-
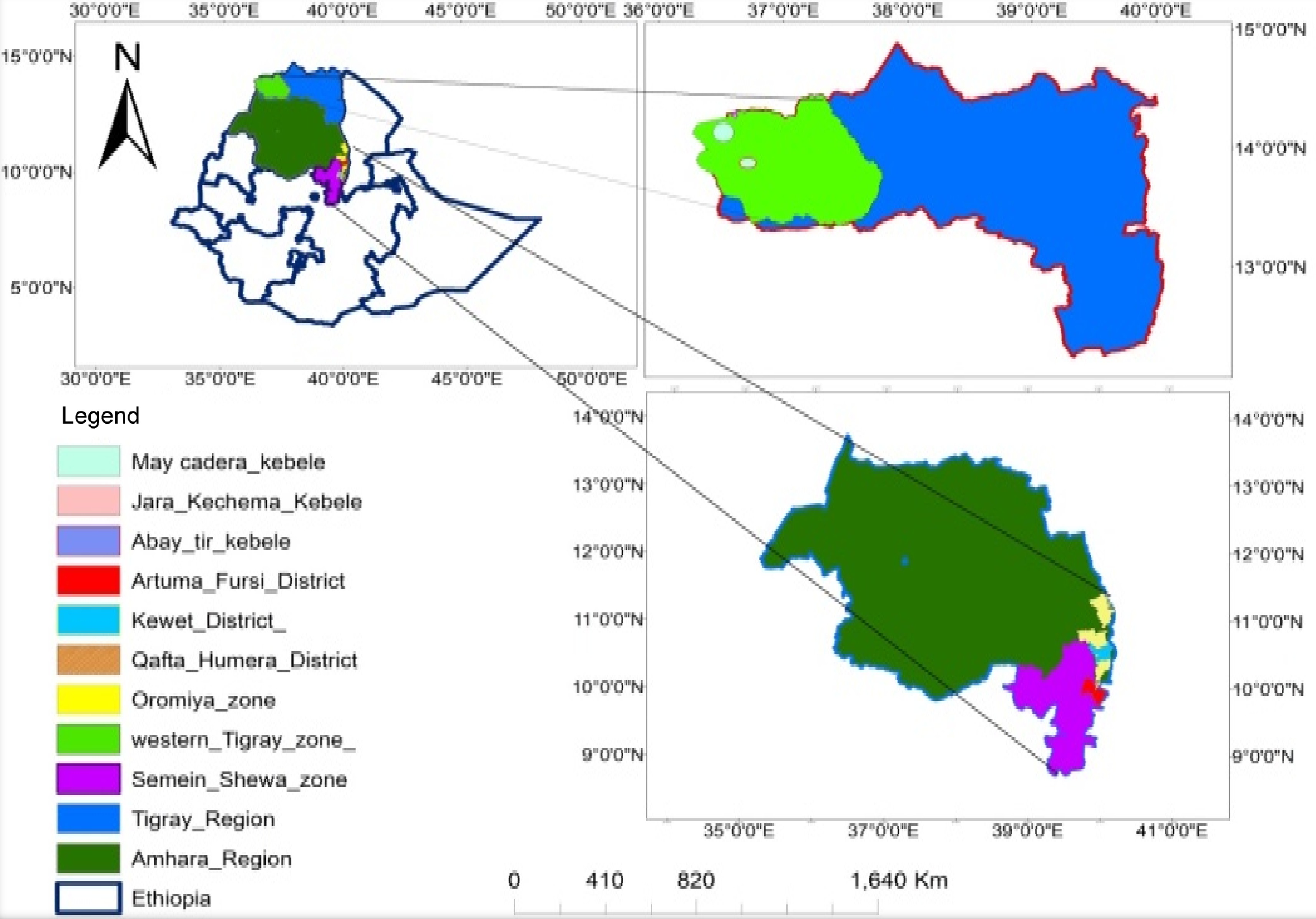
Figure 1.
Map of soil sample collection areas.
