-
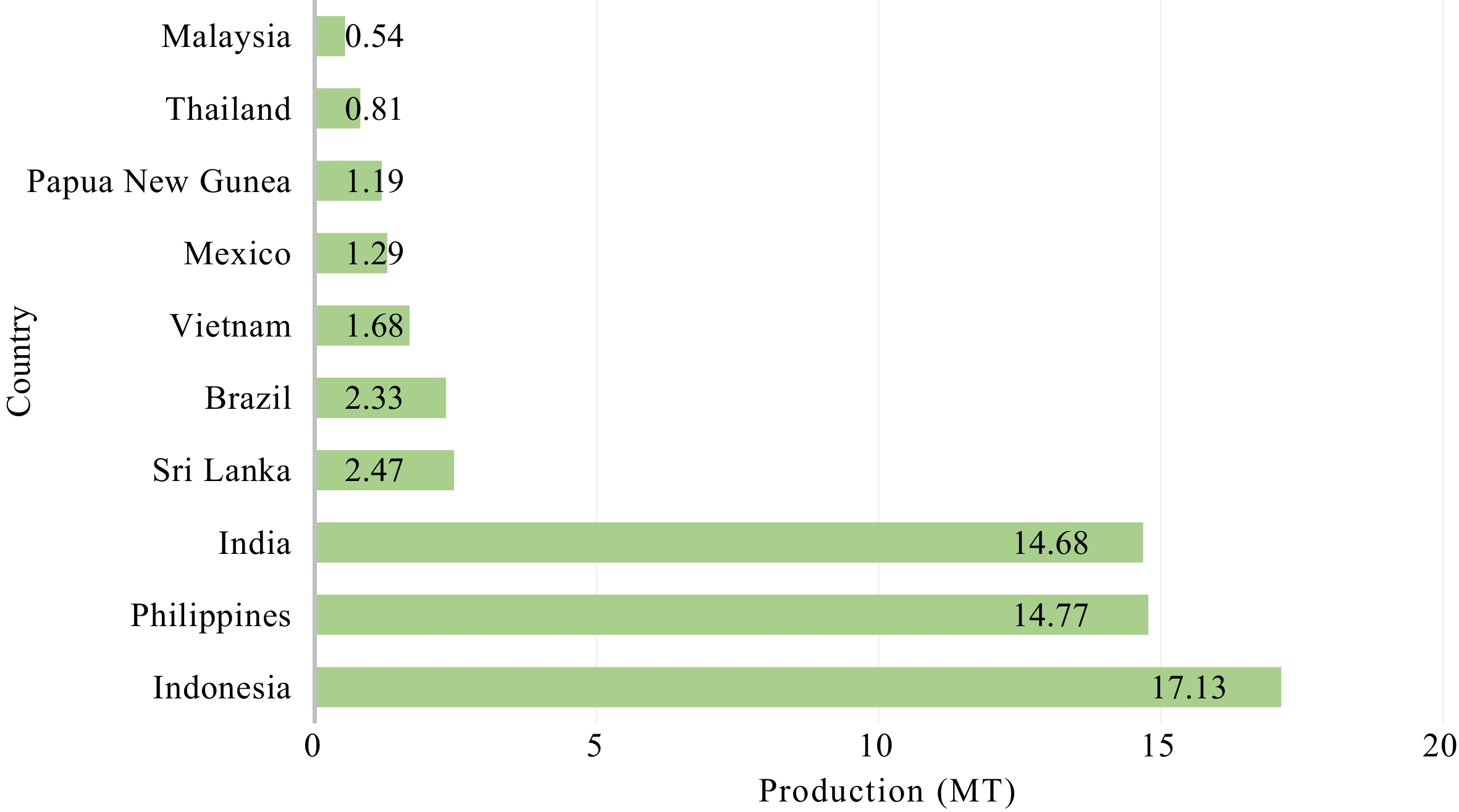
Figure 1.
