-
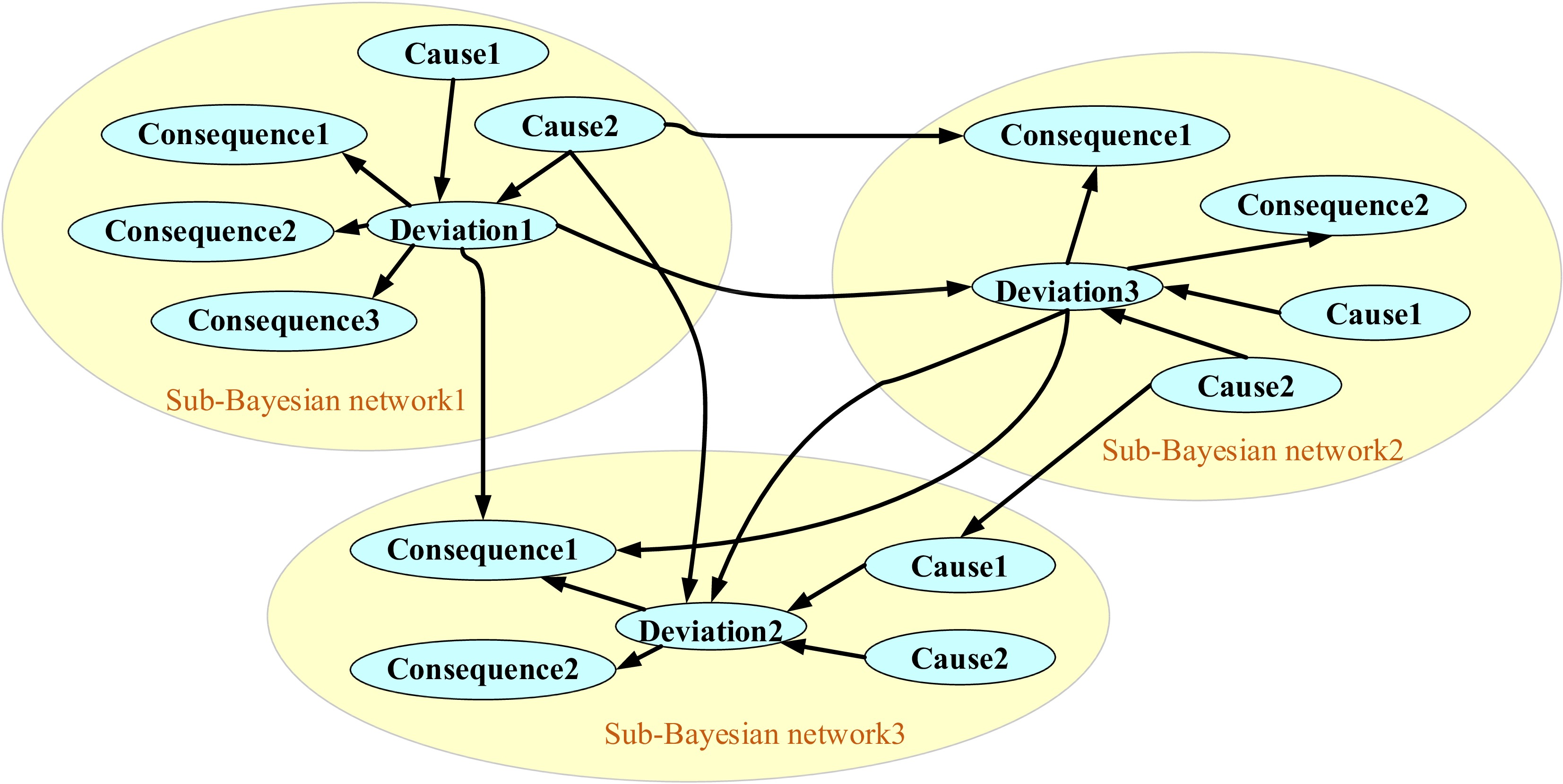
Figure 1.
