-
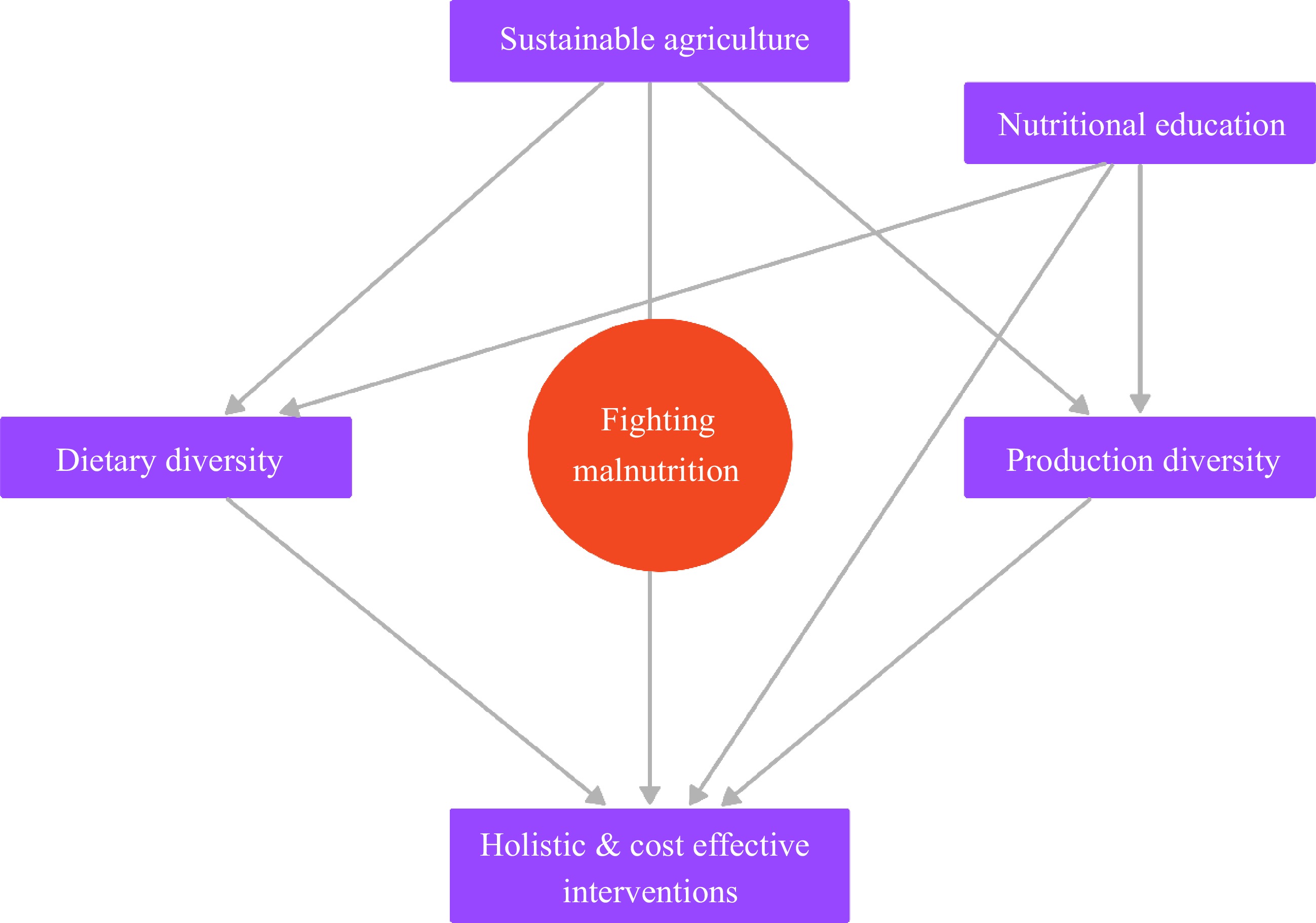
Figure 1.
Holistic and cost effective interventions to combat malnutrition.
