-
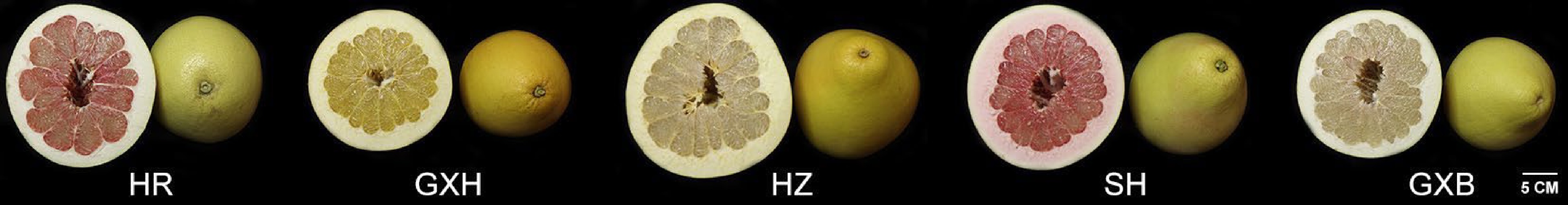

Figure 1.
Fruits of ‘Guanxi’ (GXB) pummelo and its bud mutants. HR: Hongrou; GXH: Guanxihuang; HZ: Hongzuan; SH: Sanhong.
-
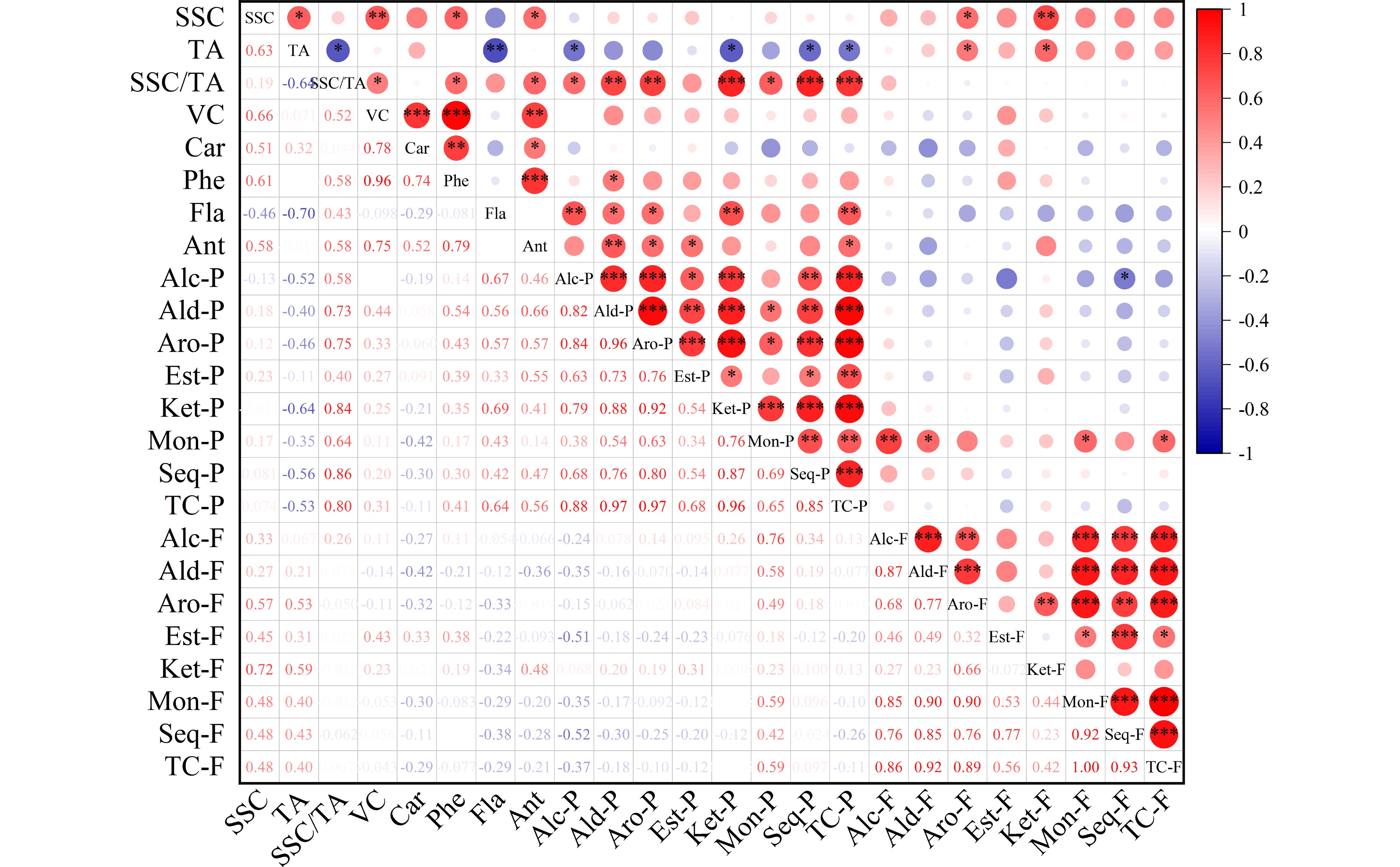
Figure 2.
