-
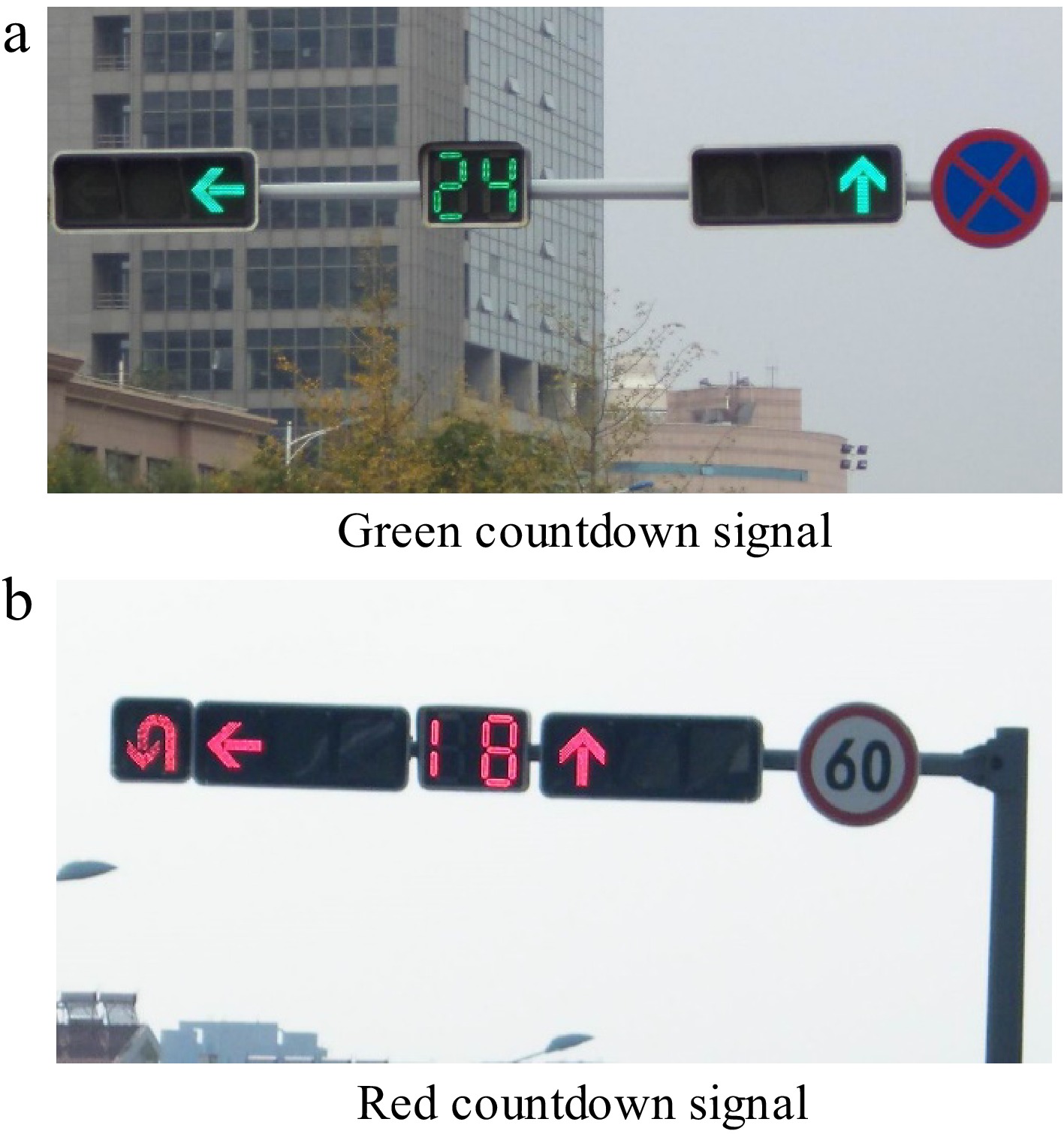

Figure 1.
Two types of motorized vehicle countdown signals.
-

Figure 2.
Main hardware for measuring physiological parameters.
-

Figure 3.
Main software for measuring physiological parameters.