-
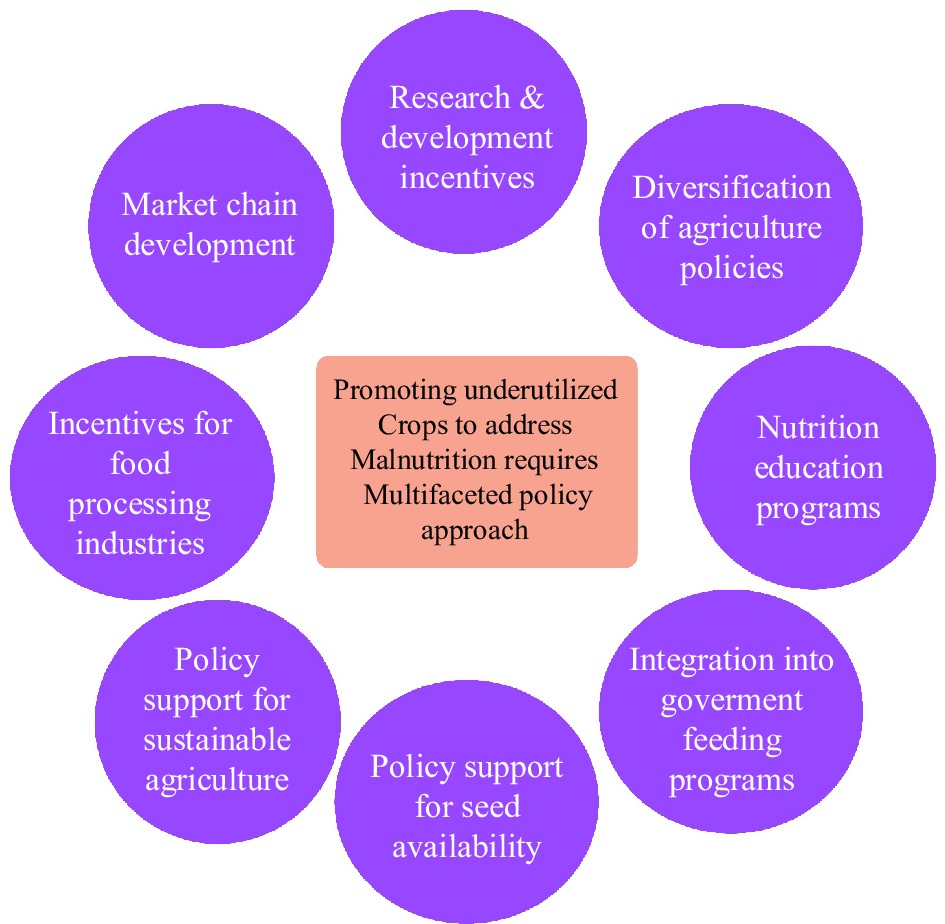
Figure 2.
Policy interventions for promoting underutilized crops.