HAZOP converted to Bayesian network.
-
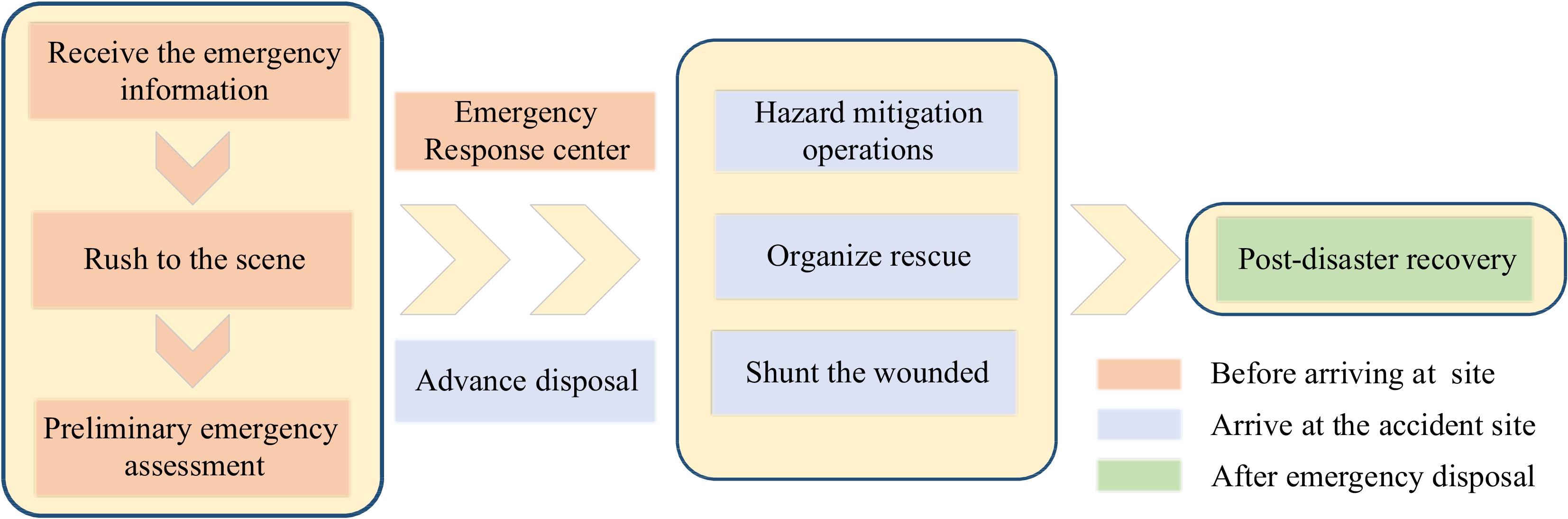
Figure 2.
Emergency response process of city gas explosion accidents.