Correlation analysis heatmap of fruit quality traits and volatiles in pummelo pulp and flavedo. The fruit quality traits included soluble solid content (SSC), acidity (TA), SSC/TA, vitamin C (VC), carotenoids (Car), phenols (Phe), flavonoids (Fla) and antioxidant activity (Ant). The volatile groups contained alcohol (Alc), aldehyde (Ald), aromatic hydrocarbon (Aro), ester (Est), ketone (Ket), monoterpene (Mon), sesquiterpene (Seq) and total compounds (TC) from the pulp (-P) and flavedo (-F) samples. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.
-
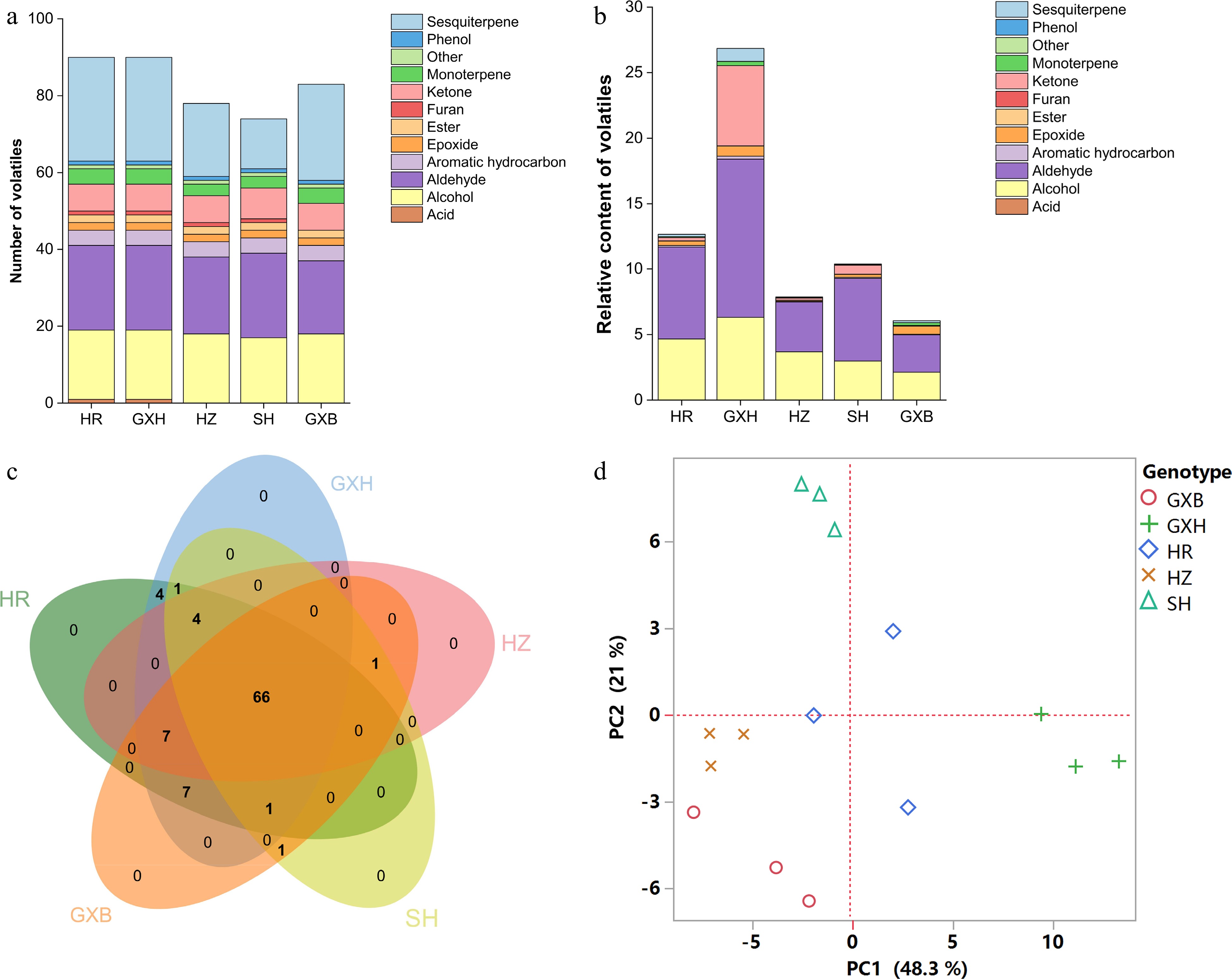
Figure 3.
