-
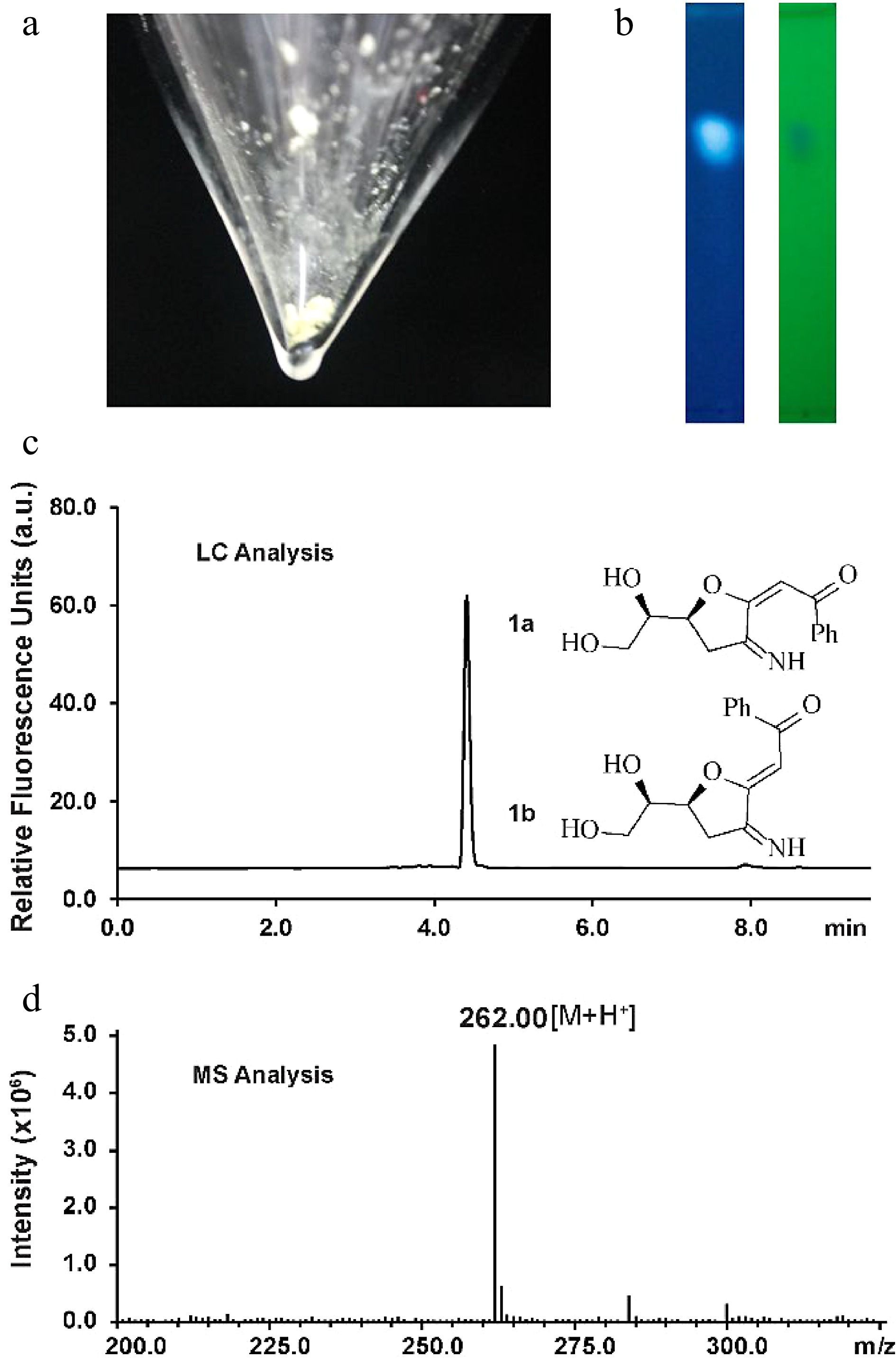
Figure 1.
Characterization of the fluorescent glucosamine derivative. (a) Isolated compound 1a and 1b mixture after silica-gel chromatography purification. (b) TLC analysis by irradiation with UV light (left: 362 nm, right: 254 nm). (c) HPLC chromatogram of compounds 1a and 1b (excitation 362 nm, emission 450 nm). (d) Positive ion electrospray-ionization (ESI) mass spectrum of compounds 1a and 1b.
