-
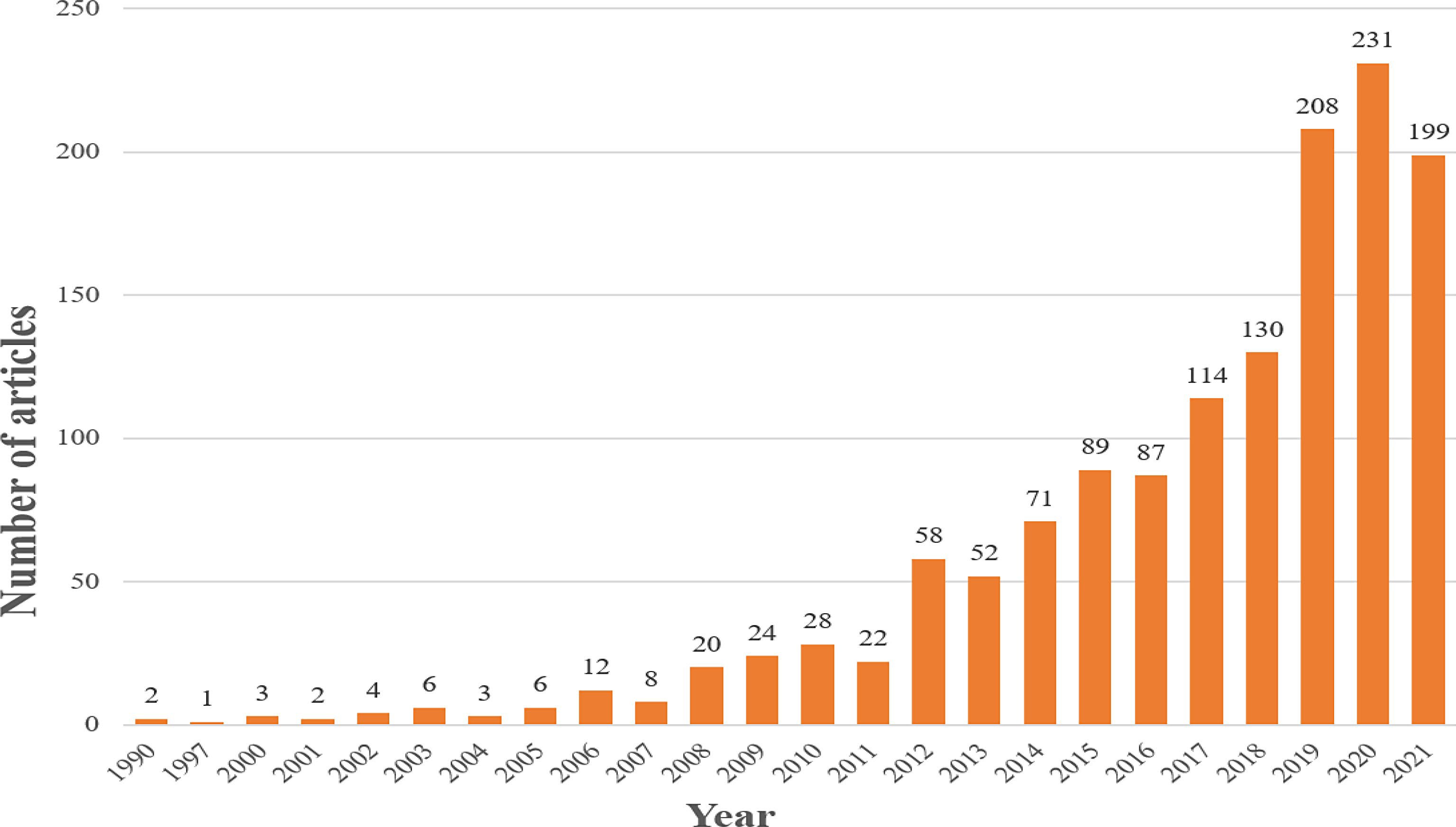
Figure 1.
Annual publications in the field of domestic safety evacuation during 1990−2021.
-
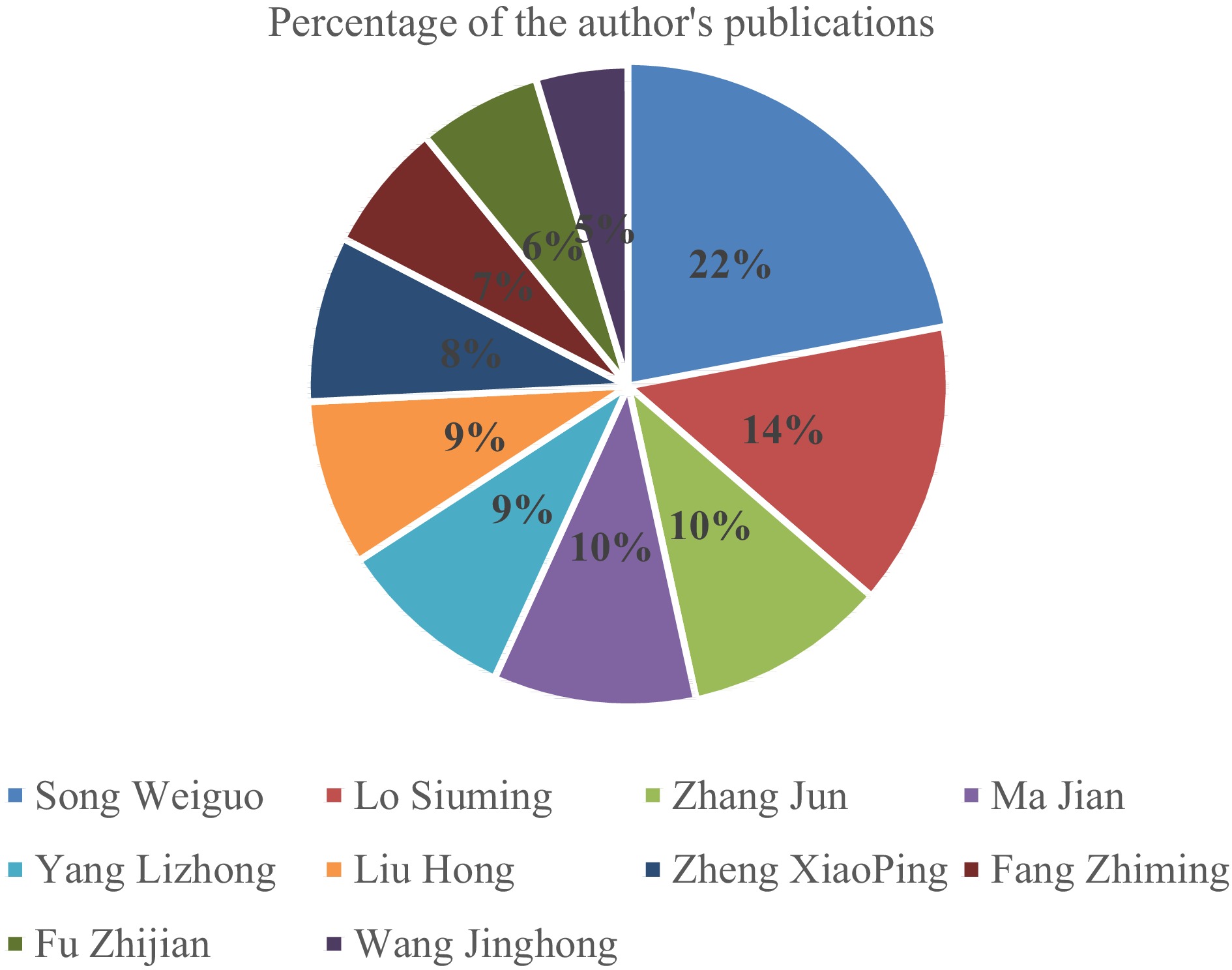
Figure 2.