-
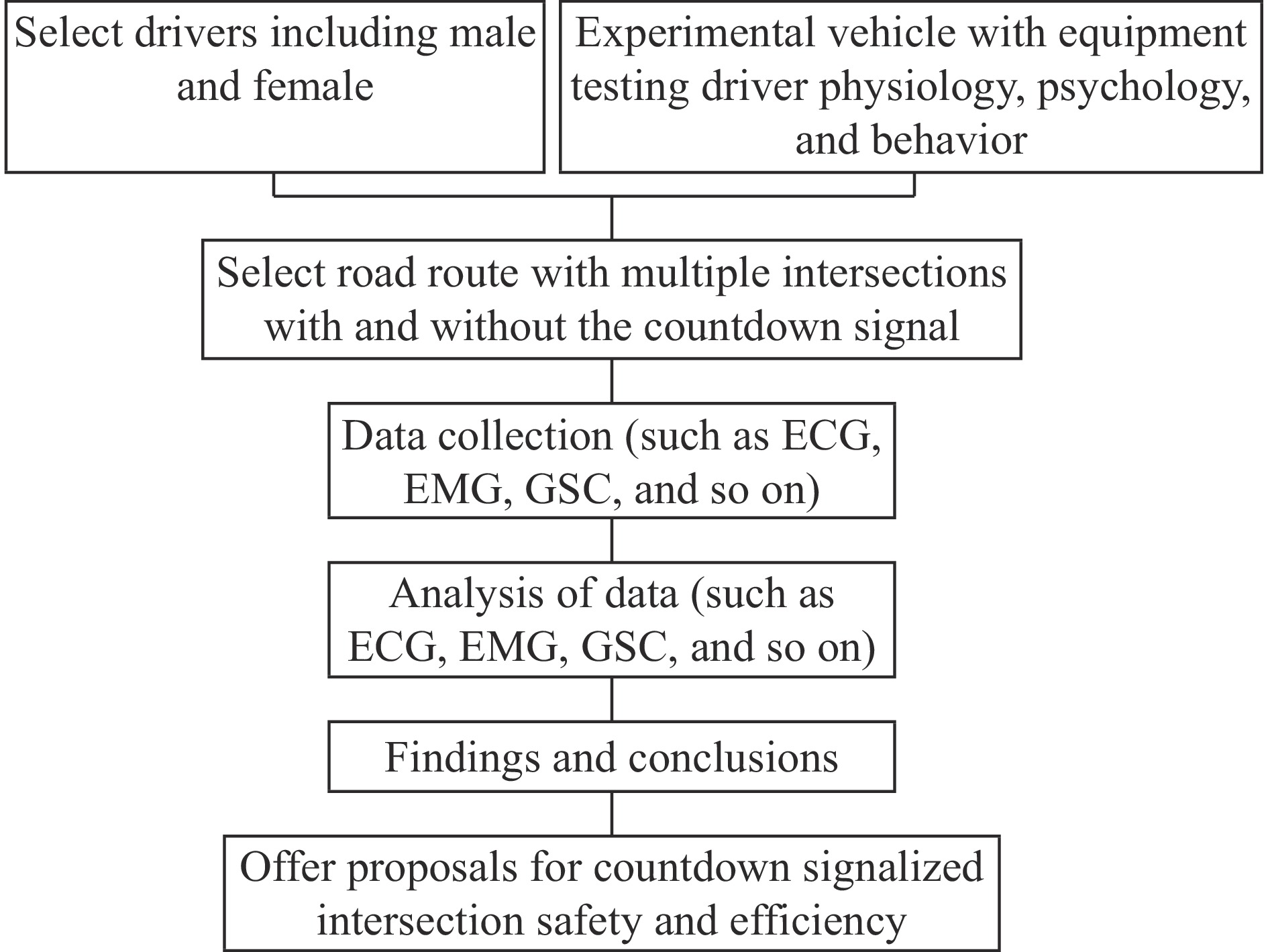
Figure 4.
Future research framework.
