-
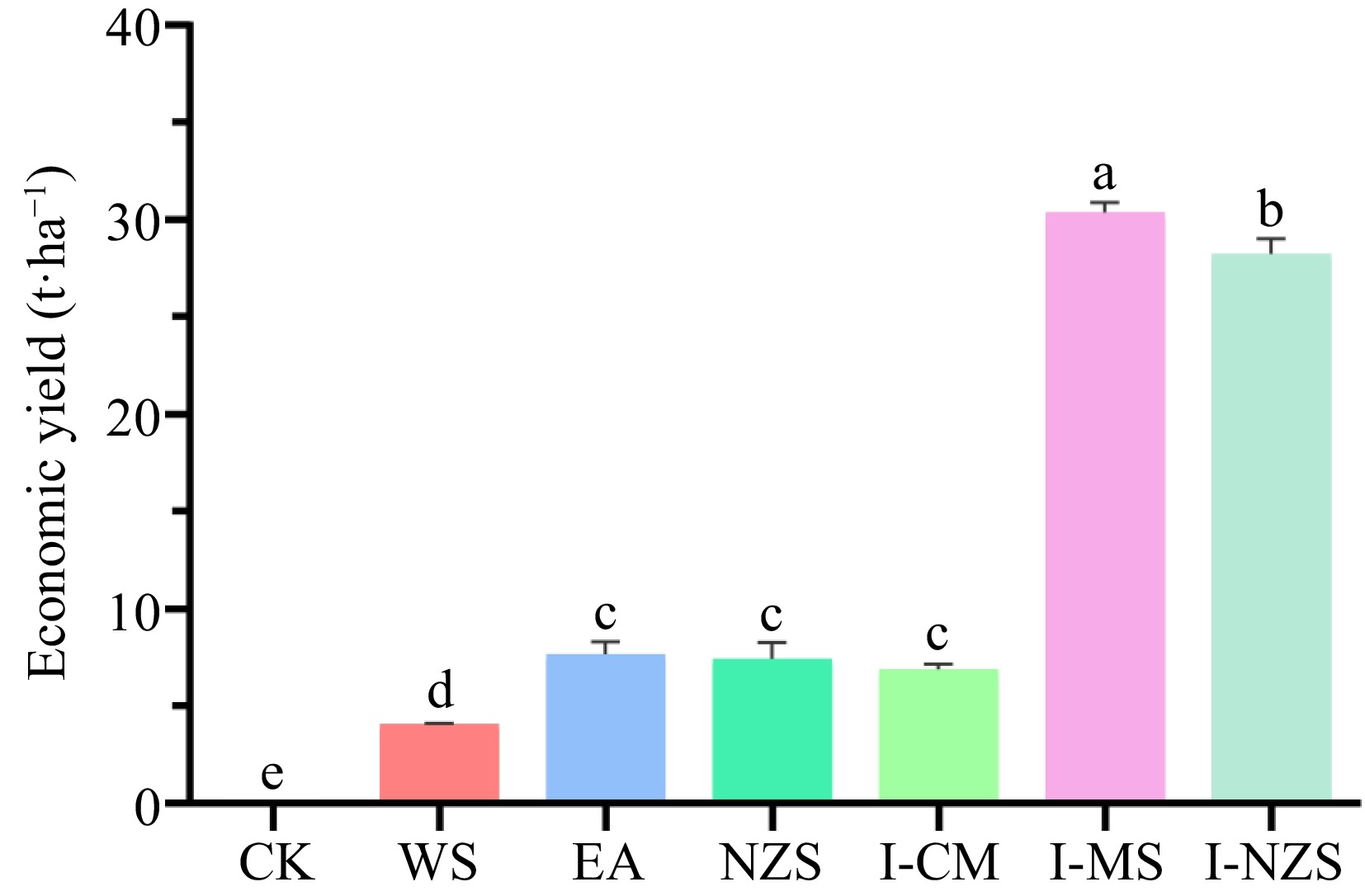
Figure 1.
Economic yield of summer catch leafy vegetables. CK, bare cultivated land as a control; WS, water spinach; EA, edible amaranth; NZS, newly planted New Zealand spinach; I-CM, previously intercropped chinese mallow; I-MS, previously intercropped malabar spinach; I-NZS, previously intercropped New Zealand spinach. The significant difference confidence level is p < 0.05.