-
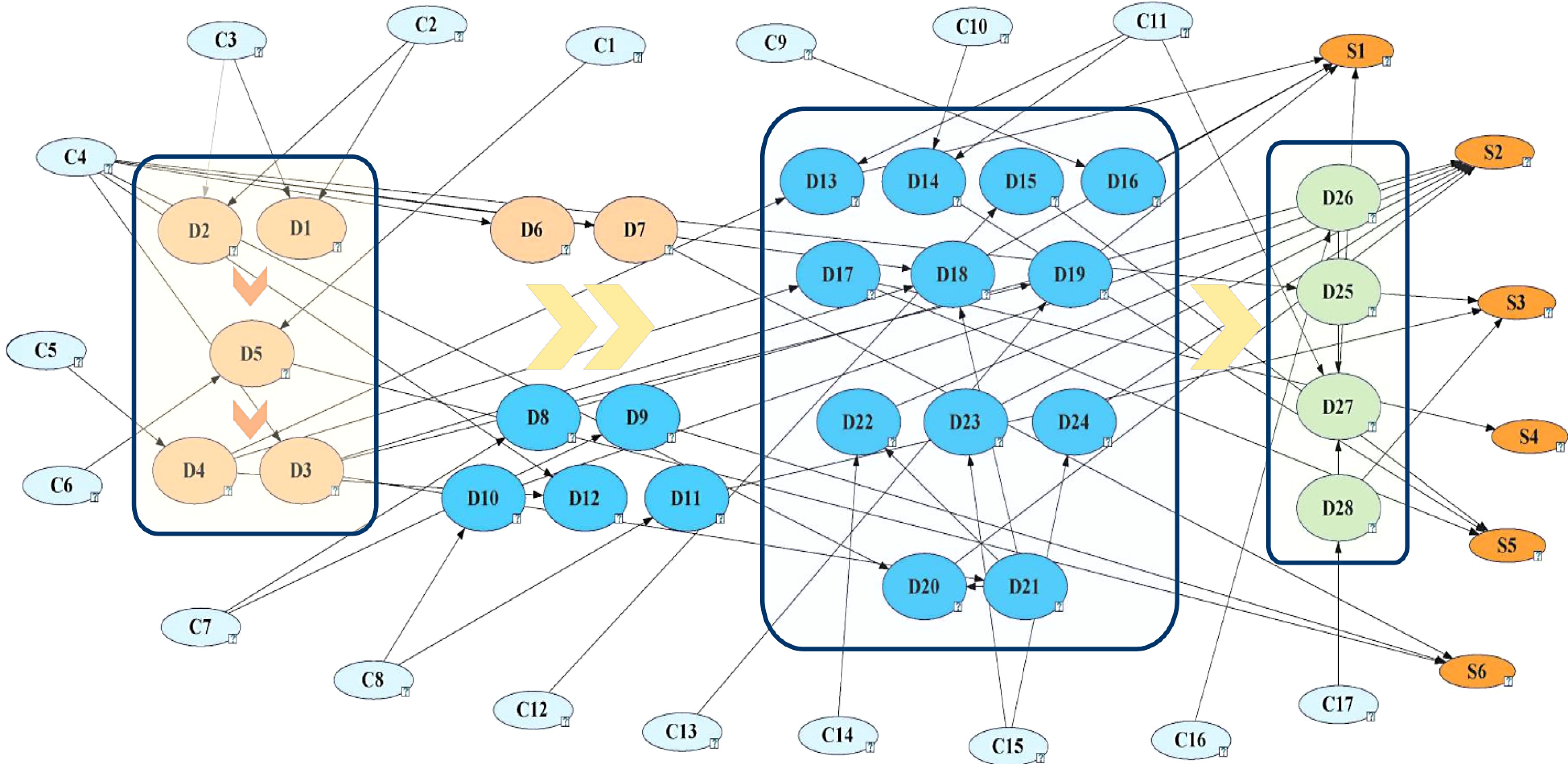
Figure 3.
Bayesian network for emergency response of city gas explosion accidents.
