-
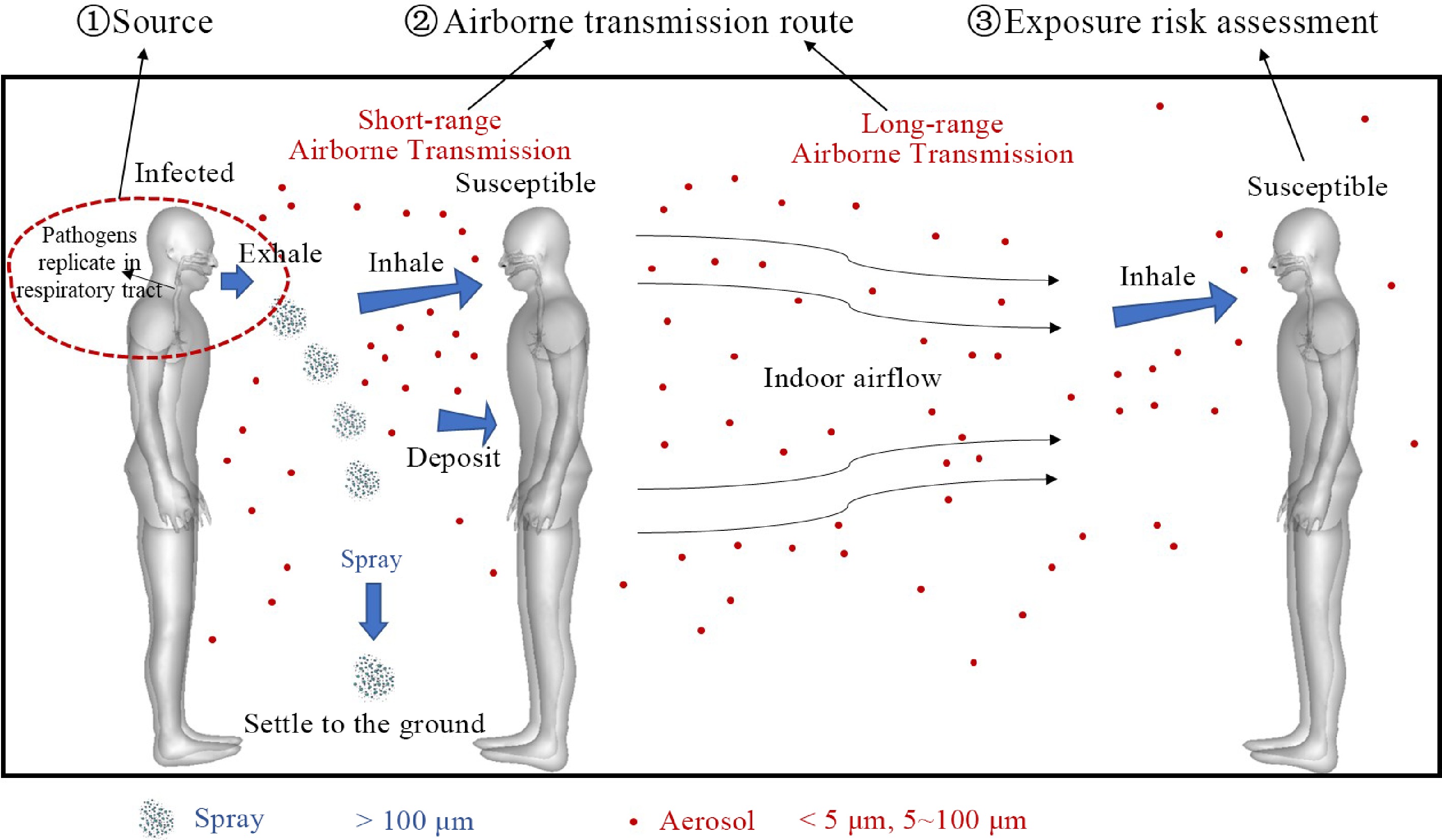
Figure 1.
Three main factors in indoor airborne transmission of respiratory infectious diseases: Source of infection, airborne transmission route, exposure risk assessment.