-
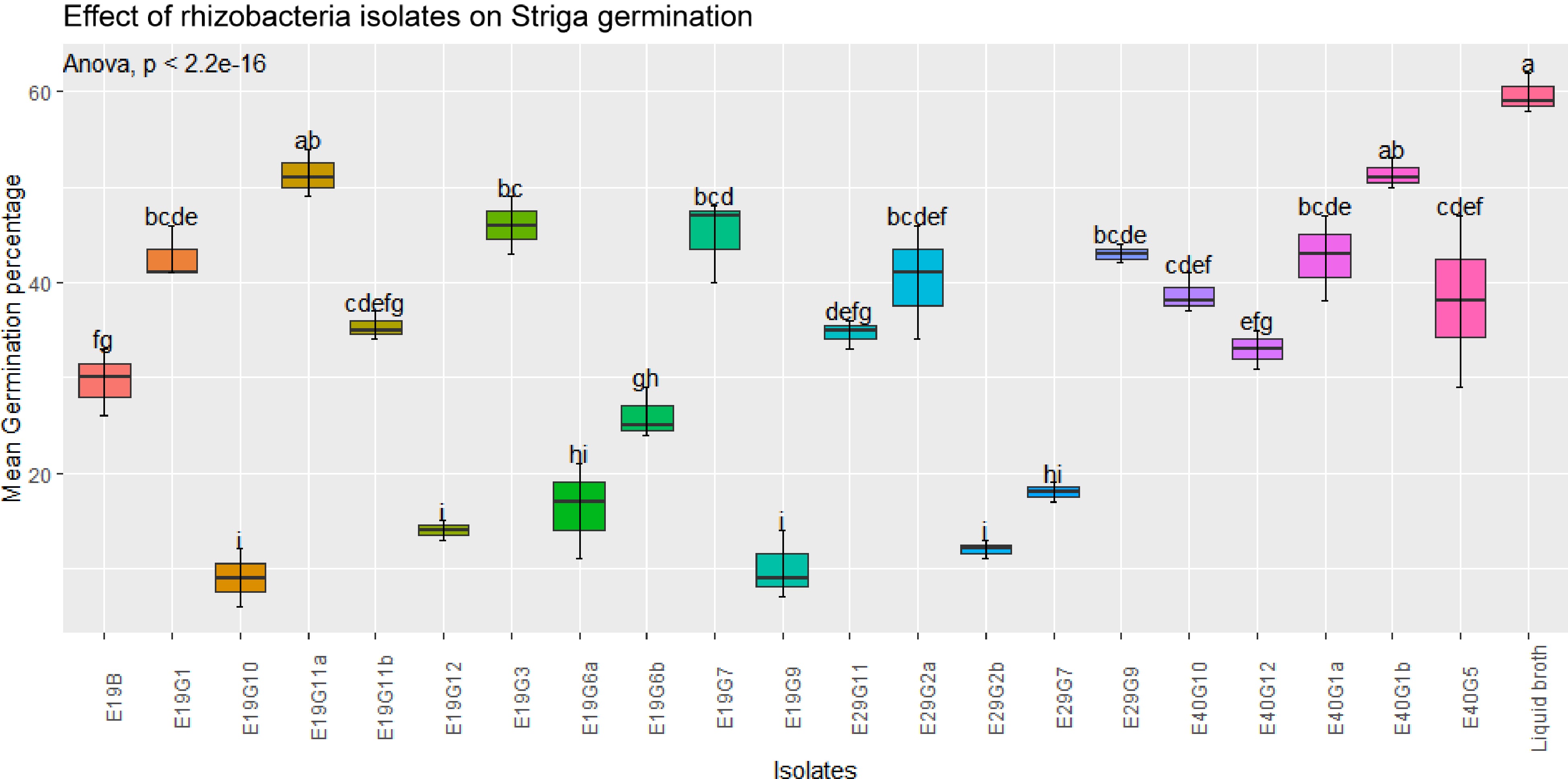
Figure 2.
Effect of rhizobacteria isolates on GR-24 induced S. hermonthica germination in filter paper assay. Values are means of combined data of three replicates each. Means followed by the same letter are not statistically different at p ≤ 0.05 according to the Tukey-test.