-
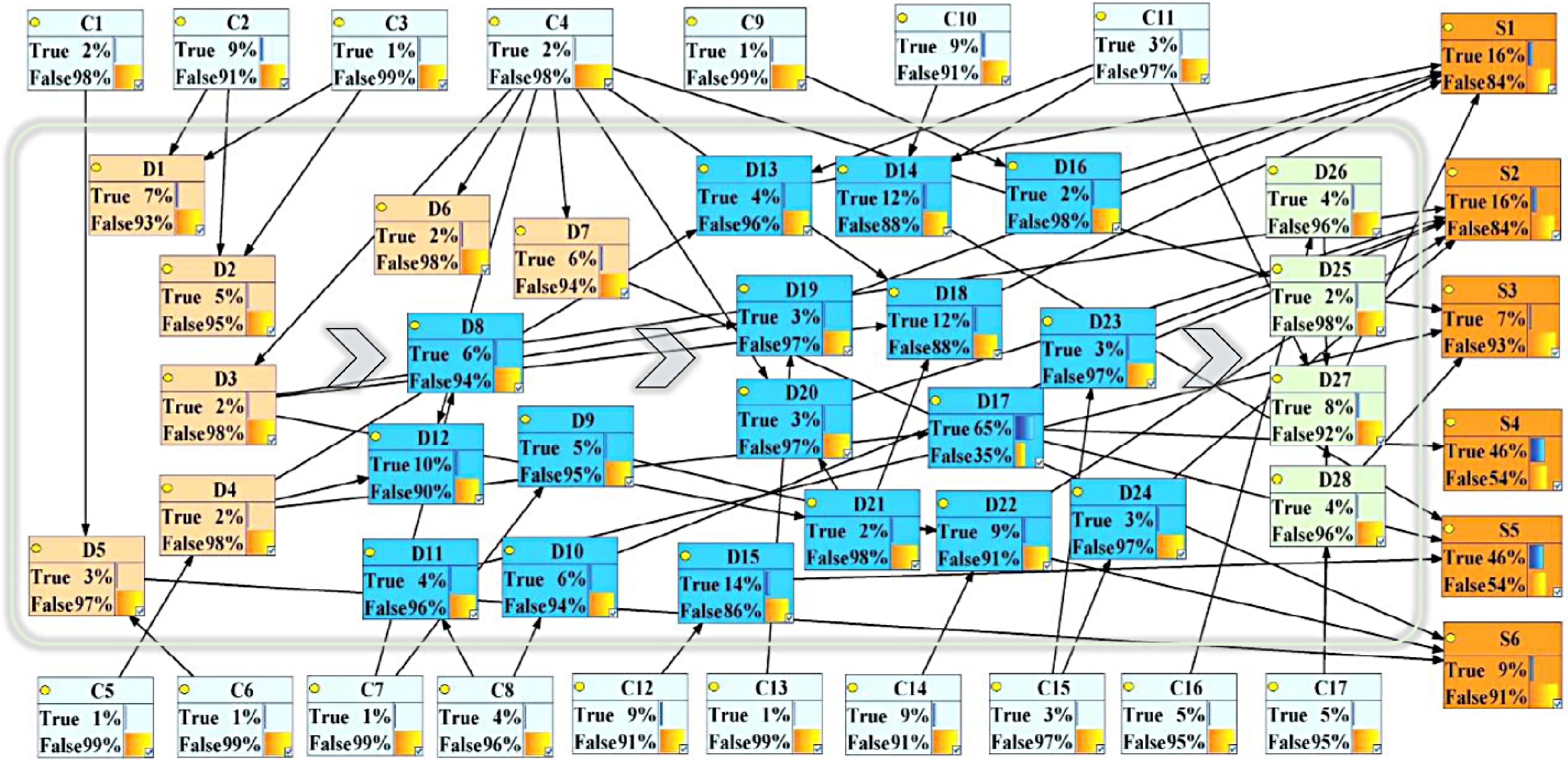
Figure 4.
Bayesian network for risk in the emergency response process.