Statistics of the top 10 authors in the number of publications in the field of safety evacuation Web of Science from 1990 to 2021.
-
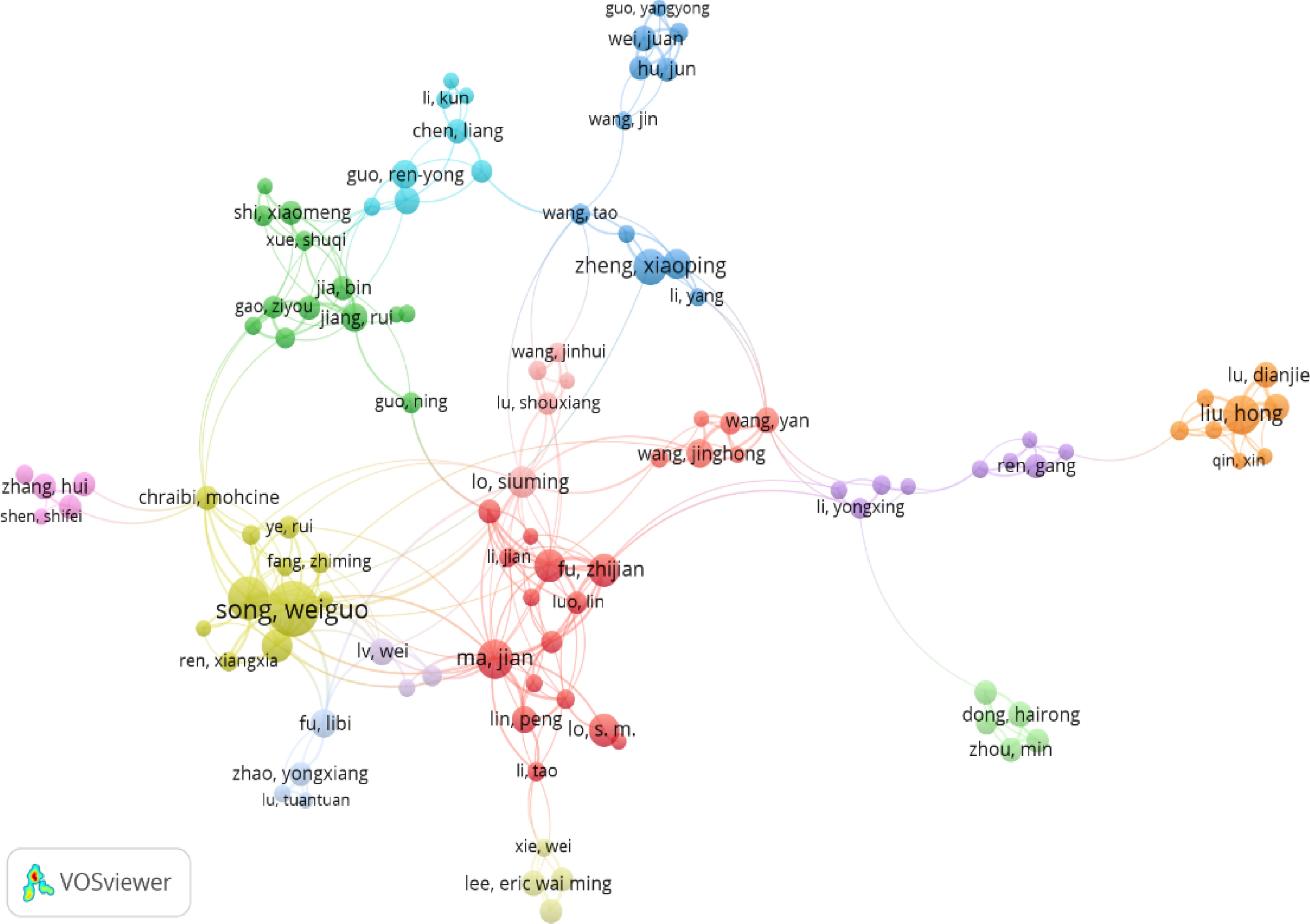
Figure 3.
Network diagram of researchers in the field of safe evacuation from 1990 to 2021.
-
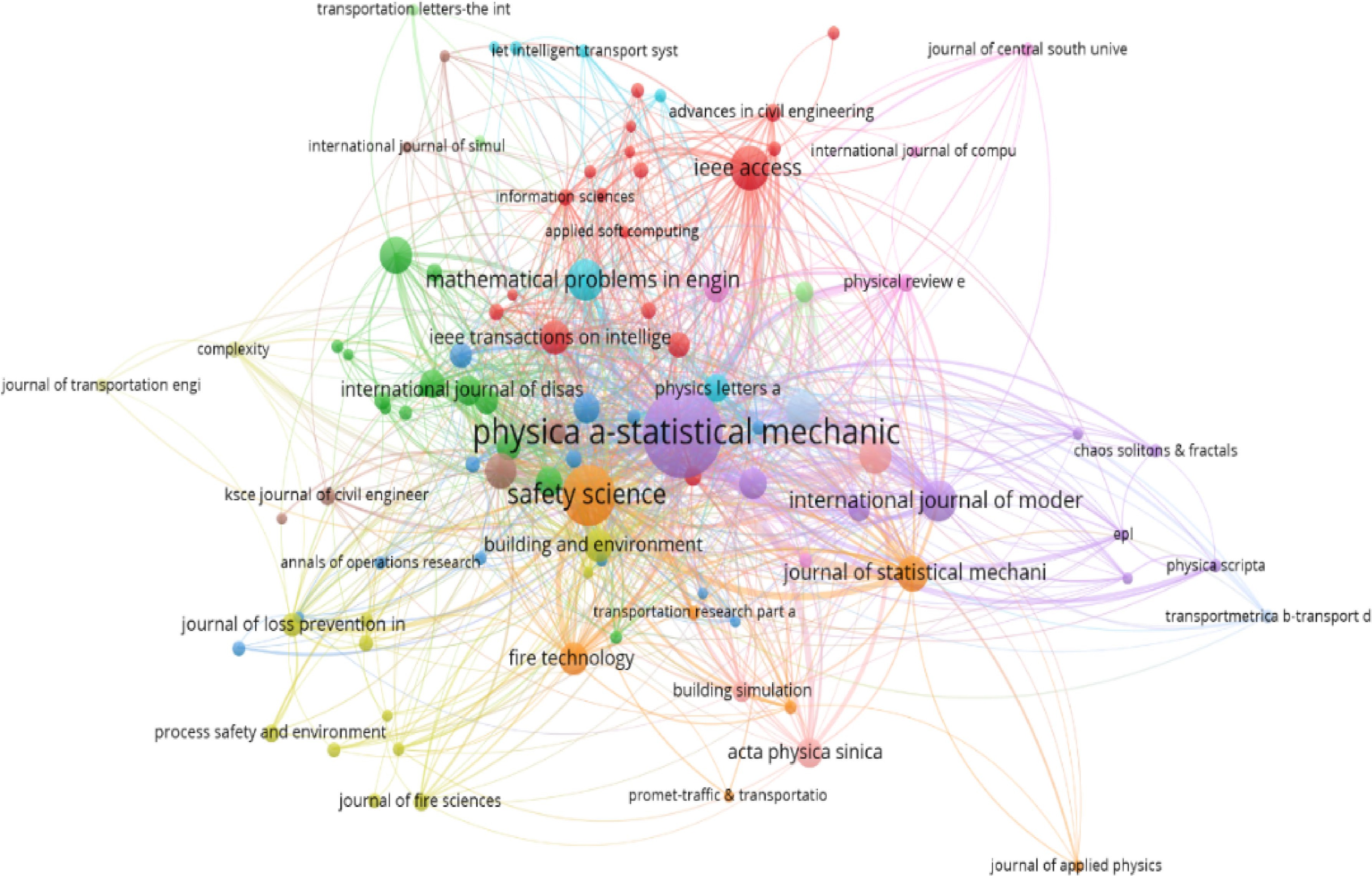
Figure 4.