Coconut production worldwide by leading countries[6].
-
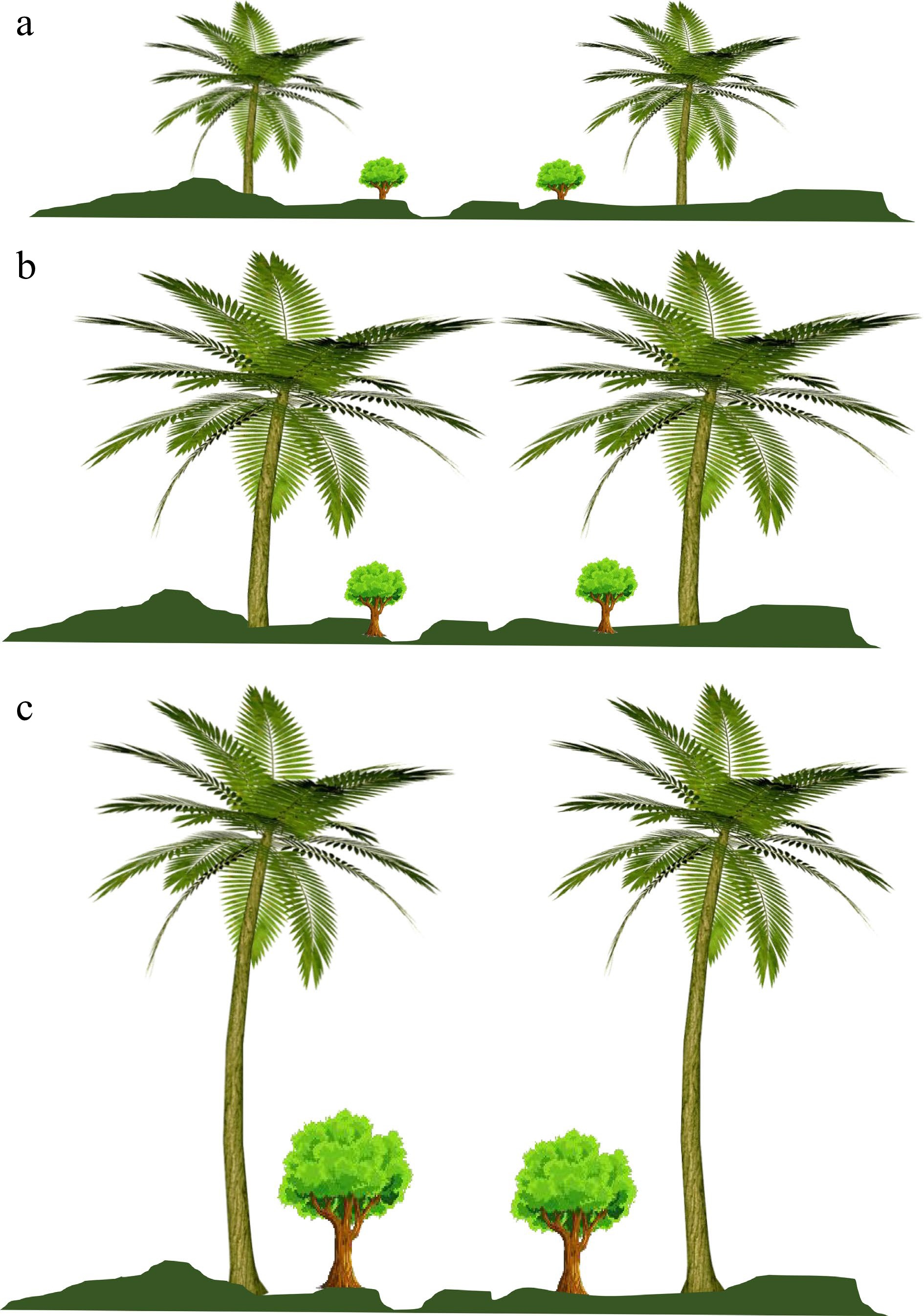
Figure 2.
