-
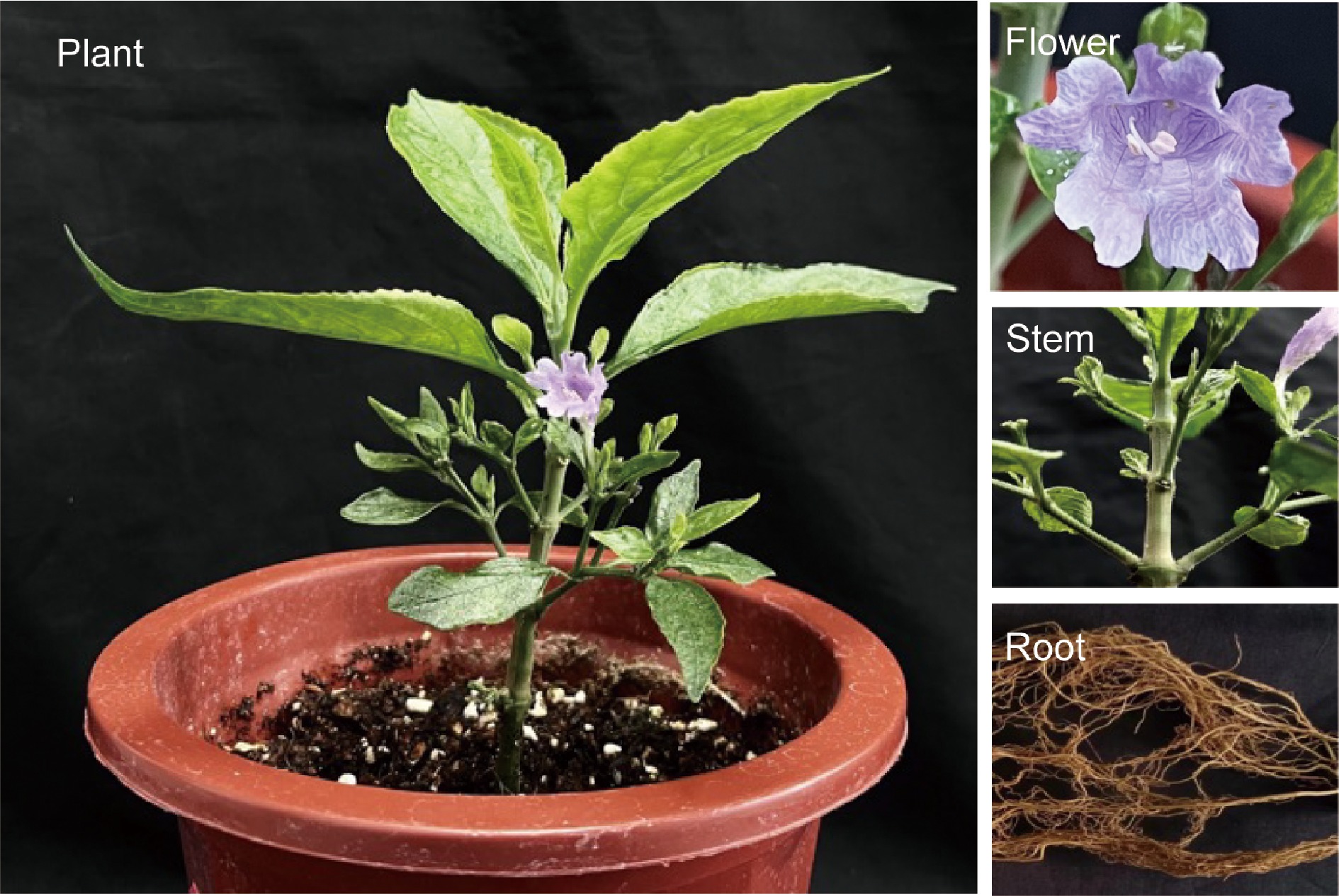

Figure 1.
Baphicacanthus cusia (Nees) Bremek.
