-
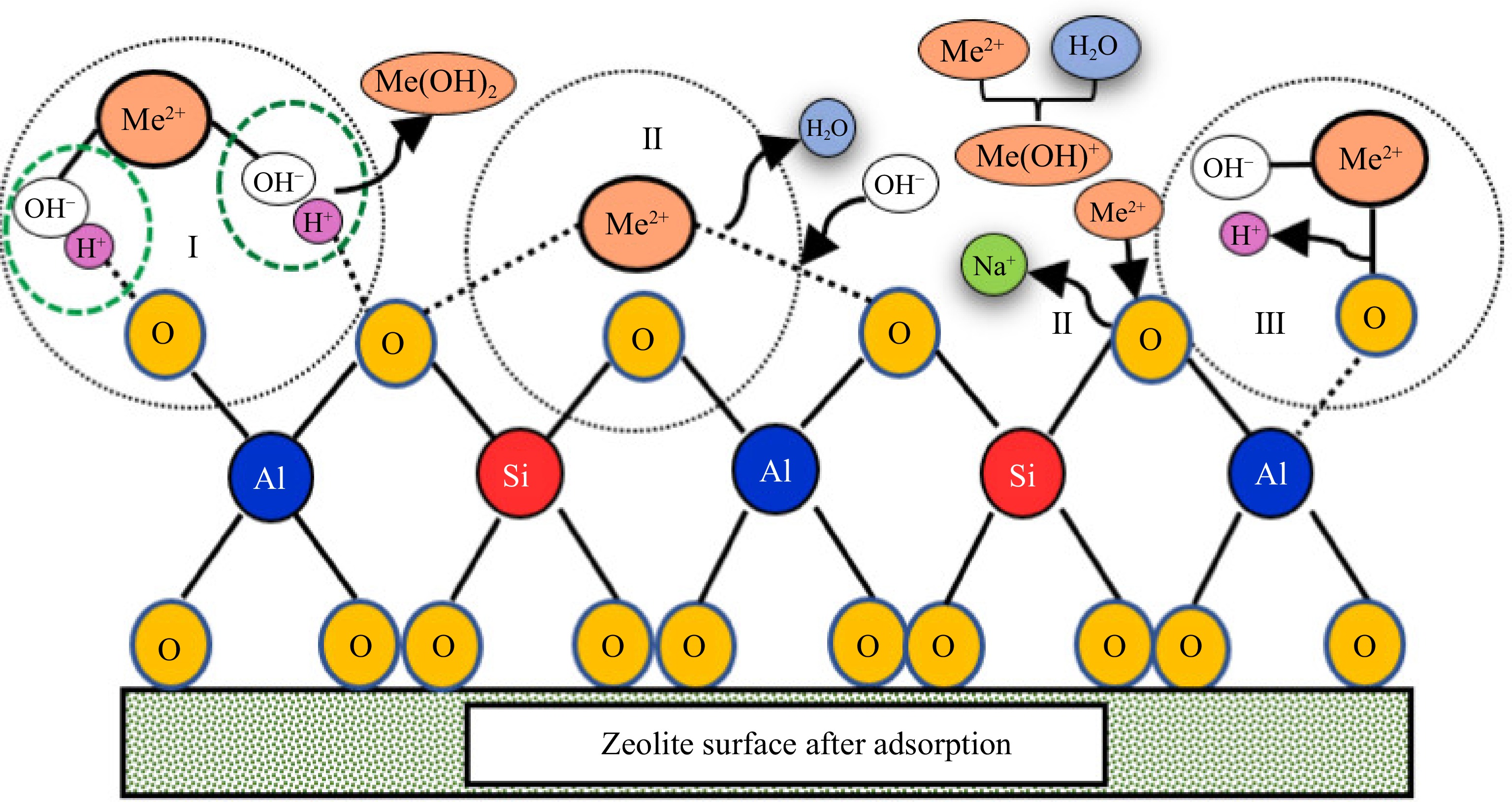
Figure 1.
Mechanisms for heavy metals by precipitation (I), ion exchange (II) and surface complexation (III)[60].
-
Zeolite modification technique Proceed Effective Ion exchange Determined ions are delivered to the zeolite surface through ion exchange processes Enhances the selectivity of the material towards specific ions or molecules Surface functionalization Adding functional groups to the surface Increases the material's affinity for specific pollutants or molecules, making it more effective in adsorption or catalytic reactions Chemical treatment Zeolites are treated with acids, bases or other chemicals to change their surface properties or expand their porous structure. Increase the adsorption capacity or interaction of the material with various substances, including light treatment, silanization, grafting Impregnatio Additional materials are introduced or impregnated onto the zeolite surface Enhances the properties of modified materials or provides additional functions. Nanostructure Create nano-sized particles or structures from zeolite Amplify their surface area, thereby enhancing their performance in various applications Mixture formation Zeolite is combined with different materials, such as polymers or nanoparticles, leading to the development of composite materials with complex properties Improve the adsorption capacity of the material Steam treatment and calcination Steam treatment can change the surface properties of zeolite. The calcination process can remove organic matter and regenerate the zeolite structure. Improve the adsorption capacity of the material. Table 1.
Some zeolite modification techniques.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(1)