-
Country Total number Number Time Malaysia 2 1 2005 1 2008 Singapore 1 1 2006 China 32 1 2006 2 2008 3 2009 6 2010 3 2011 1 2012 3 2013 4 2014 2 2015 2 2016 1 2017 2 2019 1 2020 1 2022 Korea 1 1 2017 Thailand 2 1 2009 1 2010 The US 1 1 2018 The UK 1 1 2020 India 5 1 2012 1 2015 1 2017 1 2021 1 2022 Greece 1 1 2014 Table 1.
The sources and quantitative characteristics of studies.
-
Study Country Study methodology Content and/or results Conclusions Lum & Halim[5] (2006) Singapore Compared the red-running and red-stopping characteristics before GSCD installation with those obtained after GSCD started operation and used proportional tests to evaluate the statistical significance of the results. Red-running violations were significantly reduced at 1.5 months after the installation of the GSCD, but the effectiveness of such a device dissipated over time and the violation numbers returned to almost pre-GSCD level. The long-term performance of the GSCD only encourages the layoff of red violations but does not curb them. Wang & Yang[6] (2006) China A questionnaire survey was conducted on 377 drivers in Longyan City, Fujian Province, to analyze their behavior choices and calculate the start delay time based on the survey results. GSCD partially provoked drivers to accelerate through the intersection at the end of the green signal, which may cause severe intersection accidents. GSCD must be set cautiously. Yuan et al.[7]
(2009)China The method used in this study focuses on comparative parallel research, collecting driver behavior characteristics of 4 countdown intersections and 4 non-countdown intersections in Nanjing, and comparing and analyzing the average values of the results. The countdown displays significantly affected the decision of the motor vehicle drivers, and the red-running violations were reduced without GSCD. By contrast, the start-up delay was increased without RSCD. Countdown signal lights must be installed cautiously. Chiou & Chang[8] (2010) China Three driver responses to GSCD (late-stopping ratio, dilemma zone, and decision to cross) and three driver responses to RSCD (early start ratio, start-up delay, and discharge headway) were observed and analyzed in Taiwan Province. Although GSCD can reduce late-stopping ratio, the dilemma zone is increased by about 28m, and the decision to cross will be more inconsistent among the approaching vehicles, creating a potential risk of rear-end crashes. RSCD enhances intersection efficiency. RSCD is clearly less controversial and more beneficial than GSCD. Ma et al.[9] (2010) China Investigated the impact of GSCD installation on the speed distributions for vehicles passing the stop line during the amber time and calculated the Dilemma Zone Distribution. GSCD encouraged motorists to pass the stop-line during the amber time with greater speed. Such circumstances resulted in better utilization of the amber time and increased capacity for the intersection approach. The GSCD can moderate the response of motorists toward phase transition, effectively prevent sudden speed change, and significantly reduce the number of red-light violations. Qian & Han[10] (2010) China A questionnaire survey was conducted on 390 drivers, and the driving behavior of 250 rear vehicles under the GSCD was observed. A considerable number of drivers chose to accelerate and rush over at the end of GSCD, crossing the intersection before the end of GSCD, resulting in the occurrence of speeding and rushing, leading to the need to set longer green light intervals. GSCD is not good for either traffic safety or traffic efficiency. GSCD must be used with due consideration. Qian[11] (2011) China A questionnaire survey was conducted on 390 drivers, and observations were conducted at two intersections with and without RSCD to study driving behavior and vehicle headway. Under the condition of RSCD, the average loss time of vehicles passing through the intersection can be saved by about 1.5 s. RSCD can reduce start-up lost time, calm driver emotions, and reduce fuel consumption. Zhu et al.[12]
(2012)China Collected driving behavior and speed data at SCD intersections and used descriptive statistics, analysis of variance, contingency tables, and other statistical methods to analyze the impact of signal control on speed and traffic. The GSCD significantly affected excessive speed rates, and the RSCD considerably influenced speed dispersion. Installing traffic violation detection equipment while using GSCD can effectively control vehicle speed. Lin et al.[13] (2013) China Two similar intersections with and without countdown signals were selected as the research subjects, and a one-way ANOVA was used to evaluate whether countdown signals have a significant impact on reducing the occurrence of dilemma zones. The dilemma zones mostly occurred at a distance of 30 to 75 m from the stop line at the intersection. The majority of drivers took conservative measures such as "parking" when facing the hesitation zone at the intersection while driving the vehicle. GSCD has a significant effect on cutting down the range of dilemma zones. Huang et al.