-
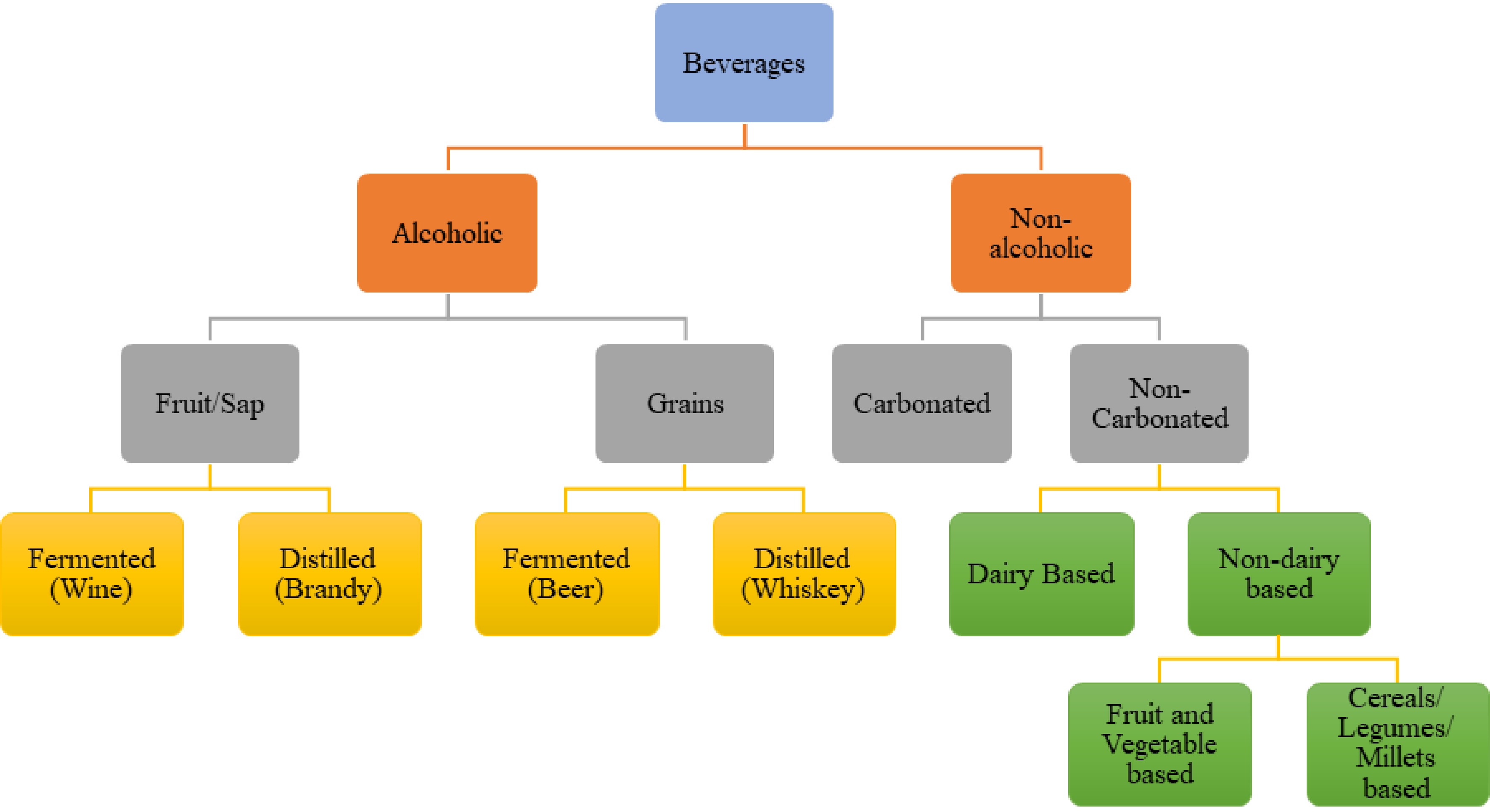
Figure 1.