-
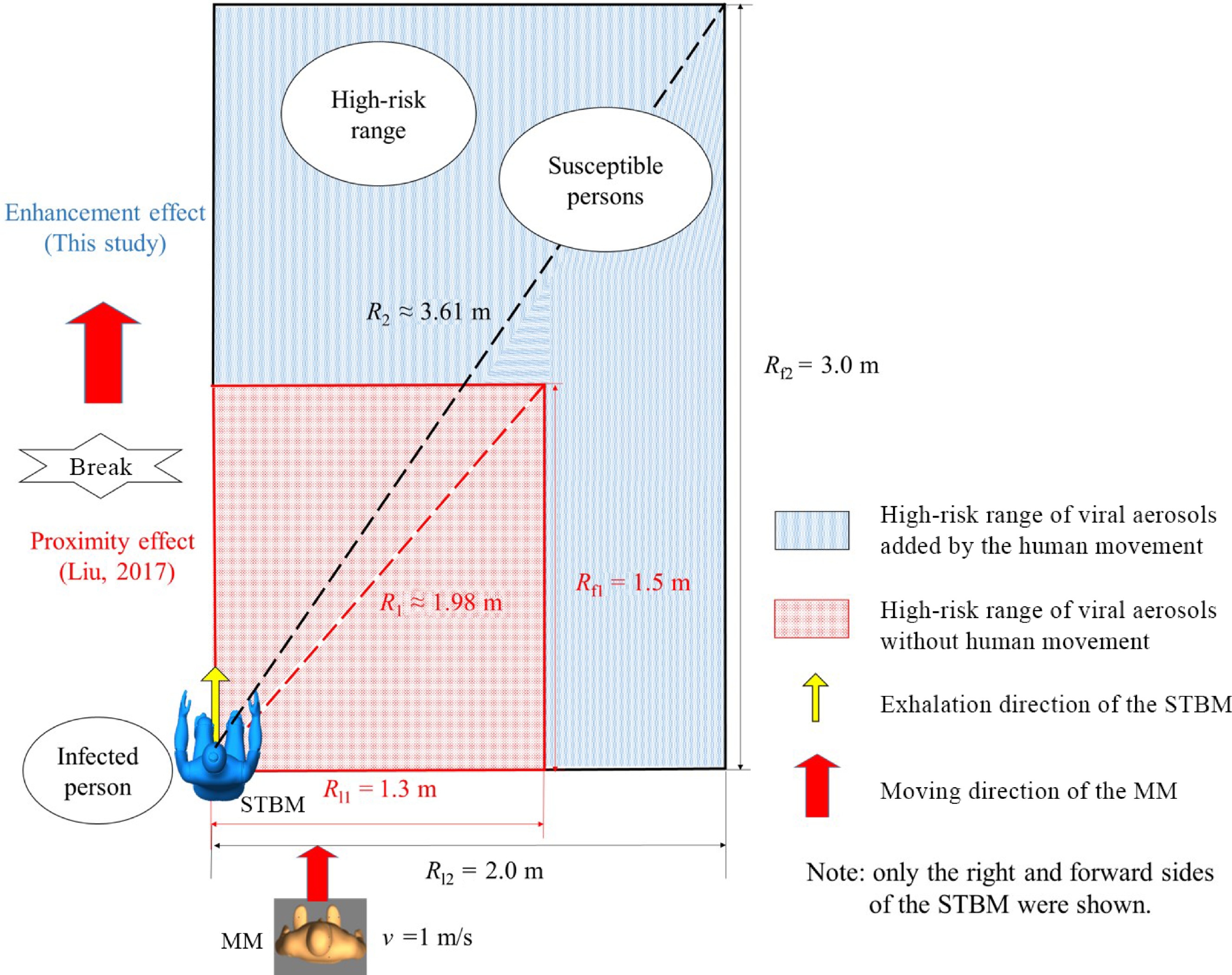
Figure 2.
The 'enhancement effect' of human movement on the high-risk range[99].