[14] (2014) China The influence of three typical signal devices with various time-reminder strategies, i.e., common signal device (CSD), green signal flashing device (GSFD), and GSCD, on drivers' decision-making processes during the period from the end of the green phase to the onset of the red phase was analyzed, and their safety performance from the aspect of red-light-running (RLR) violations was evaluated. Stop and go decisions under GSCD, stop and go decisions under GSFD and go decisions under CSD are all significantly different from stop decisions under CSD regarding their effects on RLR violations of vehicles in DZ. The odds of RLR violations for these five conditions were respectively, 11.815, 4.144, 2.452, 1.214, and 3.439 times as large as those for stop decisions under CSD. Although GSCD stimulates the drivers in dilemma zones to choose to cross the intersection during amber, which produces a higher RLR risk compared with CSD and GSFD, the intersection with GSCD is verified to own the lowest RLR violations due to its greatly positive effect in cutting down the range of dilemma zones. Ni & Li[15] (2014) China Based on the field observation carried out at 2 GSCD intersections and 2 NGSCD intersections (i.e., intersections without GSCD devices) along an arterial in Suzhou, the rear-end probabilities at GSCD and NGSCD intersections were calculated using Monte Carlo simulation. On the one hand, GSCD caused significantly negative safety effects during the flashing green interval, especially for vehicles in a zone ranging from 15 to 70 m; on the other hand, GSCD was helpful in reducing rear-end accidents during the yellow interval, especially in a zone from 0 to 50 m. GSCD can shorten indecision zones and reduce rear-end collisions near the stop line during the yellow interval, but it easily results in risky car following behavior and much higher rear-end collision probabilities at indecision ones during both flashing green and yellow intervals. Cao et al.[16] (2015) China Selected two countdown signal intersections and two non-countdown signal intersections in Dalian city, and used mathematical statistical methods to compare and analyze the vehicle speed characteristics, as well as the number of yellow light running and lane changing violations, of the two types of intersections during normal and peak hours. The countdown signal has a smaller impact on vehicle behavior of running yellow lights, while the countdown signal has a significant impact on illegal lane changing behavior. GSCD can induce some drivers to speed through intersections at the end of green light time, and has a significant influence on the number of illegal changing lane behaviors at off-peak hours. Yang et al.[17] (2015) China The differences between the first vehicle start up delay under situations of with-without RSCD, turning left and going straight vehicles were analyzed respectively by nonparametric test. There was significant difference for the first vehicle start-up delay between countdown and non-countdown signalized intersections (p = 1.83 × 10−5). Intersections with RSCD significantly reduce the delay in starting the first vehicle compared to intersections without a RSCD. Devalla et al.[18] (2015) India Observations were conducted at intersections in New Delhi with or without signal control, and extracted data was analyzed to assess the effect of GSCT on RLV and variations of vehicular speeds both in the presence and absence of timers. GSCD is found to be linked with fewer red-light violations (RLVs) cycles, lower number of mean RLV per RLV cycle, higher vehicular speeds during the phase transition at different locations upstream to the stop line, a greater number of speeding cars, and higher stop line crossing speed during amber. GSCD encourages drivers to travel at higher speeds, which could lead to accidents. Biswas et al.[19] (2017) India This study evaluated the influence of SCTs on intersection efficiency and safety by conducting "before and after" study at three signalized intersections located in New Delhi. The presence of RSCT led to higher RLVs during the last 10 s of red. It was observed that the ranges of both Type I and Type II DZs for small
cars reduced in the presence of GSCT.GSCT has no impact on saturated flow. Although RSCT can help reduce startup lost time, it can increase accident risk. Huang et al.[20] (2019) China In summer (normal road surface) and winter (road surface snow state), the approach speed, stopping or passing ratio, and maximum deceleration braking area of the target vehicle were collected and analyzed using video recording methods. Comparing the maximum deceleration models of intersections under three types of signal configurations in winter and summer, it can be found that the countdown signal can enable vehicles to slow down and brake earlier when approaching the intersection, stopping at a safe and stable deceleration. The countdown signal light helps the vehicle decelerate smoothly, especially on icy roads in winter, enabling the driver to make a stop decision earlier and reducing the occurrence of sudden braking. Paul & Ghosh[21] (2020) The UK Evaluate the effectiveness of the green signal countdown timer (GSCT) for RLV and the resulting right angle and right turn related crashes (for left hand driving) using post encroachment time (PET). Using GSCT reduced cross-conflict by 2.57%. GSCT's installation can be recommended as a cost-effective engineering countermeasure to reduce severe crash types at signalized intersections. Paul et al.