-
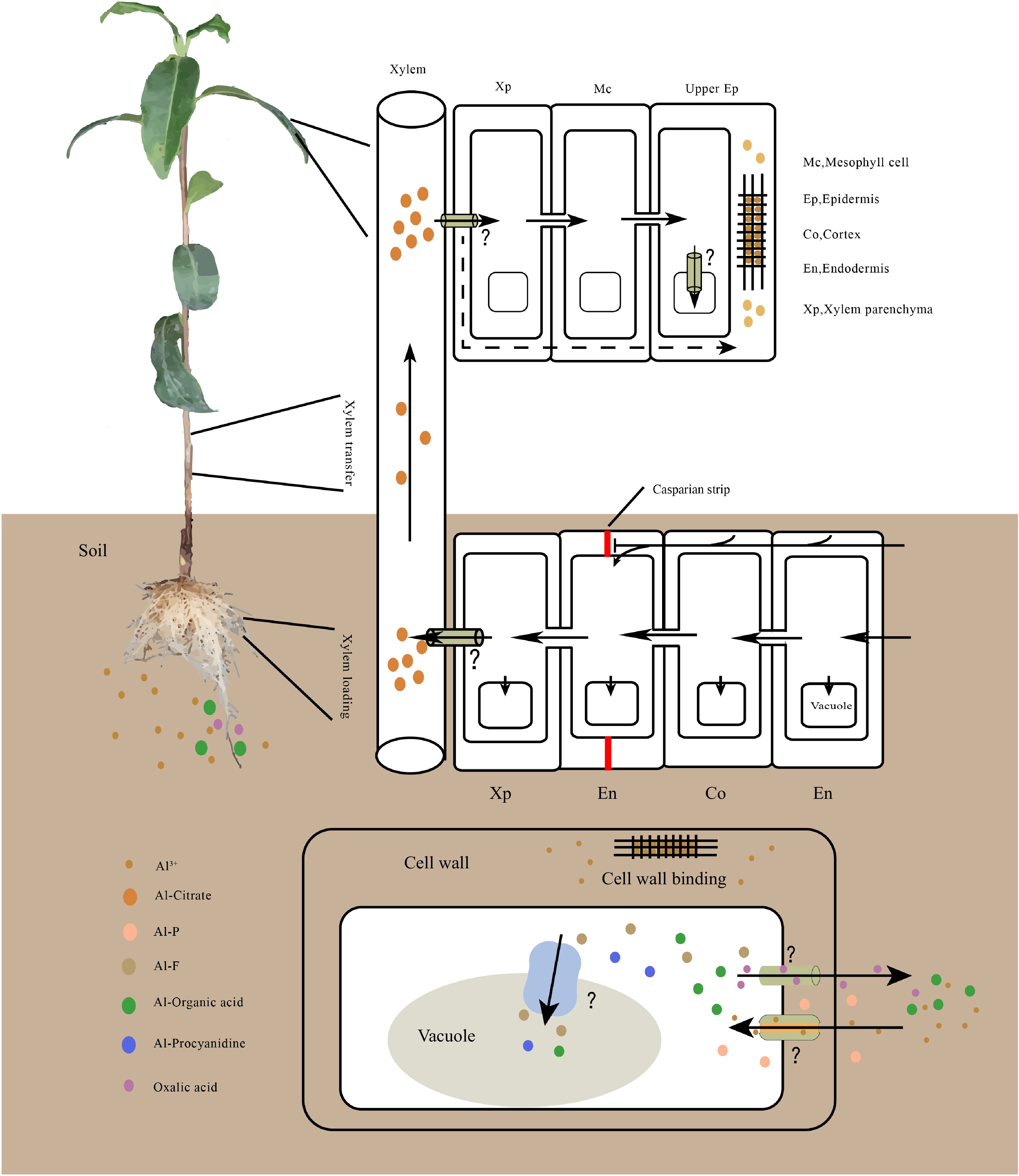
Figure 1.
Model for Al uptake, transport, accumulation in tea plant. Al is primarily absorbed by root cells, then most of the Al moves to the xylem parenchyma through symplastic and apoplastic transport. It is subsequently loaded into the xylem for root-to-shoot translocation. On leaves, Al is unloaded and transported to the upper epidermis for storage. In cells, Al is preferentially accumulated in the cell wall; once Al enters in the cytoplasm, it is chelated by organic acids or phenolic compounds and is subsequently sequestered into the vacuole. The transmembrane transport of Al requires transporters, however, the Al transporter in tea plant remains unknown. Al speciation varies in different tissues, Al-oxalate, Al-F and Al- proanthocyanidin have been detected in roots. Al-citrate is the predominant Al species in the xylem, and Al-catechin and Al-flavonol complexes have been detected in leaves.