-
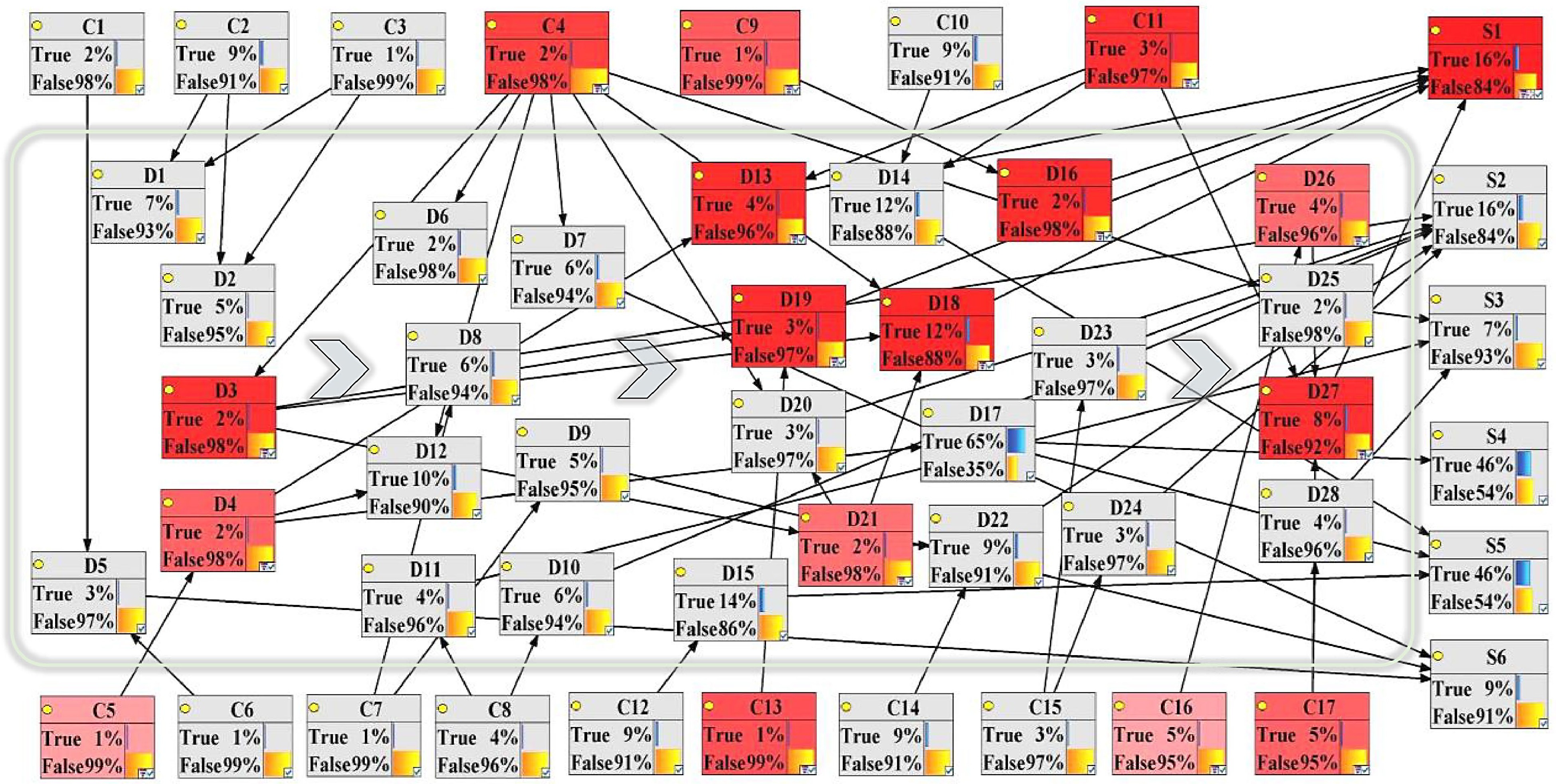
Figure 5.
Sensitivity analysis with target node as 'Accident expansion S1'.
-
Guide words Implication No The entire step is skipped completely or the specific intended action is not performed. Part of Only part of the full intent (a task involving two or more almost simultaneous actions, such as 'open valves A, B and C') is performed. More Steps are executed too fast or take too long or are executed to a greater extent than expected or are executed with too many additions. Less Steps are executed too slowly or for too short a time or not to the extent expected or the number added to the execution is too small. As well as or more than Something happens, or the operator does another action, in addition to the specified step being done correctly. Reverse Steps are executed too early or too late in the overall sequence, in other words, not in the expected order. Other than The wrong material was selected or added, or the wrong equipment was selected, read, or operated in an unintended manner, etc. Table 1.
Guide words for HAZOP.