Multivariate statistical analysis of pulp volatile profiles from the five pummelo genotypes. (a) Number and (b) relative content of volatile compounds in each chemical class. (c) Venn diagram analysis of volatile compounds. (d) PCA score plot of volatile compounds. The volatile relative content was calculated by normalizing the compound peak area to the internal standard peak area. HR: Hongrou; GXH: Guanxihuang; HZ: Hongzuan; SH: Sanhong; GXB: Guanxi.
-
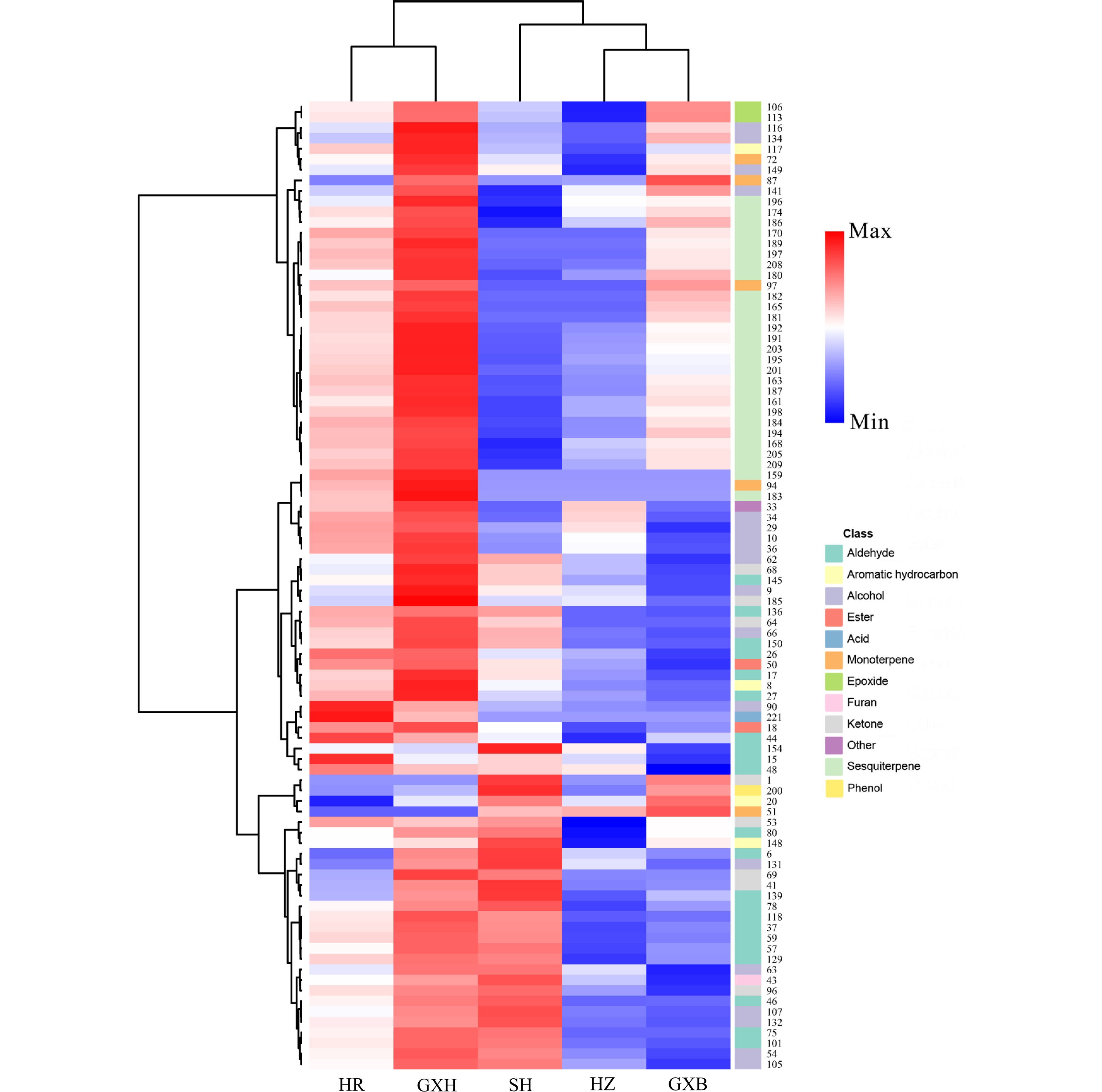
Figure 4.
HCA of pulp volatile profile from the five pummelo genotypes. The volatile codes can be found in the first column in Table S5. HR: Hongrou; GXH: Guanxihuang; HZ: Hongzuan; SH: Sanhong; GXB: Guanxi.
-