-
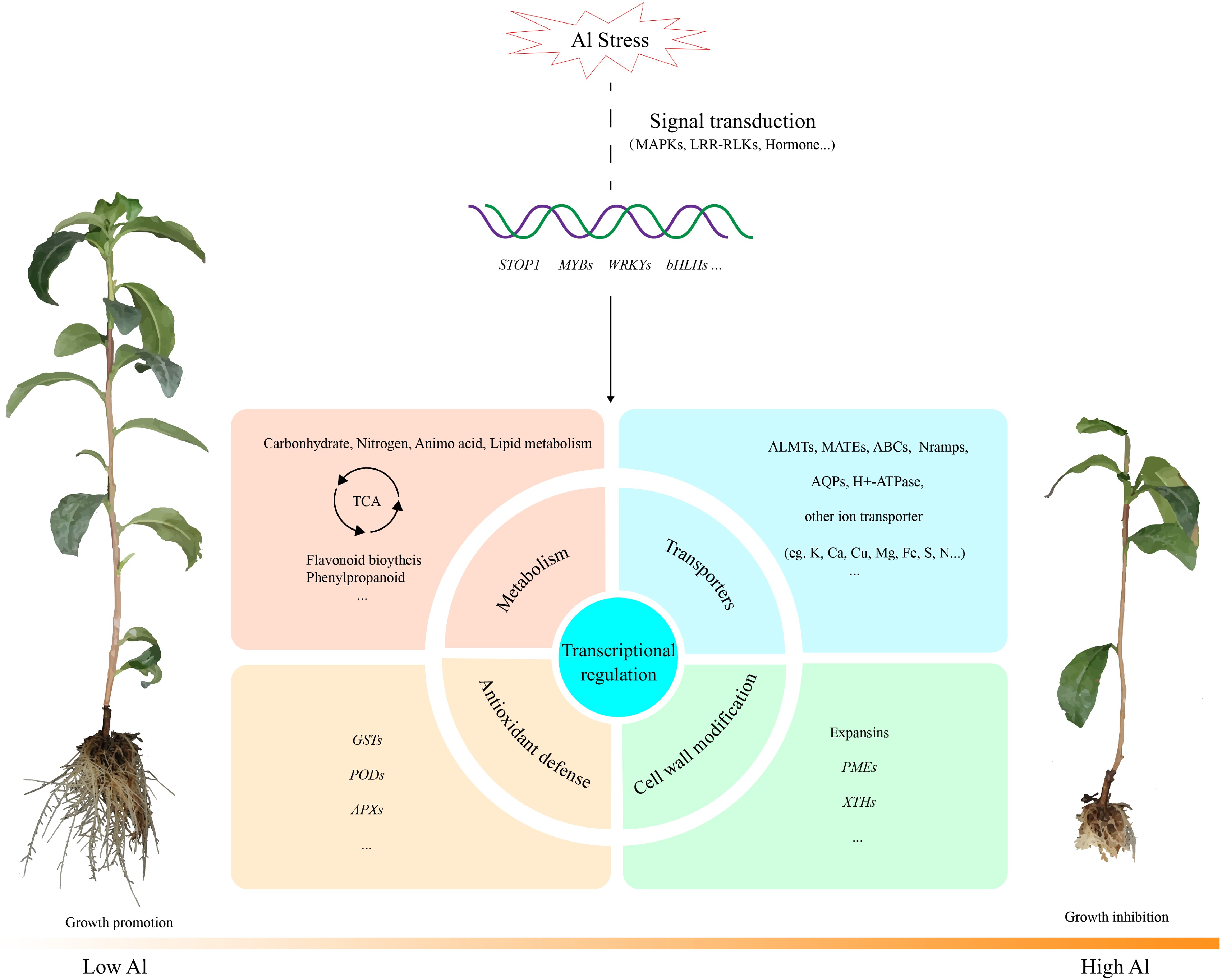
Figure 2.
General model of the major transcriptional changes in tea plant under Al stress according to transcriptomic analysis. Al alters the expression of genes involved in signal transduction, transcription factors, metabolic pathways, antioxidant defense system, transporters, cell wall modifications, etc. Abbreviations: MAPKs, mitogenactivated protein kinases; LRR-RLKs, leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinases; ALMTs, Al-activated malate transporters; MATEs, multidrug and toxic compound extrusions; Nramps, natural resistanceassociated macrophage proteins; AQPs, aquaporins; GSTs, glutathione-S-transferases; PODs, peroxidases; APXs, ascorbate peroxidases; PMEs, pectin methylesterases; XTHs, xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases.
-
Approaches Treatment time Samples Reference Transcriptomics 3 h Roots [64] Transcriptomics 7 d Leaves [68] Transcriptomics 7 d Roots [74] Transcriptomics 1, 3, 7, 14, 21, 28, 43 d Stem segment of nodal cutting [72] Transcriptomics and ionomics 6 weeks Roots [73] Transcriptomics and ionomics 0, 12, 24, 48 h Roots [34] Transcriptomics and metabolomics 0, 12, 24, 48 h Roots and leaves [82] Proteomics 12 weeks Roots and leaves [77] Metabolomics 45 d Roots and leaves of two cultivars [86] Metabolomics 7 months Tender leaves (one bud and two leaves), mature leaves, tender roots [83] Metabolomics and ionomics 8 weeks Leaves [90] Microbiomics Half a year Roots [100] Table 1.
Summary of applications of omics in Al related studies in tea plant.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)