-
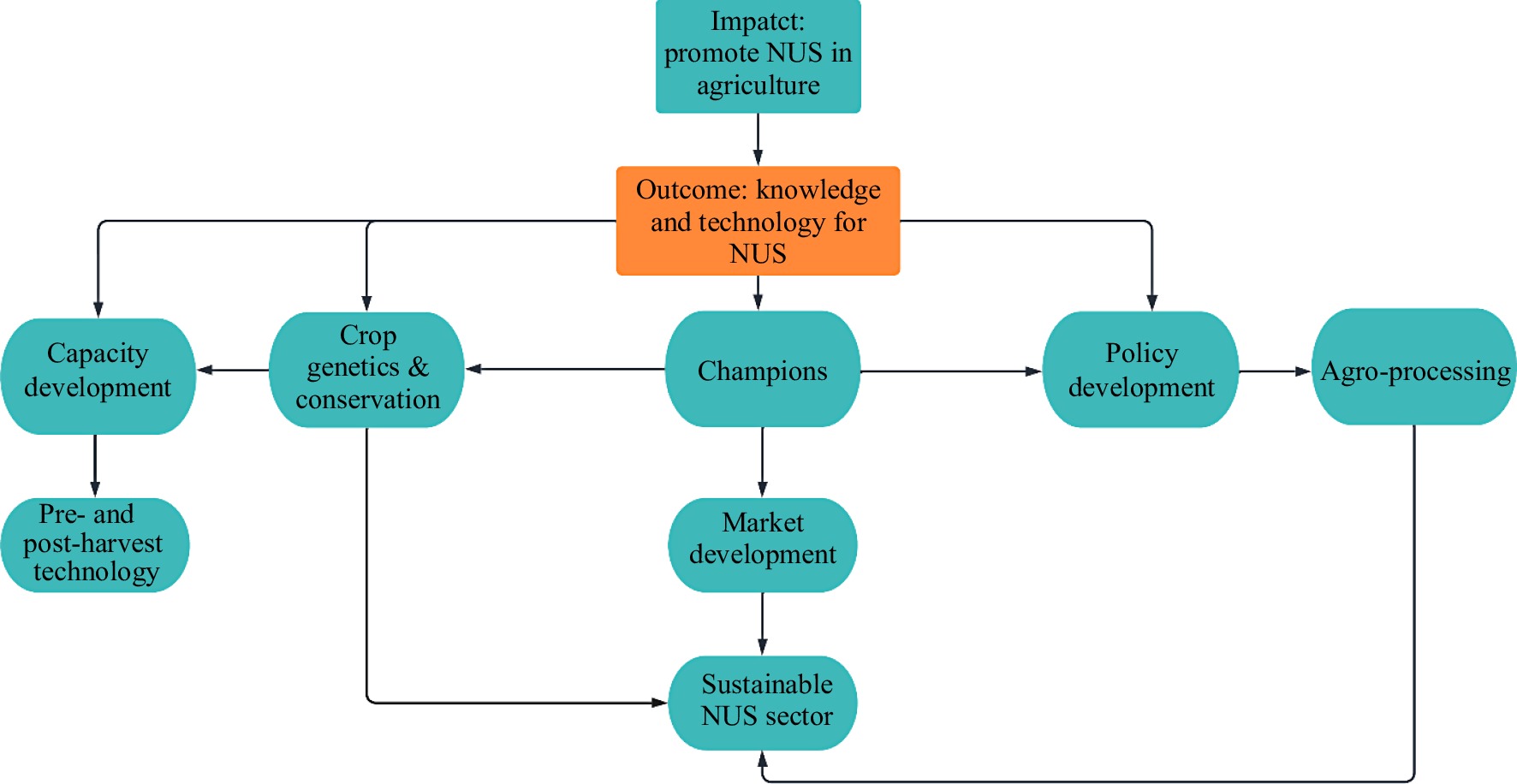
Figure 3.
Strategy for promoting underutilized crops.