Changing pattern of the canopy during the coconut palm lifespan. (a) Age less than 5 years, (b) age 5−20 years, and (c) age more than 20 years.
-
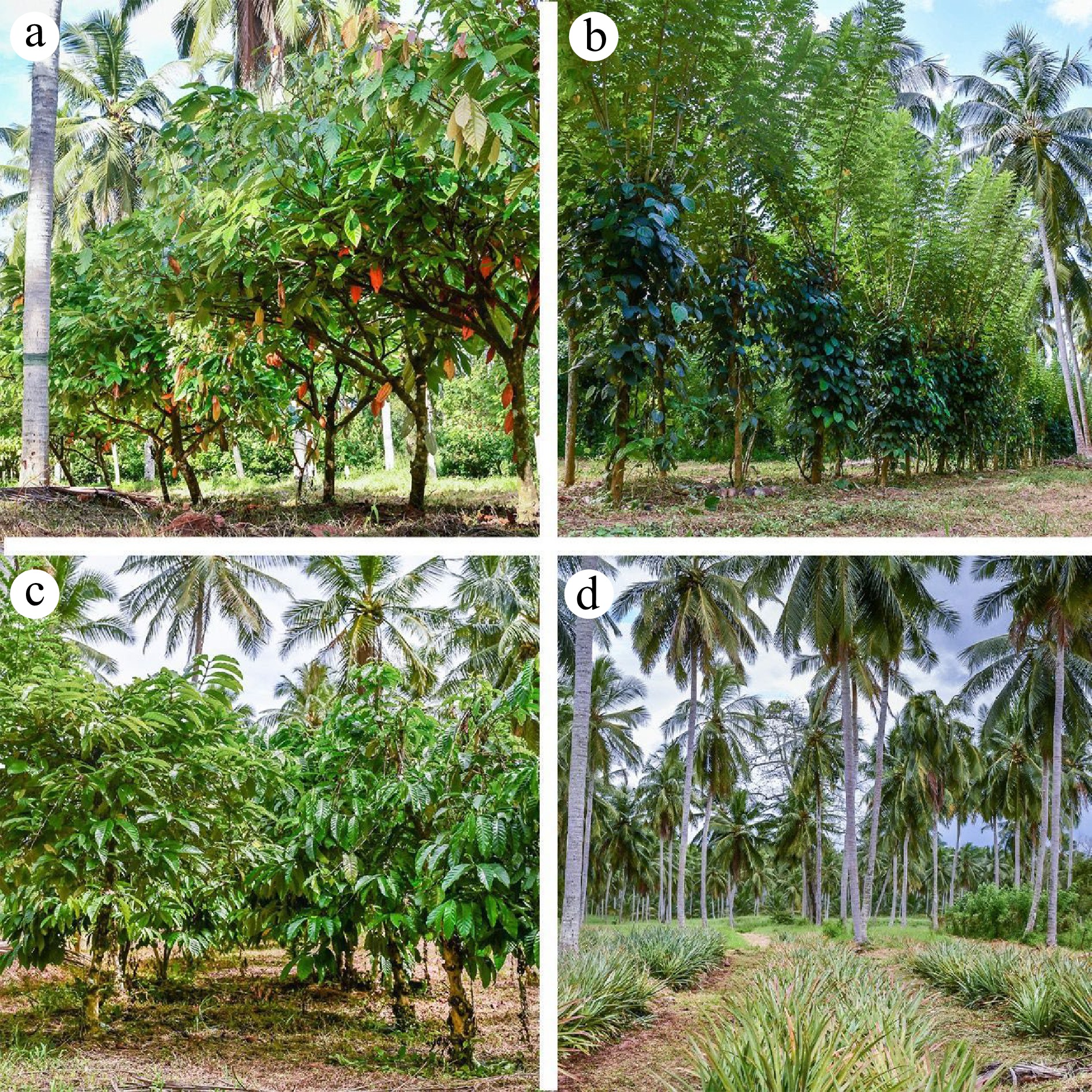

Figure 3.