Basic classification of beverages.
-
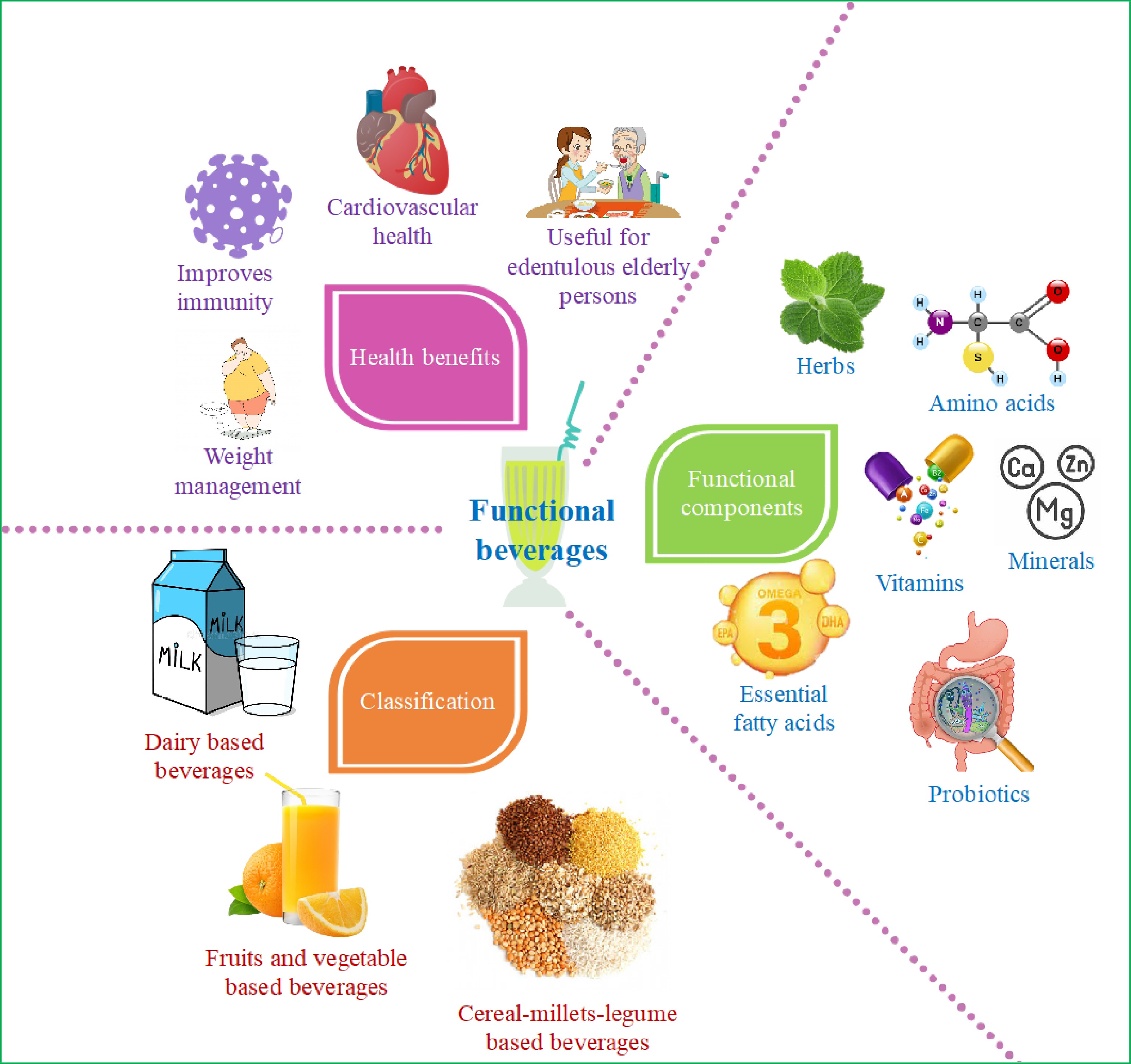
Figure 2.
