-

Figure 1.
The morpho-anatomical structures of Leptogium cochleatum (left) and Leptogium moluccanum (right).
-
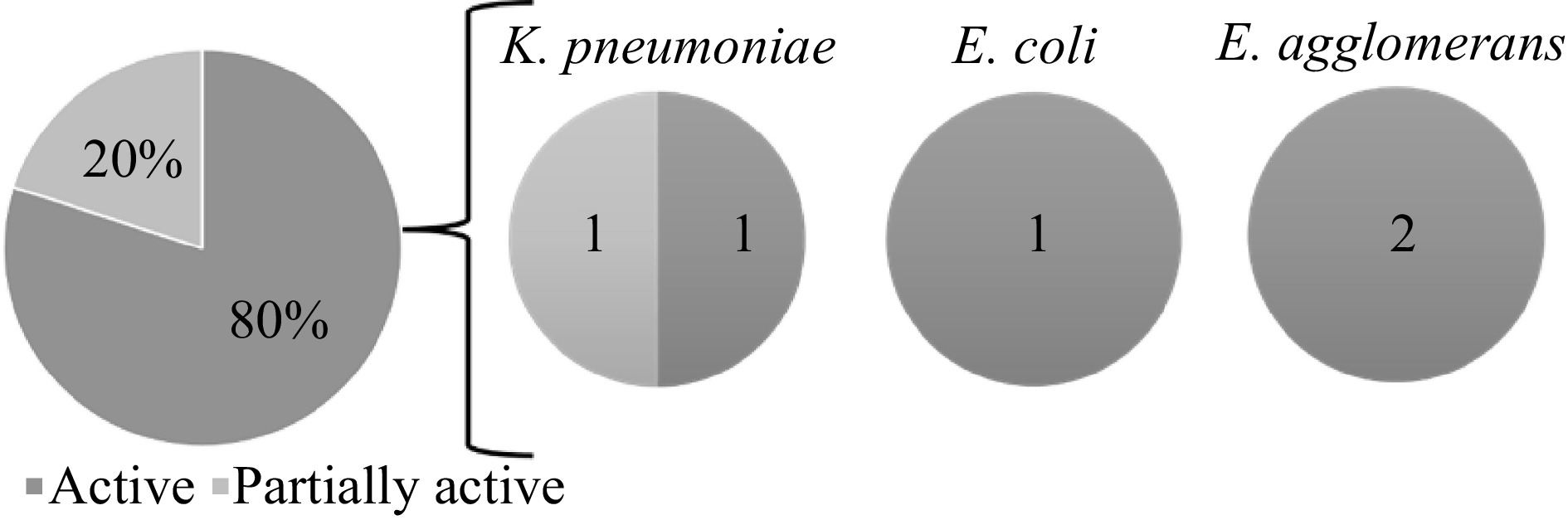
Figure 2.
Antibacterial activity of the lichen crude extracts against the test organisms based on the zone of inhibition (ZOI) standards by Guevara[21].
-
Spray
reagentPositive
resultL. cochleatum L. moluccanum Compounds present Hexane DCM Methanol Hexane DCM Methanol A Blue + + + + + + Phenols, tannins, flavonoids B Brown-orange − + + + + + Alkaloids C Blur to red-violet − − − − − − Cardenolides D Orange, Yellow, Blue − − − − − +(2) Antraquinones (1), anthrones (2), coumarines (3) E Orange-violet − − − − − − Anthraquinones F Blue violet − − − − − − Indoles G Blue violet + + + + − − Triterpenes, sterols H Blue − − − − − − Sugars The spray reagents used include A, potassium ferricyanide-ferric chloride; B, Dragendorff’s reagent; C, Kedde reagent; D, Bornträger reagent; E, magnesium acetate in methanol; F, Van-Urk-Salkowski test; G, vanillin-sulfuric acid; and H, α-Naphthol-sulfuric acid. Table 1.
Thin-layer chromatography analysis of L. cochleatum and L. moluccanum in solvent system.
-
CP TC L. cochleatum L. moluccanum Haxane DCM Methanol Hexane DCM Methanol K. pneumoniae 32.06 24.46 7.96 8.94 10 17.14 7.72 6.89 S. aureus 35.7 30.6 7.68 6.79 8.83 8.18 6.34 6 P. aeruginosa 41.54 28.13 6.33 8.14 8.33 8 9.15 7.56 E. agglomerans 25.32 24.67 15.28 15.86 6.83 7.96 7.46 6 E. coli 25.62 20.4 6.72 14.84 6 8.81 6 6 CP, chloramphenicol; TC, tetracycline. Table 2.
Mean of the ZOI (mm) of the Leptogium extracts against the test pathogenic bacteria.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(2)