Network diagram of relevant journals in the field of safety evacuation.
-
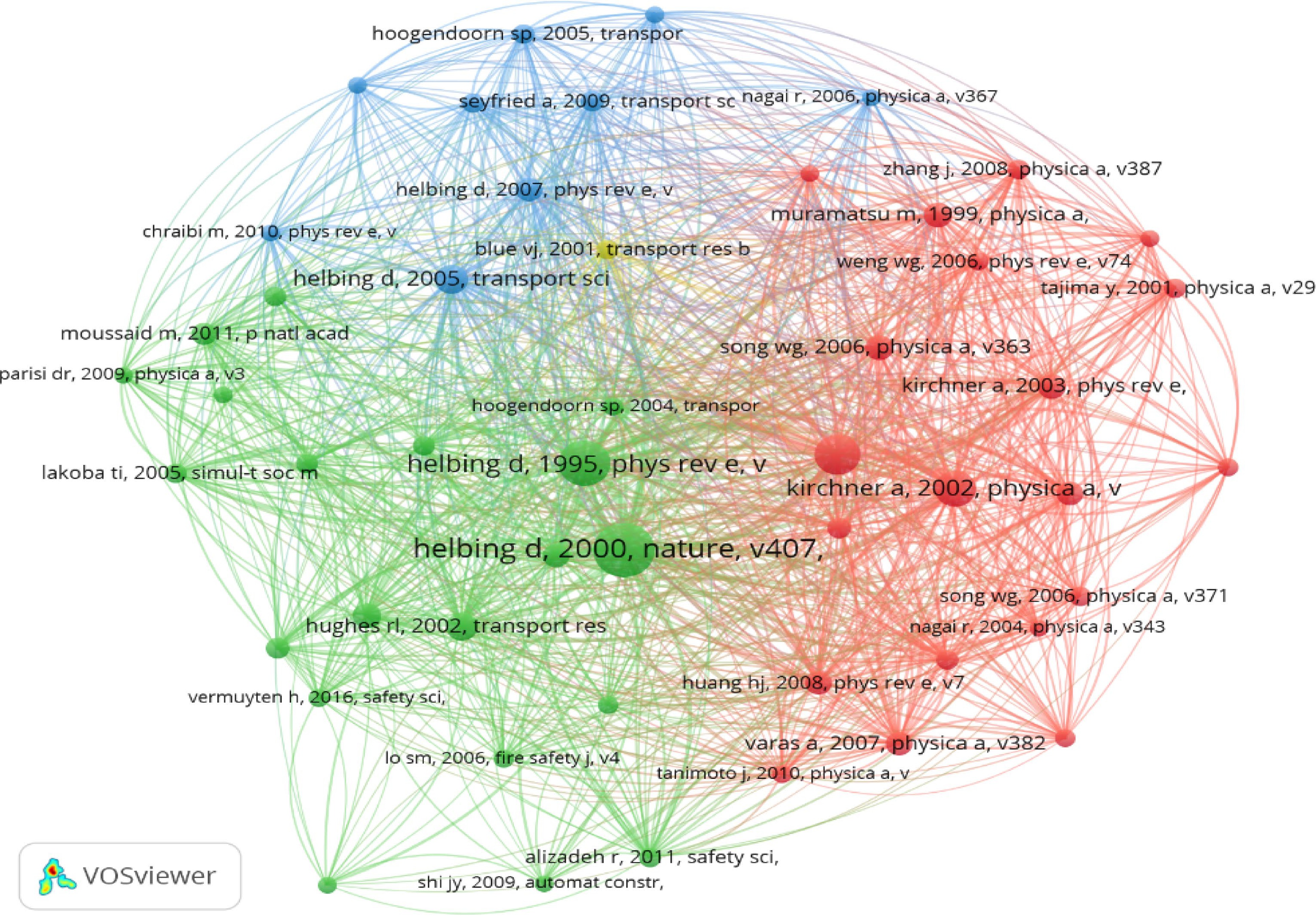
Figure 5.
The network diagram of the co-citation analysis of the relevant literature.
-
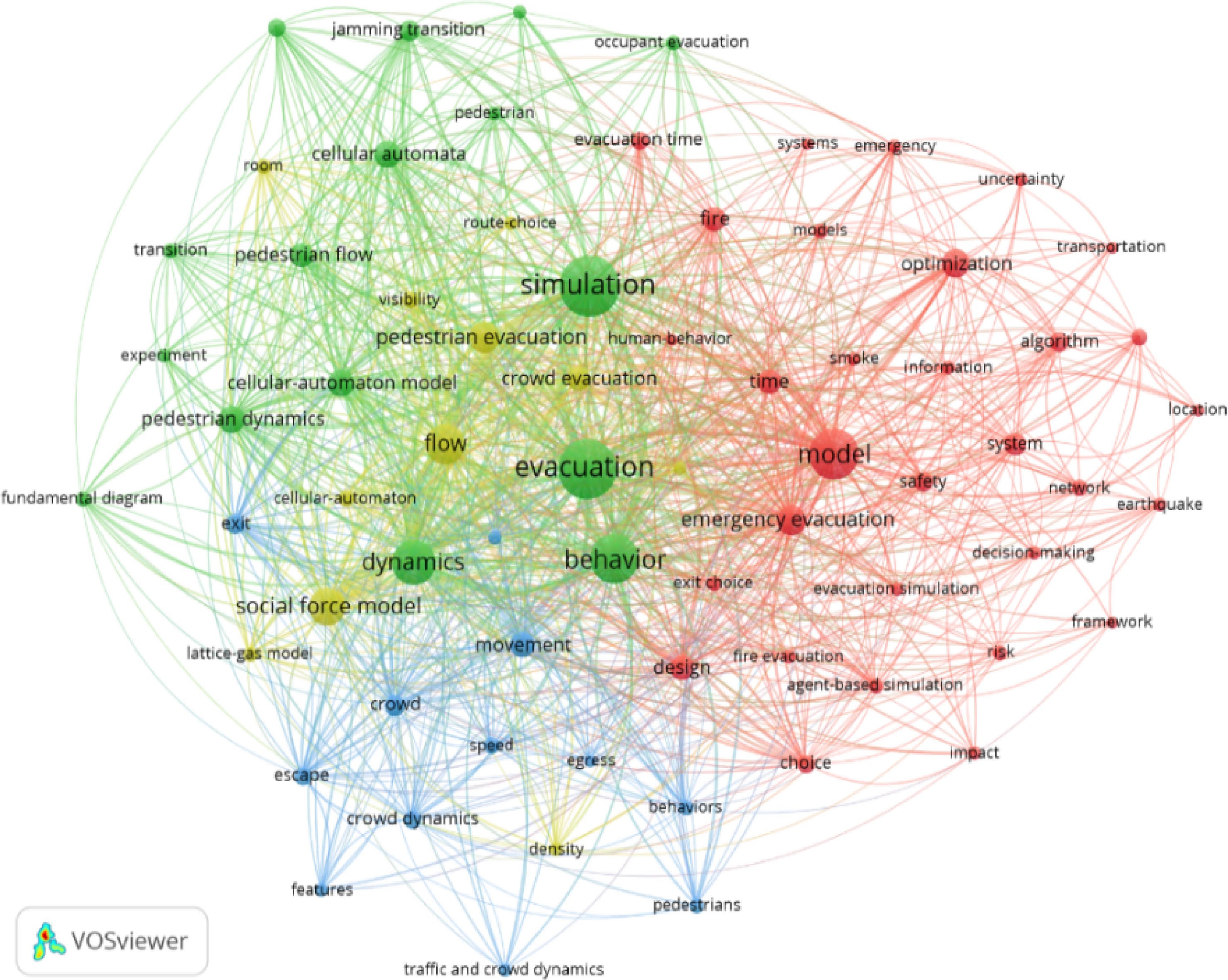
Figure 6.
