-
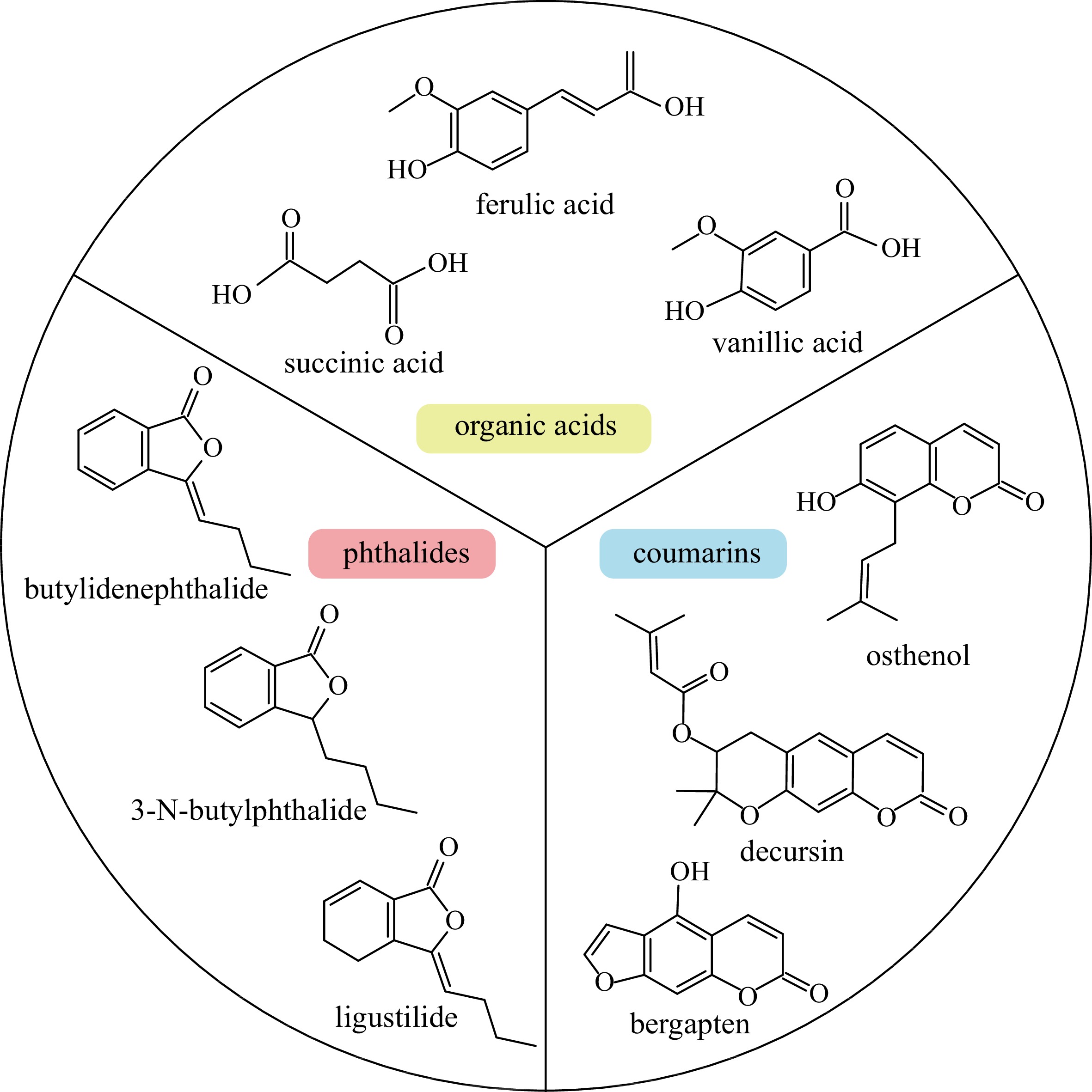
Figure 1.
Main active compounds in Angelica sinensis.