[22] (2022) India Collected collision data and on-site traffic data, and used the PTV VISSIM micro simulation tool to simulate intersections with and without GSCT signal control to conduct conflict analysis for various situations. The GSCT was found to influence driving behaviors at yellow onset, shorten the length of both type-I and type-II DZ, and reduce the rate and intensity of both RLVs and sudden stopping behaviors. The setting of GSCD is beneficial for traffic safety. Liu et al.[23] (2022) China Collected traffic flow characteristics data for two types of intersections with and without green countdown signals, mainly including location speed, vehicle start time, and headway data. Based on behavioral decision-making theory, a logistic model was constructed to evaluate the impact of green countdown signals on driver driving decisions. The GSCD prompted the driver to slow down. The probability of vehicle acceleration behavior at intersections with GSCD was lower than that at intersections without GSCD, and the probability of parking behavior was higher than that at intersections without GSCD. The GSCD has a certain positive effect on the safety and traffic efficiency of intersection driving. Table 2.
Studies on GSCD and/or RSCD
-
Study Country Study methodology Content and/or results Conclusions Kidwai et al.[24] (2005) Malaysia The effect of countdown timers on red-light violations was studied. Four intersections with timers and three intersections without timers were considered, and red-light violation data were compared. The incidents of red-light running were about two times higher in cases without countdown timers than in cases with countdown timers. Compared to no signal control, countdown signals can reduce the phenomenon of red-light violation. Ibrahim et al.[25] (2008) Malaysia Six intersections (three with countdown timers and three without) were analyzed to examine the effect of countdown timers on driving behaviors, intersection approach headways, and safety levels. The digital timer had a significant effect on discharge headway for all the cars in queue. The rate of red-light violation is more for count down intersections than for non-count down ones. Countdown signals are not as safe as no countdown signals. Limanond et al.[26] (2009) Thailand The influence of countdown timers installed at a signalized intersection on the queue discharge characteristics of through movement during the green phase in Bangkok was studied. Standard statistical t-tests were used to compare the difference in traffic characteristics between the "with timer" and "without timer" cases. During the periods where the timer was in use, the mean saturation headway gradually increased from 1.88 s/vehicle during the off-peak daytime, to 1.94 s during the night period, and finally to 2.05 s during the late-night period. Similarly, for the condition without a timer, the mean saturation headway progressively increases from 1.85 s/vehicle during the off-peak daytime to 2.05 and 2.09 s for the nighttime and late-night time periods, respectively. Countdown timers significantly affect the start-up lost time. For each through movement lane at the studied intersection, the savings in start-up lost time were estimated to equal an increase of 8 to 24 vehicles per hour. However, the effects on saturation headway were minimal. Limanond et al.[27] (2010) Thailand The traffic analysis made a comparison of traffic characteristics during an off-peak time at a selected intersection when the countdown timer was in operation against when it was switched off, and a public opinion survey was conducted on more than 300 regular local drivers. The presence of the countdown timers at the intersection would help to reduce the start-up lost time at the beginning of the green phase by 22%, and reduce the number of red-light violations during the beginning of the red phase by 50%. Countdown timers can reduce the start-up lost time and reduce the number of red-light violations. And the majority of the local drivers were favorable towards the countdown timers. Sharma et al.