Literature keyword co-occurrence network from 1990 to 2021.
-
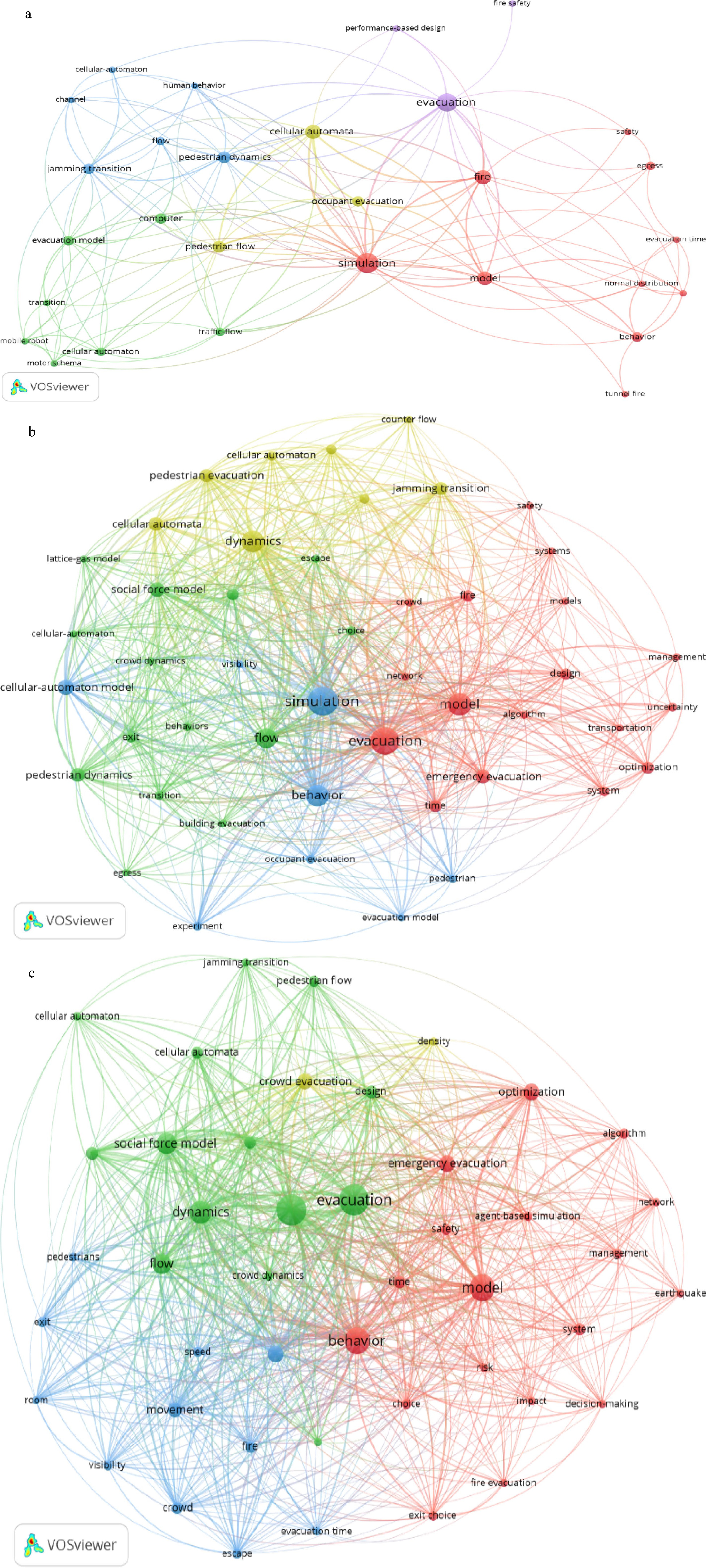
Figure 7.
Co-occurrence network of literature keywords at each stage: (a) the first stage; (b) the second stage; (c) the third stage.
-
-
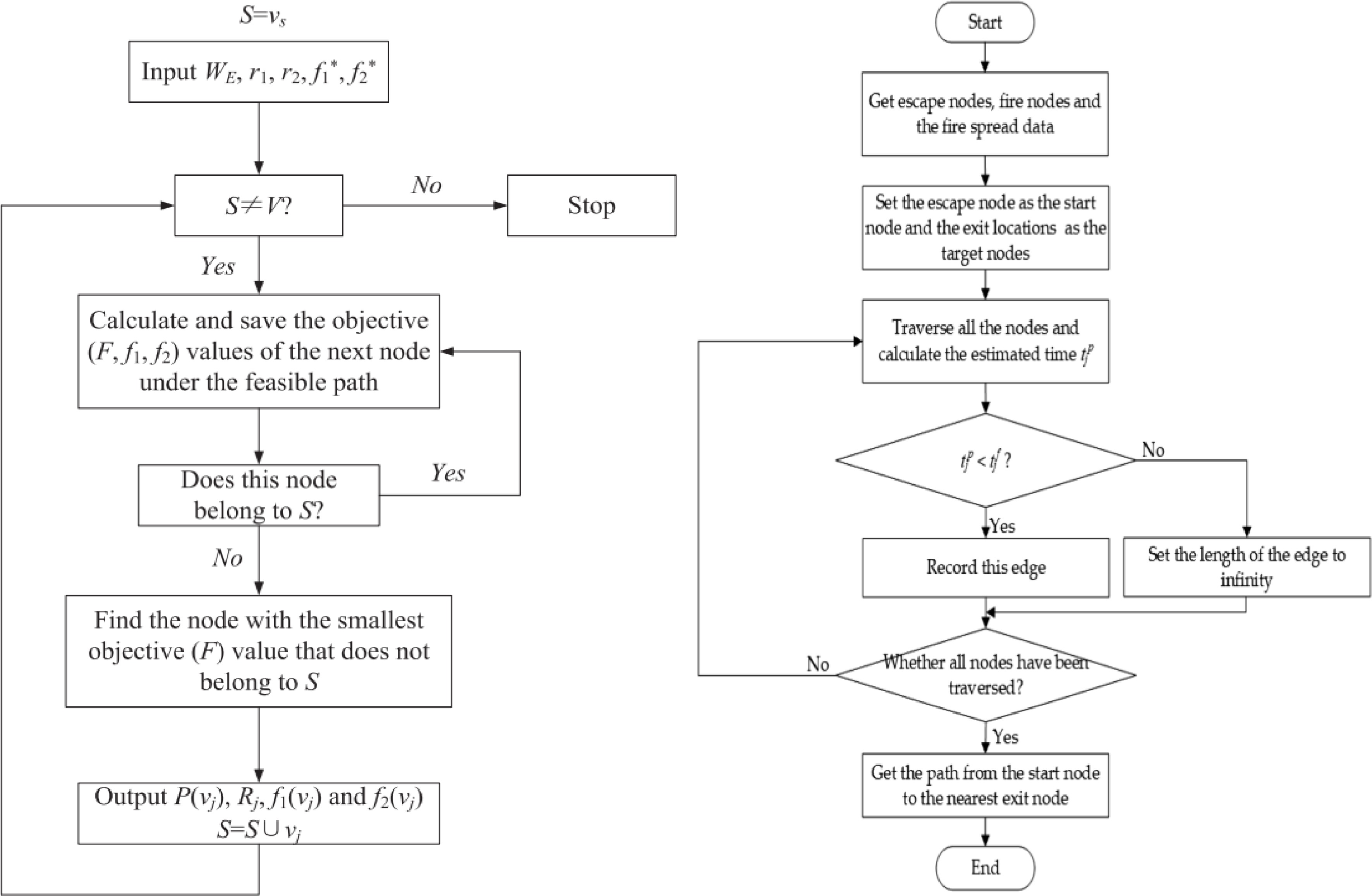
-
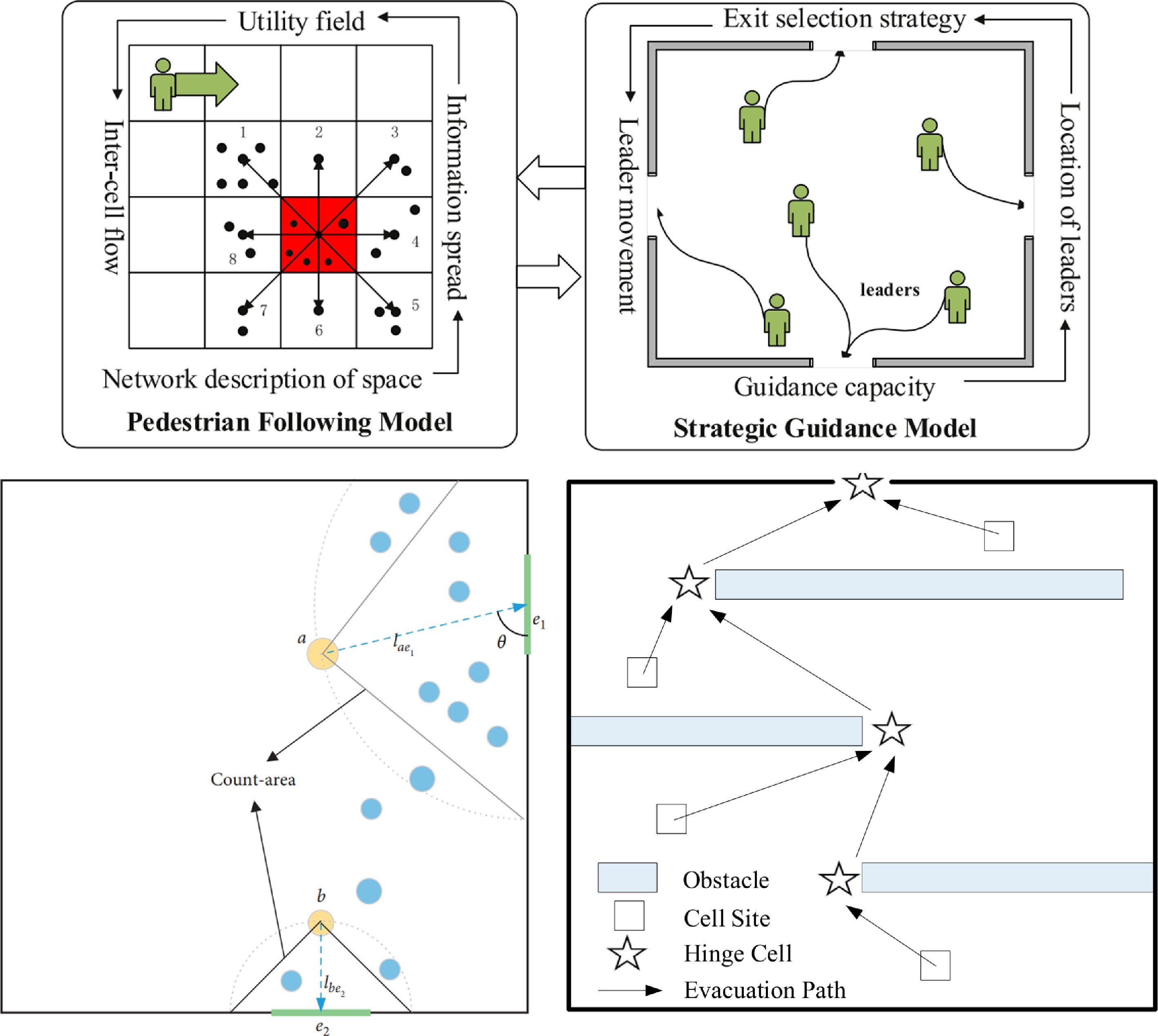
-
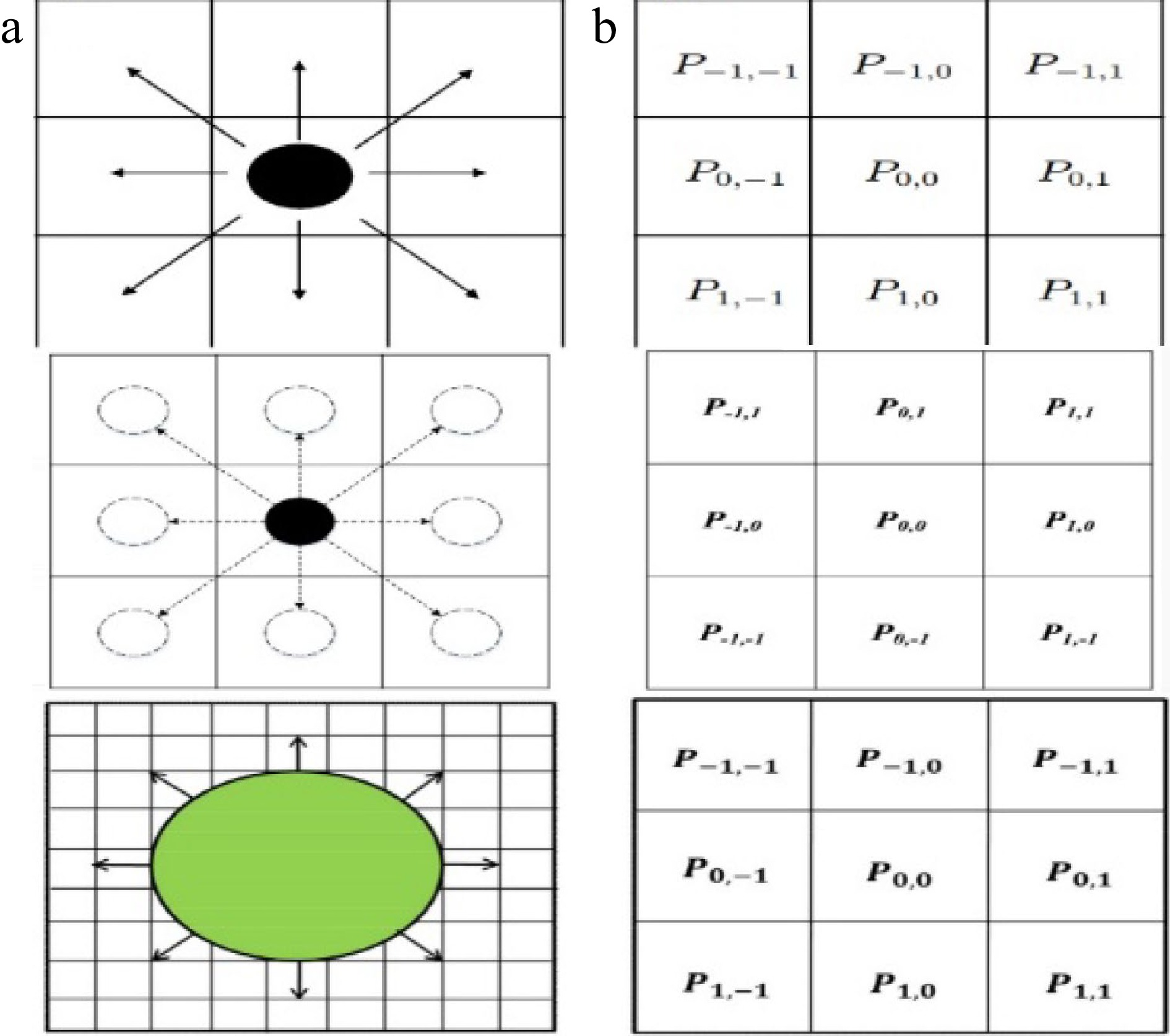
-

-
Time Location Cause of accident Number of casualties February 5, 2004 Miyun County, Beijing A light show was held, a large trampling accident occurred due to crowding and trampling on the Rainbow Bridge and negligence of security personnel[1]. 37 people died and 37 people were injured December 31, 2014 The Bund of Shanghai A light show was held and someone overbalanced and there were too many people in the venue, resulting in multiple falls and subsequent crowding and trampling accidents[2]. 36 people died and 49 people were injured November 18, 2017 Beijing Daxing Xhongmen Town A householder refitted a building without authorization, the personnel after the fire did not get timely evacuation, causing a fire accident[3]. 19 people died and 8 people were injured February 25, 2017 Honggu Tan New District, Nanchang City, Jiangxi A hotel was privately closed for renovation without the approval of relevant authorities, resulting in blocked evacuation routes. People failed to evacuate in time after a fire broke out[4]. 10 people died and 13 people were injured April 2, 2017 Daguan Economic Development Zone,
Anqing CityA dust explosion occurred in a workshop. Due to non-compliance with the layout of the workshop and a certain exit was blocked by flammable materials, personnel did not escape in time[5]. 5 people died and 3
people were injuredMay 16, 2019 Changning District,
ShanghaiA plant collapse occurred. Due to the chaotic management of the plant site, serious casualties were ocurred[6]. 12 dead and 10 seriously injured March 7, 2020 Quanzhou, Fujian Province A major collapse occurred at a hotel where people were not evacuated in time due to the building's poor design[7]. 29 people died and 42 people were injured Table 1.
