-
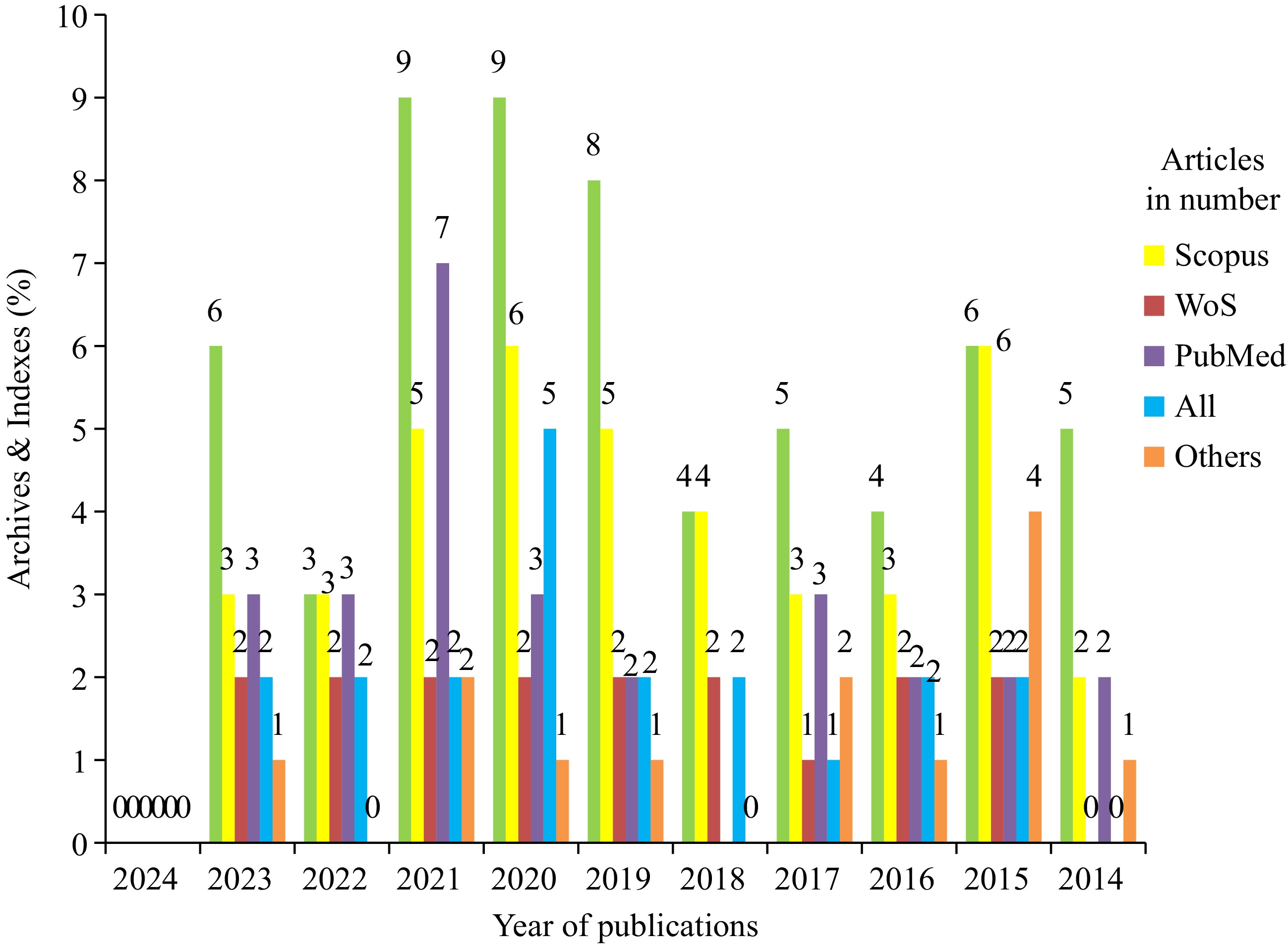
Figure 1.
Graphical representations portraying strategies for collecting articles related to sweet potato cultivation.