[28] (2012) India The changes in queue-discharge characteristics and red-light violations were analyzed under Indian traffic conditions with the presence of a timer. A before-and-after analysis was conducted using the data collected from a selected intersection in Chennai. It was found that the propensity of RLV decreased from 59% to 31% at the start of red and increased from 12% to 75% at the end of red. Also, the intensity of RLV for both the start of red and the end of red decreased from 3.32 to 2.30 vehicles and 8.52 to 5.60 vehicles. The time information provided at the start of the green light (end of the red light) enhances efficiency and reduces start-up lost time, but increases red-light violations. Wang[29] (2008) China It introduced the current status of traffic signal countdown equipment in China and abroad, and qualitatively analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of countdown signals. GSCD tended to trigger speeding, and GSCD reduced delays and improved roadway capacity. It is recommended that a countdown for red lights be used, and that no countdown be used for green and yellow lights. Ma[30] (2008) China The camera method was used to observe the behavioral differences of drivers at intersections with and without countdown signals. The logistic model was used to establish a behavioral decision-making model for drivers at countdown signal intersections. The countdown signal showed that the remaining 1 second is the decision point for the driver's acceleration or constant speed behavior. At intersections without countdown signals, the speed at a distance of 20m from the parking line should be controlled within the range of 13−22 m/s. Countdown displays significantly affect the decision-making behavior of motorists. And the number of traffic conflicts increases at intersections with countdown displays. Wu et al.[31] (2009) China Based on the two aspects of vehicle types and speed, a logistic model was used to construct the model of behavioral decision at countdown-signalized intersections. The sensitivity of "signal light display time" to uniform speed behavior was the strongest. The second was deceleration behavior. The sensitivity of acceleration behavior was relatively lower than the first two. Countdown signal display remarkably influences the decision-making behavior of motorists. Zhang et al.[32] (2009);
Zhang et al.[33] (2010)China The survey collected 20 survey questionnaires from drivers and pedestrians to understand the opinions of traffic participants on countdown signal lights, and observed driving behavior for 7 consecutive days before and after the installation of countdown signal lights in Beijing. The survey results showed that over 85% of drivers and pedestrians are willing to choose signal control methods with countdown display. The Zstat-test showed whether there is a significant decrease in yellow light passing behavior after countdown installation compared to when not installed at a 95% confidence level. Traffic volumes were considerably similar before and after the countdown signal was installed. Meanwhile, the yellow-crossing and red-light running incidents significantly decreased after the countdown signal was installed. Gong[34] (2010) China The driving behaviors of motorists in red-light running at six countdown-signalized intersections were explored and analyzed the rate of this type of incident. The red-light violation rate at intersections with countdown was slightly higher than that at intersections without countdown. Installing a countdown timer must be considered carefully. Li & Wang[35] (2010) China An analysis was conducted on the light color regulations in urban road traffic signal control in China and the influencing factors of some commonly used signals in both positive and negative aspects. They analyzed some problems in Chinese urban road traffic signal control and stressed that motorized vehicle countdown signals didn't provide other benefits except psychological comfort to drivers. Such signals even endangered traffic safety. These researchers don't recommend the use of motorized vehicle countdown signals. Long et al.[36] (2011) China The researcher surveyed the signal phase and traffic operation at four signalized intersections and collected 24-hour red light time, driver's position and actions after yellow light appearance, red light violation driving, and other intersections with and without countdown timers. Measured driver behavior through driver decisions (parking or driving) and vehicle entry using binary logistic regression (BLR) and non-parametric testing. Countdown timers can indeed influence driver behaviors, in terms of decisions to stop or cross the intersection as well as the distribution of vehicle entry times. There was a strong correlation between the presence of countdown timers and an increase in red light violations. Countdown timers may lead to entering intersections in the later stages of yellow or even red, so consider carefully before deploying countdown timers at intersections. Long et al.[37] (2011) China Data were collected at three intersections with and without countdown signals, and binary logistics regression was applied to establish the driver decision type selection model after the yellow light was on. With the installation of the countdown timer, the average vehicle crossing time has increased from 1.52 to 2.92 s. Countdown signals have an adverse effect on the safety of intersections. Long et al.