Summary of crowd evacuation casualty accidents in China.
-
No. Document type Number of
literature/articleProportion (%) 1 Articles 1,352 97.97 2 Early Access 20 1.45 3 Meeting 19 1.38 4 Review Articles 16 1.16 5 Others 12 0.87 Table 2.
Literature category and quantity.
-
Rank Title of article First author Source Citation
ratesPublished
yearAddress 1 Modeling crowd evacuation of a
building based on seven methodological approachesZheng Xiaoping Building And Environment 349 2009 Beijing Univ Chem Technol 2 Simulation of evacuation processes
using a multi–grid model for
pedestrian dynamicsSong Weiguo Physica A Statistical Mechanics And Its Applications 208 2006 Univ Sci & Technol China 3 Static floor field and exit choice for pedestrian evacuation in rooms with internal obstacles and multiple exits Huang Haijun Physical Review E 198 2008 Beijing Univ Aeronaut & Astronaut 4 Agent–based modelling and simulation
of urban evacuation: relative
effectiveness of simultaneous and
staged evacuation strategiesChen Xuwei Journal of The Operational Research Society 183 2008 SW Texas State Univ 5 Route choice in pedestrian evacuation under conditions of good and zero visibility: Experimental and simulation results Guo Renyong Transportation Research Part B–Methodological 178 2012 Inner Mongolia Univ 6 A game theory based exit selection
model for evacuationLo Siuming Fire Safety Journal 164 2006 City Univ Hong Kong 7 Agent–based evacuation model of large public buildings under fire conditions Shi Jianyong Automation in Construction 162 2009 Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ 8 Evacuation behaviors at exit in CA
model with force essentials: A
comparison with social force modelSong Weiguo Physica A Statistical Mechanics And Its Applications 151 2006 Univ Sci & Technol China 9 A social force evacuation model with
the leadership effectHou Lei Physica A Statistical Mechanics And Its Applications 145 2014 Shanghai Univ Sci 10 A dynamic evacuation network optimization problem with lane reversal and crossing elimination strategies Xie Chi Transportation Research Part B–Logistics And Transportation Review 137 2010 Univ Texas Austin Table 3.
The top 10 cited literature of Chinese scholars in safety evacuation from 1990 to 2021.
-
Rank Subject category Number of
publicationsPercentage of total
publications (%)1 Engineering 542 39.275 2 Physics 349 25.290 3 Computer Science 303 21.957 4 Transportation 143 10.362 5 Operations Research Management Science 112 8.116 6 Mathematics 103 7.464 7 Construction Building Technology 97 7.029 8 Science Techology Other Topics 83 6.014 9 Environmental Sciences Ecology 80 5.797 10 Materials Science 73 5.290 Table 4.
Statistics on the distribution of the top 10 disciplines in the literature related to the field of safety evacuation in China during the period 1990−2021.
-
Rank Literature research institution Number of publications 1 University of Science and Technology of China 149 2 Beijing Jiaotong University 109 3 Tsinghua University 107 4 City University of Hong Kong 78 5 Southwest Jiaotong University 67 6 Wuhan University of Technology 50 7 Tongji University 48 8 Chinese Academy of Sciences 41 9 Southeast University 38 10 Beihang University 38 Table 5.
Statistics on the number of articles issued by each institution.
-
Rank Journal name Number of articles Percentage
of total
publications (%)Impact factor* 1 Physica A Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications 172 12.464% 3.295 2 Safety Science 80 5.797% 5.16 3 IEEE Access 42 3.043% 4.983 4 Mathematical Problems in Engineering 37 2.681% 1.125 5 International Journal of Modern Physics C 36 2.609% 1.453 6 Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 31 2.246% 3.336 7 Sustainability 30 2.174% 2.966 8 Chinese Physics B 29 2.101% 1.265 9 Journal of Statistical Mechanics Theory and Experiment 28 2.029% 1.425 10 Fire Safety Journal 27 1.957% 2.802 11 IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 24 1.739% 8.632 * Impact factor taken from 2021 Table 6.
Information of core journals in the field of safety evacuation.
-
No. 1990–2007 2008–2016 2017–2021 1990–2021 1 simulation simulation simulation simulation 2 fire model behavior evacuation 3 model behavior model model 4 computer dynamics evacuation behavior 5 jamming transition flow dynamics dynamics 6 pedestrian dynamics evacuation flow flow 7 cellular automata cellular-automata mode social force model social force model 8 pedestrian flow social force model pedestrian evacuation pedestrian evacuation 9 evacuation pedestrian dynamics optimization emergency evacuation 10 occupant evacuation jamming transition emergency evacuation pedestrian dynamics Table 7.
Hot keywords in different stages.
