-
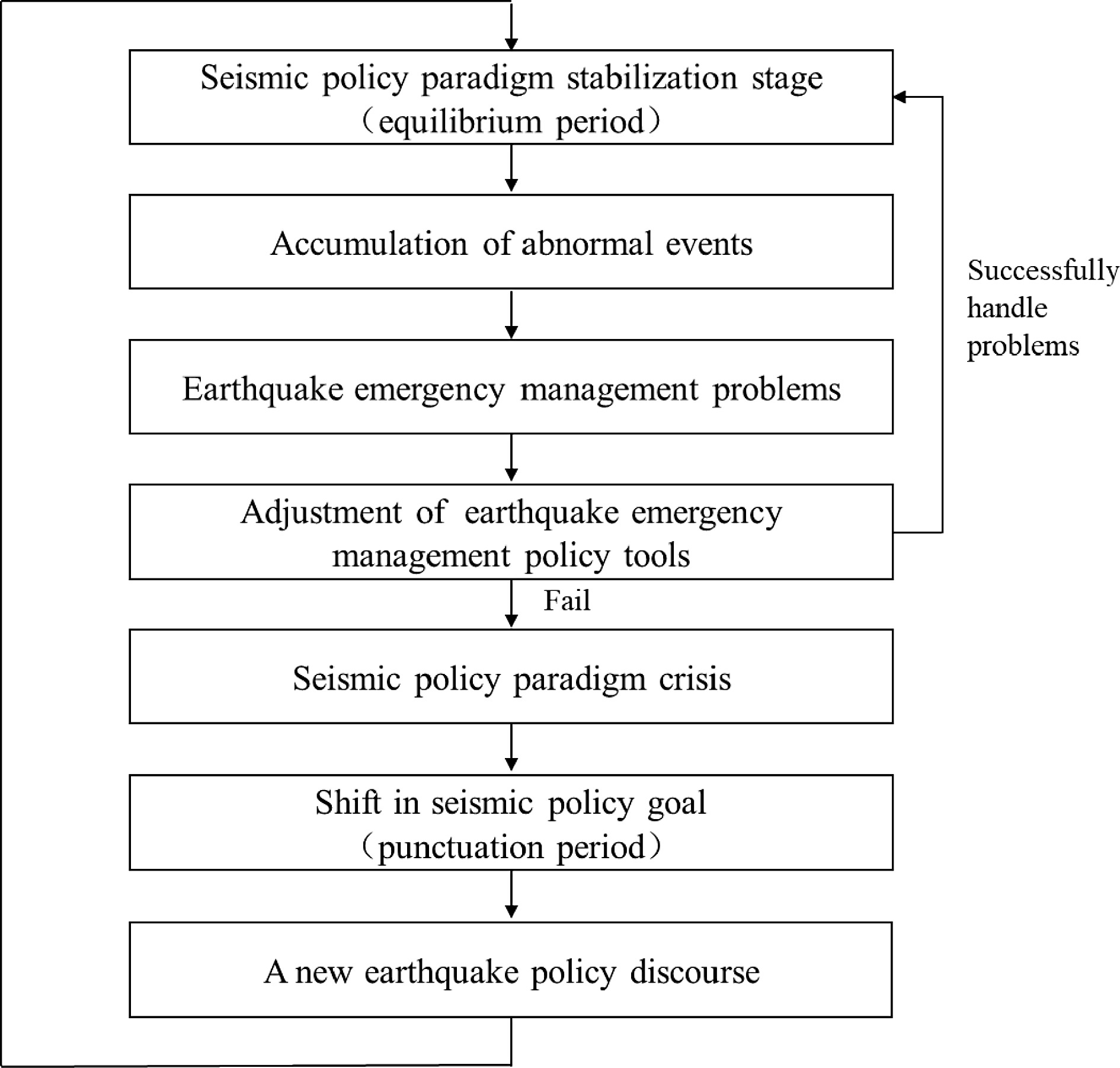
Figure 1.
A historical institutionalism framework for paradigm shift in earthquake emergency management policies.