-
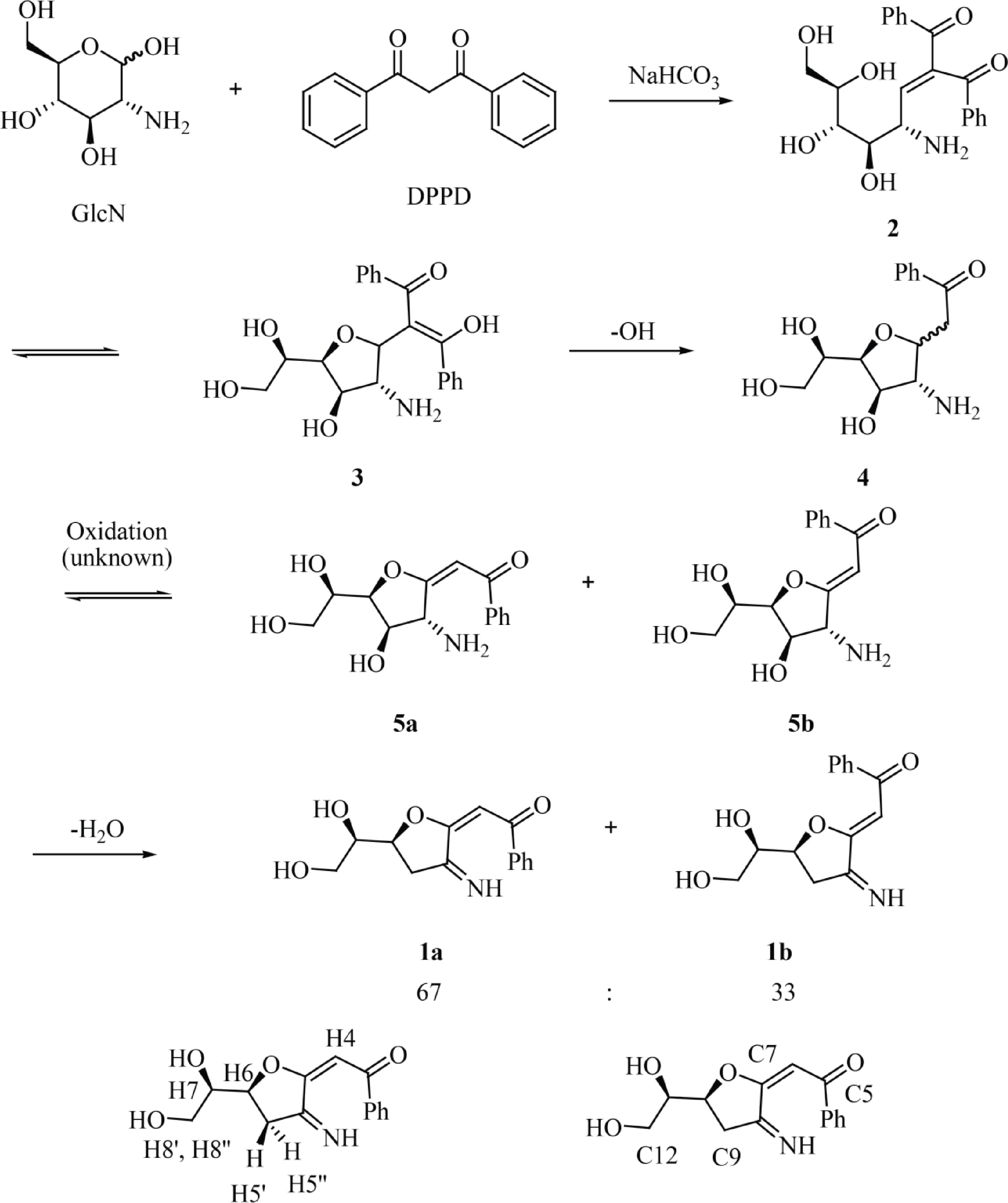
Figure 2.
Reaction of GlcN with DPPD to afford fluorescent glucosamine derivatives 1a and 1b with atom numbering corresponding to that used for NMR assignment.