-
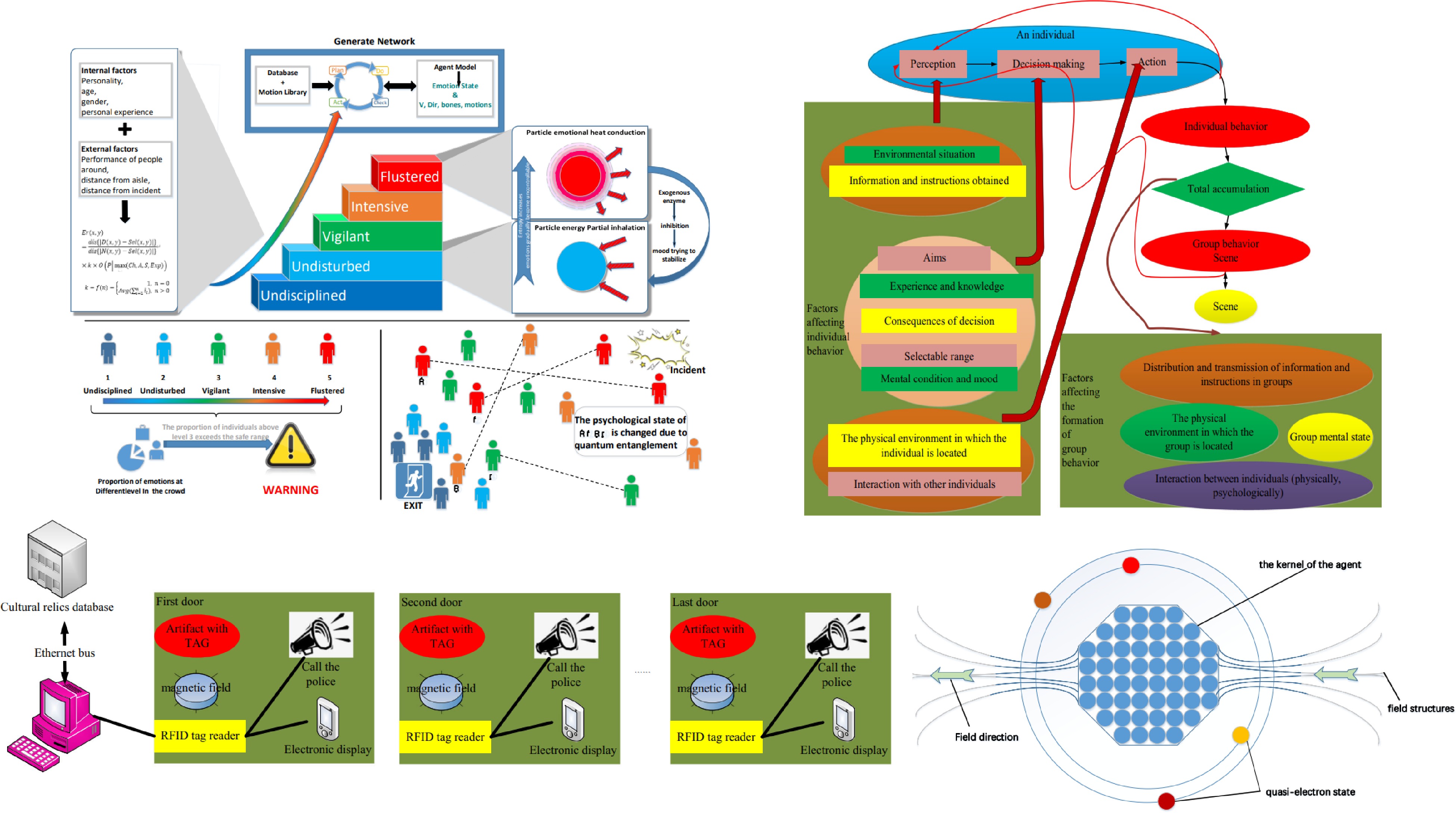
Author, year Panic Model Algorithm Measured variables Main research contents Wang, 2012 √ √ The numbers evacuated; correct rate of evacuation direction; speed; human traffic The model reproduces a well-known phenomenon in crowd evacuation, namely fast is slow, and confirms that the severity of disaster exponentially positively correlates with the panic spread, and the effectiveness of rescue guidance is influenced by the leading emotion in the crowds as a whole. Wang, 2013 √ √ Density The effectiveness of rescue strategies was found to be strongly related to crowd density. The higher the crowd density, the larger the minimum number of passageways for effective evacuation will be. Cui, 2016 √ This paper proposes an audience behavior rehearsal and simulation system that can be applied to the real activity. The system can realize the behavior planning of the audience in the early period of large-scale organization and modularize the organization flow. Zhan, 2019 √ √ Time A route selection model for anti-typhoon crowd evacuation vehicles was built. The vehicle road impedance coefficient was used to embody the abilities of different vehicles in executing evacuation tasks. And the proposed method can provide emergency decision makers with a scientific and reasonable route selection scheme for anti-typhoon crowd evacuation vehicles. Ma, 2020 √ √ √ Density; speed This paper proposes a large-scale crowd evacuation method based on the mutation theory of RFID. The advantage of this algorithm is that it can overcome the contradiction between the prediction accuracy and the tracking speed, and the accuracy of the algorithm to predict the flow of large-scale people is improved, making the evacuation model more relevant to the actual situation. Mei, 2020 √ √ √ Time; density; human traffic This paper proposes a particle model, and the simulation method of the entangled emotional model (EEM) is used to deal with the gathering phenomenon and group collisions in the evacuation process. The model simulates the crowd’s kinship by forming multiple entangled pairs, which can form multiple motion clusters for a large number of people. Table 8.
Specific analysis of the cited literature on mass crowd evacuation.
-
Author, Year Experiment Model Algorithm Visibility Obstacles Main research content Yang, 2021 √ √ √ √ This paper proposes an obstacle avoidance method in the microscopic SFM, which emphasizes the solution of choosing which obstacle to detour and which side to detour in the multiple obstacle scene. Herding behavior, individual preference affected by obstacles and walls are taken into consideration when defining the desired direction of pedestrians with local information in this algorithm. Lu, 2021 √ √ This paper carries out a series of pedestrian evacuation experiments on a staircase for both ascent and descent based on video tracking technology to extract the trajectories of pedestrians. Pedestrians tend to use the enclosure for help when ascending and descending without visibility, and offset angle is correlated with pedestrians’ route-choice behavior. These studies are helpful to understand pedestrian evacuation characteristics on stairs without visibility. Song, 2021 √ √ By combining GIS and a fire hazard assessment method for indoor spaces, a new evacuation route selection approach that considers hazards and time is proposed in this paper. Xu, 2021 √ √ This paper constructs a multi-indicator emergency risk assessment method that considers the evacuation speed of different population types and health consequences caused by various risk components. Then he proposes a modification of the well-known Dijkstra algorithm to deal with the problem for emergency route selection under the real effect of disaster extension. The proposed model provides reliable and practical emergency route planning services for various personnel types under different accident scenarios. Liu, 2021 √ √ This study uses an IACS to analyze the multi-path dynamic planning of emergency evacuations on cruise ships. And the ACS is combined with the increasing flow method to improve the evacuation efficiency. Liu, 2021 √ √ √ √ A potential-based three-dimensional route choice model for pedestrian evacuation on terraced stands is proposed. The proposed potential field algorithm reflects the influence on route choice behavior of heterogeneous heights, route distance, pedestrian congestion, and route capacity. Zhang, 2021 √ √ √ A double-level model was established to describe passengers’ path planning behaviors. The avoiding force model including common avoiding force and additional horizontal avoiding force was established, and the route and node choice models were established to describe pass engers’ path planning in long-range space. Wang, 2020 √ √ This paper proposes a real-time dynamic fire escape path prediction analysis method with BIM, and designs single and multi-person escape route planning method. The shortest path is planned by Dijkstra algorithm. Zhao, 2020 √ √ √ This paper proposes a new crowd evacuation simulation method. The proposed MABCM algorithm can effectively improve the performance of ABC, and the method balances distance and congestion and shortens evacuation time to a certain extent. Niu, 2020 √ √ This work proposes a real-time evacuation strategy. Experiments are conducted to simulate five different scenarios in a fire evacuation. The evacuation strategy with a comprehensive route constraint has a significant improvement in the evacuation efficiency and has higher robustness. Ping, 2018 √ To quantify the influence of evacuation route selection on crew evacuation efficiency, two scenarios are considered. It is reasonable to prescribe the evacuation routes in advance. Table 9.