Classification, functional components and health benefits of functional beverages.
-
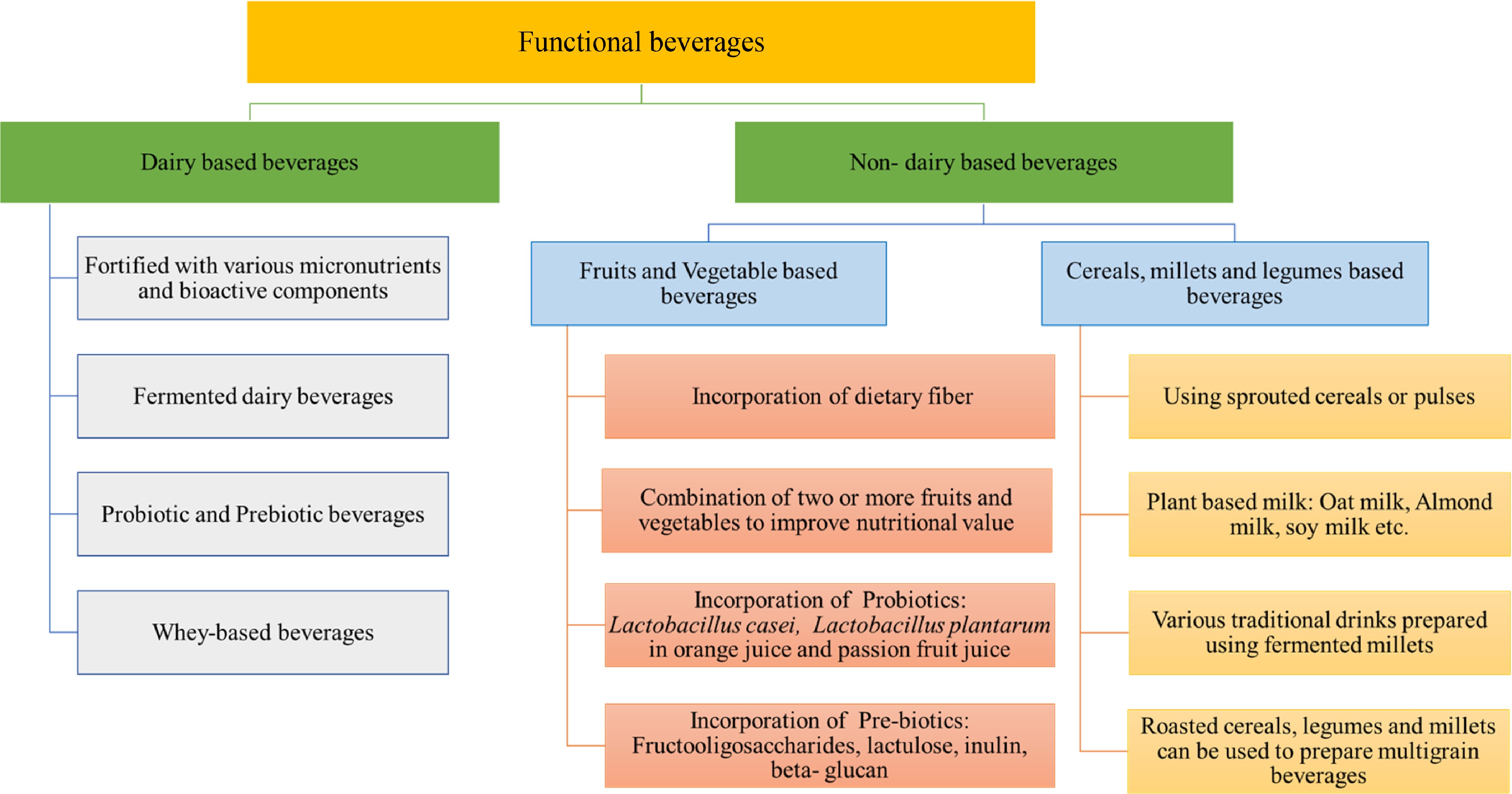
Figure 3.