-
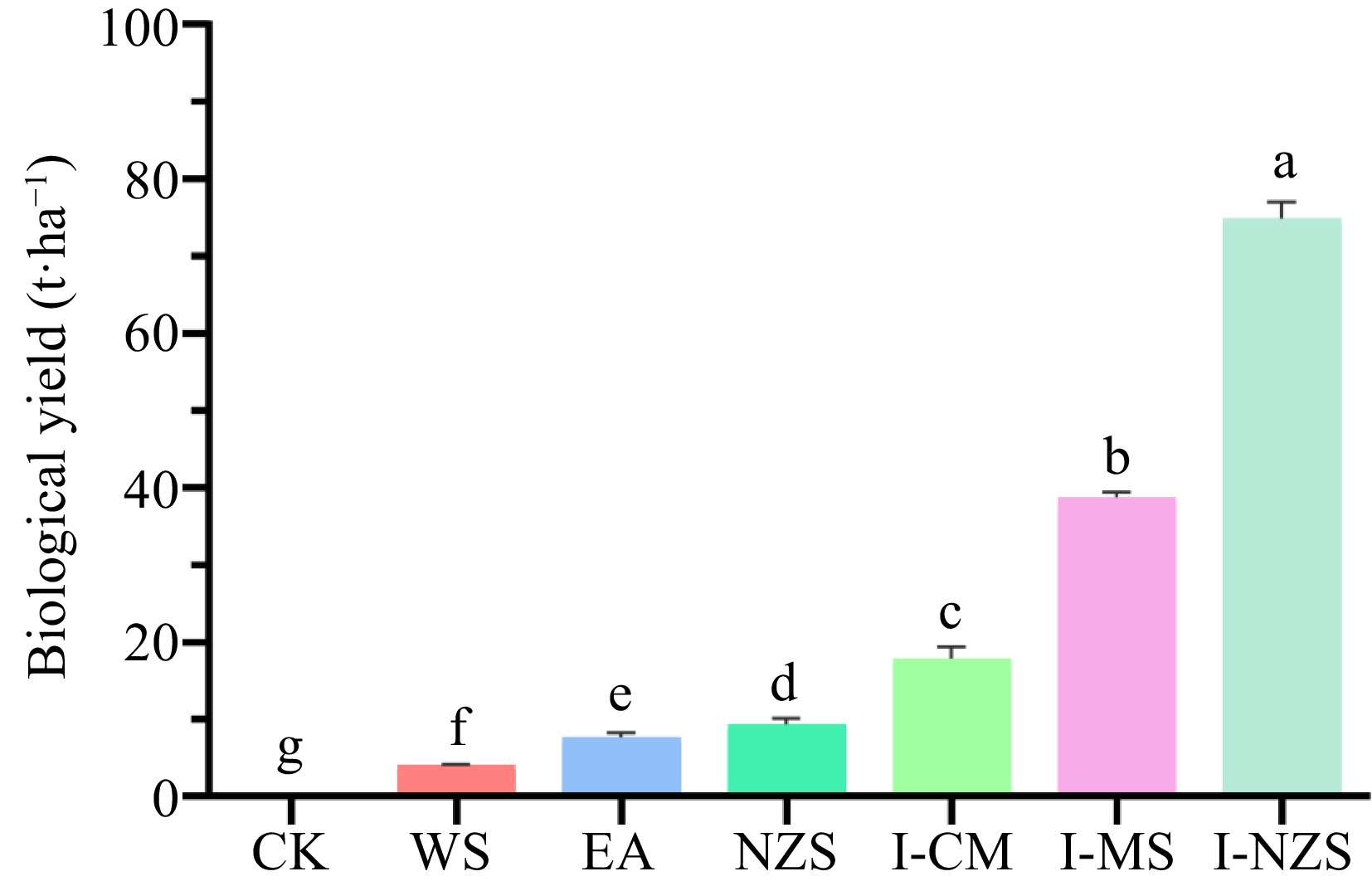
Figure 2.
Biological yield of summer catch leafy vegetables. CK, bare cultivated land as a control; WS, water spinach; EA, edible amaranth; NZS, newly planted New Zealand spinach; I-CM, previously intercropped chinese mallow; I-MS, previously intercropped malabar spinach; I-NZS, previously intercropped New Zealand spinach. The significant difference confidence level is p < 0.05.