-
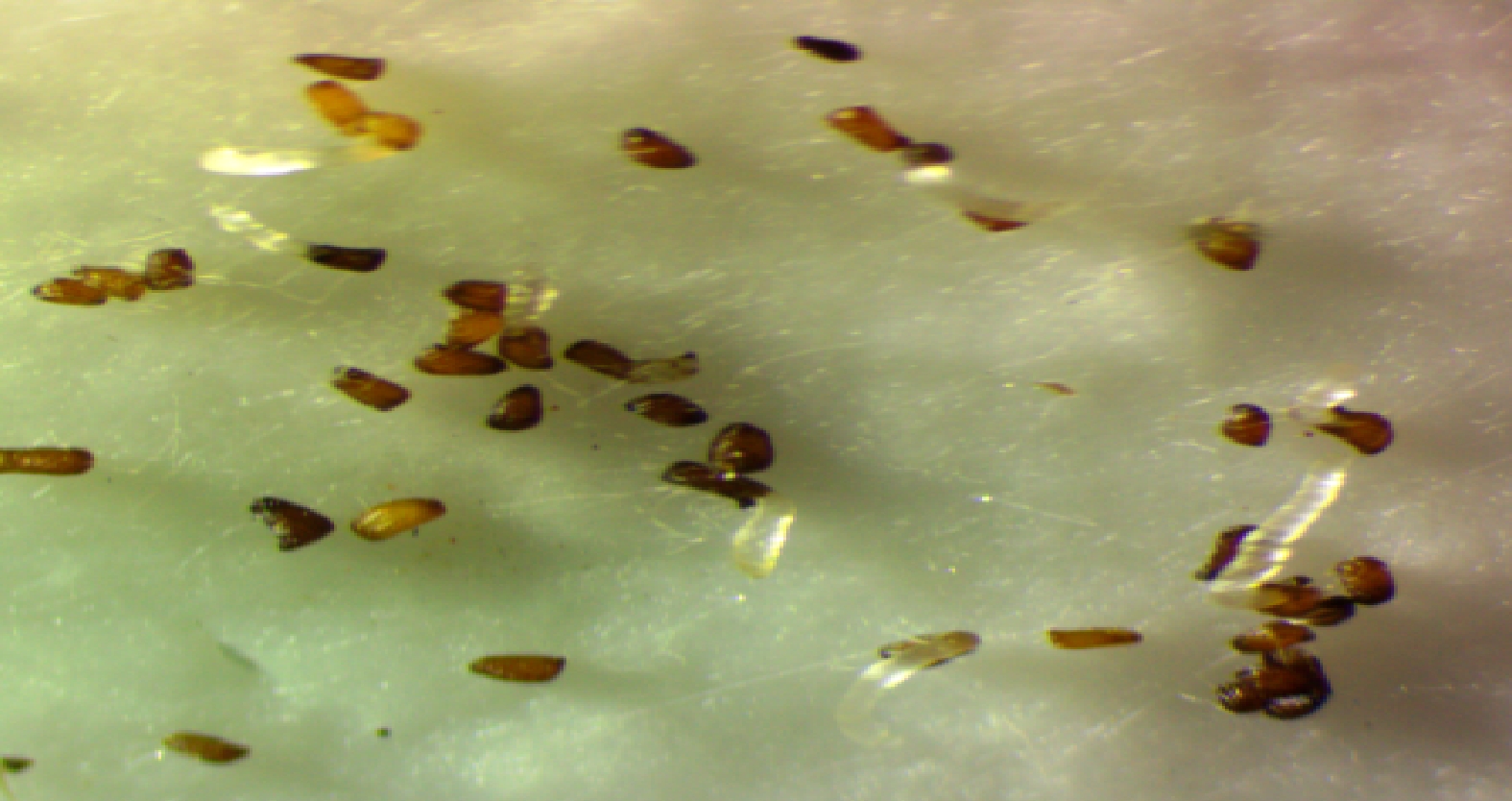

Figure 3.
Glass fiber filter paper based S. hermonthica germination assay.
-
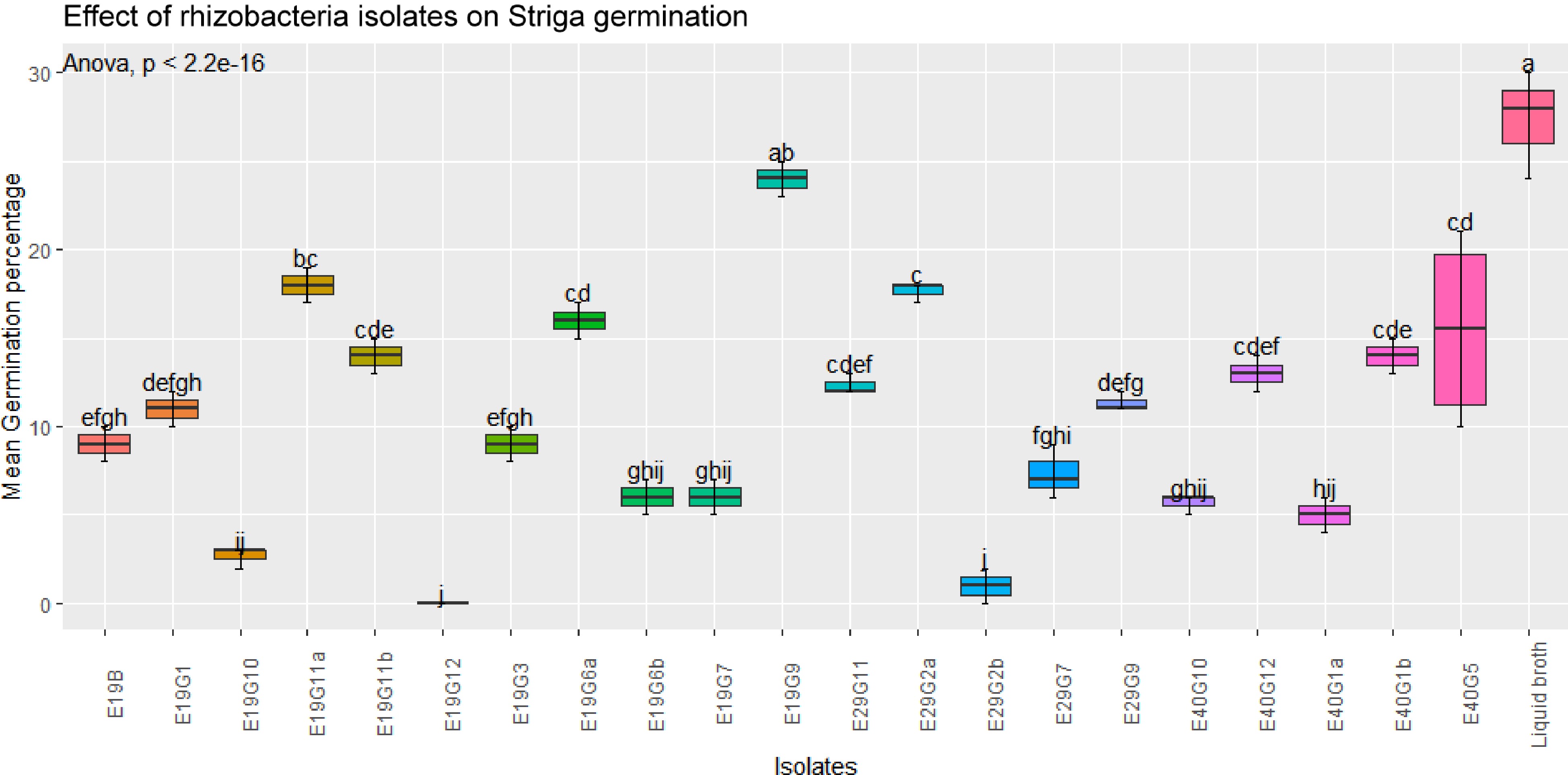
Figure 4.
Effects of rhizobacterial isolates on S. hermonthica seed germination in the presence of susceptible host plant.Values are means of combined data of three replicates each. Means followed by the same letter are not statistically different at p ≤ 0.05 according to the Tukey-test.
-
Figure 5.
Striga seed germination using agar gel assay.
-
Code Name Source Character Selection criteria G1 ETSL101847 Tigray Local land race Land race and widely used G2 ETWS 90754 Amhara Wild type Wild type G3 ETWS 91242 Beneshangul Wild type Wild type G4 Framida Purdue University Striga resistance Striga resistant and widely used G5 ETSL100046 Land race LGS Land race and LGS G6 ETSL101853 Land race HGS Land race, widely used and HGS G7 Misikir MI_Drought_Score Drought tolerant Drought tolerant G8 S35 ICRISAT Stay green Stay green or Drought tolerant G9 Shanqui red China Striga susceptible variety HGS and Striga susceptible variety G10 SR5-Ribka IBC Striga resistant and fusarium compatibility Striga resistant and fusarium compatibility G11 SRN39 Purdue University Striga resistance Striga resistant and widely used G12 Teshale ICRISAT Best released susceptible varieties Widely used LGS = low germination stimulant; HGS = high germination stimulant, G = genotype. Table 1.