Schematic flowsheet for dairy and non-dairy functional beverages.
-
Beverage type Description Reference Dairy-based Whey protein-based beverage • Whey protein isolate was used for the preparation of the beverage mix.
• Additional antioxidant components (polyphenols from marjoram extract, astaxanthin, and vitamins) were incorporated into the feed.
• Spray drying was carried out to get instant beverage powder.[50] Kefir powder • Fermented milk product
• Kefir grains are used for fermentation.
• Spray drying was carried out using skim milk powder/ whey permeate/ maltodextrin as carrier agent.[51] Probiotic pineapple lassi powder • Freeze drying was used to develop the product.
• Bifidobacterium bifidum was used as probiotic culture.
• Probiotic curd was blended with pasteurized pineapple juice along with addition of sugar, maltodextrin and CMC (Carboxymethyl cellulose).[52] β-glucan fortified milk powder • β-glucan is a soluble dietary fibre.
• β-glucan in liquid milk causes instability.
• Spray drying technique was used to formulate the beverage mix.[53] Fruits and vegetable-based White dragon fruit juice powder • Dragon fruit is rich in antioxidants and helps lowering the blood cholesterol.
• Spray drying technique was employed using maltodextrin as wall material.
• RSM was used for process optimization.[54] Sugarcane juice powder • Sugarcane juice is used for treatment of jaundice and health issues related to liver.
• Vacuum evaporation of sugarcane juice was done to achieve 30°Brix.
• Maltodextrin was added to aid in spray drying.[55] Beetroot extract-based
beverage powders• Beetroot, quince fruit and cinnamon extracts were used (75:24:1).
• Foam-mat freeze drying (FMFD) and foam-mat hot air-drying (FMHD) methods were used.
• 3% albumin powder and 20% of maltodextrin were used for foam preparation.
• Beverage prepared with FMFD powders had more overall acceptability.[56] Mix fruit and vegetable instant drink powder • Red spinach, red bean, guava and beetroot were used.
• Foam mat drying technique was used.
• Mix juice was rich in iron content.[57] Cereals-millets-legume based Millets based instant health mix
(millets : legumes - 3:1)• Millets used: Ragi, sorghum, bajra
• Legumes used: green gram
• Malting of all the grains followed by extrusion of malted flour and then grinding
• 1% probiotic culture of Lactobacillus rhamnosus[58] Quinoa based fermented probiotic beverage mix • Raw and roasted quinoa grains were fermented for 6 h and 9 h respectively
• Fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum
• Reduction in phytate content
• Fruit flavours were used to improve the acceptability[59] Pearl millet-based beverage powder • Two varieties of pearl millet were used
• Raw and malted pearl millet flour followed by extrusion, were used individually and in combinations also.
• Improved protein and starch digestibility[60] Black rice based instant beverage mix • Burma black rice was combined with germinated lentil flour, sweet potato and mulberry flour.
• Black rice was soaked for 30 min and then steamed (50 min) and dried to prepare flour.
• Improved nutritional characteristics.[61] Chickpea based enzyme treated
beverage powder• Raw and extruded chickpea flours treated with alcalase and alpha-amylase sequentially.
• Thermo-extrusion followed by enzymatic catalysis improves the nutritional profile.
• Protein digestibility and protein digestibility corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) was improved.[62] Sattu mix (multigrain) • Canadian peas, maize, chickpea, wheat, barley and oats were used, to prepare two different formulations.
• Chickpea based traditional sattu was used as control.
• Roasting was carried out as preliminary processing of grains.
• Combination of cereals and legumes improved the nutritional quality of the product.[63] Table 1.
Recent studies on instant beverage mix based on dairy, fruits and vegetables and cereals, millets and legumes.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)