(a) Cocoa + Coconut intercrop, (b) Pepper + Coconut intercrop, (c) Coffee + Coconut intercrop, (d) Pineapple + Coconut intercrop.
-
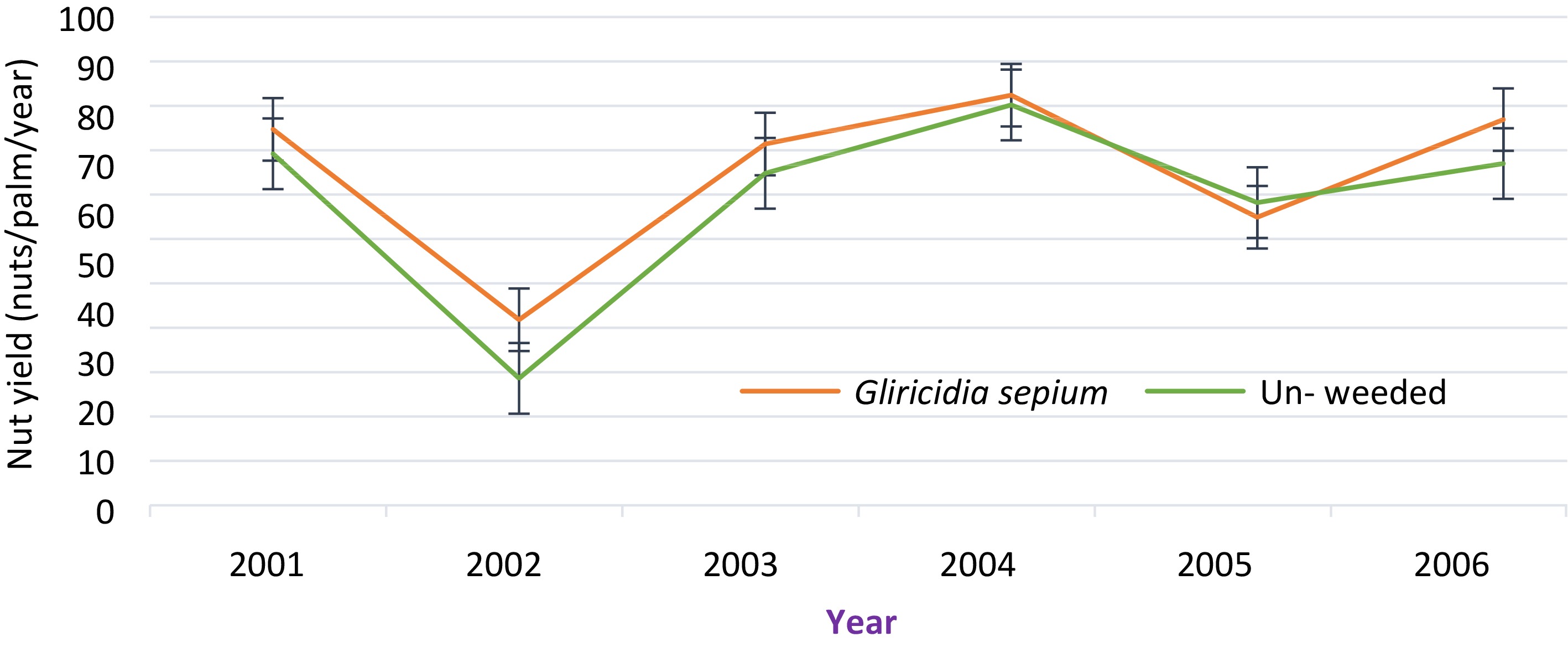
Figure 4.