[38] (2013) China The difference in driver's stop/go decisions at the countdown and non-countdown timer installed intersections were investigated with binary-logistical regression analysis. The probability of driver choosing to stop at a countdown timer equipped intersection was only 0.282 times of that at a non-countdown timer intersection when the signal turned red. Countdown timer can better assist drivers in their decision-making process and thus may reduce hazardous driving maneuvers during the phase transition period. Li et al.[39] (2014) China Drivers' perception–reaction time (PRT) with and without a countdown timer were comparatively analyzed based on the RGB color model and the fuzzy c-means clustering was utilized for PRT classification and comparison. The drivers' PRT was decreased from 2.12 to 1.48 s with countdown signals. The countdown signal significantly shortens the driver's PRT. Papaioannou & Politis[40] (2014) Greece A survey was conducted at an intersection in the city of Komotini, Greece, with or without a countdown signal timer (CST). A total of 60 h of observation time were recorded to observe vehicles' movement characteristics. The percentage of the violations of the early start at the intersection with SCD was observed to 24% whereas the respective percentage for the intersection without SCD was less than 1%. The CST devices (with green signal countdown displays-GSCD-and red signal countdown displays-RSCD), should be carefully used since they tend drivers to early start behavior. Sun et al.[41]
(2013)China Data collection was conducted in Guangzhou, collecting raw video data from 36 h of peak hours on weekdays. Discovering the effects of countdown timer on capacity and headway. The countdown timer decreased the headway fluctuation of vehicles in the queue, with the standard deviation reducing by 10% to 25%. And the capacity of the through movement improved by about 5% to 10% after the countdown timers were installed. Countdown signal can reduce the mean headway of vehicles and increase road capacity. Yu et al.[42] (2014) China The study collected relevant data from 9 signalized intersections and a total of 13 entry lanes, using the situation of vehicles passing through parking lines and the number of traffic conflicts during the red and yellow light periods as alternative safety evaluation indicators. The data on the entry lanes of intersections with and without signal countdown devices were compared. In both straight and left turn directions at the intersection, the frequency of adventurous traffic and the number of traffic conflicts at the intersection entrance have significantly increased due to the influence of signal countdown devices. SCD significantly increases the red-yellow running violation and traffic conflicts at signalized intersections for both through and protected left turn movements. SCD negatively affect the safety performance of the signalized intersections and should be used more cautiously. Zou[43] (2016) China Based on video data, parameters such as driver's response time to start, headway, and vehicle retention rate in weaving areas during yellow light periods under different commutation prompts were extracted to analyze the effectiveness of the countdown signal. The driver's reaction time at intersections with countdown signal lights has been reduced by 14.51%, and the time when vehicles pass the parking line has been advanced by 9.85% after reaching the saturation headway. During the yellow light period, the vehicle retention rate in the weaving area has increased by 38.68%. The countdown signal commutation reminder device can improve the operational efficiency of intersections, but may have a certain potential negative impact on intersection traffic safety. Ma et al.[44] (2017) China Based on the measured data, the speed distribution characteristics of each section of the signal-controlled entrance road were analyzed, and a cellular automata model considering driving psychology under signal countdown was proposed. At an intersection with a countdown signal 14m away from the stop line, the driver acceleration ratio was 19%. Countdown signals are not conducive to traffic safety and may cause traffic hazards. Chang &
Jung[45] (2017)Korea Using a driving simulator, 20 traffic lights with countdown indicators were compared from the perspectives of driver reaction time and subjective satisfaction scores, and their performance was compared with standard traffic lights. The reaction time of the countdown separation (43.0 s) and countdown superposition (67.5 s) signals was significantly shorter than that of the standard signal (3.5 s). The satisfaction score of the countdown separation (6.3 points) and countdown superposition (8.0 points) signals was higher than that of the standard signal (06.0 points). Countdown signals can shorten the driver's reaction time more than standard signals, helping to reduce the length of dilemma areas at intersections. Almutairi[46]