-
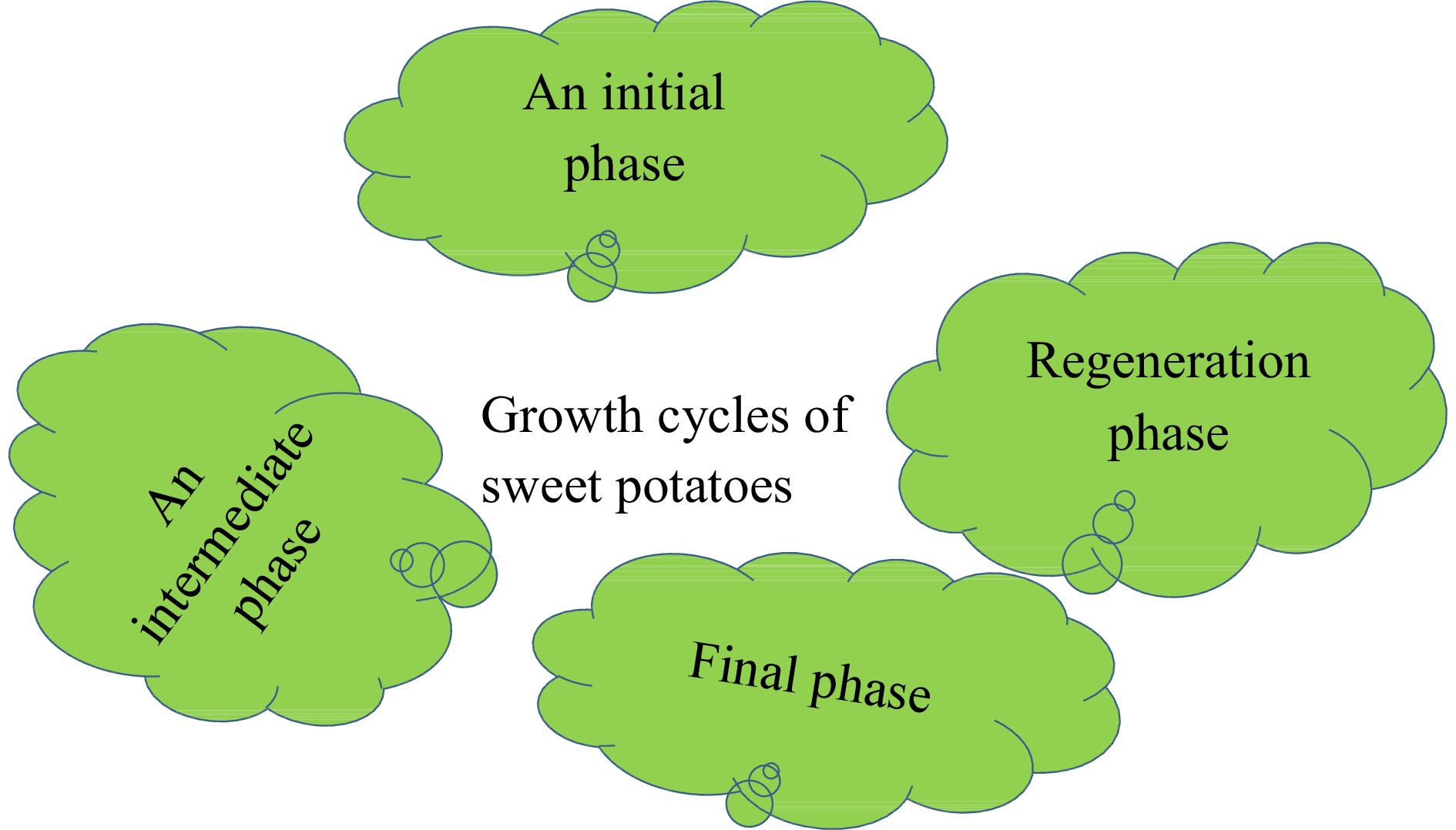
Figure 2.
Growth phases of sweet potato.
