-
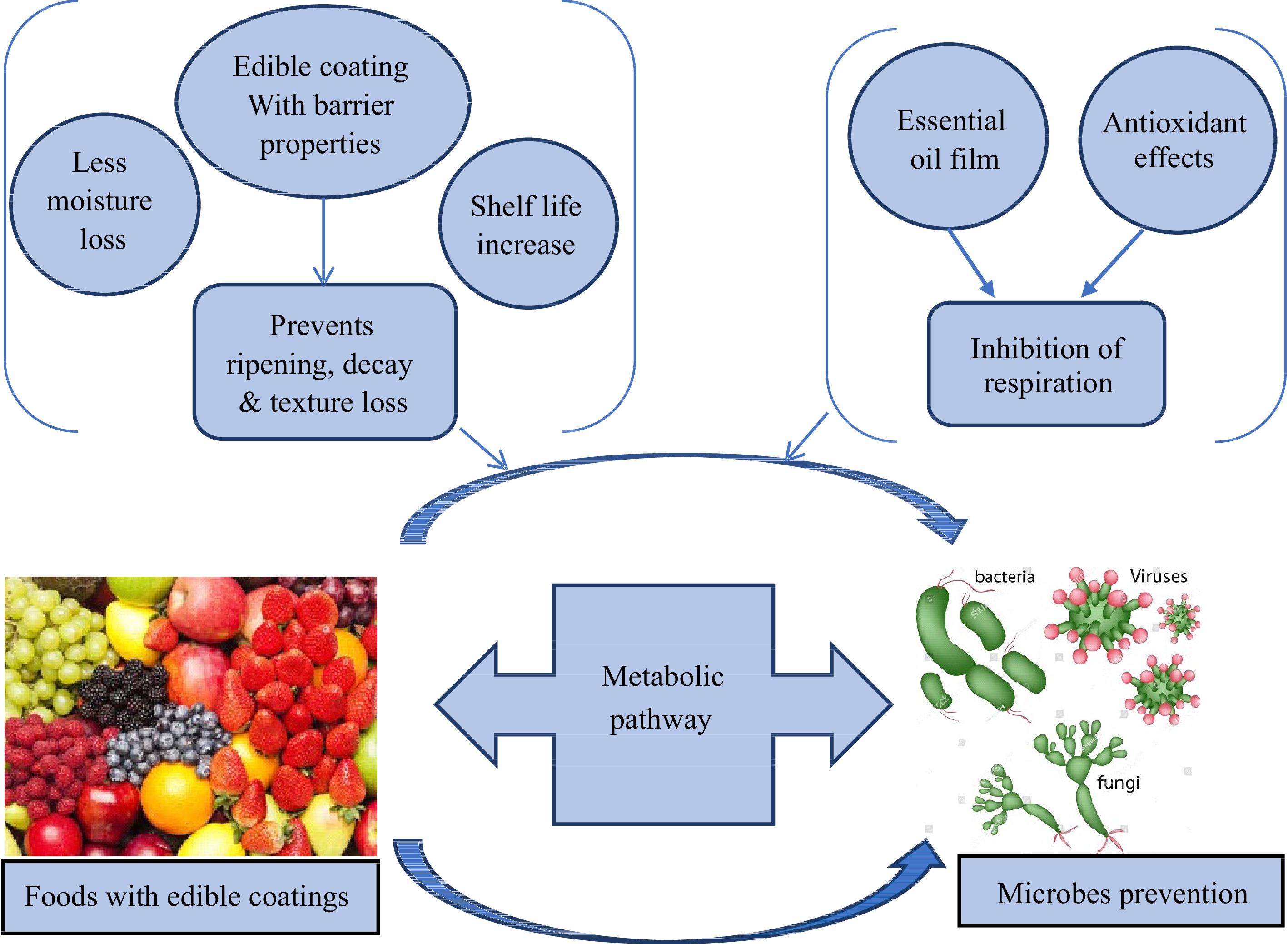
Figure 1.
Edible coating enhances the life-span of fresh produce.