Specific analysis of the cited literature in evacuation path planning.
-
Author, Year Model Algorithm Leader Obstacles Object of study Main research content Zhang, 2021 √ √ Distance from a pedestrian to an exit; Pedestrian density
near an exit; Exit widthThis paper proposes a multi-exit evacuation model based on a continuous model. And the model takes into account the distance between pedestrians and exits, the pedestrian density near exits, and the width of exits. The model can reproduce the phenomenon of pedestrian congestion and exit congestion, and improve the evacuation efficiency as well as utilization rate of exits significantly. Ma, 2021 √ √ Exit quantity; Exit position A dynamic exit decision model (EDM) is proposed to simulate decisions of evacuees in the multi-exit evacuation. The model can accurately evaluate the evacuation efficiency of different multi-exit layouts and optimize the design rules. Yue, 2021 √ √ √ An exit with a prepositive obstacle In this paper, a retardation coefficient is introduced to describe the effect of obstacles slowing down pedestrian movement. A special technique is adopted to calculate the shortest estimated distance from cell site to exit considering obstacle layout and retardation coefficient. The repulsion and isolation effect of obstacles on pedestrian flow is manifested by the clusters of evacuation path chains. Zhang, 2021 √ √ √ Position of leader; Number of leaders;
Exit selection strategyA simulation algorithm is proposed to integrate a pedestrian following model and strategic guidance model based on the follower-leader interaction. The guidance strategy can realize the full use of guidance capacity, information confusion reduction and uniform exit usage, all of which contribute to a reduction in evacuation time. Wang, 2020 √ Visual radius; Initial crowd distribution; exit layout; By integrating game theory into a cellular automata simulation framework, the pedestrian exit choice mechanism is explicitly modeled in this paper. The model is used to study the visual radius and choice firmness of a pedestrian, initial crowd distribution of the room, exit layout as well as exit width. Gao, 2020 √ √ Exit quantity; Exit width; Distribution of pedestrians In this paper, A modified cellular automata model based on Floor Field theory is proposed to solve the problem of congestion in front of exits caused by the asymmetrical layout of exits or pedestrians in a multi-exit building. Yang, 2020 √ √ √ The limited visibility and guide quantity; Export position; Exit width This paper chooses the fuzzy logic theory to investigate the problems of guide selection by informed followers and exit selection by guides. Guide’s normalized distance to the exit and the normalized density around the exit are chosen as the input variables of the fuzzy inference system to assist in deciding which exit to choose for guides. Liu, 2020 √ √ √ Exit quantity; Exit width; Export position; Obstacle attributes This paper proposes a cellular automata model based on fuzzy logic method for simulating the evacuation of pedestrians from a multiple-exit room. The combination of the output variable of fuzzy logic, exit width and herding behavior can effectively determine the target exit and solve the position conflict among pedestrians. Cao, 2018 √ √ The effect of utility threshold
on evacuation, active
occupant on evacuationThe exit selection based on random utility theory, as well as the pedestrian movement in fire, is investigated. The effects of different occupant types, the utility threshold, heat release rate of fire, burning materials and pre-movement time on evacuation are discussed. Li, 2017 √ √ Exit width Based on estimated evacuation time and shortest distance, pedestrian exit choice model is established considering pedestrian preference. Table 10.
Specific analysis of the cited literature regarding planar exits.
-
Author, Year Model Algorithm Experiment Object of study Main research content Li, 2022 √ The convex exit structure Using social force model-based software, MassMotion, this paper studies the influence of geometric structure characteristics of the convex exit on crowd evacuation and put forward the optimal design strategy of this structure, so as to improve the efficiency of evacuation in an emergency. Li, 2022 √ The evacuation efficiency of the 30° corner exit In this paper, Massmotion based on social force model is used to carry out a numerical simulation on exit position and corner exit form to find out the mechanism and influence law of the slight architectural adjustment on the flow at bottleneck. The 30° angle may be a more appropriate corner exit option. In this layout, pedestrian walking direction changes less and the steering angle is smaller. Wu, 2022 √ √ Railings at evacuation exits To alleviate the congestion of the evacuation in a largescale and multifunctional subway station, the utilization of different exits and the optimization of congestion at bottlenecks were investigated in this study. When the number of exits in the divided area is large, setting railings can alleviate the congestion at the exit. Wang, 2022 √ √ √ The exit location; the bottleneck length; an obstacle near an exit This paper studies pedestrian flow at narrow exits and explored the effects of exit location, bottleneck length, and obstacles on evacuation efficiency. With the increasing of bottleneck length, pedestrian flow efficiency gradually decreases. Placing an obstacle near exits in an emergency may not make the evacuation worse. Wang, 2022 √ Corner exit; the size
and location of the
obstacleThis paper studies the effect of adding obstacles of different sizes and locations in front of 30° angle exits on evacuation. The distance from the obstacle to the exit has the greatest influence on evacuation. At the short distance, the length of the obstacle can be increased to shorten the evacuation time. Li, 2020 √ √ √ Different exit widths
and operating doorsConsidering the differences in the individual characteristics of pedestrians and the influence factors of buildings, we proposed a safety evacuation model for limited spaces. Evacuation efficiency, bottleneck area density, escape route characteristics, and similar factors were analyzed on the basis of different exit widths and operating doors. When the exit widths are 1.0, 1.1, 1.8 and 1.9 m, the exit crowd and average densities are at their lowest. Wang, 2019 √ √ Exit buffer zone In this paper, a tentative experiment was designed to preliminarily reveal the role of buffer zone in crowd evacuation. Then a social force based simulation model was established by Massmotion according to the properties of the experiment. The longer the buffer zone, the faster the agents can escape. Song, 2018 √ √ √ Non-competitive and competitive pedestrian behaviors near exit bottlenecks Active rotation torque is proposed to model the active rotation behavior of pedestrians turning their torsos in the desired direction. A three-circle model is adopted to represent the shape of pedestrians to study the phenomenon of people actively squeezing to pass through an exit. The torque model can be applied to manifold scenarios with various door widths and different safety separation belt settings. And the model can simulate both non-competitive and competitive pedestrian behaviors near exit bottlenecks more accurately than the circular social force model. Wang, 2019 √ Pedestrian flow features at bottlenecks, i.e. room exits In this paper, pedestrian flow features at bottlenecks are investigated with human-experiments considering varying door sizes and locations. The time lapses between two successive pedestrians displayed heavy-tailed distribution. In narrow door scenarios, the specific capacity was continuously decreased from the middle exit scenarios to the corner exit scenarios. Shi, 2019 √ Different exit locations and obstacles near exit This study aims to examine the effect of different geometrical layouts at the exit towards the pedestrian flow via controlled laboratory experiments with human participants. Corner exit performed better than middle exit under same obstacle condition. the effectiveness of obstacle is sensitive to its size and distance from the exit. Tian, 2015 √ √ Different widths and positions of the exits In this paper, we proposed an improved and simple method to calculate the floor field. In our method, the pedestrians are treated as the movable obstacles which will increase the value of the floor field. The additional value is interpreted as the blocking effect of preceding pedestrians. Wang, 2015 √ √ Pedestrian congestion behavior at the exit A new multi-agent based congestion evacuation model incorporating panic behavior is proposed in this paper. Pedestrians in this model are divided into four classes and each pedestrian’s status can be either normal, being overtaken, or casualty. The agents gather in front of the exits and present arched shapes close to the exits. Under the panic state the agents cohere closely and almost do not change the target exit. If there are obstacles, the congestion can be alleviated. Table 11.
Specific analysis of the cited literature on non-planar exits.
Figures
(12)
Tables
(11)