-
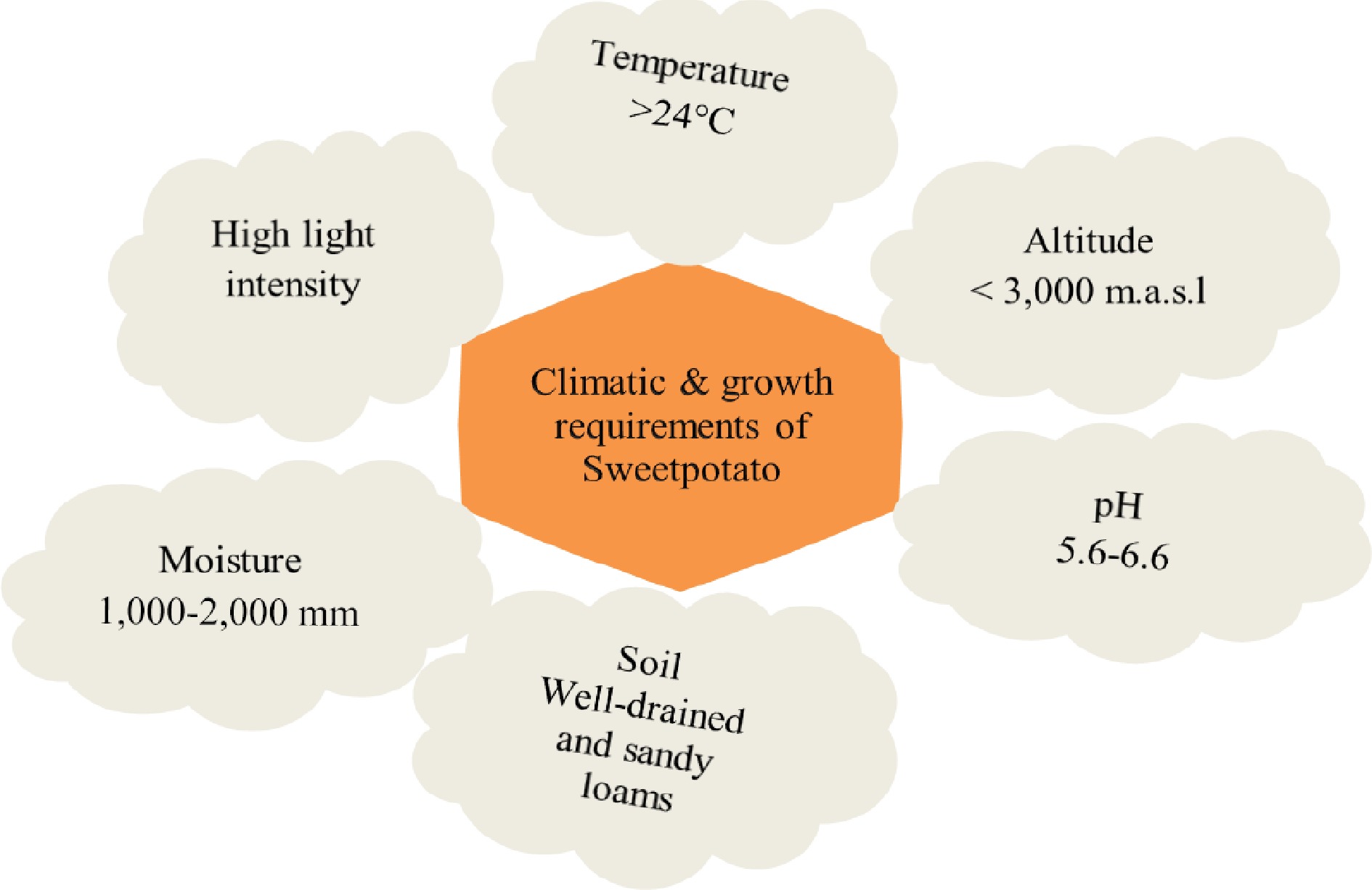
Figure 3.
Range of climatic conditions and growth needs for cultivating sweet potatoes.
