-
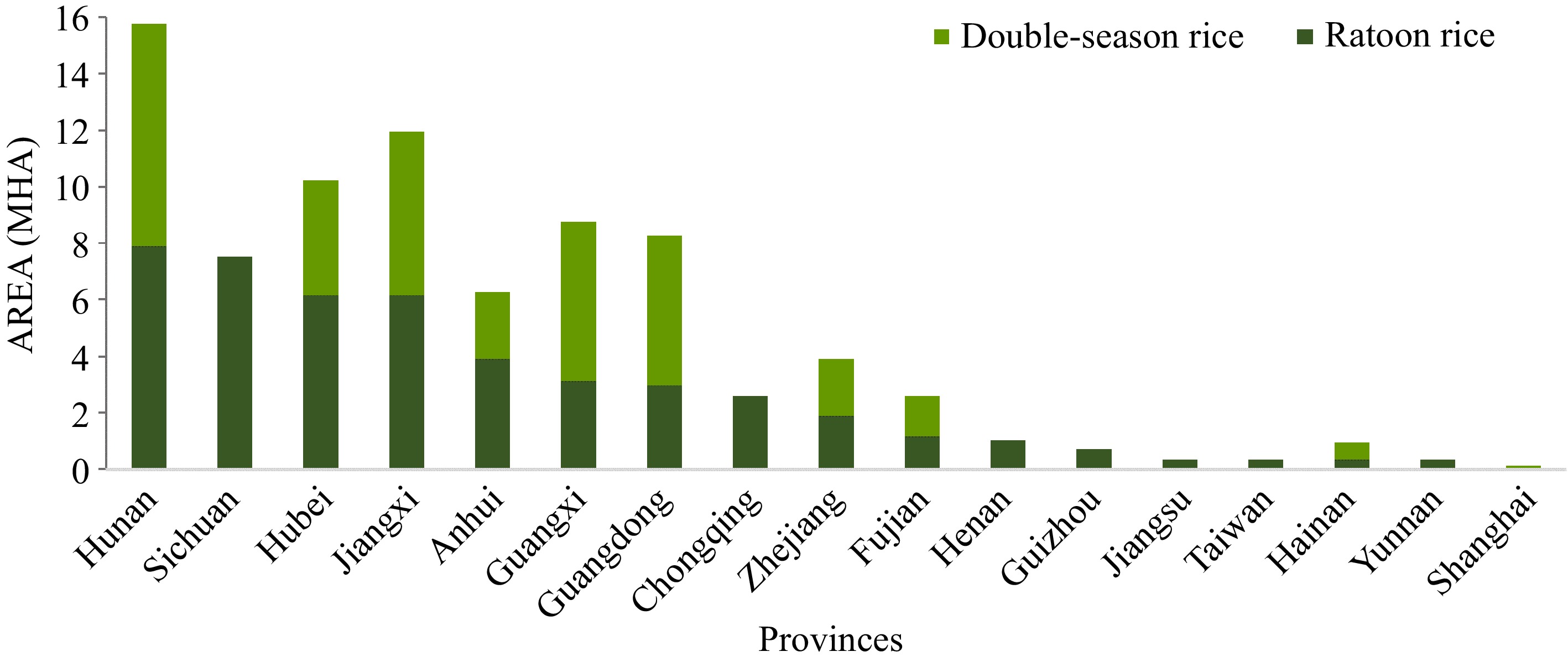
Figure 1.
Potential suitable regions and proportions for DR and RR: Area of DR and RR in each province[11].