-
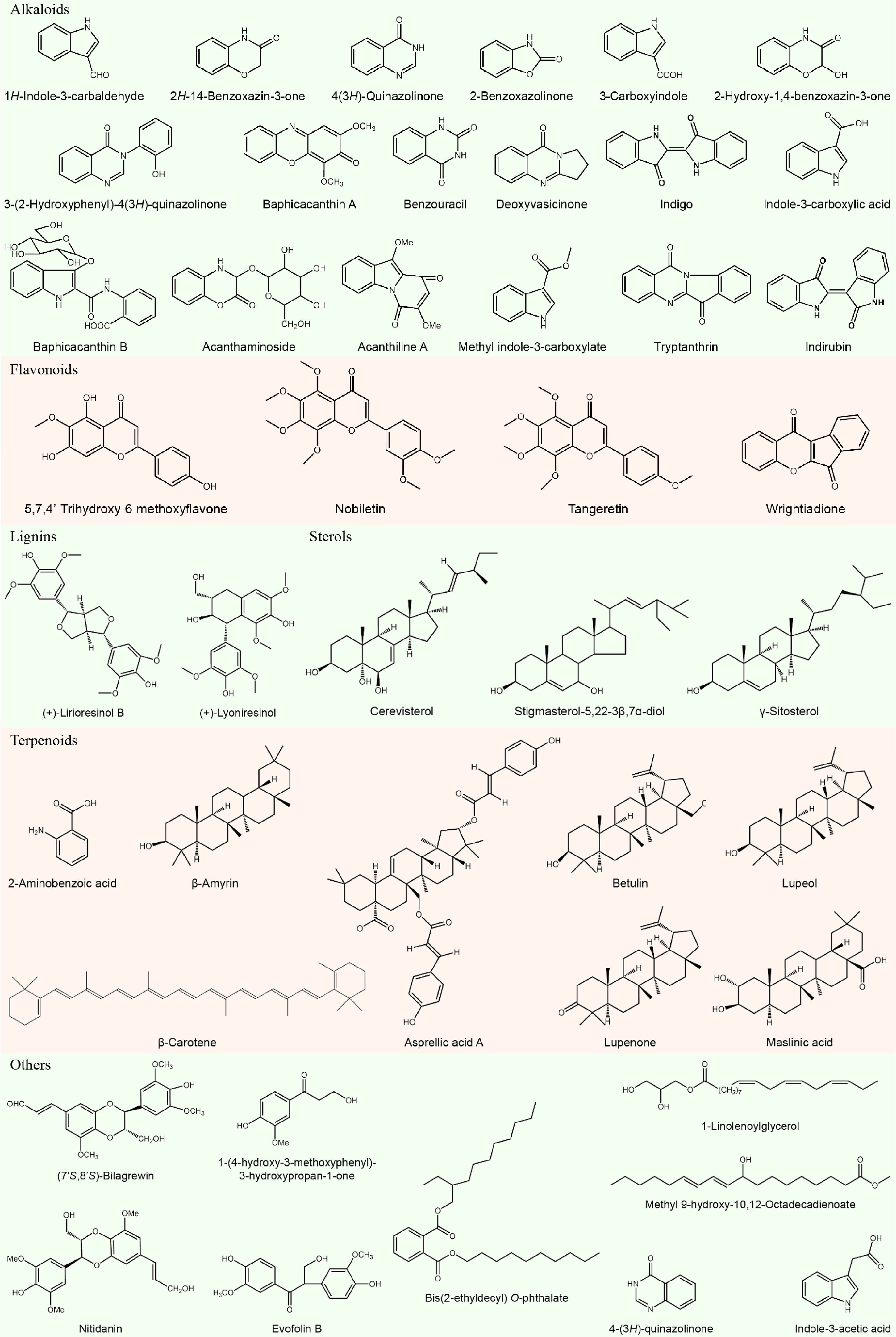
Figure 2.
Chemical compositions of Baphicacanthus cusia (Nees) Bremek.
