-

Figure 1.
The classification scheme of non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs). Italics represent the NSPs chosen under each category to depict the effect on starch. Cellulose serves as the fiber microfibrils, non-cellulosic polymers serve as cell walls or fiber matrix, and pectic substances function as intercellular cement.
-
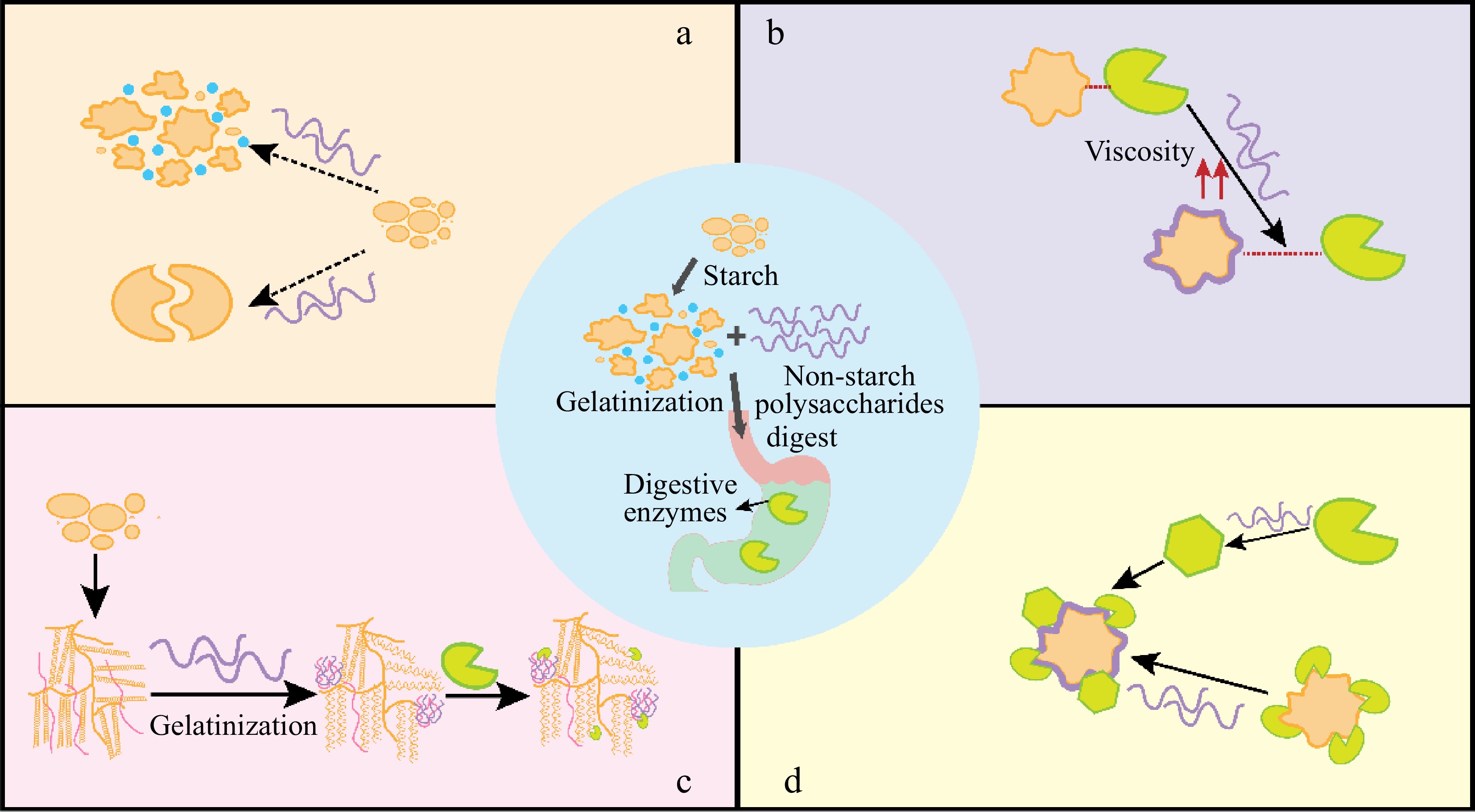
Figure 2.
Mechanisms from lowering effects of NSPs on starch digestion.