Yield variation planting Gliricidia sepium as an intercrop for weed control[[40]].
-
Crop Common name Botanical name Fruit crops Pineapple Ananas comosus Banana Musa spp. Papaya Carica papaya Pomegranate Punica granatum Guava Psidium guajava Mango Mangifera indica Rambutan Nephelium lappaceum Durian Durio zibethinus Dragon fruit Hylocereus undatus Lemon Citrus limon Vegetable crops Chilies Capsicum frutescens Snake gourd Trichosanthes cucumerina Drumstick Moringa oleifera Brinjal Solanum melongena Bottle gourd Lagenaria siceraria Okra Abelmoschus esculentus Spice and beverage crops Pepper Piper nigrum Clove Syzygium aromaticum Cardamom Elettaria cardamomum Nutmeg Myristica fragrans Cinnamon Cinnamomum verum Cocoa Theobroma cacao
Tubers and root cropsCassava Manihot esculenta Sweet potato Ipomoea batatas Yam Dioscorea alata Taro Xanthosoma sagittifolium Ginger Zingiber officinale Turmeric Curcuma longa Cereals and millets Maize Zea mays Finger millet Eleusine coracana Foxtail millet Setaria italica Sorghum Sorghum bicolor Legume crops Groundnut Arachis hypogaea Soybean Glycine max Pigeon pea Cajanus cajan Cowpea Vigna unguiculata Green Gram Vigna radiata Gliricidia Gliricidia sepium Table 1.
Annuals and perennials grown as intercrops in Sri Lankan coconut plantations.[17]
-
Stage 1
(age 0−5 years)Stage 2
(age 5−20 years)Stage 3
(age more than 20 years)Pineapple Yam Cocoa Passion fruit Lemon Pepper Banana Chili Coffee Ginger Capsicum Vanilla Turmeric Ginger Avocado Cassava Turmeric Wild sunflower Guava Pasture Gliricidia Table 2.
Intercrop use as function of coconut crops growth stage[19].
-
Cropping system Mean nut yield (ha/year) % increase Coconut only 6,123 − Coconut + Cocoa 7,504 22 Coconut + Coffee 8,216 34 Coconut + Pepper 6,424 5 Coconut + Clove 7,191 17 Coconut + Cinnamon 7,623 26 Table 3.
Effect of mixed cropping systems on coconut yield at Siri Kandura Estate, Dodanduwa (Wet zone) (1977−1989)[24].
-
Crop category N (ppm)
0−30 cmP (ppm)
0−30 cmK%
0−30 cmMg%
0−30 cmCoconut only 4,903 3.4 0.15 0.8 Coconut + Gliricidia 6444 8.1 0.23 1.1 Table 4.
Soil N, P, K, and Mg concentration under Coconut and Gliricidia based intercropping[19].
-
Treatment Nut yield (nuts/palm/year) 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Cover cropping 88 38 87 101 94 91 Planting Gliricidia sepium 77 38 74 84 59 79 Tractor slashing 78 27 81 87 75 76 Chemical weeding 81 44 97 102 99 93 Cattle grazing 83 36 75 81 66 75 Un-weeded 72 26 68 82 62 70 Significance ns ns * * * * LSD (P = 0.05) − − 15 13 17 14 Table 5.
Effect of different agronomic practices in controlling weeds on nut yield (nuts/palm/year) in Pallama Seed Garden, Sri Lanka[40].
-
Gross return (US ${\$} $ 

Net return (US ${\$} $ 

Under rainfed conditions Coconut as monocrop 1,369 319 With intercrop Cassava 2,153 694 Ginger 3,535 896 Under irrigated conditions Coconut as monocrop 2,988 1,450 Multi-storeyed cropping 4,108 1,895 Mixed farming 5,965 1,821 Table 6.
Estimated income from various coconut-based farming systems (US
${\$} $
Figures
(4)
Tables
(6)