-
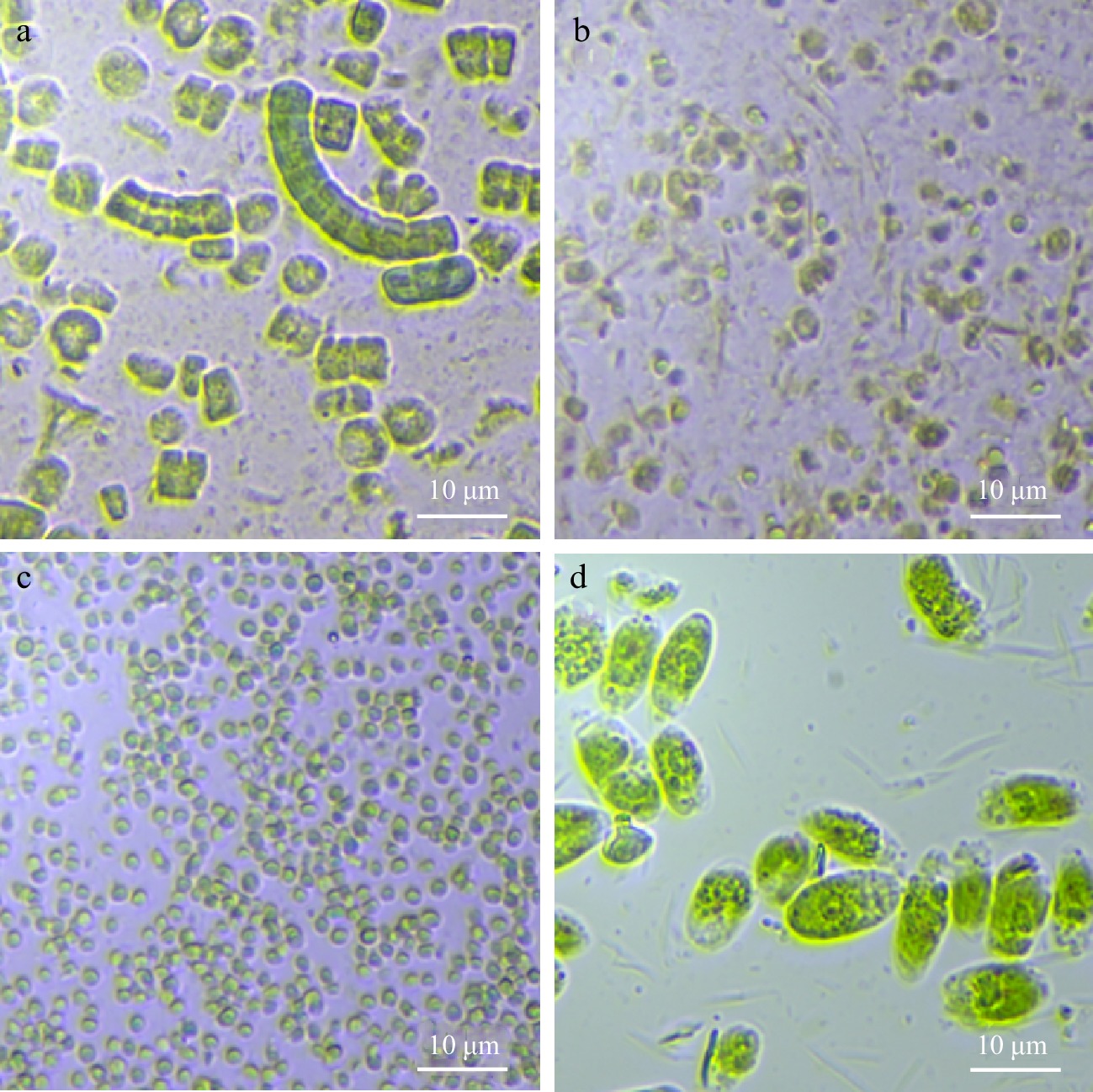
Figure 1.
Microscopic images of microalgal suspensions at 40 × magnification: (a) Arthrospira sp., (b) Isochrysis sp., (c) Nannochloropsis sp., and (d) Tetraselmis sp.
