-
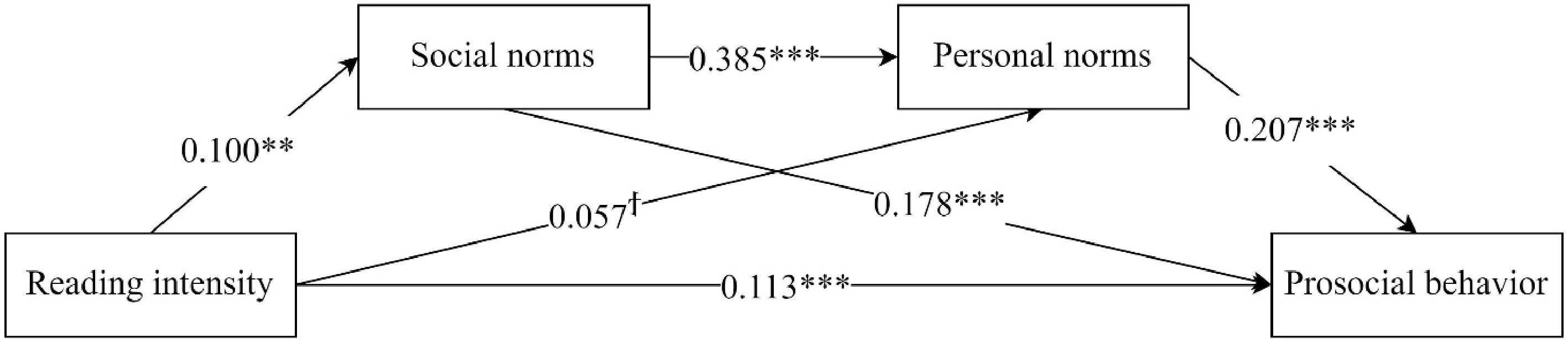
Figure 1.
Model estimation results.
-
Variables Prosocial behavior Antisocial behavior Self-reported Parental reported Self-reported Parental reported Book reading 0.011*** 0.006** −0.007*** −0.004** (0.002) (0.002) (0.002) (0.001) Media use variables Watching TV −0.008*** −0.007** 0.005*** 0.004*** (0.002) (0.002) (0.001) (0.001) Playing games −0.005** −0.004ϯ 0.014*** 0.006*** (0.002) (0.002) (0.001) (0.001) Demographic variables Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Cognitive ability Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Family relationship variables Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Teachers related variables Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Peers' relationship variables Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Class fixed effect Controlled Controlled Controlled Controlled Constant 2.668*** 2.309*** 1.955*** 1.726*** (0.224) (0.236) (0.162) (0.128) Observations 7,487 7,349 7,491 7,361 R2 0.188 0.163 0.212 0.192 Adj. R2 0.160 0.134 0.185 0.164 F 20.61 17.61 25.96 21.50 Standard errors in parentheses. ϯ p < 0.1, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. For the clarity of the table, the coefficients of each type of control variable were not listed in detail. Table 1.
Regression results of study 1.
-
M SD PB SN PN RI PB 3.647 0.785 1.000 SN 3.636 0.855 0.500 1.000 PN 3.454 0.899 0.587 0.545 1.000 RI 3.115 0.920 0.260 0.167 0.184 1.000 Note: The p values of all the correlation coefficients < 0.001. PB = prosocial behavior, SN = social norms, PN = personal norms, RI = reading intensity. Table 2.
The correlation metrics of variables.
-
Dependent variable Social norms Personal norms Prosocial behavior B SE 95% CI B SE 95% CI B SE 95% CI Book reading 0.100** 0.035 [0.031, 0.170] 0.059ϯ 0.031 [−0.002, 0.120] 0.113*** 0.023 [0.067, 0.159] Social norms 0.385*** 0.035 [0.316, 0.453] 0.178*** 0.029 [0.122, 0.234] Personal norms 0.207*** 0.030 [0.148, 0.266] Female 0.150* 0.064 [0.025, 0.275] −0.010 0.056 [−0.119, 0.100] −0.010 0.042 [−0.092, 0.072] Age −0.072*** 0.019 [−0.11, −0.034] −0.057** 0.017 [−0.091, −0.024] −0.013 0.013 [−0.039, 0.012] Parents' education −0.016 0.032 [−0.078, 0.047] −0.009 0.028 [−0.064, 0.045] 0.025 0.021 [−0.016, 0.065] Income −0.068 0.053 [−0.173, 0.036] −0.064 0.047 [−0.155, 0.028] −0.018 0.035 [−0.086, 0.051] Empathy 0.451*** 0.045 [0.363, 0.539] 0.516*** 0.042 [0.434, 0.599] 0.374*** 0.035 [0.305, 0.442] constant 2.909*** 0.387 [2.149, 3.669] 1.037* 0.352 [0.345, 1.730] 0.675* 0.266 [1.197, 0.152] R2 0.200 0.452 0.530 F 25.966*** 73.264*** 87.834*** ϯ p < 0.1, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Table 3.
Regression results of study 2.
-
B SE 95% CI Total effect 0.151 0.025 [0.101, 0.201] Direct effect 0.113 0.023 [0.067, 0.159] Indirect effects Total indirect effect 0.038 0.012 [0.015, 0.064] Book reading → SN → PB 0.018 0.007 [0.005, 0.033] Book reading → PN → PB 0.012 0.007 [0.000, 0.027] Book reading → SN → PN → PB 0.008 0.003 [0.002, 0.015] Note: The standard error (SE) and 95% CI of indirect effects are based on bias-corrected bootstrap samples. SN = social norms, PN = personal norms, PB = prosocial behavior. Table 4.
Direct and indirect effects.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(4)