-
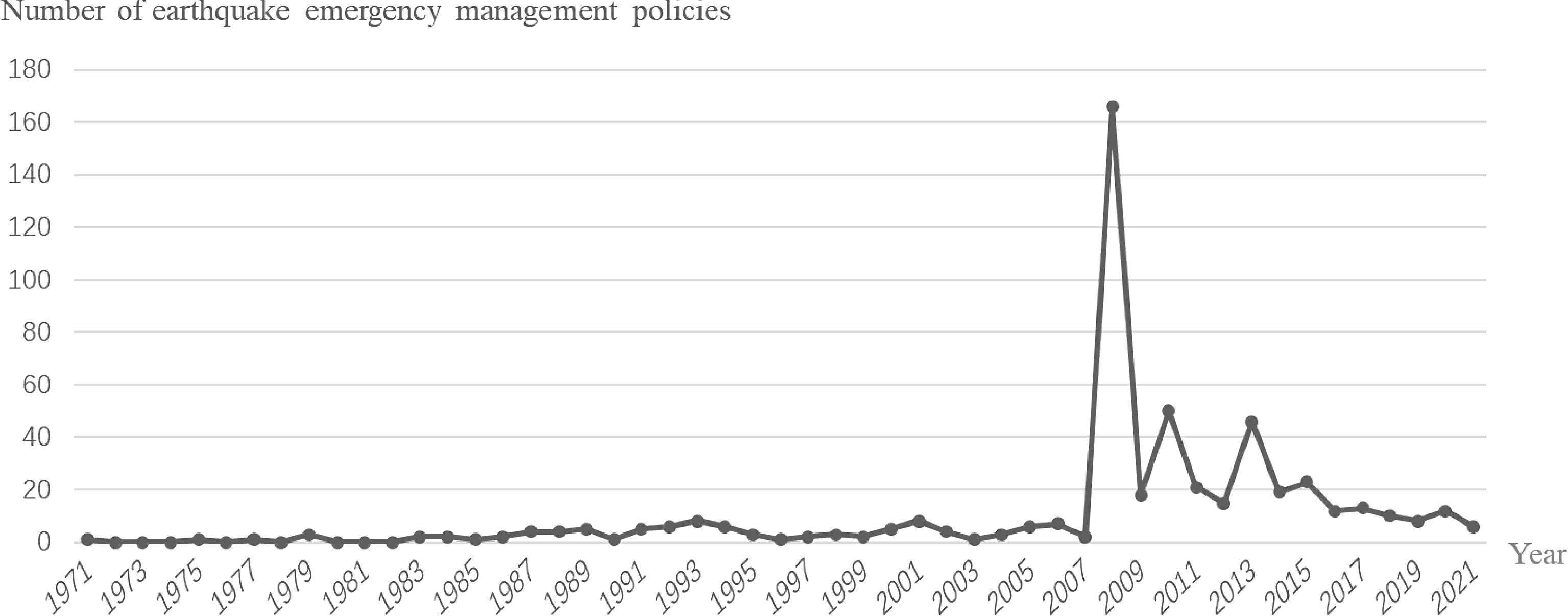
Figure 2.
The history of changes in China's earthquake emergency management policies.
-
Policy goal keyword extraction Example of policy text content Policy examples Disaster relief Local governments and civil affairs departments carry out research on earthquake relief countermeasures, not only......, but also for future scientific guidance of our disaster relief work. Proceedings of the Symposium on Earthquake Disaster Response Research (No.21 Document of Ministry of Civil Affairs[1987]) Disaster prevention Must effectively strengthen the monitoring and forecasting work of the seven key surveillance areas, and suggest that the local people's government take practical measures as early as possible to strengthen and implement disaster prevention work in these areas. Earthquake Administration, Ministry of Construction, Ministry of Civil Affairs on Strengthening Earthquake Disaster Prevention in Key Earthquake Surveillance Areas (No.113 Document of State Earthquake Administration [89]) Disaster mitigation Incorporate the knowledge of earthquake prevention and disaster reduction into the national quality education system, ......, and persistently publicize the knowledge of earthquake prevention and disaster reduction to make it known to every household and everyone. Notice from China Earthquake Administration, Ministry of Science and Technology on Strengthening the Popularization of Earthquake Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Science (No.20 Document of China Earthquake Administration[2014]) Combination of disaster prevention, mitigation
and reliefFirmly establish the concept of disaster risk management,......,disaster prevention, mitigation and relief into the overall planning of national economic and social development at all levels, as an important element of the construction of the national public security system. The CPC Central Committee and State Council on promoting disaster prevention, mitigation and disaster relief institutional reform views (No.35 Document of CPC Central Committee [2016]) Table 1.
Extraction of key words from China's earthquake emergency management policy goals.