-
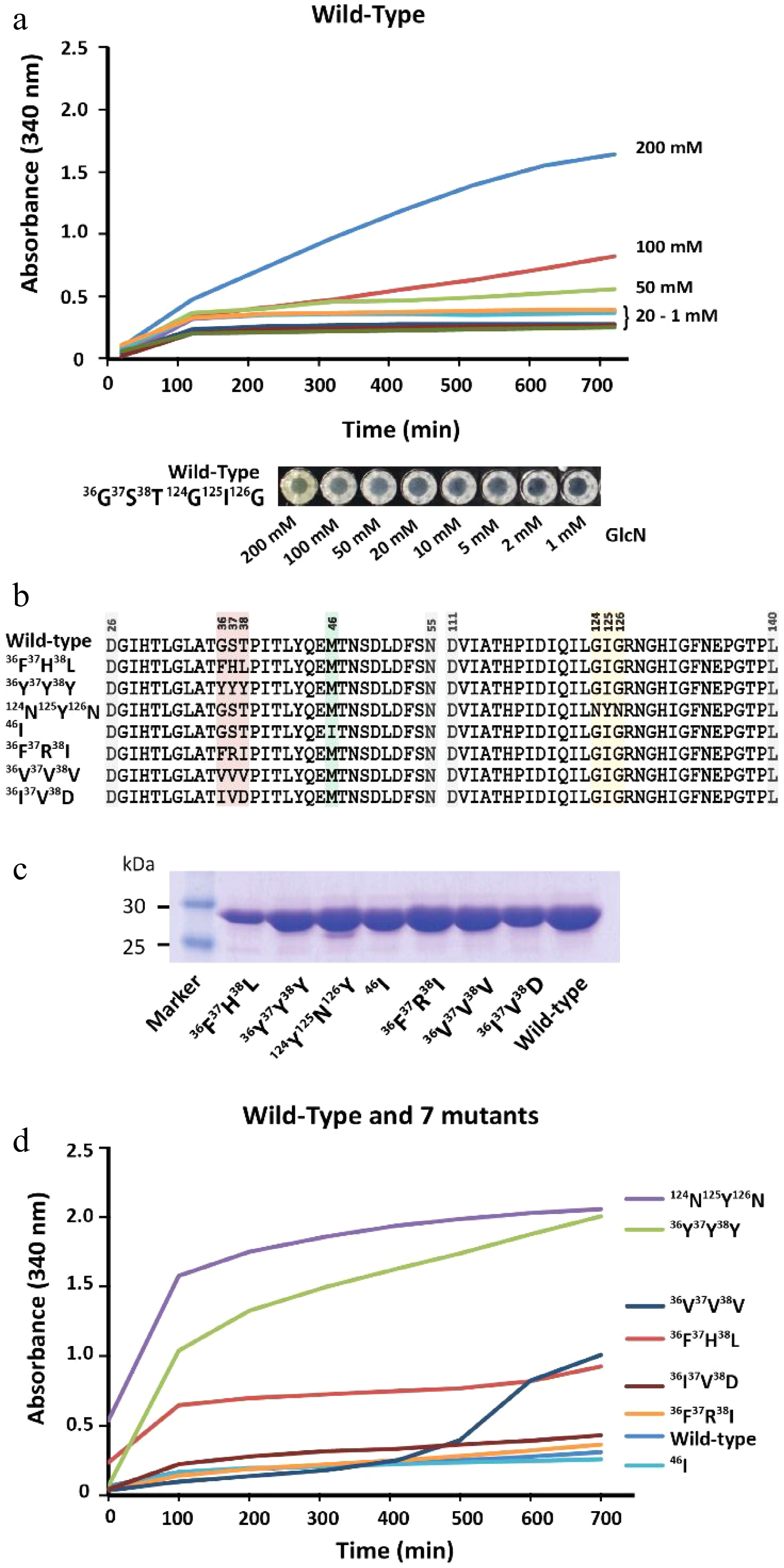
Figure 3.
Characterization of GPDA wild-type and mutant variants. (a) Precipitation behavior of wild-type GPDA in the presence of various concentrations of GlcN. (b) Protein sequence comparison of the selected GPDA mutant variants. (c) Comparison of protein yields of GPDA mutant and wild-type variants. (d) Precipitation behavior of the GPDA variants in the presence of 50 mM GlcN.