-
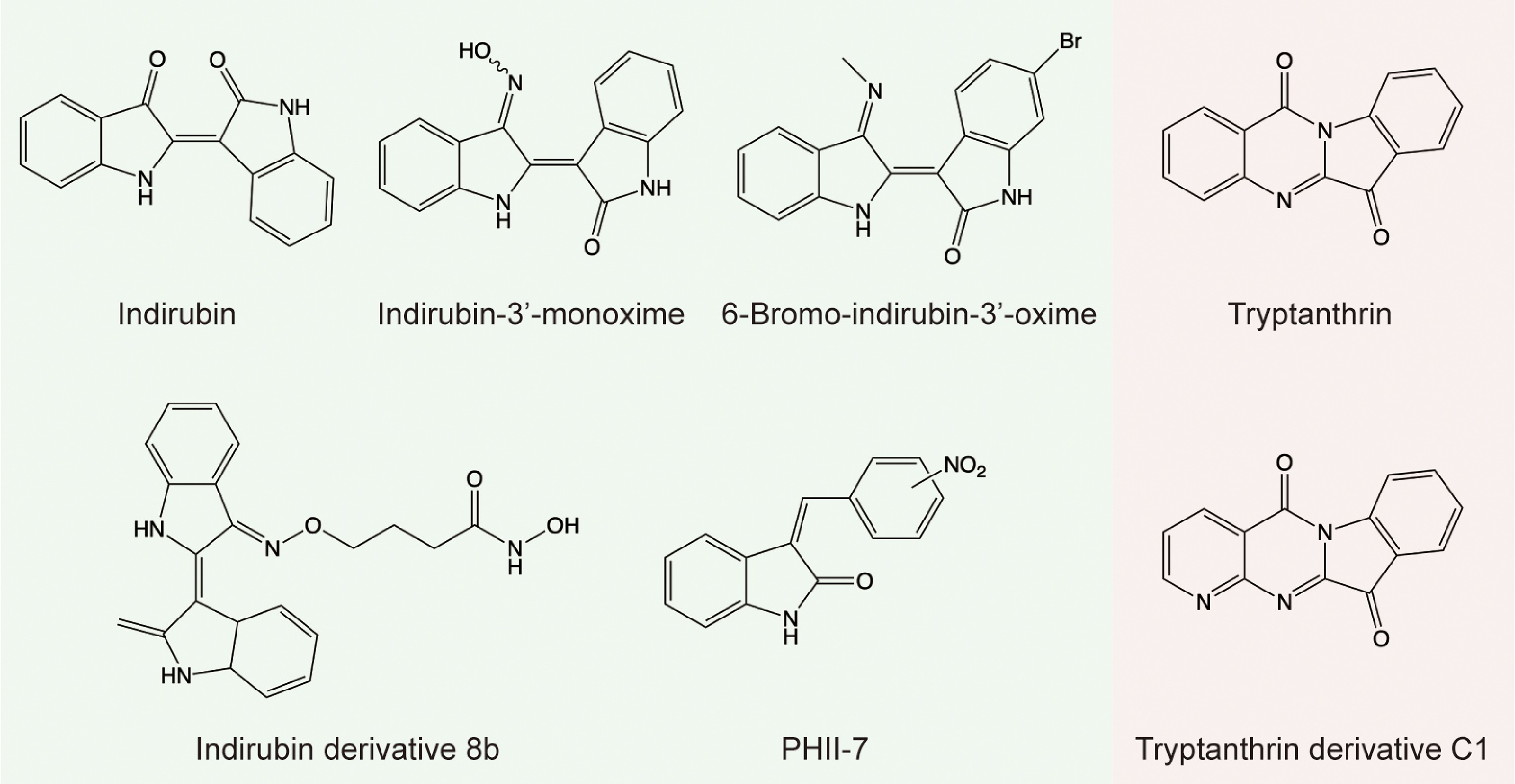
Figure 3.
Structures of indirubin and tryptanthrin and their derivatives.