-
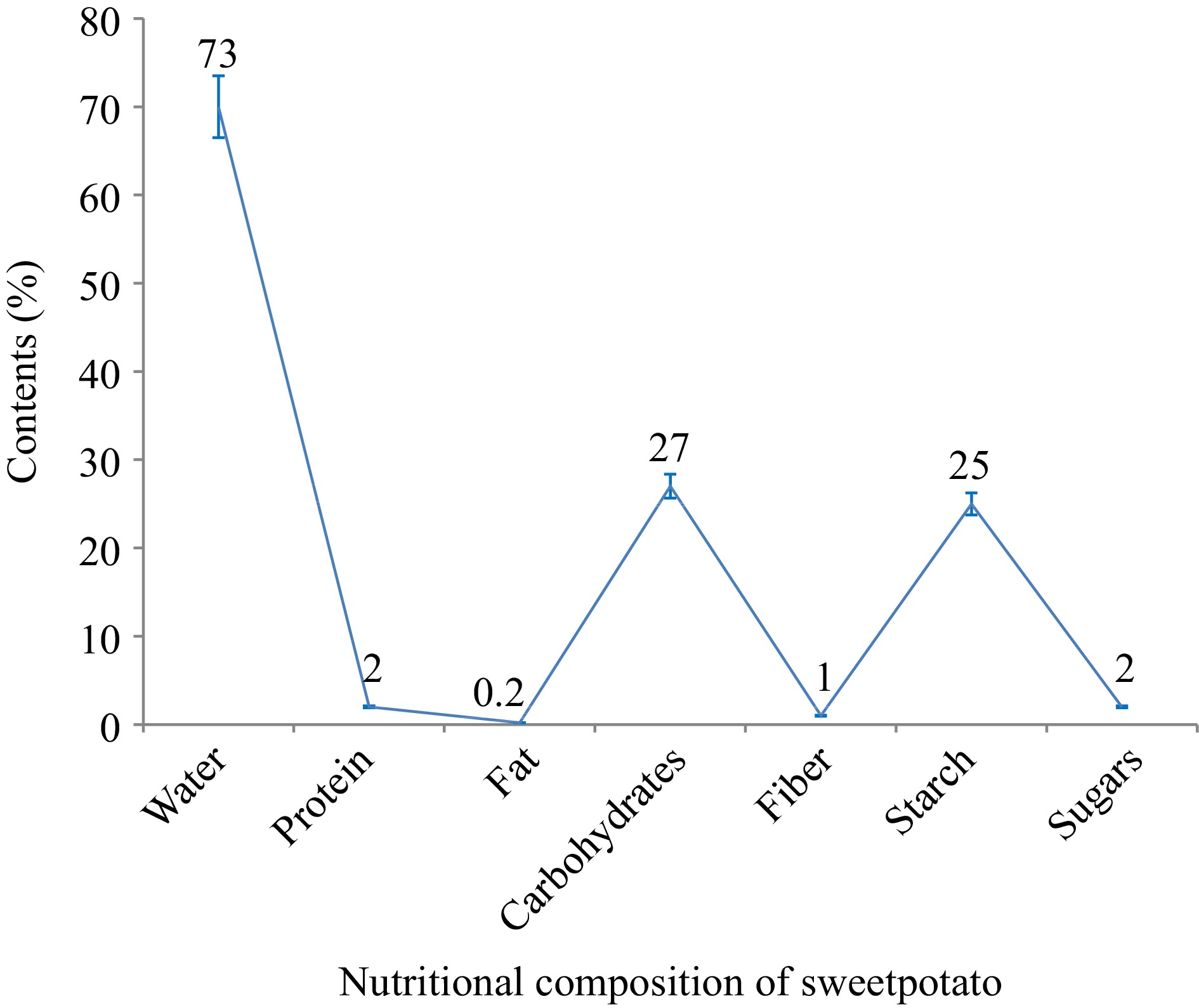
Figure 4.
Nutritional composition of sweet potato.
-
Advancing sweet potato cultivation and the descriptors in Ethiopia Ref. Enhancing food security Cultivating sweet potatoes, a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals, can help address food security challenges in Ethiopia by enhancing nutritional intake. [9] Diversification of diets Integrating sweet potatoes into diets diversifies nutrition, potentially mitigating malnutrition and associated health concerns. [44] Climate resilience Promoting the cultivation of resilient sweet potatoes in diverse Ethiopian regions can enhance climate change resilience. [45] Economic opportunities Cultivating sweet potatoes can generate income for rural farmers, especially where agriculture is predominant. [46] Soil health improvement Sweet potatoes enhance soil health by reducing erosion and boosting fertility through their root systems. [47] Livestock feed Utilizing sweet potato foliage and vines as livestock feed enhances animal health and productivity through their rich nutritional content. [48] Sustainable agriculture Sweet potato farming promotes sustainable practices by reducing reliance on chemicals and embracing agroecology. [49] Cultural significance Promoting sweet potato cultivation in Ethiopia preserves cultural heritage and boosts nutrition. [50] Market potential Promoting sweet potato cultivation meets rising demand, boosting agricultural incomes and exports. [46] Health benefits Sweet potatoes, rich in nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, may enhance immunity and reduce chronic disease risks. [51] Table 1.
Importance of cultivating and promoting sweet potatoes in Ethiopia.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(1)