-
Name Scientific name Property Nutrient composition Health benefits Ref. African yam bean Sphenostylis stenocarpa Legume High in protein, fiber, and antioxidants Improves blood sugar control, boost immunity, and reduce inflammation [18] Amaranth Amaranthus spp. Gluten-free pseudocereal Rich in essential amino acids, fiber, and micronutrients High levels of squalene, which may have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [19] Amur Cork Tree Phellodendron amurense Seeds from the amur cork tree Contains silymarin and antioxidants Potential liver-protective effects, may aid in digestion, and offer antioxidant properties [20] Bambara Groundnut Vigna subterranea Legume High in protein, fiber, and iron Improves blood sugar control, reduce cholesterol levels, and promote weight loss [21] Bamboo Rice Oryza rufipogon Rice variety derived from bamboo seeds High in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals Support digestion, provide energy, and offer essential nutrients [22] Bamboo Shoots Oryza rufipogon Edible shoots of bamboo plants Low in calories, high in dietary fiber Good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants [23] Baobab Adansonia digitata Fruit pulp from the baobab tree High in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants Immune-boosting and anti-inflammatory properties [24] Black Currants Ribes nigrum Berries from the black currant shrub High in vitamin C, anthocyanins, and antioxidants Strong antioxidant properties, may support immune function and cardiovascular health [25] Buckwheat Fagopyrum esculentum Gluten-free pseudocereal Contains rutin (a flavonoid), fiber, and protein Potential cardiovascular benefits due to rutin content [26] Camelina Camelina sativa Oil from camelina plant seeds Rich in omega-3 fatty acids Potential cardiovascular benefits [27] Camu Camu Myrciaria dubia Fruit from the camu camu tree Exceptionally high in vitamin C Immune-boosting, potential anti-inflammatory effects, and skin health benefits [28] Celeriac Apium graveolens var. rapaceum Root vegetable Good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals Supports digestive health, provides antioxidants, and may help regulate blood pressure [29] Chayote Sechium edule Green, wrinkled fruit Low in calories, high in fiber and antioxidants Promotes weight loss, support heart health, and provide immune-boosting properties [30] Chia Salvia hispanica Seeds from the chia plant High in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants Considered a superfood with various health benefits [31] Chokeberry Aronia melanocarpa Fruit from the chokeberry shrub High in anthocyanins, vitamins, and antioxidants Supports cardiovascular health, may have anti-inflammatory properties, and offer immune-boosting benefits [32] Cloudberry Rubus chamaemorus Berry from the cloudberry plant High in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants Supports immune function, skin health, and may have potential anti-inflammatory properties [33] Cowpea Vigna unguiculata Legume High in protein, fiber, and folate Improves blood sugar control, boost immunity, and promote healthy pregnancy [34] Elderberries Sambucus nigra Berries from the elderberry shrub High in anthocyanins, vitamins, and fiber Immune-boosting, potential antiviral properties, and relief from cold and flu symptoms [35] Fonio Digitaria exilis Small-grained cereal Good protein and fiber content Nutrient-rich and gaining recognition for its nutritional value [36] Ground Cherries Physalis peruviana Fruit from the ground cherry plant Good source of vitamin C, fiber, and beta-carotene Immune-boosting, potential anti-inflammatory properties, and improved eye health [37] Jerusalem Artichoke Helianthus tuberosus Tuber of the Jerusalem artichoke plant Contains inulin, a prebiotic fiber Promotes gut health and improved digestion [38] Jicama Pachyrhizus erosus Root vegetable Low in calories, high in fiber and vitamin C Supports digestion, promote weight loss, and provide immune-boosting benefits [39] Lacinato Kale Brassica oleracea var. sabellica Type of kale Rich in vitamins A, C, and K, and fiber Supports eye health, bone health, and digestion [40] Lotus Root Nelumbo nucifera Rhizome of the lotus plant Rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals May support digestion and overall health [41] Mesquite Genera Prosopis Leguminous tree or shrub High in protein, fiber, and minerals May help regulate blood sugar, support digestion, and have antioxidant properties [42] Millet Varied, e.g., Panicum miliaceum Pseudocereal High in fibre, magnesium, and iron Improves blood sugar control, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve digestion [43] Moringa Moringa oleifera Leaves and pods of the moringa tree Rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants Anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, and overall health-promoting properties [44] Nance Fruit Byrsonima crassifolia Fruit from the nance tree High in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants Immune-boosting, potential anti-inflammatory properties, and digestive health benefits [45] Nopal Cactus Opuntia spp. Pads of the prickly pear cactus Rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals Aid in weight management, support blood sugar control, and promote heart health [46] Perilla Seeds Perilla frutescens Seeds from the perilla plant Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants Support heart health, reduce inflammation, and offer potential benefits for allergies and asthma [47] Purple Carrots Daucus carota Variety of carrots with purple flesh High in anthocyanins, vitamins, and fiber Antioxidant properties, supports eye health, and may have anti-inflammatory effects [48] Quinoa Chenopodium quinoa Whole grain, complete protein source Rich in essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals Gluten-free and with antioxidant properties [49] Red Clover Trifolium pratense Legume plant Rich in isoflavones, vitamins, and minerals Supports hormonal balance, may relieve menopausal symptoms, and offer antioxidant properties [50] Red Spinach Amaranthus dubius Variety of spinach Rich in vitamins A, C, and K, and antioxidants Supports eye health, bone health, and offers potential anti-inflammatory benefits [51,52] Sea Buckthorn Hippophae rhamnoides Berries from the sea buckthorn shrub Rich in vitamins, omega fatty acids, and antioxidants Supports skin health, may improve heart health, and have immune-boosting properties [53] Sea Vegetables Varied, e.g., Saccharina japonica Edible seaweeds Rich in vitamins, minerals, and iodine Supports thyroid health, may have detoxifying properties, and provide essential nutrients [54] Sorghum Sorghum bicolor Whole grain, gluten-free Rich in antioxidants, low glycemic index Good option for individuals with diabetes and source of antioxidants [55] Soursop Annona muricata Fruit from the soursop tree Contains vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds May have potential anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties [56] Teff Eragrostis tef Gluten-free whole grain High in fiber and protein, source of iron and calcium Suitable for those with dietary restrictions and potentially beneficial for health [57] Tiger Nuts Cyperus esculentus Tubers from the tiger nut sedge Rich in fiber, healthy fats, and minerals May support digestion, provide energy, and have potential prebiotic effects [58] Watercress Nasturtium officinale Leafy green vegetable Excellent source of vitamin K, C, and antioxidants Supports bone health, may reduce cancer risk, and promotes skin health [59] Winged Beans Psophocarpus tetragonolobus Leguminous plant Rich in protein, fiber, and vitamins Good source of essential nutrients, supports digestion, and may help regulate blood sugar [60] Yacon Smallanthus sonchifolius Tuber of the yacon plant Contains fructooligosaccharides (FOS) and antioxidants Supports gut health, may aid in weight management, and improve blood sugar control [61] Table 1.
Health benefits of consuming underutilized crops.
-
Benefit Description Ref. Enhanced biodiversity Promotes agricultural diversity, preserving unique genetic resources [87] Nutritional diversity Offers a rich source of diverse nutrients for a balanced diet [70] Resilience to climate change Better adaptation to adverse weather, pests, and diseases [88] Economic opportunities Access to niche markets, potentially higher prices for specialty crops [89] Soil health improvement Balances soil nutrient levels, breaking up soil compaction, suppressing weeds, fixing nitrogen, and improving soil tilth [90] Cultural significance Preserves traditional farming practices and local heritage [91] Reduced input costs Lower requirements for fertilizers and pesticides [92,93] Sustainability Contributes to sustainable farming systems and ecological balance [94] Risk diversification Reduces economic risk by not relying on a single crop type [95] Market demand for novelty Meets consumer demand for new and unique food products [96] Water efficiency Some underutilized crops require less water, beneficial in areas with water scarcity [97] Pest and disease resistance Natural resistance to certain pests and diseases, reducing the need for pest control measures [98,99] Adaptability to marginal lands Suitable for growth in less fertile or challenging terrains, utilizing otherwise unproductive land [100] Local food security Contributes to local and regional food security by offering alternative food sources [101] Empowerment of smallholders Small-scale farmers can benefit from growing unique crops that are not viable for large-scale commercial farming [102,103] Improved community engagement Cultivating traditional or local crops can strengthen community ties and knowledge sharing [104,105] Agro-tourism potential Unique crops can attract tourists, offering additional income through farm visits and local markets [106] Heritage conservation Helps in preserving heirloom varieties and traditional farming methods, enriching cultural heritage [107] Alternative income sources Opportunities to sell crop by-products or engage in value-added processing [89] Learning and Innovation Encourages farmers to learn new agricultural techniques and innovate in crop management [108] Table 2.
Analysis of benefits to farmers from cultivation of underutilized crop species.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(2)