-
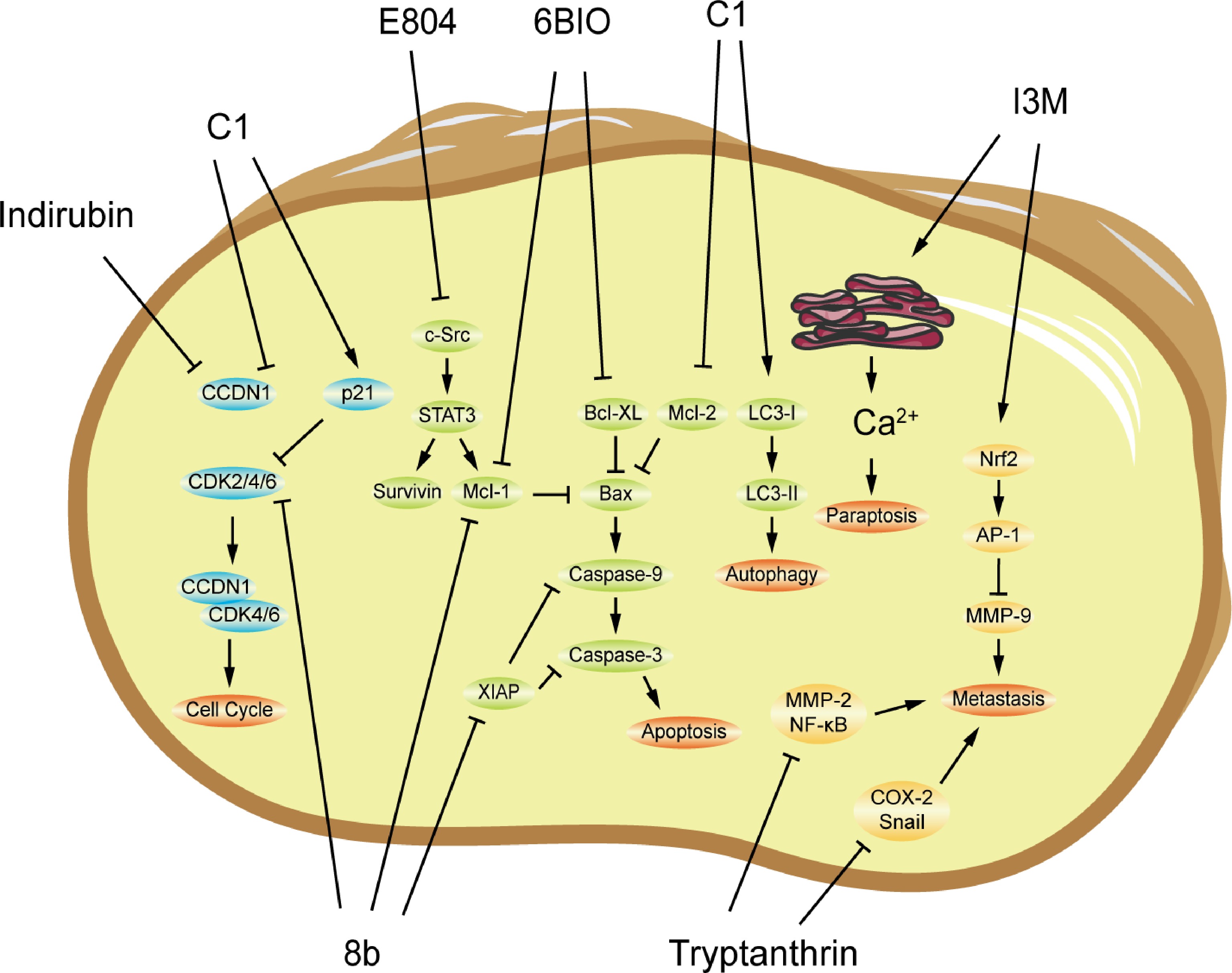
Figure 4.
The possible mechanisms of antitumor activity of indirubin and tryptanthrin and their derivatives. 8b, 6BIO E804, and I3M are indirubin derivatives; and C1 is tryptanthrin derivative. AP-1, activator protein-1; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-xL, B-cell lymphoma extra-large; CCND, cyclin D; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; IL, interleukin; LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; Mcl-1, mantle cell lymphoma 1; MMP, matrix metalloprotein; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ B; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; Src, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; and XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis.