-
Types of policy instruments Key words Policy examples Organizational policy tools Establishment, abolition, earthquake working group, earthquake bureau, earthquake working agency, earthquake management system Notice of the State Council on Strengthening the Central Earthquake Working Group and Establishing the National Earthquake Bureau (No.56 Document of State Council) Information policy tools Forecast, communication, notification, science and technology, publicity, education, information sharing Seismic Information Network Management Interim Regulations (No.140 Document of China Earthquake Administration[2008]) Regulatory
policy toolsWork system, management methods, standardization, administration according to law, serious discipline, clean up and regulate China Earthquake Administration on the comprehensive promotion of administrative implementation of the law (No.122 Document of China Earthquake Administration[2007]) Economic
policy toolsPayroll, allowances, insurance, budget management, auditing, bidding and procurement Management of special reserve for earthquake catastrophe insurance for urban and rural residential buildings ( No.38 Document of the Ministry of Finance[2017]) Table 2.
Types of policy tools for earthquake emergency management in China.
-
Policy paradigm Focusing on disaster relief Policy problem Focused on economic development (ignored the earthquake problems) Policy goal 'Catch up with the United Kingdom and surpass the United States'. 'Rely on one's own efforts'. 'Develop the economy'. 'Work with stamina and diligence' Subjects of responsibility Central Committee of the CPC, the central government, the Ministry of the Interior, Central Disaster Relief Committee, Chinese Academy of Sciences Policy tools • Organizational policy tools
Established the Central Disaster Relief Committee
Established the Earthquake Working Committee
• Information policy tools
Established the seismic network
• Regulatory policy tools
Stopped the blind exodus of people from disaster areas
• Economic policy tools
Reduced taxes for the affected areas
Developed agricultural production
Disbursed loans and handoutsPolicy discourse Mobilizing language
'Mobilize and relocate the production of people in the disaster area''
'Mobilize and organize the masses to fight against natural disasters'Table 3.
Seismic policy paradigm before the Xingtai earthquake.
-
Policy paradigm Focusing on earthquake prevention Policy problem Earthquake prevention and prediction Policy goal 'Focus on prevention' Subjects of responsibility Central Committee of the CPC, the Revolutionary Committee, Seismological Bureau, seismic group, seismic crew, Earthquake Relief Headquarter Policy tools • Organizational policy tools
Organized the central Earthquake team
Established the national Seismological Bureau
• Information policy tools
Improved the seismic network
• Regulatory policy tools
Stopped the blind exodus of people from disaster areas
• Economic policy tools
Increased the issue of subsidies for earthquake workersPolicy discourse Mobilizing language
'Uphold the unified leadership of the Party' 'Lead people's war'Table 4.
The seismic policy paradigm from the Xingtai earthquake to the Tangshan earthquake.
-
Policy paradigm Focusing on earthquake prevention Policy problem Used seismological science to strengthen earthquake prediction and monitoring and reduced earthquake disasters Policy goal 'Focus on prevention' Subjects of responsibility CPC, governments, Seismological organizations such as the Seismological Bureau, the Seismological Monitoring and Research Center and the Seismological Office, Earthquake Relief Headquarters, Leading Group for earthquake relief work Policy tools • Organizational policy tools
Adjusted the earthquake organization and improved the earthquake management system; Adjusted the seismological scientific research institutions; Organized professional earthquake teams and mass survey and prevention teams
• Information policy tools
Strengthened the education and training of earthquake personnel; Conducted academic exchanges and international cooperation; Block some news; Publicized knowledge of earthquake prevention and aseismic resistance; Paid attention to science and technology management and science and technology achievements management;
• Regulatory policy tools
Stopped the blind exodus of people from disaster areas; Promulgated the
'Regulations on the Administration of Earthquake Analysis and Forecast of the State Earthquake Administration'; Promulgated the 'Regulations on the Release of Earthquake Forecasts'
• Economic policy tools
Set up funds for local earthquake projects; Reformed the wage and subsidy system for personnel working in earthquake institutions; Awarded seismological achievements
• Other policy tools
Took earthquake fortification and reinforcement measuresPolicy discourse Managerial language
'Strengthen earthquake prediction and engineering earthquake research', 'Promote the modernization of earthquake science and technology', 'Promote the modernization of earthquake science and technology', 'Give play to the role of earthquake science in national economic construction and social progress'Table 5.
The seismic policy paradigm from the Tangshan earthquake to the establishment of the China National Committee of the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction.