-
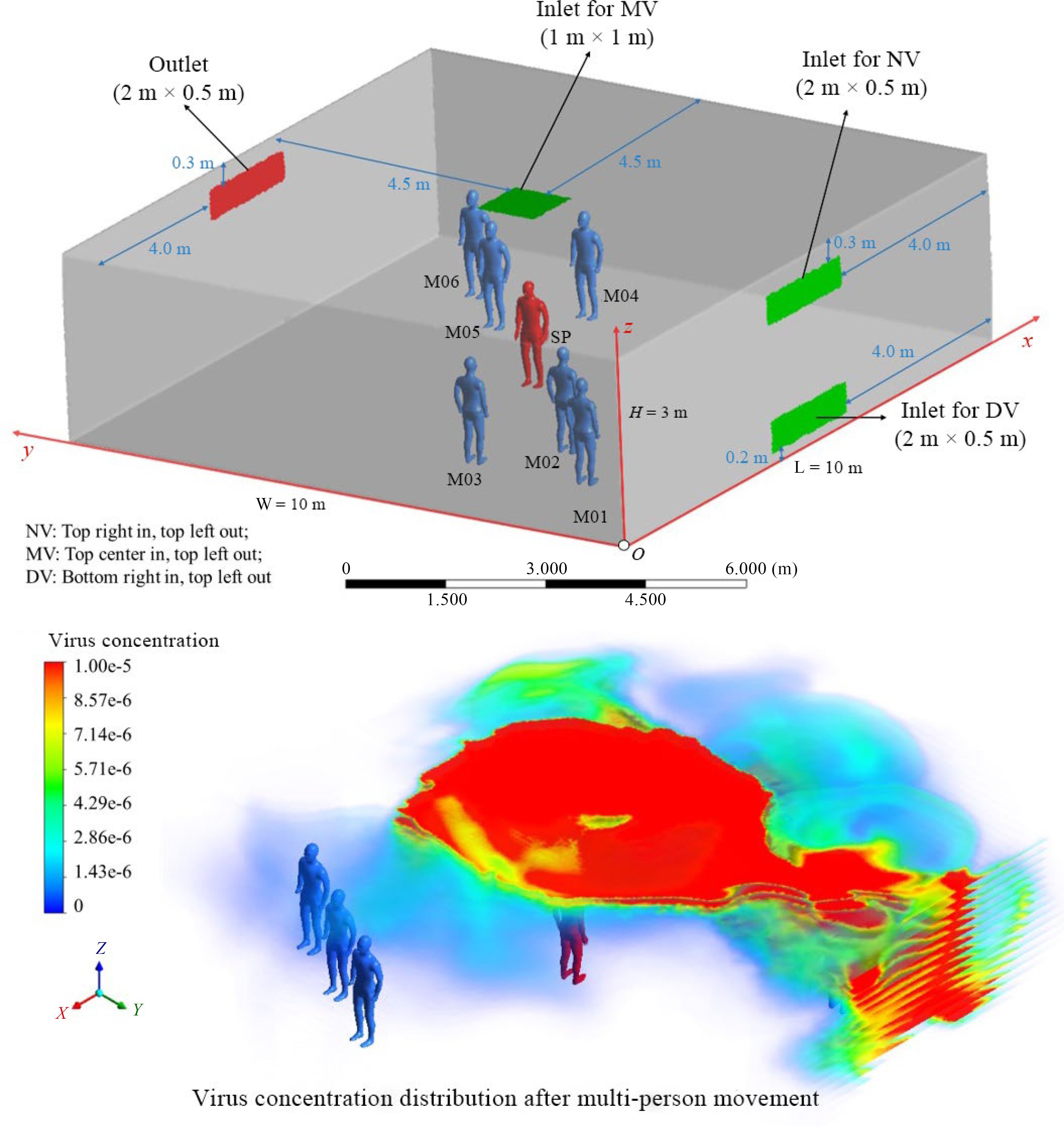
Figure 3.
Multi-person movement's effects on airborne transmission[124].