-
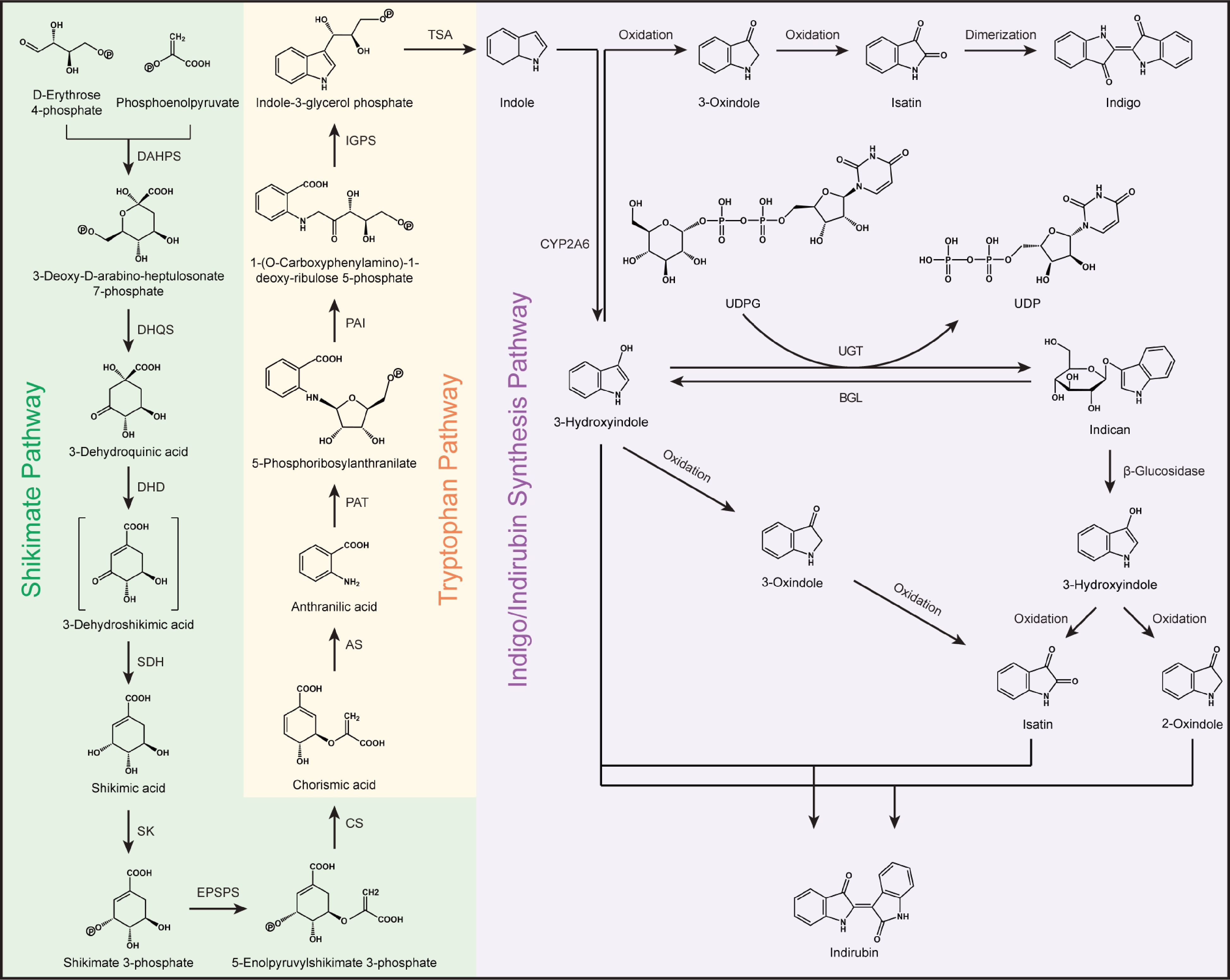
Figure 5.
Possible metabolic pathways of indigo and indirubin in B. cusia. AS, anthranilate synthase; BGL, β-glucosidase; CS, chorismate acid; CYP2A6, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; DAHPS, 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-Phosphate synthase; DHD, 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase; DHQS, 3-dehydroquinate synthase; EPSPS, 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase; IGPS, indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase; PAI, phosphoribosyl anthranilate isomerase; PAT, phosphoribosyl anthranilate transferase; SDH, shikimate dehydrogenase; SK, shikimate kinase; TSA, tryptophan synthase alpha-subunit; UDPG, uridine diphosphate glucose; UDP, uridine diphosphate; and UGT, uridine diphosphate glucuronide transferase.