-
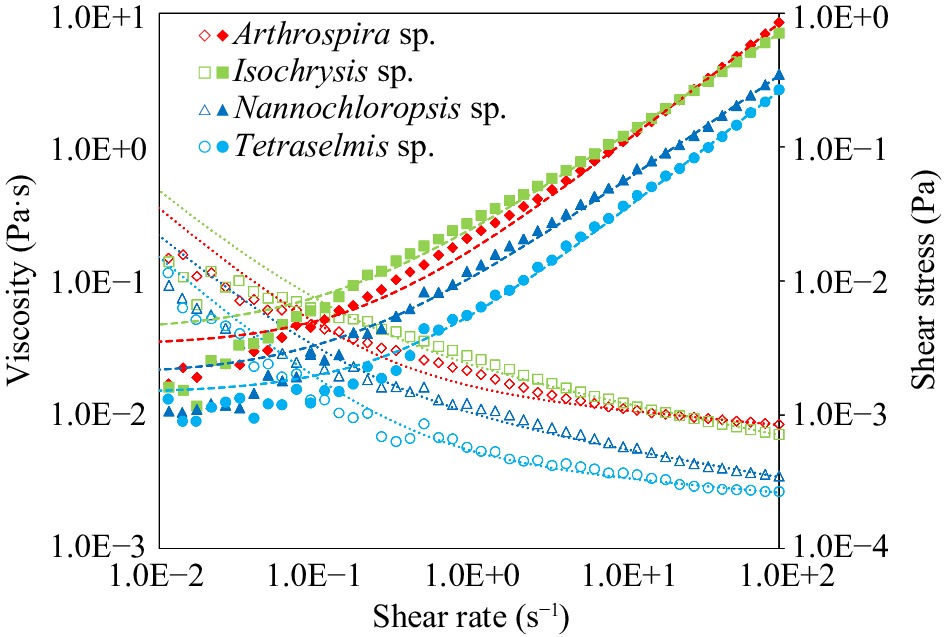
Figure 2.
Viscosity (Pa·s) and shear stress (Pa) vs shear rate (s−1) of untreated microalgal suspensions of Arthrospira sp., Isochrysis sp., Nannochloropsis sp., and Tetraselmis sp. Data points are means based on three replicates. Lines represent the Herschel-Bulkley fit.
-
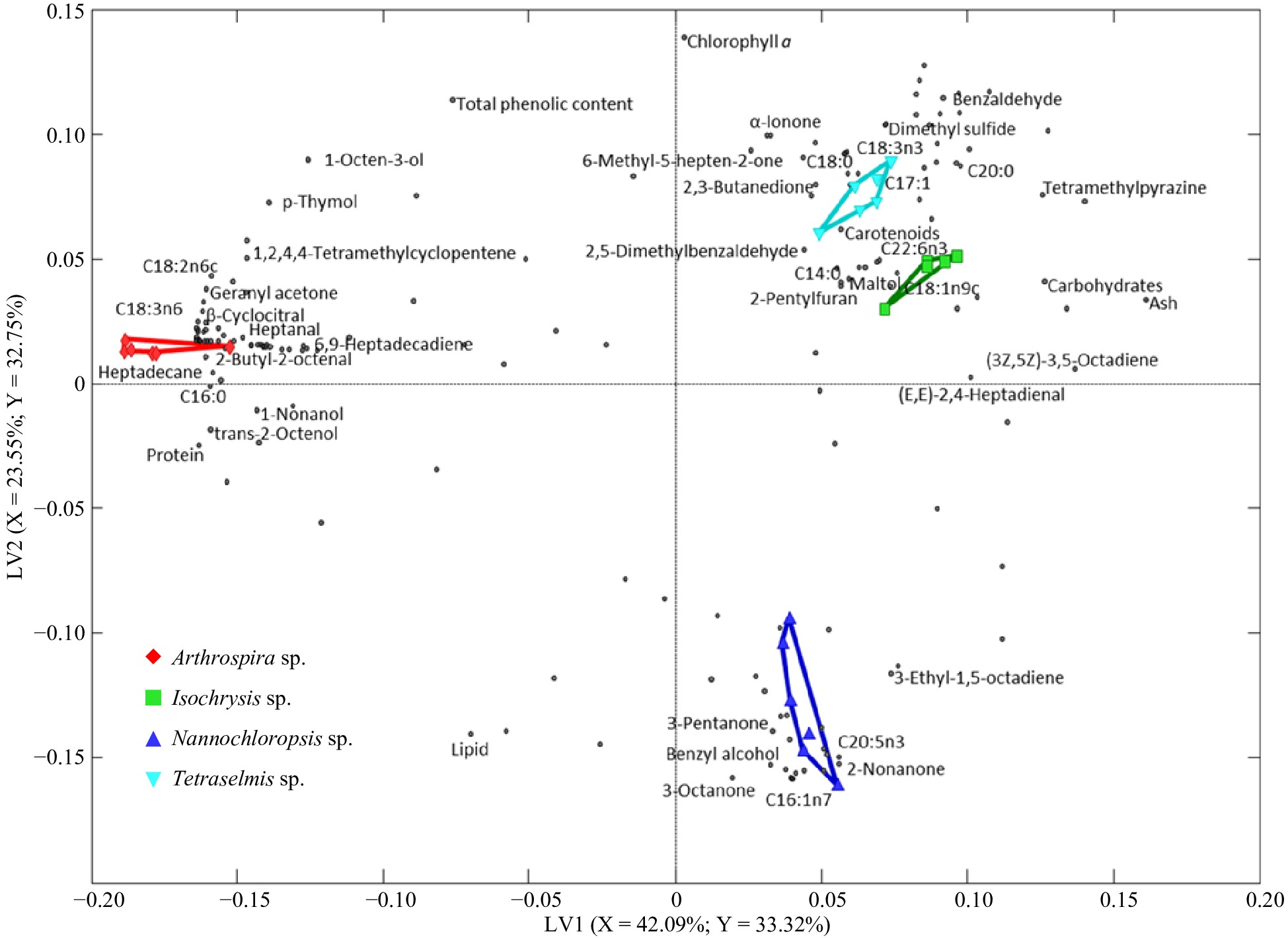
Figure 3.
PLS-DA biplots describe the variation among the selected microalgae. Differently shaped symbols represent the different microalgae: Arthrospira sp., Isochrysis sp., Nannochloropsis sp., and Tetraselmis sp. The dots represent components.
-
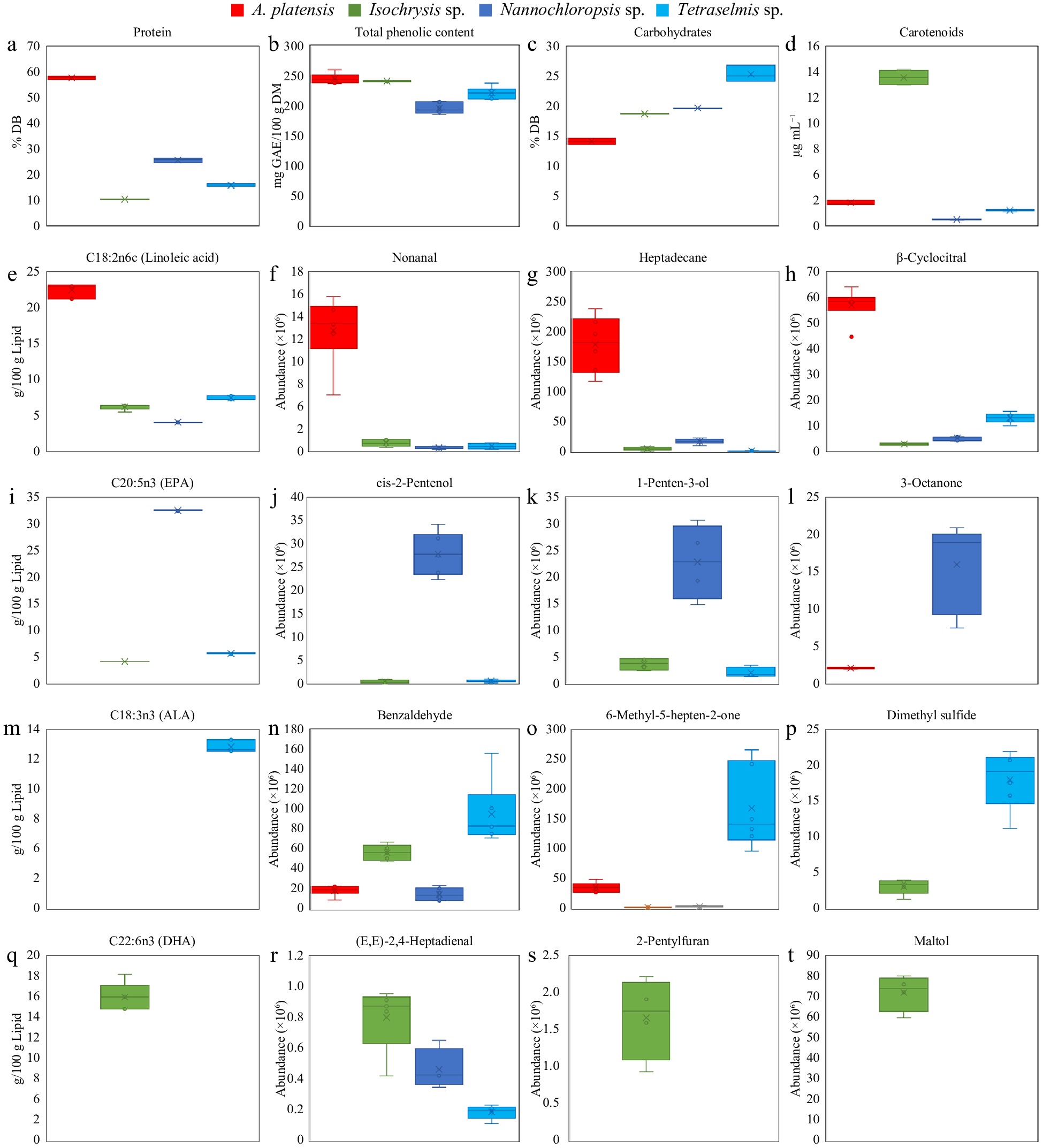
Figure 4.
