-

Figure 1.
Sex determination system by the 'two mutations' model[13]. (A) One of a pair of autosomes has obtained a mutation of a certain sex sterility gene, 'M' to 'm' is a recessive mutation, 'f' to 'SuF' is a dominant mutation. (B) The other one autosome acquires the mutation corresponding to another sex sterility gene, thus generating proto-X and proto-Y, the precursor of sex chromosome. (C) Sterile genes are linked and sex chromosomes are preliminarily formed and dioecious plants emerged. The shaded part of the Y chromosome in (C) represents the sex-linked region.
-
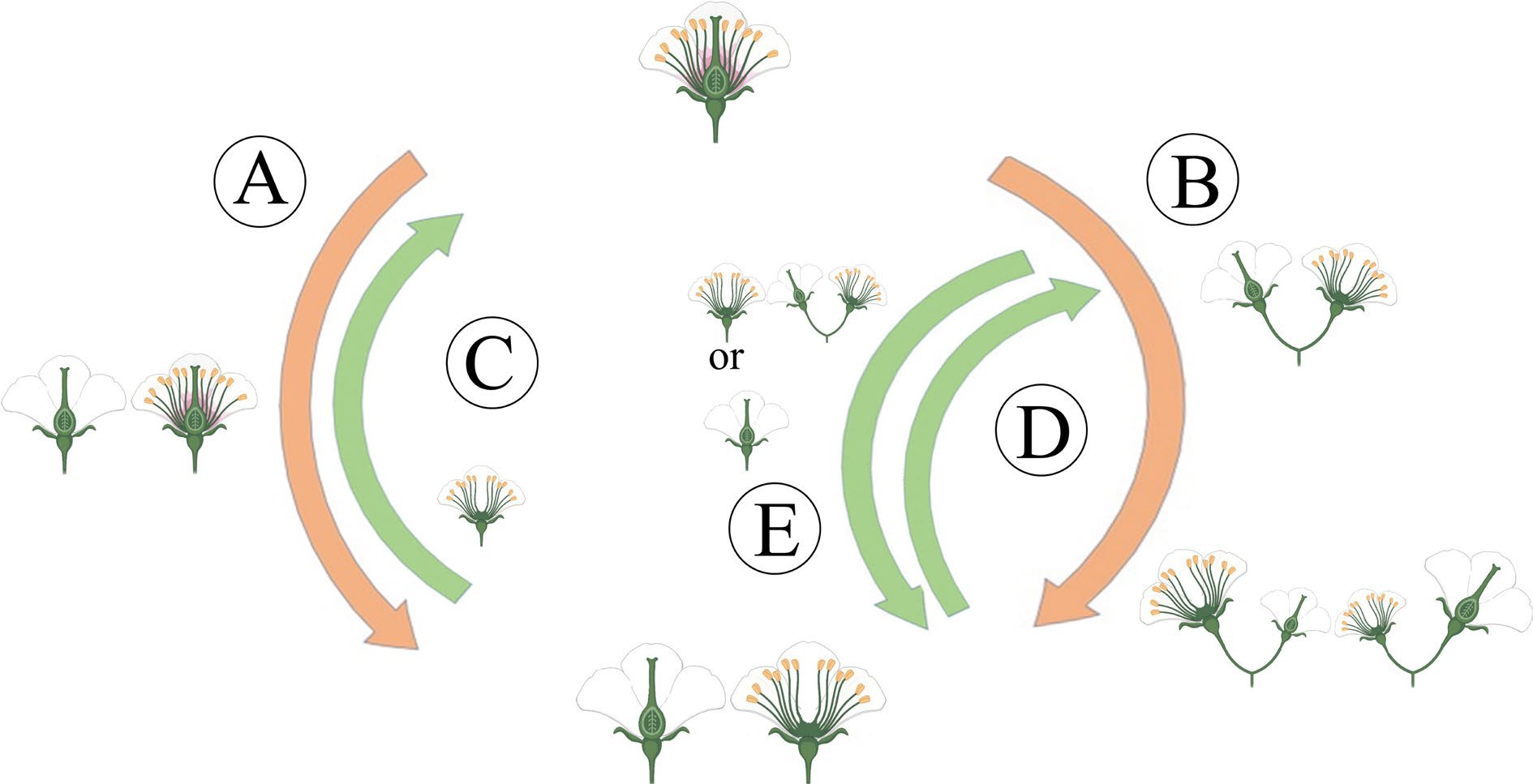
Figure 2.
The main evolutionary routes to dioecy. (A) The gynodioecy-dioecy routes. (B) The monoecy-dioecy routes. (C), (D) It has been highlighted that dioecy may frequently revert to hermaphroditism. (C) In the gynodioecy-dioecy routes, inconstant males may help reversions to hermaphroditism. (D), (E) In the monoecy-dioecy route, there may be cycles between monoecy and dioecy.
-

Figure 3.
Two transposition pathways (copy and paste) leading to the emergence of XY and ZW sex determination systems in Populus deltoides.
-
Taxon Species Sex determination system Sex-linked region or genes Ortholog gene or family Reference Bryophyte Marchantia
polymorphaXY 14 male-specific genes — [27,30] Gymnosperm Ginkgo biloba ZW GbMADS18, Gb_15883,
Gb_15884, Gb_15885,
Gb_15886, Gb_28587MADS-box (GbMADS18),
RR12 (Gb_15883),
RR2 (Gb_15884),
ELF6 (Gb_15885),[30−33] AtBAT1 (Gb_15886), AGL8 (Gb_28587) Angiosperm Fragaria virginiana ZW GMEW, RPP0W GDP-mannose 3,5- epimerase 2 (GMEW),
60S acidic ribosomal
protein P0 (RPP0W)[5, 34] Spinacia oleracea XY LG4 (66.98−69.72 cM and
75.48−92.96 cM)— [35,20] Silene latifolia XY SlAP3, SlSTM, SlCUC AP3 (SlAP3), STM (SlSTM), CUC1/CUC2
(SlCUC)[36,37] Phoenix dactylifera XY CYP703, GPAT3 — [38] Actinidia chinensis
A. deliciosaXY SyGl, FrBy ARR24(SyGl),
FAS1(FrBy)[39,40] Asparagus officinalis XY SOFF, aspTDF1 DUF247 (SOFF),
TDF1 (aspTDF1)[41,42] Diospyros lotus,
D. kakiXY MeGI, OGI HB40 (MeGI) [42,43] Cucumis melon — ACS7, ACS11,
WIP1, CRC— [43−46] C. sativus — ACS7, ACS11,
WIP1, CRC— [43−46] Carica papaya XY CpSVPL, CpSERK, CpCAF1AL — [41,47−49] Myrica rubra ZW 59 kb female- specific
region on chromosome 8— [50] Cannabis sativa XY sex chromosomes — [51] Vitis vinifera XY VviINP1, VviYABBY3 INP1 (VviINP1), [52] YAB1 (VviYABBY3) Populus deltoides,
P. tremula, P. alba, P. trichocarpa, P. balsamifera,
P. tomentosaXY, ZW FERR-R’, FERR,
MmS, ARR17ARR17
[22,53,54]Humulus lupulus XY Gr09-M — [55] Salix purpurea, ZW RR RR9/ARR17 S. triandra
[55,56]Table 1.
Results of sex determination of representative plants.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)