-
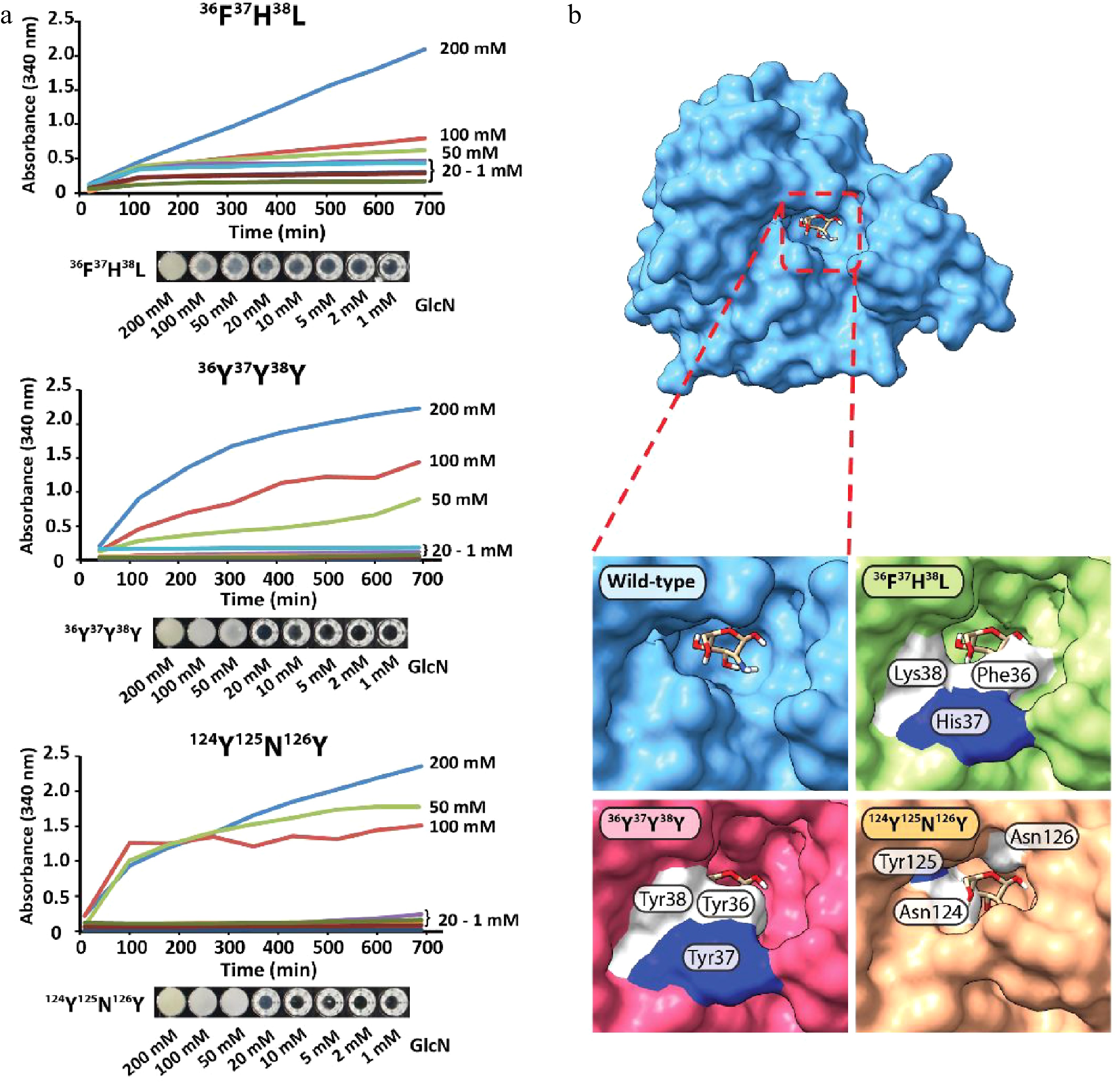
Figure 4.
(a) Protein precipitation behavior of GPDA mutant variants and (b) visualization of the GlcN binding site of the GPDA wild-type and mutant variants protein models generated by AlphaFold.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(0)