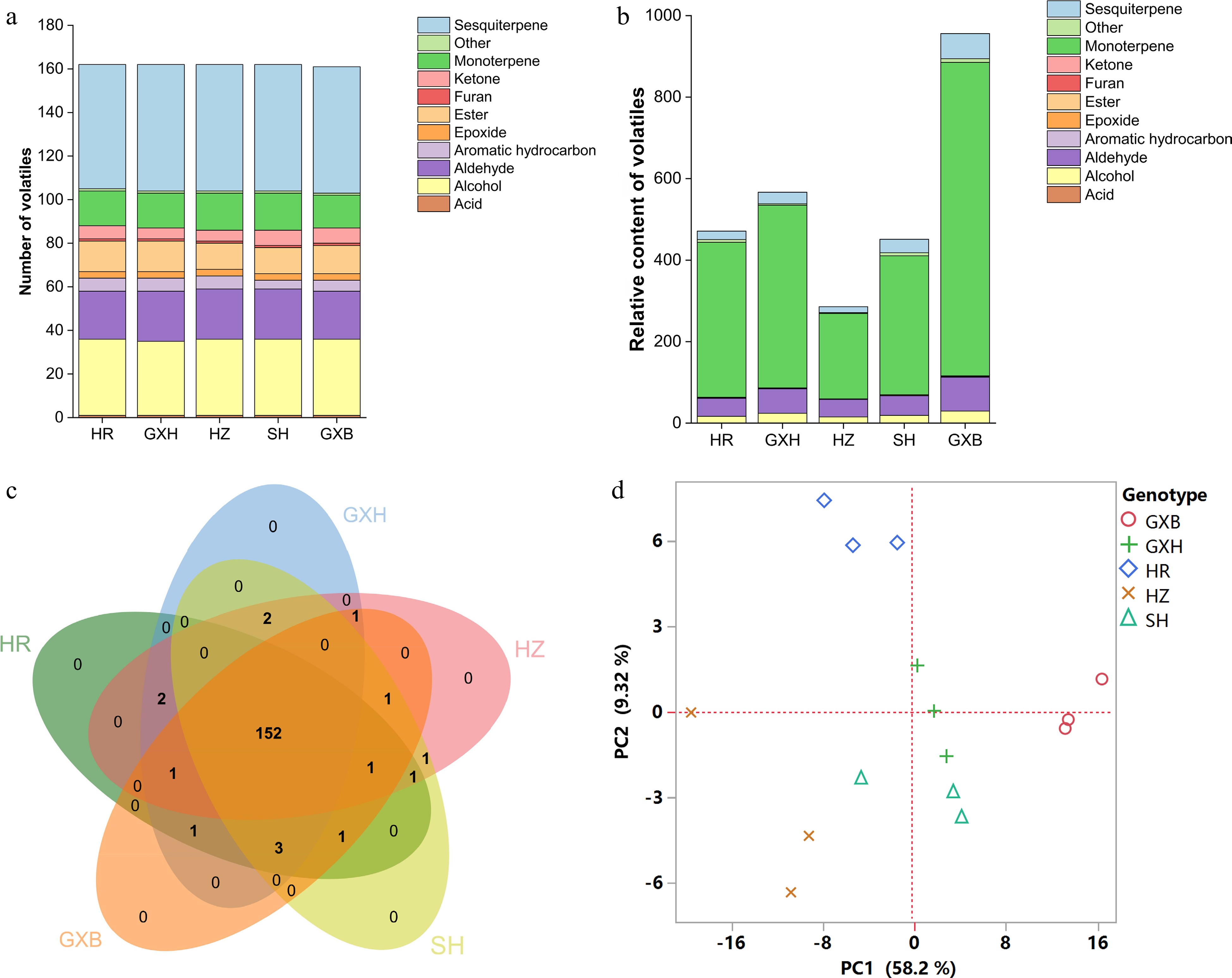
Figure 5.
Multivariate statistical analysis of flavedo volatile profiles from the five pummelo genotypes. (a) Number and (b) relative content of volatile compounds in each chemical class. (c) Venn diagram analysis of volatile compounds. (d) PCA score plot of volatile compounds. The volatile relative content was calculated by normalizing the compound peak area to the internal standard peak area. HR: Hongrou; GXH: Guanxihuang; HZ: Hongzuan; SH: Sanhong; GXB: Guanxi.
-
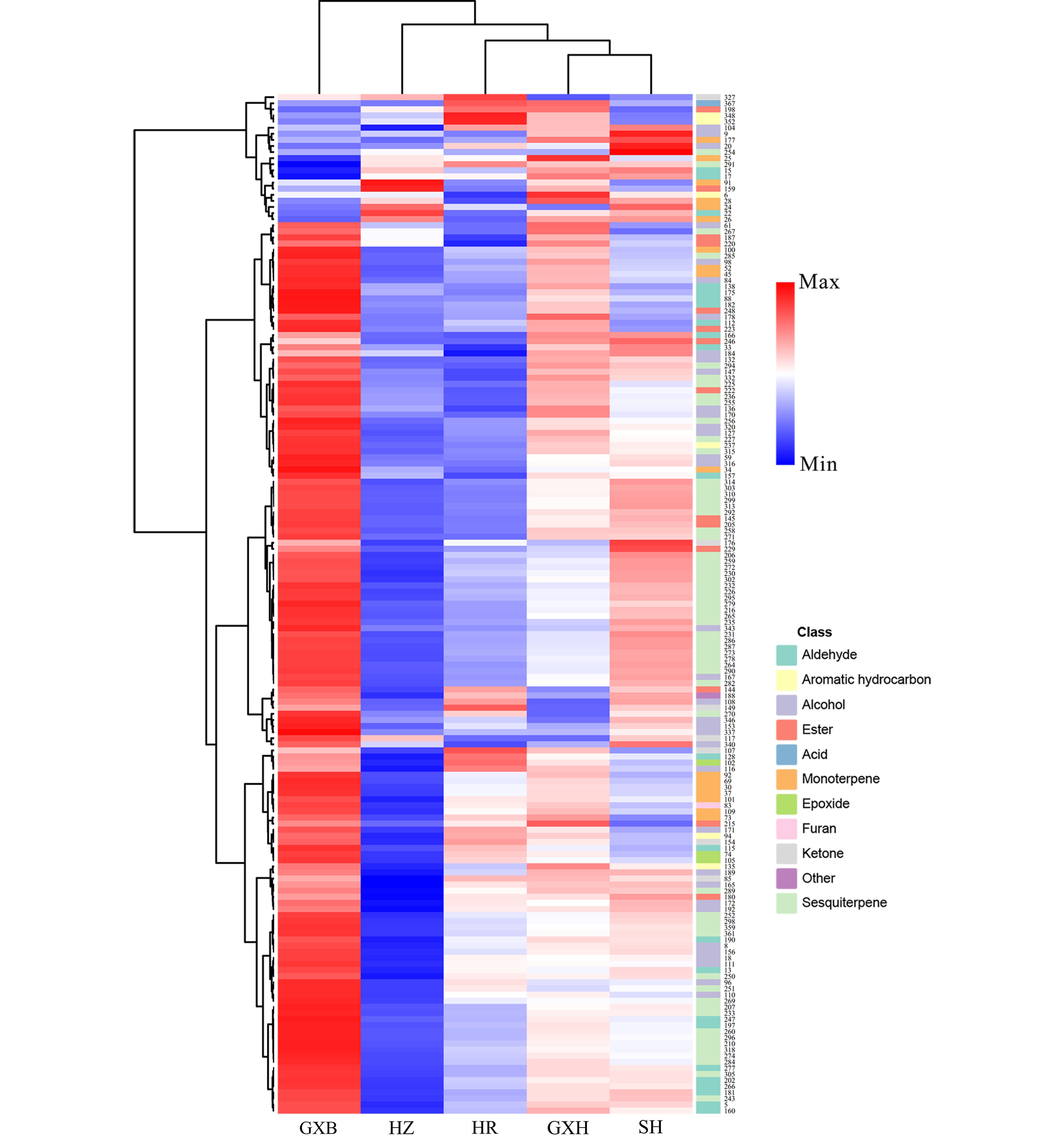
Figure 6.
HCA of flavedo volatile profile from the five pummelo genotypes. The volatile codes can be found in the first column in Table S8. HR: Hongrou; GXH: Guanxihuang; HZ: Hongzuan; SH: Sanhong; GXB: Guanxi.