-
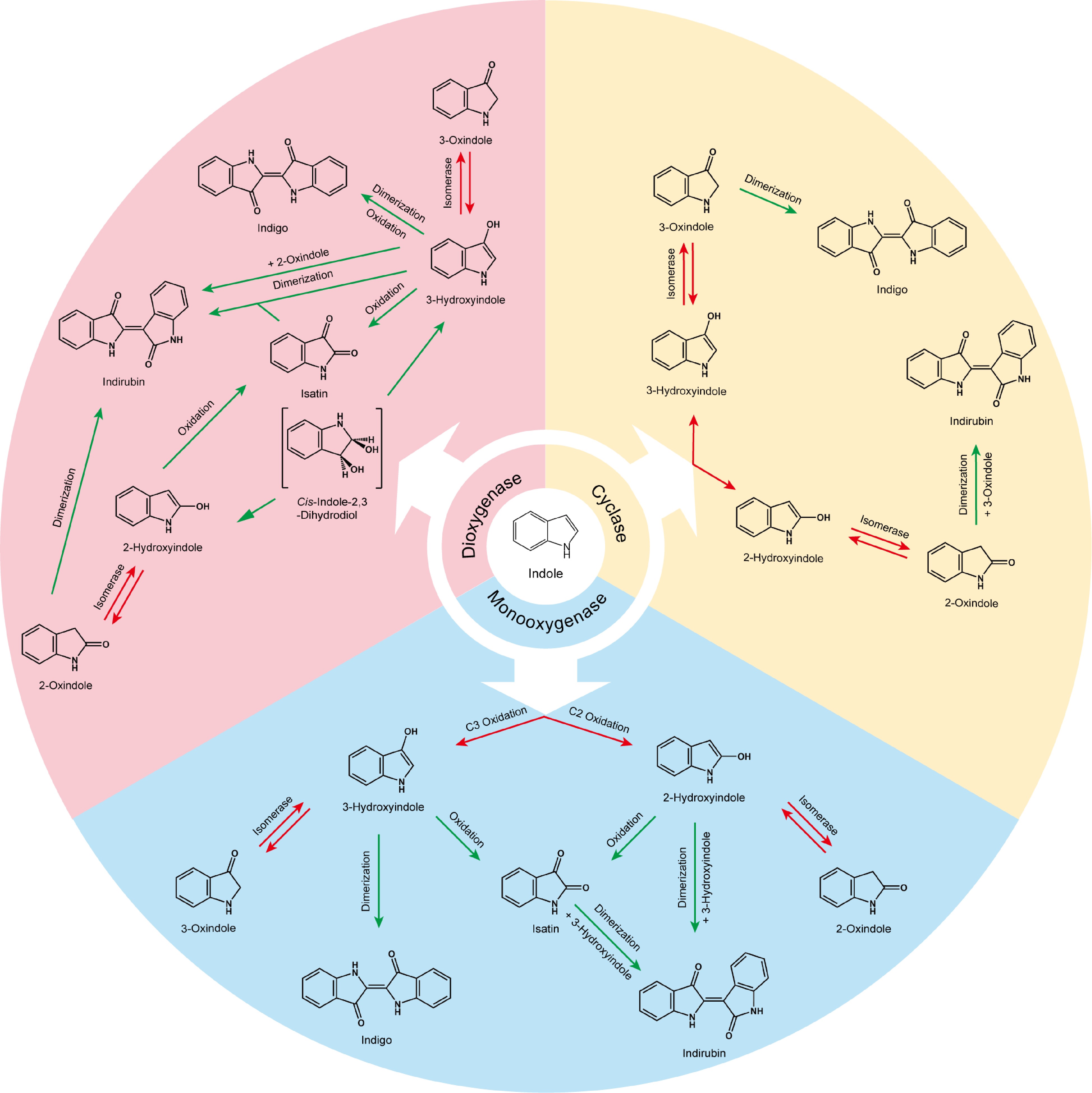
Figure 6.
The pathways of biosynthetic production of indigo and indirubin from indole. Three strategies can be applied for biosynthesis. Monooxygenase oxidizes indole into indole oxide, eventually producing indigo and indirubin; dioxygenase oxidizes indole into cis-indole-2,3-dihydrodiol, then generating indigo and indirubin; and cyclase catalyzes the hydroxylation of indole to produce indigo or indirubin. The red arrow indicates enzymatic reaction; the green arrow indicates spontaneous process.