-
Origin Name Solubility Major composition Molecular weight (kDa) Main function Reference Botanical Cellulose derived molecules Methyl Cellulose Soluble β (1,4) D-glucose 20~1,000 Thickening, gelling, stabilizing, emulsification [71,73] Cellulose derived molecules Carboxy methylcellulose Soluble β (1,4) D-glucose 95~1,100 Thickening [74] Cellulose derived molecules Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose Soluble β (1,4) D-glucose 20~1,000 Thickening, gelling, stabilizing, emulsification [74] Plant tissue extracts Pectin Soluble α-(1–4)-linked D-galacturonic and mannuronic acid. 50~150 Stabilizing, gelling [71,73] Tree gum exudates (Acacia Sap) Gum Arabic Soluble Galactose 200~800 Emulsification, film forming [71,73] Roots of chicory (Asteraceae) Inulin Soluble β-D-fructose 0.5~13 Prebiotic, thickening [71] Tubers Konjac-glucomannan Soluble D-glucose and D-mannose, 10~2,000 Thickening, gelling, texturing, water binding [73] Viscous plant substances (Seeds mucilages) Locust bean gum Soluble D-mannose and D-galactose 500~1,000 Stabilizing, thickening, [71,73] Viscous plant substances (Seeds mucilages) Tara gum Soluble D-mannose and D-galactose ~1,000 Stabilizing, thickening, gelling [71] Plant tissue extracts β-glucan Soluble D-glucose 10~1,000 Stabilizing, thickening, emulsification [74] Seed endosperm of Cyamopsis tetragonolobus Guar gum Soluble Linear chain of Galactomannan unit 100~2,000 Stabilizing, thickening [73] Tree gum exudates (Dried sap of several legumes of the Astragalus, including A.
adscendens, A. gummifer,
and A. tragacanthus)Tragacanth gum Soluble: tragacanthin; Insoluble: bassorin Tragacanthin and tragacanthic acid ~840 Stabilizing, thickening, emulsification [73,74] Viscous plant substances (mucilages) Psyllium Soluble Arabinoxylan 35~3,800 Thickening, gelling [74] Brown seaweeds Alginate Soluble β-D-Mannuronic Acid 32~400 Stabilizing, gelling [71] Red seaweeds (Sphaerococcus euchema) Agar Soluble in hot water β-D-Galactopyranose 80~140 Stabilizing, gelling [71,73] Red seaweeds Carrageenan (kappa-, lambda- and iota-) Soluble Sulphated D-galactose and L-anhydrogalactose 400~700 Stabilizing, gelling, thickening [71,73,75] Animal Crustaceans, Invertebrates Chitosan Soluble in acetic aqueous solutions 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-D-glucose 4~500 Gelling [73,77] Microbial Aureobasidium
pullulansPullulan Soluble α-D-glucan 40~600 Thickening, gelling, foaming, flocculating, stabilizing, binding [10,75] Fermentation gums (Xanthomonas campestris exudate) Xanthan Gum Soluble β-D-glucose u, two mannose and one glucuronic acid 1,000~50,000 Structure formation, thickening, stabilizing [71,73] Fermentation gums (Pseudomonas elodea) Gellan gum Soluble in hot water The basic unit is composed of 1,3- and 1,4-linked 2 glucose residues, 1,3-linked
1 glucuronic acid
residue, and 1,4-linked
1 rhamnose residue~500 Gelling, film forming [74−76] Fermentation gums
(of microbial origin)Curdlan Soluble in an alkaline aqueous solution linear glucan D-glucose 53~5,800 Gelling [77] Fermentation gums
(of microbial origin)Dextran Soluble Composed of D-glucose, the main chain is α-1,6 bonds, and there are also branched chains with
α-1,4 or α-1,3 bonds40~70 Stabilizing, thickening, emulsification [74] Table 1.
Summary of important molecular characteristics of some common non-starch polysaccharides used in foods.
-
Type of non-starch polysaccharide Type of starch To Tp Tc ΔH Reference Botanical Arabinoxylans Wheat starch ↑/↓ (depends on arabinoxylans molecular weight) ↑/— ↑/↓/— — [28] β-glucans Rice starch ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ [25] Corn fiber gum Wheat starch — — — ↑ [29] Carboxymethyl cellulose Wheat starch ↑ N ↑ ↑ [23] Carboxymethyl cellulose Nixtamalization maize dough ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ [24] Fenugreek gum Corn starch ↑/↓(depends
on starch
nitrationation)N N — [31] Guar gum Chestnut starch ↑ ↓/—(depends
on guar concentration)↑ ↑ [38] Guar gum Acorn starch ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ [40] Inulin Wheat starch ↑ ↑ ↑/—(depends
on inulin DP)↓/—(depends
on inulin DP)[27] Konjac glucomannan Corn starch ↑ ↑ ↑ — [34] Konjac glucomannan Potato starch — ↑ ↑ ↓ [35] Konjac glucomannan Maize starch/potato starch — — —/↑(depends
on starch origin)↓ [36] Mesona chinensis polysaccharide Waxy maize starch/normal maize starch ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ [44] Okra extract Wheat starch/corn starch ↑ ↑ N ↑(wheat starch)/ ↓(corn starch) [43] Pectin/Inulin Potato starch ↑(pectin)/↓(inulin) ↑(pectin)/↑(inulin) ↑(pectin)/ —(inulin) ↓(pectin)/ —(inulin) [37] Sodium alginate Wheat starch ↑ N N ↓ [48] Tamarind Waxy/normal/high amylose corn starch N ↑ N ↑ [30] Yellow mustard mucilage Wheat starch/rice starch N — N ↑ [42] Animal Chitosan Maize starch ↑ ↑ ↑ ↓ [45] Microbial Xanthan Rice starch — — — ↓ [50] Multiple types β-glucans (curdlan, oat, barley and yeast β-glucans) Rice starch — — — ↓ [26] Guar gum/xanthan Tapioca starch ↑(guar) —(guar)/
↑(xanthan)— ↓ [51] Guar gum /CMC/Xanthan gum/tapioca extracts/tamarind seeds extracts Waxy rice starch/non-waxy rice starch — — — — [8] Konjac glucomannan/ CMC/chitosan Corn starch — —(konjac glucomannan, CMC)/↑(chitosan) — ↓(konjac glucomannan)/ ↑(CMC)/ —(chitosan) [46] Xanthan gum/Guar gum Yam starch — — — — [41] To, Tp, and Tc represent the gelatinization beginning, highest, and end temperatures, respectively. The ΔH represents enthalpy (the heat energy required by the test starch during the endothermic transition). The arrow (↑, ↓, —) represents an increase/decrease or a no change in temperature, respectively. The letter "N" represents the corresponding parameters not mentioned in the research. Table 2.