-
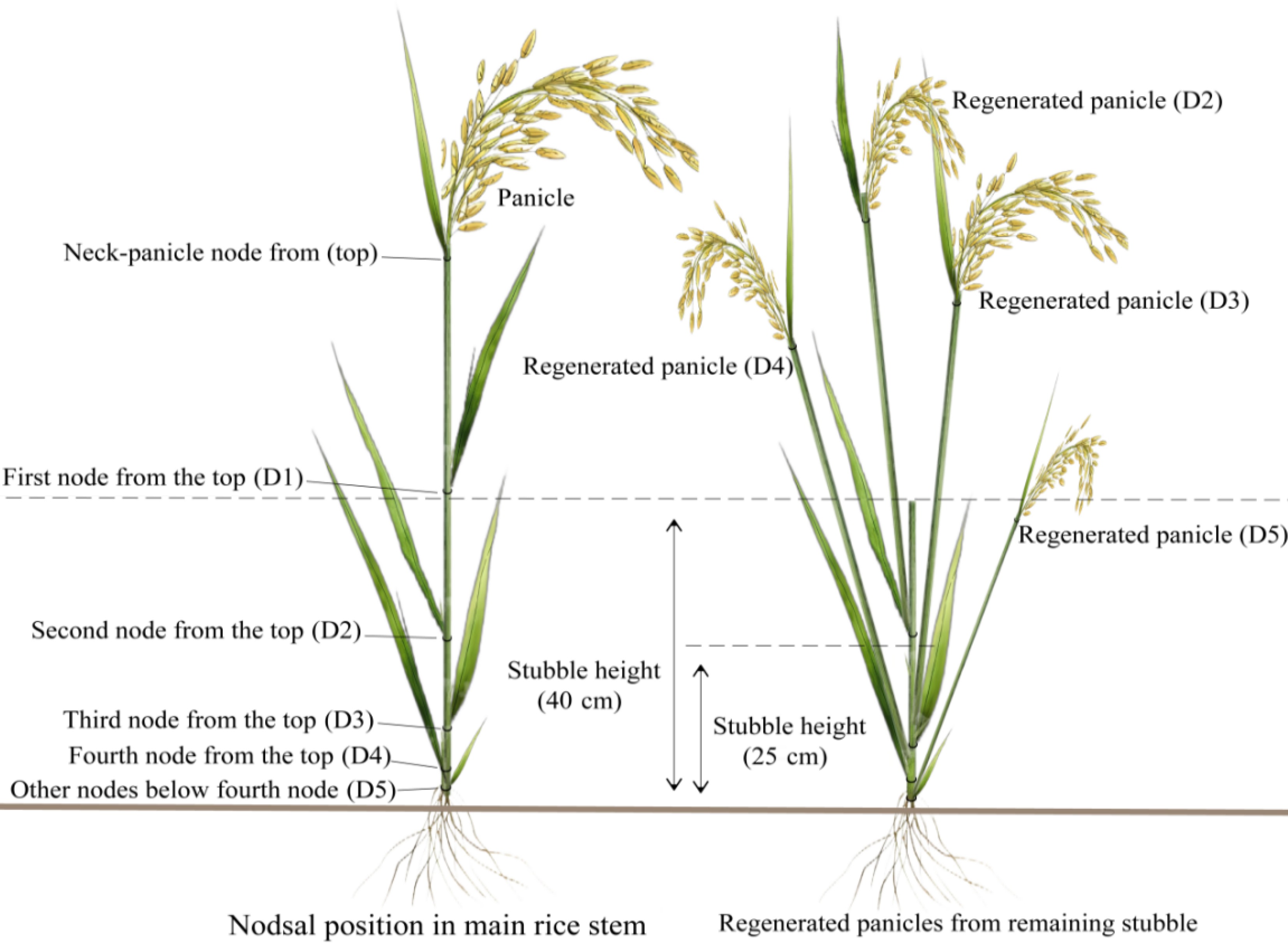
Figure 2.
Diagrams of the nodes and regenerated panicles in ratoon rice systems.
-
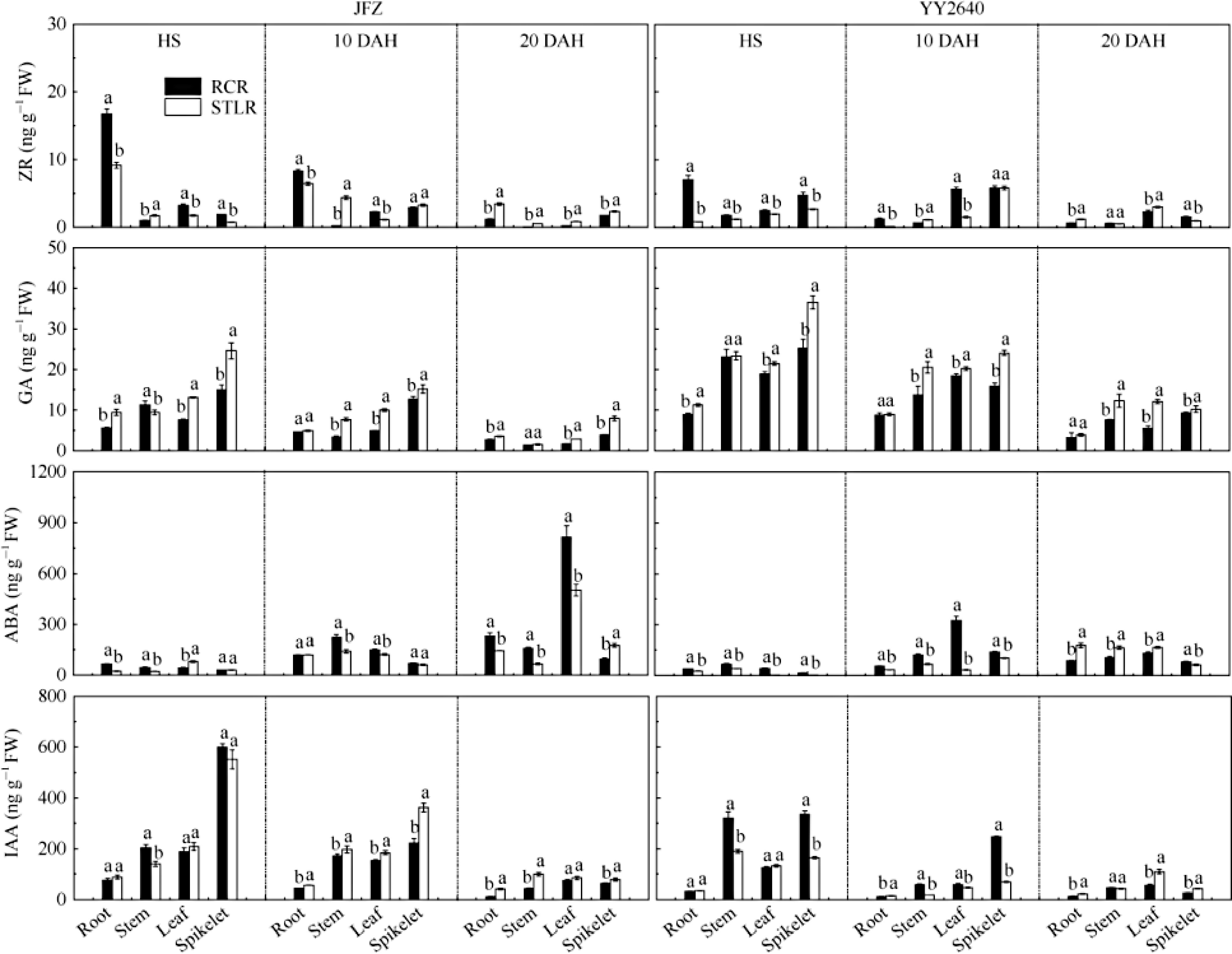
Figure 3.
Differences of hormone contents in roots, stems, leaves and spikelets of rice under different cropping patterns[37]. JFZ: conventional rice, Jiafuzhan; YY2640: hybrid rice, Yongyou 2640. RCR and STLR refer to ratooning rice and late rice with the same genotype of main crop synchronously heading with RR in late season. HS: heading stage. DAH: day after heading. Differences in lowercase or uppercase letters after each data in the same column in the same year indicate significant difference at the 0.05 or 0.01 probability levels, respectively.
-
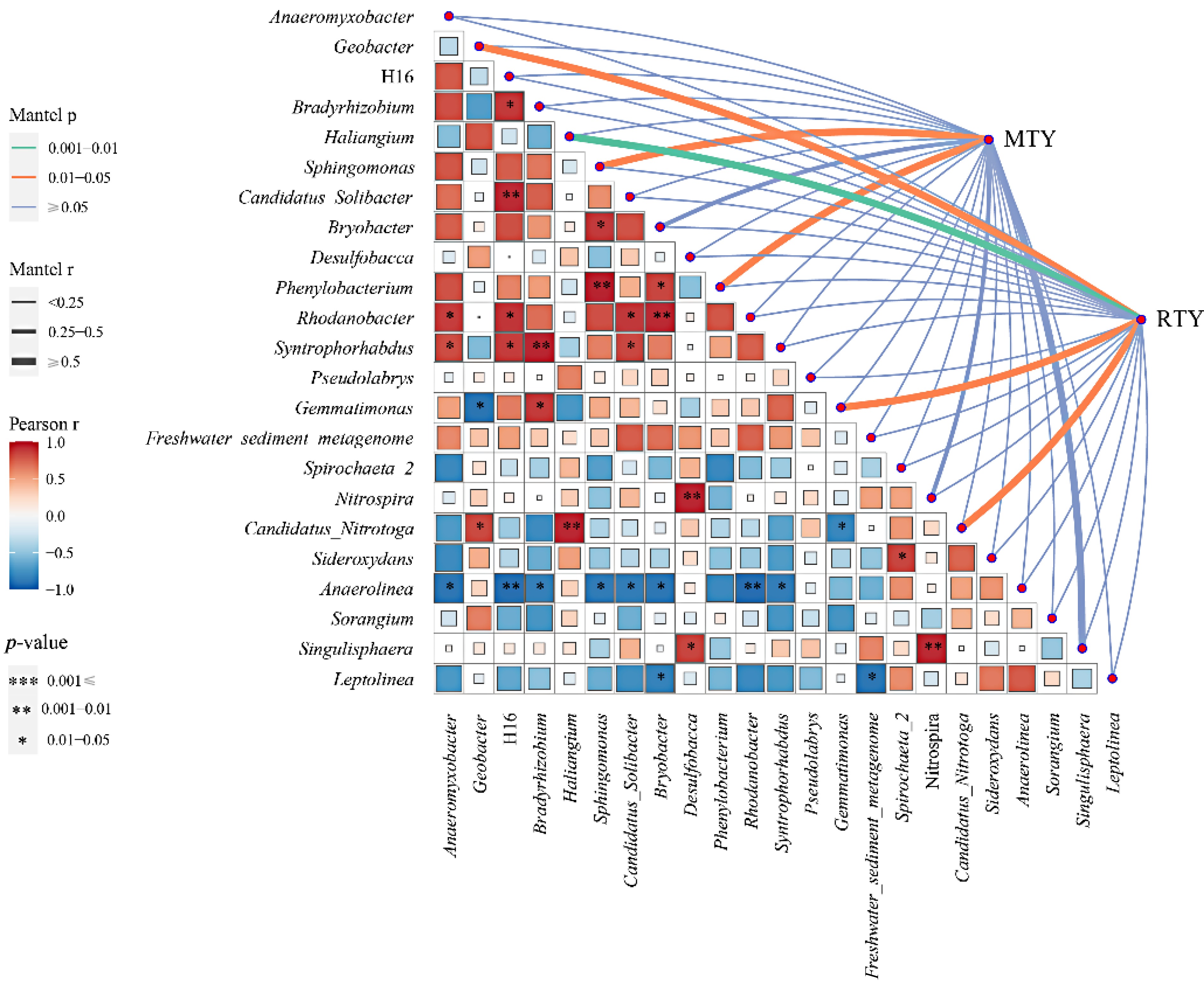
Figure 4.