Individual plots of some representative discriminant compounds show variation among A. platensis, Isochrysis sp., Nannochloropsis sp., and Tetraselmis sp. Values are mean ± standard error (n = 3).
-
Parameters Arthrospira sp. Isochrysis sp. Nannochloropsis sp. Tetraselmis sp. Proximate composition Crude lipid (%, DB) 15.60 ± 1.12a 12.01 ± 0.24b 17.62 ± 0.84a 8.80 ± 0.22c Crude protein (%, DB) 57.92 ± 0.52a 10.11 ± 0.12d 25.44 ± 0.79b 15.54 ± 0.49c Total ash (%, DB) 5.81 ± 0.02d 38.55 ± 0.08a 25.82 ± 0.15c 33.50 ± 0.39b Carbohydrate (%, DB) 14.06 ± 0.40c 18.75 ± 0.05b 19.68 ± 0.04b 25.42 ± 0.65a Pigments Chlorophyll a (mg/g DM) 0.051 ± 0.003b 0.070 ± 0.001a 0.008 ± 0.001c 0.046 ± 0.001b Carotenoids (mg/g DM) 0.023 ± 0.001b 0.137 ± 0.003a 0.005 ± 0.000d 0.014 ± 0.000c Total phenolic content (mg GAE/100 g DM) 245.64 ± 7.92a 242.80 ± 2.92a 195.63 ± 8.55c 221.50 ± 9.24b Particle size distribution d (0.1) (µm) 5.65 ± 0.10 2.69 ± 0.02 1.40 ± 0.00 5.80 ± 0.06 d (0.5) (µm) 9.08 ± 0.13 4.21 ± 0.03 2.35 ± 0.01 8.82 ± 0.03 d (0.9) (µm) 14.48 ± 0.16 6.44 ± 0.08 4.27 ± 0.04 13.13 ± 0.05 Rheological properties Consistency coefficient, K (Pa·sn) 0.013 ± 0.000b 0.020 ± 0.001a 0.008 ± 0.000c 0.004 ± 0.000d Flow behaviour index, n (−) 0.900 ± 0.002a 0.774 ± 0.002c 0.802 ± 0.006b 0.907 ± 0.013a Yield stress, σ0 (Pa) 0.003 ± 0.001a 0.004 ± 0.002a 0.002 ± 0.000a 0.001 ± 0.000a Values are mean ± standard deviation from independent replicates (n = 3). Means with different superscripts in the same row indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05). % DB refers to % dry basis. Table 1.