Effect of non-starch polysaccharides on starch gelatinization.
-
Type of non-starch polysaccharide Type of starch Some findings and conclusions Reference Psyllium (Gluten-free bread) Rice PSY reduces the chickpea flour-based bread glycemic response. [86] Gellan gum Rice Gellan gum reduced starch digestion and GI index. [87] Guar gum/sodium alginate xanthan gum/ Waxy rice The NSPs decreased the starch digestion rate. [88] Xanthan gum Rice Xanthan increased the glycemic index of the mixture. [89] Nano-cellulose Corn Higher nano-cellulose amounts slow down the initial glucose release rates. [90] Carboxymethyl cellulose/ xanthan gum/ guar gum Fried-natural fermented
rice noodles (rice)NSPs improve digestion. [72] psyllium Rice /cassava The psyllium decreased starch digestion. [91] Nano-fibrillated cellulose Corn NSPs reduced the level of hydrolysis glucose. [92] CMC/ guar/ xanthan gum High amylose rice NSPs decreased the surge of blood glucose. [93] Pectin Corn Pectin hindered starch digestion. [62] Chitosan Waxy maize Chitosan modification altered starch digestion. [94] Guar/ xanthan gum/ sodium alginate Wheat/buckwheat The hydrocolloid's addition reduced starch hydrolysis. [95] Xanthan/ guar gum/ pectin/ konjac-glucomannan Gelatinized potato NSPs hindered starch digestion and the extent perform on blood glucose depends highly on the types. [96] Locust bean/ guar/ fenugreek/ xanthan/
flaxseed gumCorn The XG showed a prominent effect in interfering with glucose. [97] Extracted malva nut gum Wheat bread (wheat) MNG-containing breads showed low glucose levels. [98] Table 3.
Effect of non-starch polysaccharides on starch digestibility.
-
Type of non-starch polysaccharide Type of starch RDS SDS RS C∞ (equilibrium concentration) k (kinetic constant) Reference Xanthan Rice ↓ ↑ — ↓ ↓ [78] Creeping fig seed polysaccharide Potato ↓ ↓ ↑ ↓ ↓ [79] Pectin Corn ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ [80] Arabic/ xanthan/ guar gum Corn ↓ ↓/↑(xanthan) ↑/↓(xanthan) N N [7] Guar gum Rice ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ [8] Chitosan/ xanthan/
sodium alginateWet sweet potato ↑(chitosan)/
↓(xanthan, SA)↑(chitosan, xanthan)/
↓(SA)↓(chitosan)/
↑(xanthan, SA)N N [81] Guar gum Lotus seed ↓ — ↑ N N [68] Pullulan/pectin Fried potato ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ [60] Konjac glucomannan Quinoa/maize ↓ ↓ ↑ N N [82] Chitosan Lotus seed ↓ ↑ — N N [68] Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC)/ carboxymethyl cellulose/ xanthan gum (XG)/ apple pectin (AP) gluten-free potato steamed bread(potato starch) ↓ ↓ ↑ ↓ ↓ [83] Pectin Corn ↓ ↑ ↑ N N [84] Cellulose nanocrystals Corn /pea /potato ↓ ↓ ↑ N N [85] Pullulan Rice ↓ ↑ ↑ ↓ ↓ [10] High methoxylated pectin/ guar gum/ carboxymethyl cellulose/ xanthan gum/ hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose Corn /potato ↑/↓(guar gum in terms of potatoes starch) ↓(corn starch)/ —(potatoes starch) —/↓(xanthan and HPMC in terms of corn starch)/
↑(potatoes starch exception of HPMC)↑(corn starch by adding CMC, potatoes starch by adding guar gum and pectin)/ ↓(xanthan in corn starch) N [11] The arrow (↑, ↓, —) represents an increase/decrease or a no change in temperature, respectively. The letter "N" represents the corresponding parameters not mentioned in the research. Table 4.
Non-starch polysaccharides influence on RDS, SDS, RS and digestion parameters.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(4)