-
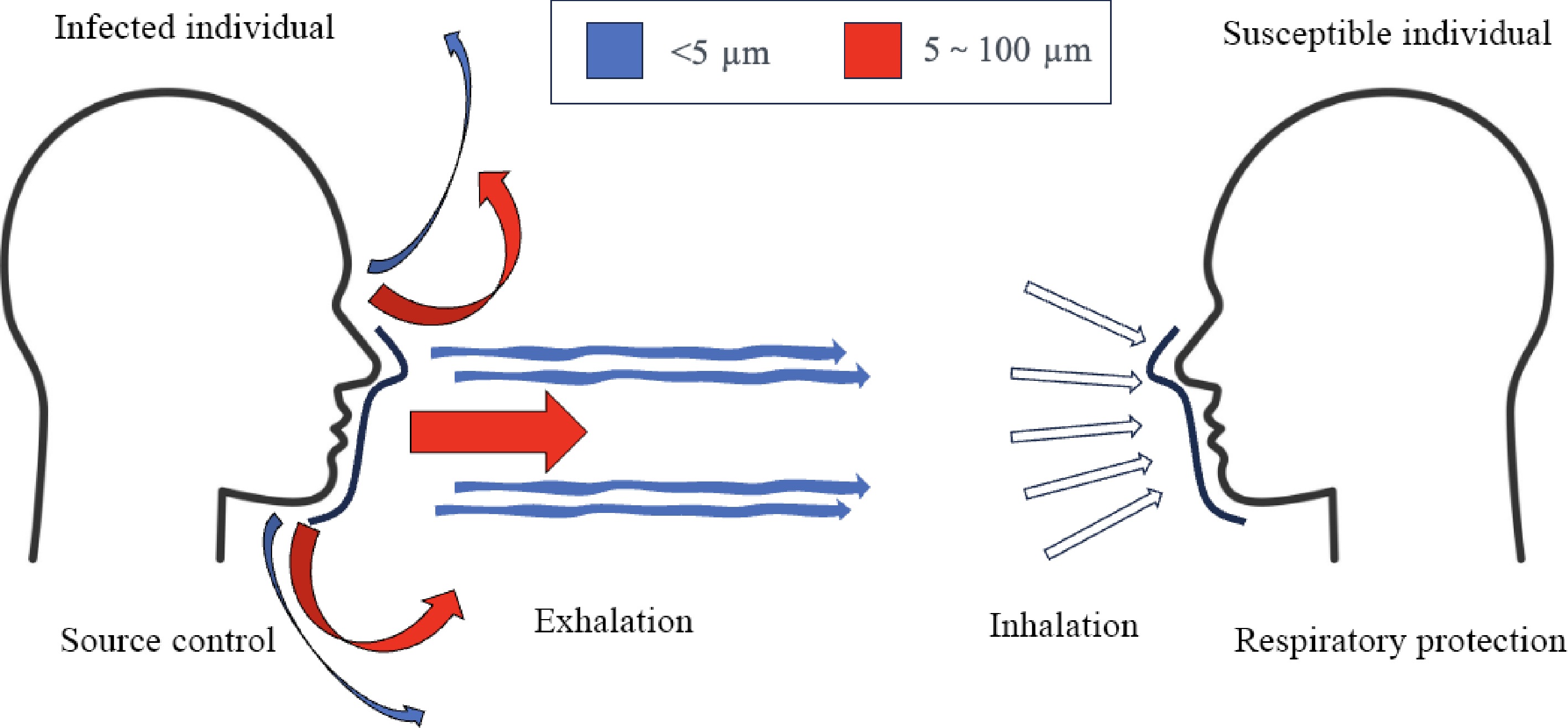
Figure 4.
Model of facemask protection. Source control aims to reduce virus-laden droplets exhaled from infected individuals, and respiratory protection aims to protect susceptible individual from inhaling droplets emitted by infection sources.