Sorghum genotype selection for greenhouse planting and isolation of bacteria.
-
Isolates Morphological characterization Pigment Shape Size Elevation Margin Gram staining E19G6a White Circular Medium Raised Entire – E19G9 White Circular Medium Raised Entire – E19G6b Brown Circular Medium Raised Entire + E19G10 White Circular Medium Raised Entire – E19B Brown Irregular Large Raised Flat – E19G12 Brown Circular Medium Raised Entire + E29G2a White Irregular Large raised Mucoid – E29G7 White Circular Medium Raised Entire – + = Positive for a given test, – = Negative for a given test under consideration. Table 2.
Morphological characterization and identification of the most effective rhizobacteria isolates.
-
Isolates Biochemical tests Glucose Fructose Sucrose Catalase Methyl red Tentative identification E19G6a + + – + + Pseudomonas sp. E19G9 – – – + + Pseudomonas sp. E19G6b – + – + + Bacillus sp. E19G10 + + + – – Klebsiella sp. E19B + + – + + Pseudomonas sp. E19G12 – + – + + Bacillus sp. E29G2a – + + – – Entrobacter sp. E29G7 + + – + + Pseudomonas sp. – = no sugar utilization, catalase and methyl red negative, + = sugar utilization, catalase and methyl red positive. Table 3.
Biochemical characterization of the most effective rhizobacteria isolates.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(3)