-
Stages Emergency response special measure Organize rescue Personnel placement; Material transfer Shunt the wounded Treat the severely injured people; Treat the slightly injured people Post-disaster recovery Recover gas supply; Site recovery and cleanup operation Hazard mitigation operations Gas source cut-off; Gas dilution dispersion; Environmental quality detection; Fire appraisal; Fight the fire Advance response Alerting zone; Resident evacuation; Traffic control; Determine the site conditions Table 2.
Specific measures for emergency response.
-
Stage Parameter Guide word Deviation Possible causes Consequences Hazard mitigation operations Operation No Flammable gas concentration not monitored 1) Emergency Personnel Paralysis
2) Situation on site not identifiedAccident expansion Reverse Not cutting off the gas source first 1) Serious damage to valves, pipelines and other facilities
2) Emergency Personnel ParalysisAccumulation combustible gas Less Inaccurate gas concentration monitoring Unreasonable gas monitoring way Accumulation combustible gas Incomplete fire extinguishing Firefighter paralysis Accident expansion Incomplete gas dilution 1) Inaccurate gas concentration monitoring
2) Situation on site not identified1) Accumulation of combustible gas
2) Personnel suffocationTime Less Fire not extinguished in time 1) Unreasonable preliminary assessment of disaster
2) Insufficient emergency rescue equipment
3) Improper command of emergency centerCasualties Procedure Other than Unreasonable fire extinguishing 1) Improper command of emergency center
2) Emergency personnel paralysisAccident expansion Table 3.
HAZOP analysis for the emergency response process.
-
Node Risk factors Node Risk factors D1 Incomplete alarm information D27 Accident hazards like reburning D2 Alarm not in time D28 Site cleaning recovery slow D3 Unreasonable preliminary assessment of disaster C1 Traffic congestion D4 Situation on site not identified C2 Alarm personnel panic D5 Not timely to the scene C3 Incomplete inquiry by the police receiver D6 No emergency center established in advance C4 Improper command of emergency center D7 No emergency center established in time C5 Weak operator safety skills D8 Mass evacuation not in time C6 Road traffic accident D9 Traffic control not in time C7 Improper command of emergency center D10 Warning area too small C8 Unreasonable assessment of hazard scope D11 Unreasonable division of warning area C9 Firefighters paralysis D12 Incomplete mass evacuation C10 Serious damage to valves, pipelines and other facilities D13 Flammable gas concentration not monitored C11 Emergency personnel paralysis D14 Not cutting off the gas source first C12 Unreasonable gas monitoring D15 Inaccurate gas concentration monitoring C13 Firefighter misjudgment D16 Incomplete fire extinguishing C14 Emergency search and rescue not in time D17 Incomplete gas dilution C15 Misjudgment of medical staff D18 Fire not extinguished in time C16 Post-disaster reconstruction personnel paralysis D19 Unreasonable fire extinguishing method C17 Incomplete leak stoppage and repair of gas pipeline D20 Improper placement of personnel S1 Accident expansion D21 Insufficient emergency rescue equipment S2 Casualties D22 Late treatment for the wounded S3 Affecting the lives of residents D23 Incorrect treatment S4 Personnel suffocation D24 Unreasonable distribution of wounded S5 Accumulation of combustible gas D25 Gas supply not restored S6 Delayed emergency rescue D26 On-site cleaning recovery incomplete Table 4.
Symbolic meaning of nodes.
-
Node State True False C1 0.02 0.98 C2 0.09 0.91 C3 0.01 0.99 C4 0.02 0.98 C5 0.01 0.99 C6 0.01 0.99 C7 0.01 0.99 C8 0.04 0.96 C9 0.01 0.99 C10 0.09 0.91 C11 0.03 0.97 C12 0.09 0.91 C13 0.01 0.99 C14 0.09 0.91 C15 0.03 0.97 C16 0.05 0.95 C17 0.05 0.95 Table 5.
Input node prior probability.
-
C2 True False C3 True False True False True 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.01 False 0.4 0.6 0.6 0.99 Table 6.
Conditional probability of intermediate node D2.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(6)