(2018)The US Analyzed the impact of signal timers on startup loss time (SLT), saturation time interval (STH), and the location and size of difficult areas, and modeled the observed maximum passing and minimum stopping distances based on real ground data. The quantified different effects from the intersection with no timers or camera enforcement for the saturation time headway were −0.02, 0.02, and −0.07 seconds for timers, camera enforcement, and both, respectively. The quantified different effects from the intersection with no timers or camera enforcement for the startup lost time were −1.65, −0.41, and −0.88 for timers, camera enforcement, and both, respectively. Countdown lights improve security by reducing SLT and minimizing the size of difficult areas. Huang et al.[47] (2019) China Six intersections in Shenyang were selected to analyze the behavior of vehicles under countdown signals in summer (normal road surface) and winter (road surface snow state). Based on the processed data, a distribution map and a start delay model were established. In summer and winter, the average maximum deceleration of intersections with countdown signals was approximately 1.0 m/s2 lower than that of intersections without countdown signals. Countdown traffic signals can shorten the start delay and improve traffic efficiency and safety at intersections. Zheng et al.[48] (2020) China Based on on-site shooting data of typical signalized intersections in Beijing, the impact of countdown signals on pedestrian and non-motorized vehicle gap acceptance behavior was studied using methods such as nonlinear fitting and hypothesis testing. Under normal signals, the average acceptance gap between pedestrians and non-motorized vehicles was 9.0 s, while under countdown signals, it was 7.3 s. Under the countdown signal, the acceptance gap value of pedestrians and non-motor vehicles significantly decreases, and the probability of collision increases. Jatoth et al.[49] (2021) India Research was conducted at two intersections in Hyderabad, India, to collect and analyze data such as vehicle startup loss time and capacity. The number of red-light violations (RLVs), start-up lost time, and average control delay are found to decrease in the presence of an active countdown timer. The signal countdown timer is an effective device that can enhance the traffic safety and operational performance of a signalized intersection. Table 3.
Studies on countdown signals.
-
Studies Opinion Impact on traffic safety Kidwai et al.[24] (2005); Zhang et al.[32] (2009);
Zhang et al.[33] (2010); Ma et al.[9] (2010);
Limanond et al.[27] (2010);The researchers believed that red-running violations are reduced with countdown signals. Positive Sharma et al.[28] (2012); Yuan et al.[7] (2009);
Yu et al.[42] (2014)The researchers deemed that red-running violations increase with countdown signals. Negative Zheng et al.[48] (2020) Researchers believed that under timing signals, the probability of collision increases Negative Lum & Halim[5] (2006) The authors attested that red-running violations initially decrease and then increase after a GSCD is installed. First positive,
then negative.Zou H[43] (2016); Ma et al.[44] (2017);
Biswas et al.[19] (2017)The countdown signal commutation reminder device can improve the operational efficiency of intersections, but may have a certain potential negative impact on intersection traffic safety. First positive,
then negative.Lin et al.[13] (2013); Huang et al.[14] (2014);
Chang & Jung[45] (2017); Almutairi[46] (2018);
Paul et al.[22] (2022)GSCD have a positive effect on cutting down the range of dilemma zones. Positive Paul & Ghosh[21] (2020); Liu et al.[23] (2022) Using GSCT can reduce cross conflict and traffic accident. Positive Zhu et al.[12] (2012); Devalla et al.[18] (2015) GSCD encourage drivers to travel with higher speed which could lead to accidents. Negative Table 4.
The opinion of different studies on traffic safety.
-
Studies Opinion Impact on traffic safety Ibrahim et al.[25] (2008) Countdown timers moderately affect initial delay but significantly influence headway. Positive Limanond et al.[26] (2009); Huang et al.[47] (2019) Countdown timers significantly affect the start-up lost time. However, the effects on saturation headway were minimal. Positive Chiou & Chang[8] (2010); Qian[11] (2011);
Li et al.[39] (2014); Yang et al.[17] (2015);
Xu et al.[53] (2016)The researchers deemed that start-up lost time reduction and traffic efficiency improvement. Positive Ma et al.[9] (2010); Sun et al.[41] (2013);
Jatoth et al.[49] (2021)The authors supposed that countdown timer could increase the traffic capacity. Positive Long et al.[37] (2011) The authors determined that the median value of the time a vehicle crosses a stop bar with a countdown timer is significantly. higher than that without a countdown timer. Positive Qian & Han[10] (2010) GSCD is not good for either traffic safety or traffic efficiency. Negative Table 5.
The opinion of different studies on traffic efficiency.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(5)