-
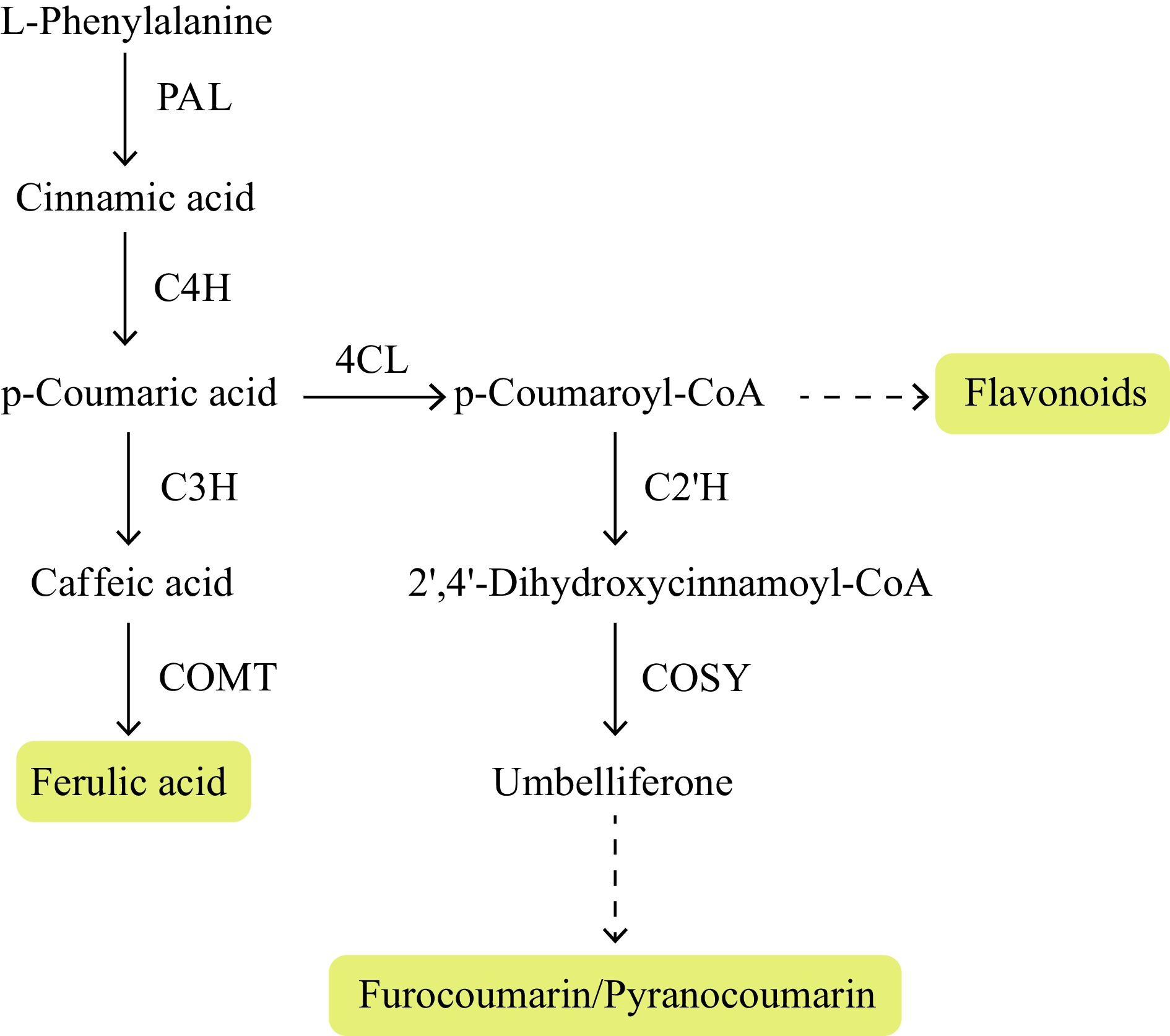
Figure 2.
Proposed ferulic acid, coumarin and flavonoid biosynthesis pathways in Angelica sinensis. Note: PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; C3H, 4-coumarate-3-hydroxylase; COMT, O-methyltransferase; 4CL, 4-coumarate CoA ligase; C2'H, p-coumaroyl CoA 2'-hydroxylase; COSY, coumarin synthase.
-
Tissues Research focus Reference Pathway of active compounds Root head and tail Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway and ferulic acid metabolites [26] Root head and tail Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis [27] Root head and tail Metabolites [31] Root Phthalides biosynthetic [32] Leaf and petiole from cultivars Mingui 1 and Mingui 2 Flavonoid biosynthesis [30] Root from cultivated and wild resources Metabolism pathway [3] Leaf from cultivars Mingui 1 and Mingui 2 Flavonoid biosynthesis [33] Root head and tail Ferulic acid biosynthesis [34] Root head, body and tail Ferulic acid biosynthesis [28] Early bolting and flowering Flower bud of early flowering Early bolting and flowering [35] Mixed sample from different growth stages Early bolting and flowering [36] Whole shoot tip and young developing leaf Early bolting and flowering [37] Leaf, stem, seed, and root from early bolting plant Early bolting and flowering [38] Seedling with different vernalization treatments Early bolting and flowering [39] Leaf from normal and early bolting plant Early bolting and flowering [40] Seedling stored at different temperature Early bolting and flowering [41] Seedling GAs biosynthetic pathway [42] Adversity and stress Leaf under UV-B radiation Adaptive mechanism under UV-B radiation [43] Table 1.
Summary of transcriptomics reports from Angelica sinensis.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(1)