-
Traits Hongrou Guanxihuang Hongzuan Sanhong Guanxi Soluble solid content (g·100 mL−1) 11.93 ± 0.25 a 11.03 ± 0.38 b 9.27 ± 0.12 c 11.90 ± 0.10 a 11.63 ± 0.40 ab Acidity (g·100 mL−1) 0.87 ± 0.06 a 0.65 ± 0.05 b 0.68 ± 0.01 b 0.81 ± 0.04 a 0.85 ± 0.04 a Soluble solids/acids 13.76 ± 0.99 b 16.97 ± 1.71 a 13.56 ± 0.21 b 14.71 ± 0.67 ab 13.77 ± 1.06 b Vitamin C (mg·100 mL−1) 39.93 ± 1.20 bc 42.01 ± 3.01 ab 34.03 ± 0.60 c 48.26 ± 3.18 a 37.50 ± 4.54 bc Carotenoids (mg·L−1) 1.94 ± 0.36 b 0.50 ± 0.02 c 0.28 ± 0.04 c 4.54 ± 1.06 a 0.24 ± 0.02 c Phenols (mg·L−1) 368.92 ± 11.82 abc 396.42 ± 34.05 ab 310.92 ± 19.15 c 441.82 ± 33.72 a 336.19 ± 39.08 bc Flavonoids (mg·L−1) 46.69 ± 1.89 b 59.90 ± 6.57 a 53.14 ± 6.03 ab 47.28 ± 0.59 b 44.33 ± 0.94 b Antioxidant activity (mg·100 mL−1) 48.08 ± 4.16 a 46.71 ± 5.11 a 34.08 ± 2.72 b 45.89 ± 4.86 ab 34.61 ± 5.20 b All the trees were grafted on sour pummelo rootstock in 2009. All values are mean ± SD of three biological replicates (15 fruits each) per cultivar; different letters in the same row indicate significant differences according to Tukey’s honestly significant difference test at P < 0.05. Table 1.
Fruit pulp quality traits of the five pummelo genotypes.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(1)