-
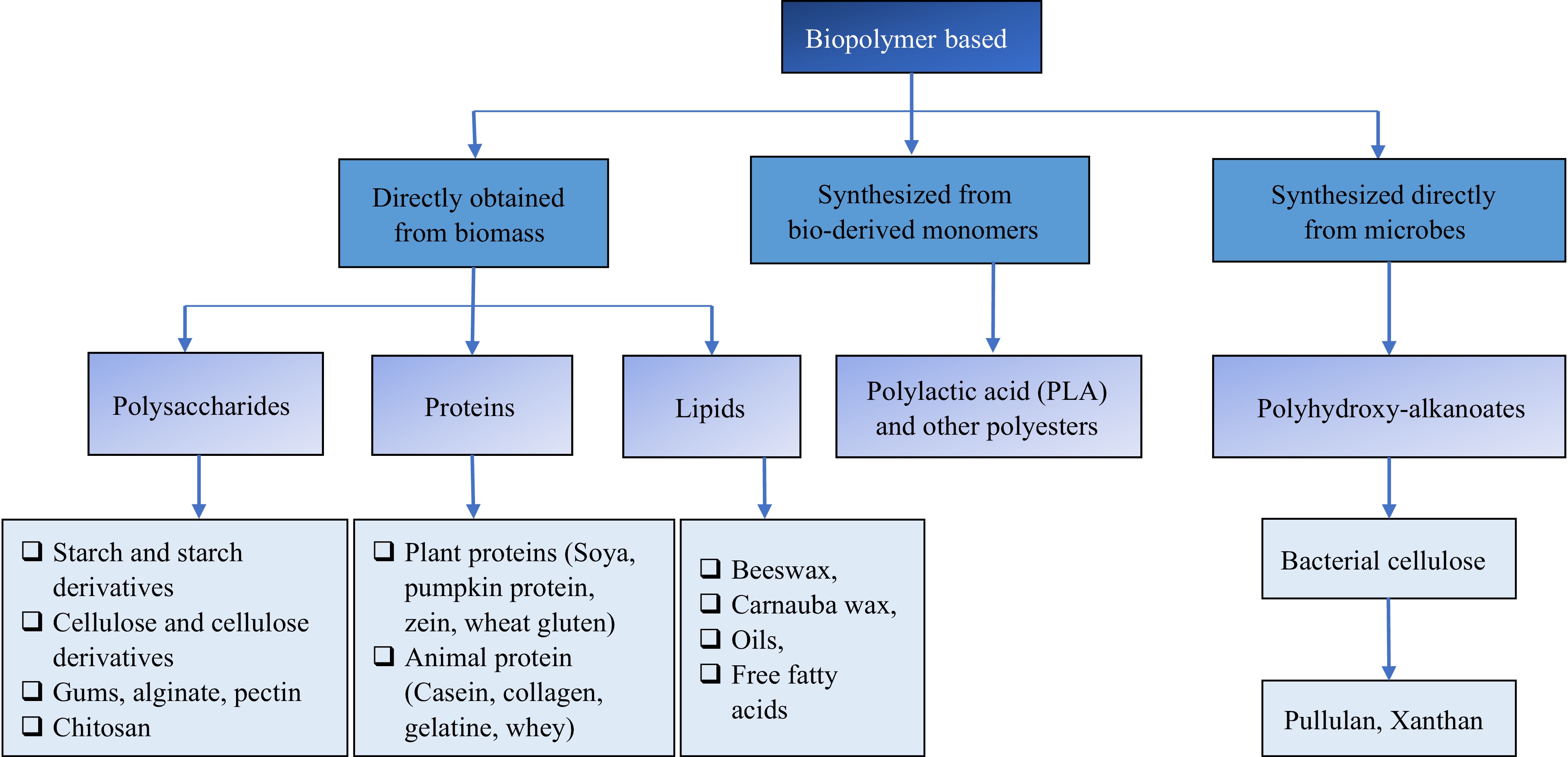
Figure 2.
Illustration of the types and sources of biopolymers.
-
Sr. No. Main component Active component
or NP'sTargeted fruit/
vegetableEffects/significance References 1 Chitosan/chitin Silver NPs Cantaloupes Enhanced antimicrobial activity and greater antibacterial effects. [40] 2 Cassava starch Zinc oxide NPs Fresh-sliced Okra Better product quality and improved packaging characteristics. [41] 3 Carrageenan Zinc oxide NPs Mango Shelf life increased up to 19 d [42] 4 Sodium alginate Citral nano-emulsions Pineapples (1) Enhanced antimicrobial activity,
(2) Improved colour quality,
(3) Less respiration ability.[43] 5 Polyvinyl pyrrolidone/glycerosomes Silver NPs Fresh-cut bell pepper Antibacterial and biocidal effect and shelf life enhancement. [44] 6 Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Guar gum Silver NPs Strawberry (1) Antimicrobial activity on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria including fungi,
(2) Strawberries packed in antimicrobial coatings lose less weight overall than non-coated strawberries.[45] 7 Pectin Magnesium NPs Cherry tomato Enhanced shelf life of cherry tomato [46] 8 Polyvinyl alcolhol (PVA) Chitosan nanoparticles Mangoes (1) Improved antifungal activity,
(2) Shelf life enhance upto 20 d.[47] 9 Cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) Nano-cellulose Spinach (1) Retentions of texture, appearance, chlorophyll and color,
(2) Moisture content retention after three days storage at 25 °C[48] Table 1.
Nano composites coatings and their quality parameters for fresh produce.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)