-
Policy paradigm Focusing on earthquake prevention and mitigation Policy problem Strengthened disaster prevention, resistance, relief and comprehensive disaster reduction Policy goal 'Prevention, taking into account the needs of peacetime and earthquake, constant readiness', 'Putting prevention first, combining prevention and rescue efforts, and comprehensively reducing disaster', 'To prevent and mitigate earthquake disasters, protect people’s lives and property, and promote sustainable economic and social development' Subjects of responsibility CPC, governments, China Earthquake Administration, China National Committee of the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (National Disaster Reduction Commission), Emergency Committees, Emergency Offices, Earthquake Relief Headquarters, Leading Group for earthquake relief work Policy tools • Organizational policy tools
Established China National Committee for Natural Disaster Reduction; Adjusted the earthquake organization and improved the earthquake management system; Clarified the work of relevant organizations on disaster prevention and mitigation; Strengthened earthquake preparedness and disaster mitigation at the city, county and community level
• Information policy tools
Strengthened earthquake prediction and improved earthquake communication systems; Formulated China's seismic intensity zoning map; Strengthened earthquake investigation and judgment, information communication, information disclosure and public opinion control and management; Strengthened education of earthquake knowledge; Strengthened seismological research; Promoted international exchanges and cooperation;
• Regulatory policy tools
Stopped the blind exodus of people from disaster areas; Established an earthquake emergency inspection system; Strengthened the construction of earthquake emergency under the rule of law; Comprehensively promoted law-based administration of the earthquake system; Introduced comprehensive emergency management laws;
• Economic policy tools
Strengthened financial management of earthquake departments; Strengthened the management of the companies belonging to the seismic system; Strengthened the assessment of earthquake losses; Mobilized units and the general public to participate in earthquake insurance and standardized enterprise insurance; Standardized the management of seismic safety assessment feesPolicy discourse Managerial language
'The work of earthquake prevention and mitigation shall be managed in a unified manner', 'Comprehensively strengthen earthquake emergency management', 'Promote coordinated, orderly and efficient earthquake emergency response', 'Ensure and promote the comprehensive, coordinated and sustainable development of earthquake preparedness and disaster reduction'Table 6.
The seismic policy paradigm from the establishment of the China National Committee of the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction to the reform of disaster prevention, mitigation and relief system.
-
Policy paradigm Focusing on integrating disaster prevention, mitigation and relief Policy problem Enhanced risk awareness and focused on disaster prevention, resistance, relief and comprehensive disaster reduction Policy goal 'Focus on prevention, and combine disaster prevention and relief', 'Integrate normal disaster mitigation with abnormal disaster relief, shift focus from post-disaster relief to pre-disaster prevention, from responding to a single type of disaster to comprehensive disaster reduction, and from reducing disaster losses to mitigating disaster risks' Subjects of responsibility CPC, governments, the Ministry of Emergency Management, China Earthquake Administration, National Disaster Reduction Commission, Earthquake Relief Headquarters, Leading Group for earthquake relief work Policy tools • Organizational policy tools
Established the Ministry of Emergency Management; Advanced the reform of disaster prevention, mitigation and relief systems; Formulated plans for earthquake prevention and disaster reduction; Standardized the evaluation of professional and technical titles
• Information policy tools
Strengthened science popularization in earthquake preparedness and disaster mitigation; Promoted the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements in earthquake; Strengthened the building of information sharing mechanisms; Strengthened the building of information sharing mechanisms
• Regulatory policy tools
Standardized the seismic safety evaluation; Promulgated the 'Administrative Measures for the standardization of earthquakes'; Promulgated the 'Rules for the Administration of the institution and revision of seismic standard System'
• Economic policy tools
Established an earthquake catastrophe insurance system for urban and rural residential buildings; Strengthened budget management and performance evaluation of the Seismological Bureau; Standardized the tendering and procurement work of the seismological BureauPolicy discourse Governance language
'Advocate extensive participation of social forces and market mechanisms'; 'Vigorously promoting the modernization of earthquake disaster prevention and mitigation in the new era'; 'Comprehensively improving the emergency rescue capacity and comprehensive disaster prevention capacity of earthquake disasters'; 'Improving the rule of law, standardization and modernization of disaster prevention, mitigation and relief work'Table 7.
The seismic policy paradigm of combining disaster prevention, reduction and relief after the reform of disaster prevention and relief system.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(7)