1: Lesion Simulating Disease 1; VPS45: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 45 homolog; CNX1: Molybdopterin adenylyltransferase; RBOHA: Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein A; CRLK2: Calcium/calmodulin-regulated receptor-like kinase 2; MYB24: MYB family transcription factor 24; MYB33 : MYB family transcription factor 33; MYB35: MYB family transcription factor 35; MYB65 : MYB family transcription factor 65; MYB103: MYB family transcription factor 103 ; MS1: Male sterility 1; MS2: Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 2; BAM1: barely any meristem 1; AMS: aborted microspores; SERK: Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase 1; SPL: sporocyteless; EX1: excess microsporocytes 1.
-
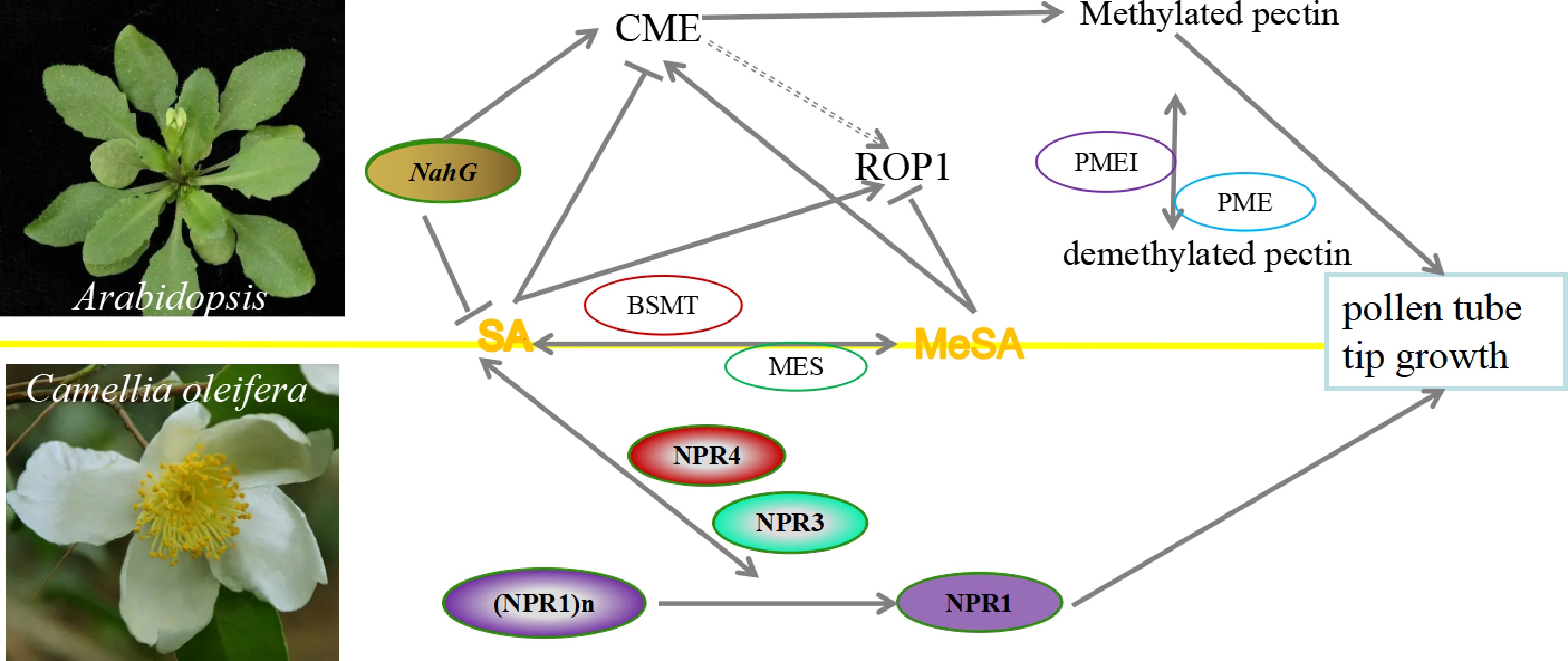
Figure 2.
The proposed SA and MeSA models inhibit and promote pollen tube tip growth in Arabidopsis and Camellia oleifera. SA promotes pollen tube tip growth in Arabidopsis by regulating clathrin-mediated endocytosis, while MeSA inhibits this process. SA and MeSA have antagonistic effects on ROP activity in pollen tubes. In C. oleifera, CoNPR1 and CoNPR3.1 may be involved in SA- and MeSA-mediated pollen tube growth. CME: clathrin-mediated endocytosis; MES: Methyl salicylate esterase; PME: Pectin methyl esterase; PMEI: PME Inhibitor; BSMT: benzoic acid and SA carboxyl methyltransferase. NahG: Naphthalene hydroxylase G, which encoding salicylate hydroxylase that inactivates SA, is unable to accumulate SA, resulting in the suppression of early flowering phenotype in Arabidopsis; NPR1: Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1; NPR3: Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related genes 3; NPR4: Non-expressor of pathogenesis-related genes 4; ROP1: Rho-of-Plantssmall GTPase 1. The line with single arrow indicates induction. The line with transverse indicates repression. The line with double arrows indicates interconversion.