-
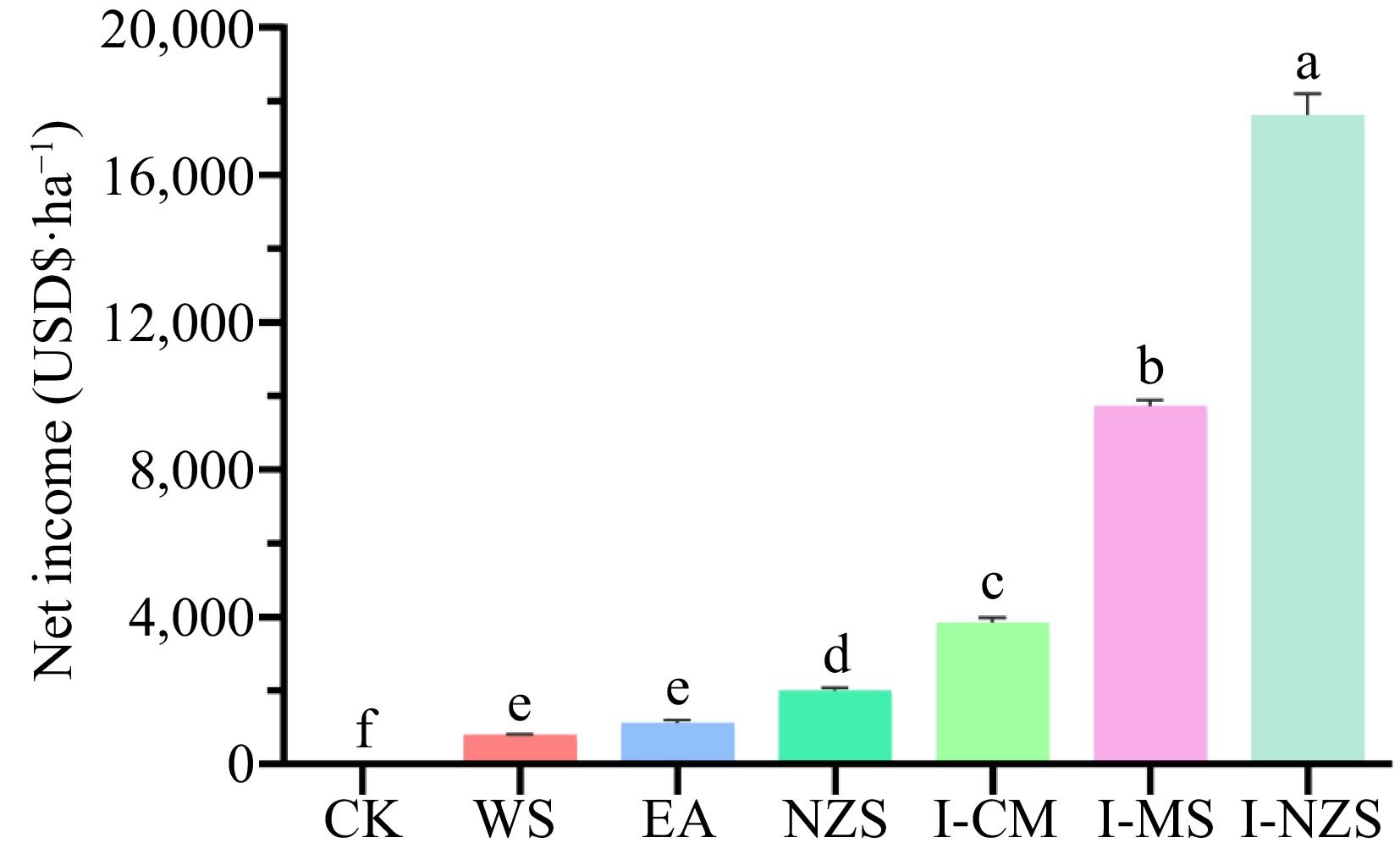
Figure 3.
Net income of summer catch leafy vegetables. CK, bare cultivated land as a control; WS, water spinach; EA, edible amaranth; NZS, newly planted New Zealand spinach; I-CM, previously intercropped chinese mallow; I-MS, previously intercropped malabar spinach; I-NZS, previously intercropped New Zealand spinach. The significant difference confidence level is p < 0.05.