Chemical composition and physical properties of the microalgal biomass used in this study.
-
Fatty acids Arthrospira
sp.Isochrysis
sp.Nannochloropsis
sp.Tetraselmis
sp.C12:0 ND ND ND 5.72 ± 0.48 C14:0 2.52 ± 0.42b 12.18 ± 1.75a 1.84 ± 0.33b 2.22 ± 0.02b C14:1 ND 7.83 ± 1.18 ND ND C16:0 45.30 ± 0.95a 9.86 ± 1.71c 21.53 ± 0.16b 22.37 ± 0.41b C16:1n7 3.34 ± 0.11c 5.40 ± 0.36b 26.87 ± 0.95a 1.33 ± 0.15d C18:0 1.81 ± 0.80b ND 0.81 ± 0.42b 15.44 ± 0.85a C18:1n9t ND ND 0.60 ± 0.01b 1.86 ± 0.07a C18:1n9c 2.89 ± 0.18b 10.16 ± 1.14a 4.46 ± 0.03b 10.21 ± 0.16a C18:2n6c 22.58 ± 1.08a 6.03 ± 0.42b 4.01 ± 0.04c 7.38 ± 0.24b C18:3n3 ND 5.20 ± 0.17b ND 12.71 ± 0.41a C18:3n6 19.61 ± 0.46a ND 0.99 ± 0.01c 2.39 ± 0.10b C20:0 ND 25.01 ± 2.97a ND 8.47 ± 0.26b C20:3n3 ND ND ND ND C20:4n6 ND ND 4.48 ± 0.12a 1.39 ± 0.13b C20:5n3 ND ND 32.76 ± 0.10a 5.59 ± 0.11b C22:6n3 ND 15.99 ± 1.57 ND ND Total SFA 49.63 ± 1.14b 47.67 ± 0.96b 24.18 ± 0.58c 53.47 ± 00.09a Total MUFA 6.23 ± 0.05d 23.73 ± 2.76b 32.14 ± 0.84a 16.52 ± 0.53c Total PUFA 42.20 ± 1.25a 27.61 ± 1.17b 42.34 ± 0.10a 29.00 ± 0.26b Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Means with a different superscript in the same row indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05). ND means not detected. Table 2.
The selected microalgae's relative fatty acid abundance as fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) by gas chromatography coupled with a flame ionisation detector (GC-FID).
-
VID Identity RI calculated RI reference Chemical class VID Identity RI calculated RI reference Chemical class Arthrospira sp. 0.982 2-Nonanone 1381 1390 Ketone 0.996 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethylpyrazine 1438 1443 Pyrazine 0.98 (Z)-2-Pentenol 1304 1318 Alcohol 0.996 Safranal 1650 1616 Aldehyde 0.976 1-Penten-3-one 1016 1019 Ketone 0.995 1-Decene 1032 1050 Hydrocarbon 0.974 C16:1n7 (Palmitoleic acid) 0.994 1R-α-Pinene 1019 1013 Terpene 0.972 C20:5n3 (Eicosapentaenoic acid, EPA) 0.993 2,2,6-Trimethylcyclohexanone 1317 1319 Ketone 0.962 1-Heptanol 1440 1453 Alcohol 0.993 C18:3n6 (γ-Linolenic acid, GLA) 0.946 3-Octanone 1247 1253 Ketone 0.992 2-Butyl-2-octenal 1664 1656 Aldehyde 0.936 Benzyl alcohol 1867 1870 Alcohol 0.992 2,4-Dimethylbenzaldehyde 1737 1728 Aldehyde 0.888 3-Pentanone 973 980 Ketone 0.982 α-Cyclocitral 1442 1425 Terpene 0.885 1-Penten-3-ol 1147 1159 Alcohol 0.98 β-Cyclocitral 1626 1611 Terpene 0.832 2,7-Octadienol 1666 − Alcohol 0.979 β-Ionone epoxide 1997 1962 Ketone 0.815 3-Ethyl-1,5-octadiene 1019 1015 Hydrocarbon 0.975 C18:2n6c (Linoleic acid) 0.812 (3E,5E)-3,5-Octadien-2-one 1566 1570 Ketone 0.97 trans-β-Ionone 1942 1940 Terpene −0.838 Chlorophyll a 0.964 Protein −0.839 Total phenolic content 0.957 Heptadecane 1690 1700 