-
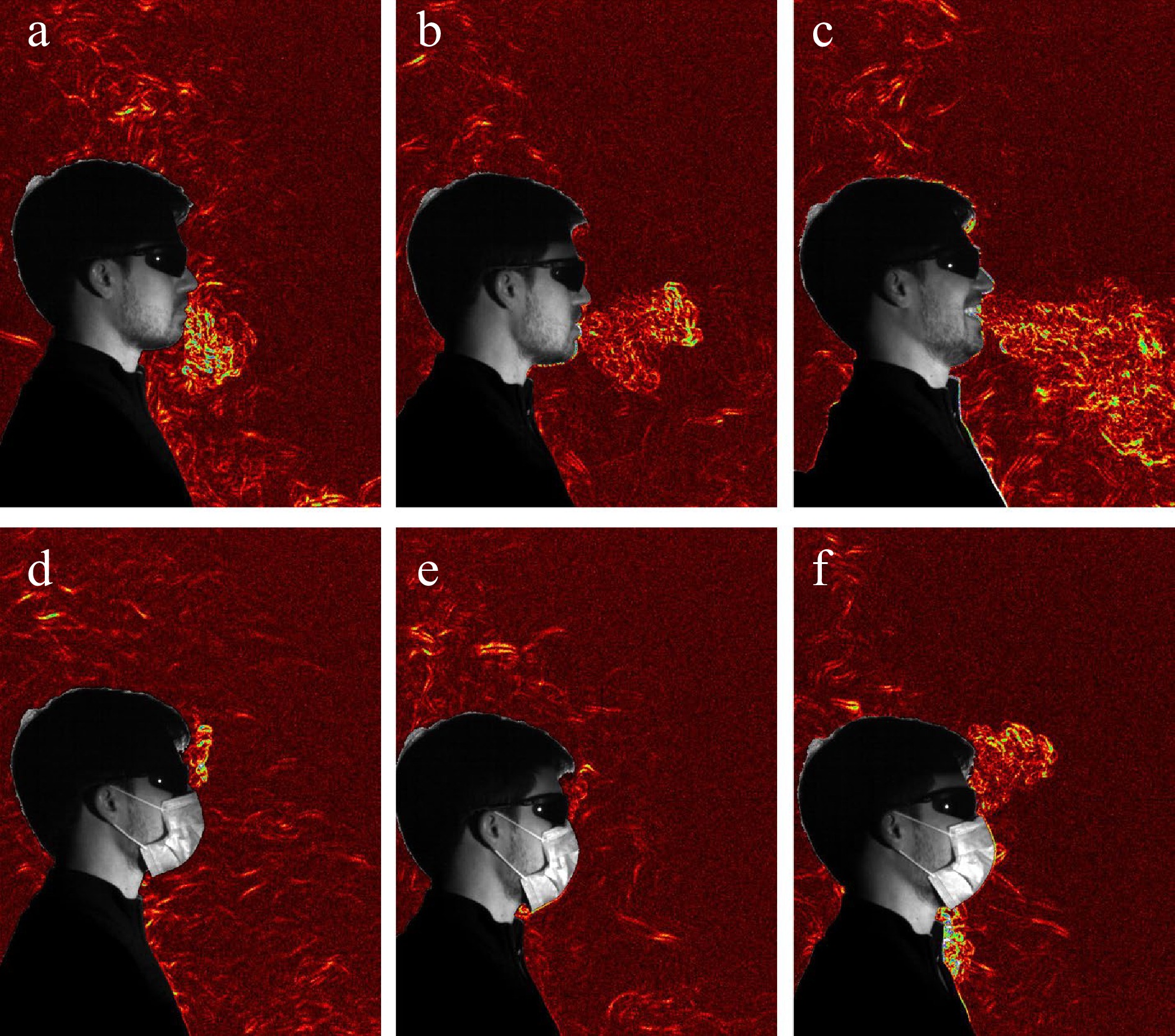
Figure 5.
Synthetic schlieren images of exhaled flows changes with and without a facemasks under different scenarios: (a), (d) breathing quietly; (b), (e) saying 'also'; (c), (f) laughing[136].
-
Region Regulation Name Particle Filtration
Effciency (PFE, %)FE test flowrate Particle diameter (µm) China GB2626-2019 KN90 ≥ 90 30~100 L/min, continuous flow 0.075 ± 0.020 KN95 ≥ 95 KN100 ≥ 99.97 Europe EN 149-2001+A1: 2009 FFP1 ≥ 80 95 L/min, continuous flow 0.02~2 FFP2 ≥ 94 FFP3 ≥ 99 America NIOSH 42 CFR Part 84-2019 N95 ≥ 95 20.0~65.0 L/min, breathing 0.075 ± 0.020 Table 1.
High-performance respirator regulations.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(1)