-
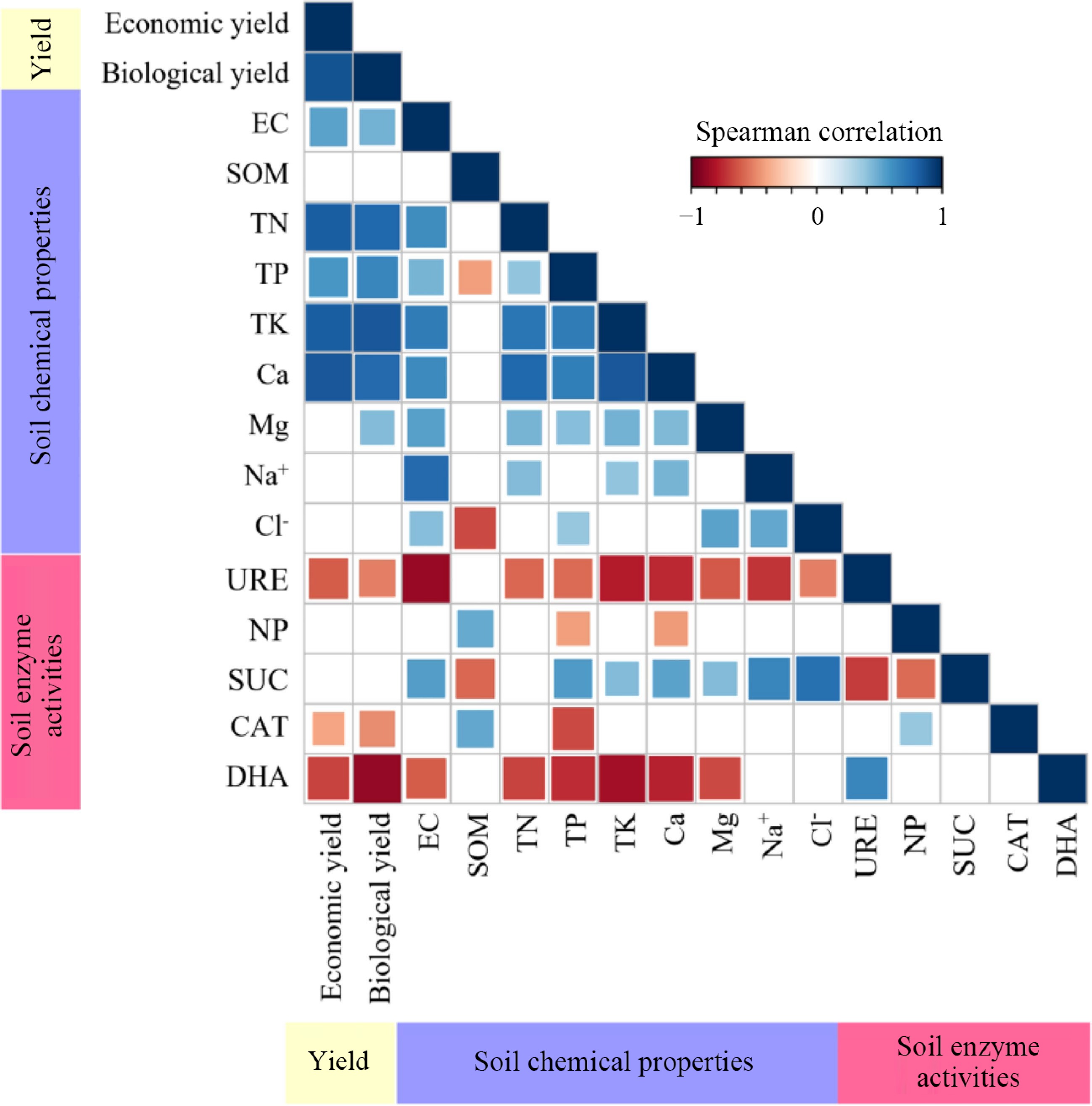
Figure 4.
The relationship between the yield of summer catch leafy vegetables and soil. EC, electrical conductivity; SOM, organic matter; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; TK, total potassium; URE, urease activity; NP, neutral phosphatase activity; SUC, sucrase activity; CAT, catalase activity; DHA, dehydrogenase activity.