The correlation analysis between the dominant bacteria at the mature stage of main crop rice and the yield of main crop rice and ratooning rice. MTY: main rice yield; RTY: ratooning rice yield[59].
-
Cultivar Allocated part Contents at full heading stage
(mg pot–1)Contents at maturity stage
(mg pot–1)The content difference of the same accessions at maturity and full heading stages (mg pot–1) RR LR RR LR RR LR JFZ 13C-soil 4.87 Ecd* 0.40 d 3.02 Cbc 2.75 Cc −1.84 Db 2.35 Db* 13C-roots 1.54 Ed 2.66 Ed* 0.44 Cc 4.33 Cc* −1.10 Db 1.67 Db* 13C-stubbles 4.11 Ecd − 1.30 Cc − −2.82 Db − 13C-stem-sheath 38.57 EAb* 34.42 Ab 9.31 Bb 20.95 Ab* −29.25 Ac −13.46 Ad* 13C-leaves 6.30 Ec 7.73 Ec* 3.33 Cc 5.36 Cc* −2.97 Db −2.36 Dc 13C-panicles 70.25 Ba* 48.35 Ba 102.26 Aa* 60.97 Ba 32.01 Aa* 12.62 Aa YY2640 13C-soil 3.35 Ec* 0.41 Ed 2.36 Cc* 1.30 Cc −0.99 Db 0.89 Db* 13C-roots 0.97 Ec 1.41 Ed 0.30 Cc 2.74 Cc* −0.68 Db 1.34 Db* 13C-stubbles 2.04 Ec − 0.91 Cc − −1.13 Db − 13C-stem-sheath 19.12 Db 20.53 Db* 9.13 Bb 16.39 Bb* −9.99 Cc −4.13 Cc* 13C-leaves 3.00 Ec 9.95 Ec* 1.88 Cc 4.05 Cc* −1.12 Db* −5.89 Cd 13C-panicles 89.07 Ca* 62.77 Ca 104.93 Aa* 70.22 Ba 15.87 Ba* 7.46 Ba RR: ratooning rice. LR: late rice synchronously heading with RR. Different letters (lowercase or uppercase) in the same column of the same cultivar have significant difference at the 0.05 or 0.01 probability levels among the different allocated parts at ratooning season under the same nitrogen application treatment. * indicates significant difference at the 0.05 probability level between different nitrogen application treatments at the same allocated part in the ratooning season. Table 1.
Contents of 13C assimilates of rice plant organs and soil in different cropping patterns[37].
Figures
(4)
Tables
(1)