-
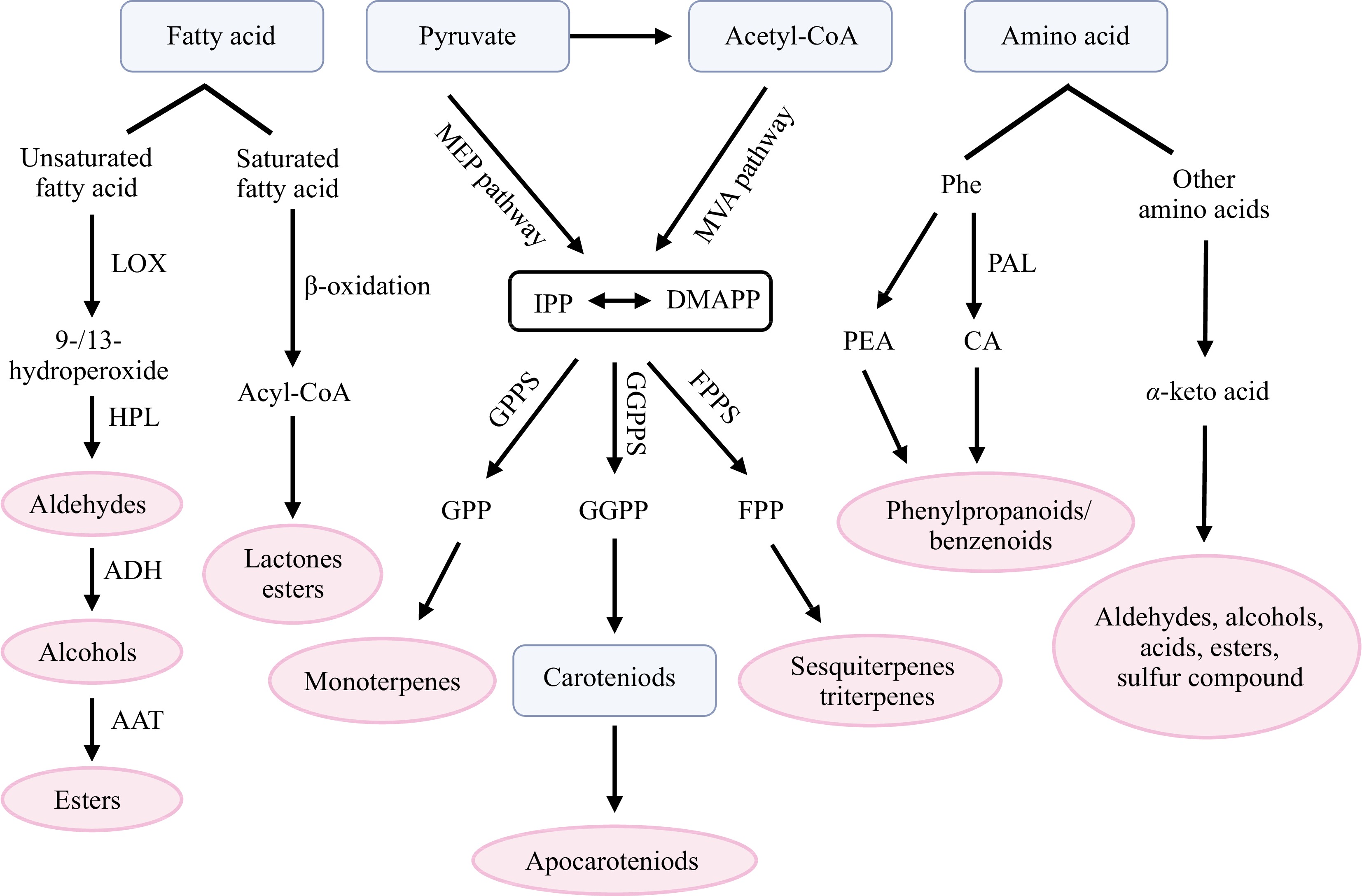
Figure 1.
Major biosynthetic pathways of aroma compounds in plants. AAT, alcohol acyltransferase; Acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme-A; ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; CA, cinnamic acid; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; FPP, farnesyl diphosphate; FPPS, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase; GGPP, geranylgeranyl diphosphate; GGPPS, Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase; GPP, geranyl diphosphate; GPPS, geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; HPL, hydroperoxide lyase; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; LOX, lipoxygenase; MEP, methylerythritol 4-phosphate; MVA, mevalonate; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; PEA, phenylethylamine; Phe, phenylalanine.
-
Genes Aroma compounds Species References BADH2 2-AP Rice, sorghum, maize, millet, soybean, cucumber, mung bean, pandan [54,56−62] SlCCD1A Carotenoid-derived volatiles (6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, geranylacetone, α-ionone, β-ionone) Tomato [81] TomLoxC Fatty acids-derived C5 and C6 volatiles and apocarotenoid
(1-penten-3-ol, 1-penten-3-one, geranial, etc.)Tomato [97,98] LiTPS2 Monoterpenoids (linalool, (E)-β-ocimene, trans-nerolidol) Lilium [87] CsTPS1 Valencene Sweet orange [89] RhNUDX1 Geraniol Rose [94] Table 1.
Functional genes in the synthesis of aroma compounds mentioned.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(1)