-
Treatments EC
(μS·cm−1)SOM
(g·kg−1)TN
(g·kg−1)TP
(g·kg−1)TK
(g·kg−1)Ca
(g·kg−1)Mg
(g/kg−1)Na+
(g·kg−1)Cl−
(g·kg−1)CK −21 ± 6.18d 0.432 ± 0.00a 0.273 ± 0.07e 0.010 ± 0.01d −0.05 ± 0.07d −0.02 ± 0.32c −0.04 ± 0.24b 0.017 ± 0.04d −0.002 ± 0.02d WS 40 ± 1.41b −0.615 ± 0.11c 0.487 ± 0.12d 0.170 ± 0.02b 0.42 ± 0.41c 0.22 ± 0.15c 0.39 ± 0.12ab 0.162 ± 0.04b 0.036 ± 0.0abc EA 81 ± 13.06a −0.649 ± 0.20c 0.676 ± 0.05c 0.207 ± 0.06b 1.05 ± 0.15b 1.54 ± 0.50b 0.99 ± 0.66a 0.336 ± 0.01a 0.051 ± 0.02a NZS 18 ± 6.65c −0.623 ± 0.08c 0.730 ± 0.10bc 0.075 ± 0.03c 0.58 ± 0.15c 0.43 ± 0.20c 0.46 ± 0.39ab 0.069 ± 0.02c 0.022 ± 0.00c I-CM 27 ± 9.43c −0.777 ± 0.24c 0.549 ± 0.06d 0.415 ± 0.04a 0.95 ± 0.13b 0.77 ± 0.02c 0.91 ± 0.39a 0.032 ± 0.02d 0.043 ± 0.01ab I-MS 40 ± 3.68b −0.592 ± 0.08c 0.819 ± 0.09ab 0.379 ± 0.07a 1.37 ± 0.20a 2.62 ± 0.57a 0.38 ± 0.33ab 0.134 ± 0.04b 0.021 ± 0.01c I-NZS 87 ± 6.50a −0.458 ± 0.04b 0.900 ± 0.05a 0.223 ± 0.04b 1.61 ± 0.14a 1.91 ± 0.58ab 0.80 ± 0.00a 0.135 ± 0.01b 0.029 ± 0.00bc CK: bare cultivated land as a control, WS: water spinach, EA: edible amaranth, NZS: newly planted New Zealand spinach, I-CM: Chinese mallow, I-MS: Malabar spinach, I-NZS: the previous New Zealand spinach. EC: electrical conductivity, SOM: organic matter, TN: total nitrogen, TP: total phosphorus, TK: total potassium. The soil chemical property data are the values corresponding to the initial stage of the summer catch period minus the values corresponding to the end of the summer catch period, the negative sign '−' indicates an increase in the value of a soil chemical property and vice versa. The significant difference in confidence level p < 0.05. Table 1.
Effects of summer catch leafy vegetables on soil chemical properties of continuous cucumber cropping.
-
Treatments URE
(mg NH3-N/g soil)NP
(mg Phenol/g soil)SUC
(mg Glu/g soil)CAT
(mmol H2O2/g soil)DHA
(μg TTC/g soil)CK 0.929 ± 0.21a −0.023 ± 0.01b 0.64 ± 0.13d 0.74 ± 0.11a 10.53 ± 0.20a WS 0.386 ± 0.00b −0.086 ± 0.00c 5.05 ± 0.53bc −0.28 ± 0.02d −1.27 ± 0.14b EA −0.230 ± 0.00c −0.168 ± 0.02ef 6.33 ± 0.66a 0.69 ± 0.21a −3.29 ± 0.31d NZS 0.802 ± 0.25a −0.137 ± 0.02de 4.27 ± 0.19c 0.07 ± 0.00c −2.68 ± 0.25c I-CM 0.360 ± 0.03b −0.133 ± 0.02d 4.97 ± 0.33bc −1.31 ± 0.23e −5.48 ± 0.40e I-MS 0.319 ± 0.02b −0.185 ± 0.02f 5.21 ± 0.74b −1.63 ± 0.00f −3.52 ± 0.42d I-NZS 0.164 ± 0.12b 0.072 ± 0.01a 4.49 ± 0.08bc 0.32 ± 0.07b −11.18 ± 0.05f CK: bare cultivated land as a control, WS: water spinach, EA: edible amaranth, NZS: newly planted New Zealand spinach, I-CM: Chinese mallow, I-MS: Malabar spinach, I-NZS: the previous New Zealand spinach. URE: urease activity, NP: neutral phosphatase activity, SUC: sucrase activity, CAT: catalase activity, DHA: dehydrogenase activity. The enzyme activity data are the values corresponding to the initial stage of summer catch period minus the values corresponding to the end of summer catch period, the negative sign '−' indicates an increase in soil enzyme activity and vice versa for a decrease in enzyme activity. The significant difference confidence level p < 0.05. Table 2.
Effects of summer catch leafy vegetables on soil enzyme activities of continuous cucumber cropping.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(2)