-
Prescription Formula Chinese ancient books Baidai Powder Bark of Phellodendron chinense, 2 qian (6 g); Leaves and/or stems of Baphicacanthus cusia, Polygonum tinctorium, Indigofera tinctoria or Isatis indigotica, 2 qian (6 g) Dongtian Aozhi Bijing Pill Calomel, 1.5 qian (4.5 g); Talcum, 1.5 qian (4.5 g);
Tubers of Arisaema erubescens, A. heterophyllum or A. amurense, 1 qian (3 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 5 fen (1.5 g)Puji Fang Biyu Tongshen Powder Bark of P. chinense, 5 qian (15 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 fen (0.3 g);
Camphor (Branches, stems, leaves and roots of Cinnamomum camphora), a modicum (~ 0.1 g)Puji Fang Chaihu Qingdai Decoction Roots of Bupleurum chinensie or B. scorzonerifolium, 5 fen (1.5 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 5 fen (1.5 g);
Rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus, 1 qian (3 g); Rhizomes of Ligusticum chuanxiong, 1 qian (3 g);
Pericarps of Citrus reticulata or its cultivated varieties, 8 fen (2.4 g);
Rhizomes of Coptis chinensis, C. deltoidei or C. teeta, 8 fen (2.4 g);
Fruits of Cardenia jasminoides, 8 fen (2.4 g);
Roots and rhizomes of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, G. inflata or G. glabra, 8 fen (2.4 g)Miscellaneous Diseases Chaya Niuhuang Qingdai Powder Gallstones of Bos taurus, 5 fen (1.5 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 5 fen (1.5 g);
Borax, 2 qian (6 g); Cinnabar, 1 qian (3 g);
Naturally deposited solids in healthy human urine, 2 fen (0.6 g);
Skeletal fossils of ancient mammals, 2 fen (0.6 g); Borneol, 3 fen (0.9 g)Yizong Jinjian Chunbi Biyu Powder Refined nitrokalite, 1 fen (0.3 g); Camphol, 1 qian (3 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 qian (3 g)General Records of Saints Daibai Powder Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 qian (3 g);
Bark of P. chinense, 2 qian (6 g); Borneol, 1 qian (3 g)Integrative Medicine Dermatology Daiehuang Powder Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 2 qian (6 g);
Bark of P. chinense, 2 qian (6 g); Bassanite, 2 liang (60 g);
Liuyi Power (Talcum : Roots of G. uralensis = 6 : 1), 24 qian (72 g)Drug dowry secret Daige Powder Shell of Meretrix meretrix or Cyclina sinensis, 10 liang (300 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 liang (30 g)Medical Theory Danggui Longhui Pill Roots of Angelica sinensis, 1 liang (30 g);
Roots and rhizomes of Gentiana scabra, G.triflora or G.manishurica, 1 liang (30 g);
Fruits of Gardenia jasminoides, 1 liang (30 g);
Rhizomes of C. chinensis, C. deltoidea or C. teeta, 1 liang (30 g);
Bark of Phellodendron chinense, 1 liang (30 g); Roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, 1 liang (30 g);
Roots and rhizomes of Rheum palmatum, R. tanguticum or R.officinale, 5 qian (15 g);
Concentrated dried juices of Aloe barbadensis or A.ferox, 5 qian (15 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 5 qian (15 g);
Roots of Aucklandia lappa, 1 fen (0.3 g);
Secretions from mature male sachets of Moschus berezovskii, M. sifanicus or M. Moschiferus,
5 fen (1.5 g)Danxi Xinfa Daihong Powder Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica;
Rhizomes of Coptis chinensis, C. deltoidei or C. teeta; Flowers of Carthamus tinctorius;
with each equal divisionFamous selection and sequel Daihuang Powder Bark of P. chinense, 1 liang (30 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 2 qian (6 g);
Rhizomes of Coptis chinensis, C. deltoidei or C. teeta, 1.5 qian (4.5 g);
Roots of A. dahurica or A. dahurica, 1.5 qian (4.5 g);
Roots of Paeonia lactiflora or P. veitchii, 1 qian (3 g); Tea, 1 qian (3 g);
Secretions from mature male sachets of M. berezovskii, M. sifanicus or M. Moschiferus,
2.5 fen (0.75 g)Continued name family selection Gualou Qingdai Pill Seeds of Trichosanthes kirilowii or T. rosthornii, 1 liang (30 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 3 qian (9 g)Danxi Xinfa Hezi Qingdai Pill Fruits of Terminalia chebula;