-
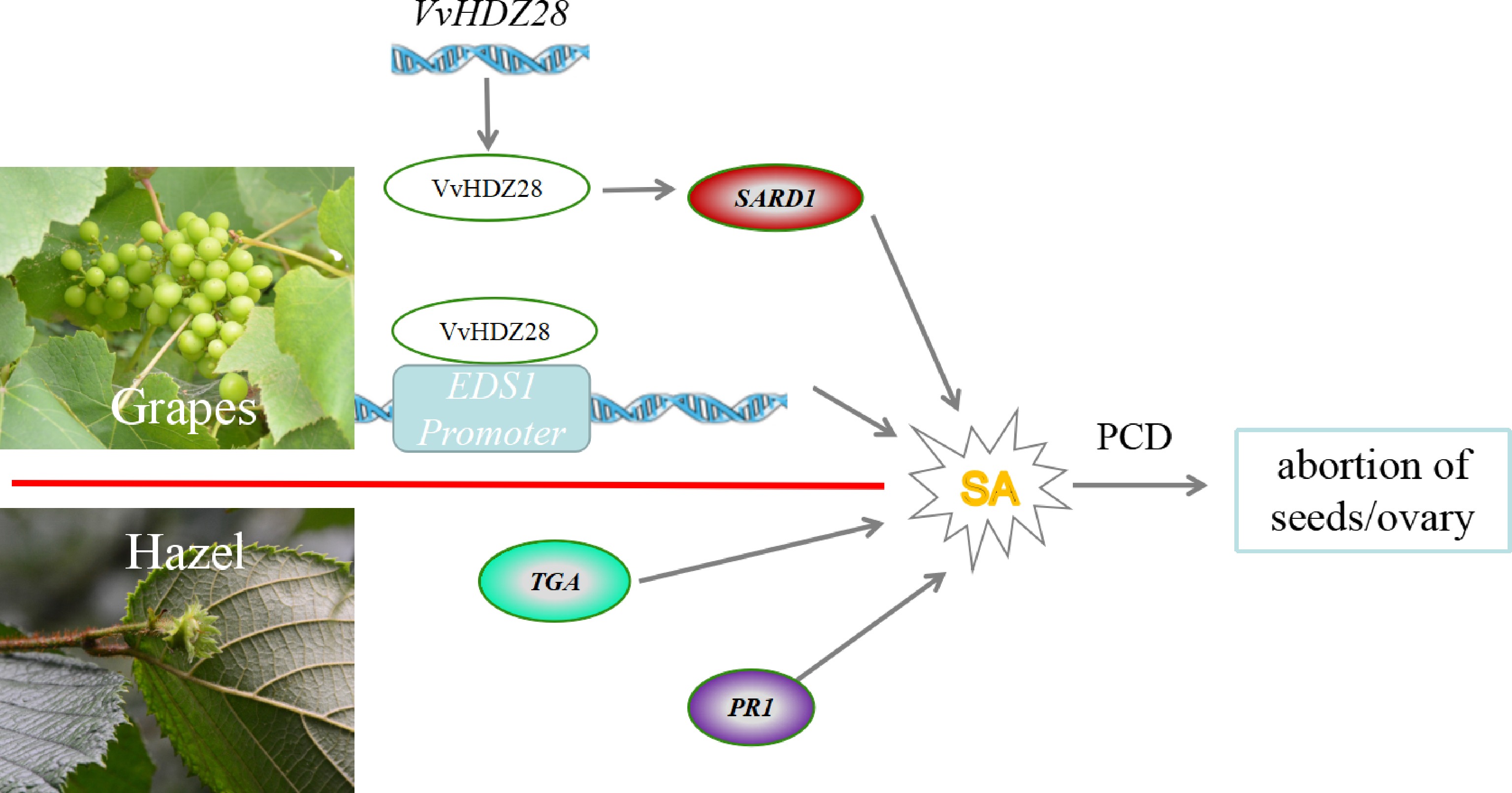
Figure 3.
The proposed model of genetic and molecular interactions of the regulatory network during embryo abortion in grape and Corylus spp. (hazel) ovary abortions. In grape, VvHDZ28 up-regulates VvEDS1 expression by binding to its promoter, and VvHDZ28 can also indirectly upregulate the positive expression of VvSARD1. In hazel, the SA signal transduction pathway may contribute to the regulation of abortive ovary formation via up-regulation of the TF TGA and pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR1). The line with single arrows indicates induction. The line with transverse indicates repression. The line with double arrows indicates interconversion, SARD1: Systemic acquired resistance deficient 1; EDS1: Enhanced disease susceptibility1; VvHDZ28: Homeobox domain-Zip family28 in Vitis vinifera L..
Figures
(3)
Tables
(0)