Hydrocarbon Tetraselmis sp. 0.953 Heptanal 1177 1184 Aldehyde 0.976 C18:3n3 (α-Linolenic acid, ALA) 0.947 trans-2-Octenol 1598 1614 Alcohol 0.974 Dimethyl sulphide 743 754 Sulphur compound 0.942 C16:0 (Palmitic acid) 0.969 C12:0 (Lauric acid) 0.942 Nonanal 1387 1391 Aldehyde 0.957 2-Ethyl-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazine 1505 1506 Pyrazine 0.937 Pentadecane 1487 1500 Hydrocarbon 0.955 (Z)-4-Heptenal 1234 1240 Aldehyde 0.936 Hexadecane 1587 1600 Hydrocarbon 0.947 C18:0 (Stearic acid) 0.929 Geranyl acetone 1846 1859 Ketone 0.925 α-Ionone 1853 1840 Terpene 0.925 Octanal 1281 1289 Aldehyde 0.918 C18:1n9c (Oleic acid) 0.893 Isophorone 1404 1591 Ketone 0.894 Carbohydrates 0.887 1,2,4,4-Tetramethylcyclopentene 932 − Hydrocarbon 0.857 Benzaldehyde 1526 1520 Aldehyde 0.869 2,2,4,6,6-Pentamethylheptane 944 949 Hydrocarbon 0.853 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one 1329 1338 Ketone 0.863 β-Pinene 1091 1112 Terpene 0.844 2,3-Butanedione 970 979 Ketone 0.858 D-Limonene 1187 − Terpene −0.87 Lipid 0.856 1-Nonanol 1643 1660 Alcohol Isochrysis sp. 0.851 m-Xylene 1131 1143 Hydrocarbon 0.96 C22:6n3 (Docosahexaenoic acid, DHA) 0.851 α-Ionene 1697 1565 Hydrocarbon 0.96 C14:1 (Myristoleic acid) 0.843 1-Dodecene 1227 1243 Hydrocarbon 0.951 C20:0 (Arachidonic acid) 0.818 Hexyl acetate 1261 1272 Ester 0.948 Carotenoids 0.801 1-Octen-3-ol 1431 1450 Alcohol 0.936 3-Methyl-1,4-heptadiene 914 − Hydrocarbon −0.8 (3Z,5Z)-3,5-Octadiene 925 − Hydrocarbon 0.933 C14:0 (Myristic acid) −0.945 Ash 0.916 3-Methyl-2-(3,7,11-trimethyldodecyl) furan 2097 − Furan Nannochloropsis sp. 0.906 2,5-Dimethylbenzaldehyde 1746 1683 Aldehyde 0.991 2-Undecanone 1591 1598 Ketone 0.886 Maltol 1960 1969 Ketone 0.986 (E)-2-Pentenal 1125 1127 Aldehyde 0.865 (E,E)-2,4-Heptadienal 1460 1495 Aldehyde 0.985 1,3-Pentadiene 97 624 Hydrocarbon 0.835 2-pentylfuran 1221 1231 Furan Retention indices (RI) for the individual volatile compounds were calculated and reference obtained from the National Institute Standards and Technology Standard Reference Database (National Institute of Standards and Technology n.d.). Individual fatty acids were identified by matching retention time with commercial standards. Table 3.
Discriminant compounds and attributes selected per microalgal species based on the VID method confirmed with significant testing, listed in decreasing order of VID coefficient. Retention indices (RI) for the individual volatile compounds were calculated, and references were obtained from the National Institute Standards and Technology Standard Reference Database[60]. Individual fatty acids were identified by matching retention time with commercial standards.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(3)