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica;
Seeds of Armeniaca vulgaris, A. vulgaris, A. sibirica or A. mandshurica;
Egg-banding of Notarchus leachii cirrosus; Rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus;
Seeds of T. skirilowii or T. rosthornii; Rhizoma Pinelliae Fermentata;
with each equal divisionMiscellaneous Disease Origin Rhinoceros Candle Hupo Biyu Powder Talcum, 6 liang (180 g); Roots and rhizomes of G. uralensis, G. inflata or G. glabra, 1 liang (30 g);
Amber, 5 qian (15 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 8 fen (2.4 g)Yizong Jinjian Jiujing Pill Above ground part of Mentha haplocalyx, 3 qian (9 g);
Larvae of Bombyx mori infected or artificially inoculated with Beauveria bassiαna, 3 qian (9 g);
Roots of Saposhnikovia divaricate, 3 qian (9 g); Tubers of Gastrodia elata, 3 qian (9 g);
Buthus martensii, 3 qian (9 g); Roots and rhizomes of G. uralensis, G. inflata or G. glabra, 3 qian (9 g);
Dried exudate from stems of Bambusa tertilis or Schizostachyum chinense, 3 qian (9 g);
Stems and branches containing hooks from Uncaria rhynchophylla, U. macrophylla, U. hirsute, U. sinensis or U. sessilifructus, 3 qian (9 g);
Mixture of prepared tubers of A. erubescens, A. heterophyllum or A. amurense and bile from Bos spp., Ovis spp. or Sus spp., or fermented mixture of tuber power of A. erubescens, A. heterophyllum or A. amurense and bile from Bos spp., Ovis spp. or Sus spp., 4 qian (12 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria, or I. indigotica, 4 qian (12 g);
Tubers of A. erubescens, A. heterophyllum or A. amurense, 4 qian (12 g);
Tubers of Typhonium giganteum, 2 qian (6 g); Cinnabar, 2 qian (6 g); Amber, 2 qian (6 g);
Secretions from mature male sachets of M. berezovskii, M. sifanicus or M. Moschiferus, 8 fen (2.4 g);
Gallstones of Bos taurus, 5 fen (1.5 g); Pearl, 5 fen (1.5 g)National Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescription Collection Kexue Recipe Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 2qian (6 g);
Seeds of T. skirilowii or T. rosthornii, 3 qian (9 g);
Egg-banding of Notarchus leachii cirrosu, 3 qian (9 g);
Fruits of G. jasminoides, 3 qian (9 g); Fruits of Terminalia chebula, 2 qian (6 g)Danxi heart method Lijing Pill Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 qian (3 g);
Calomel, 1 qian (3 g); Power of seeds of Ipomoea nil or I. biflora, 5 qian (15 g);
Dried exudate from stems of B. tertilis or S. chinense, 2 qian (6 g)Children's medicine certificate straight recipe Qingdai Shigao Decoction Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1.5 qian (4.5 g);
Fresh roots of Rehmannia glutinosa, 2 liang (60 g); Gypsum, 8 qian (24 g);
Rhizome of Cimicifuga heracleifolia, C. dahurica or C. foetida, 6 fen (1.8 g);
Roots of S. baicalensis, 2 qian (6 g); Processing fruits of Gardenia jasminoides, 3 qian (9 g);
Allium fistulosum, 3 piecesRedefinition of popular typhoid theory Yangdu Neixiao Powder Secretions from mature male sachets of M. berezovskii, M. sifanicus or M. Moschiferus, 2 qian (6 g);
Borneol, 2 qian (6 g);
Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 2 qian (6 g);
Tubers of Bletilla striata, 3 qian (9 g);
Tubers of A. erubescens, A. heterophyllum or A. amurense, 3 qian (9 g);
Prepared scales of Manis pentadactyla with Rhizomes of Curcuma longa, 3 qian (9 g);
Camphor (Branches, stems, leaves and roots of Cinnamomum camphora), 3 qian (9 g);
Verdigris, 3 qian (9 g); Chalcanthite, 3 qian (9 g)Drug dowry secret Yanhou Biyu Powder Leaves and/or stems of B. cusia, P. tinctorium, I. tinctoria or I. indigotica, 1 liang (30 g);
Mirabilite, 1 liang (30 g); Pollen of Typha angustifolia, T. orientalis or similar plants, 1 liang (30 g);
Roots and rhizomes of G. uralensis, G. inflata or G. glabra, 1 liang (30 g)Yuyao Yuanfang Note: Li, fen, qian, and liang are units of measurement in ancient China. 1 liang = 10 qian = 100 fen = 1000 li = 30 g. Table 1.
Traditional Chinese Medicine prescriptions containing indigo naturalis (Qing-Dai).
Figures
(6)
Tables
(1)