-
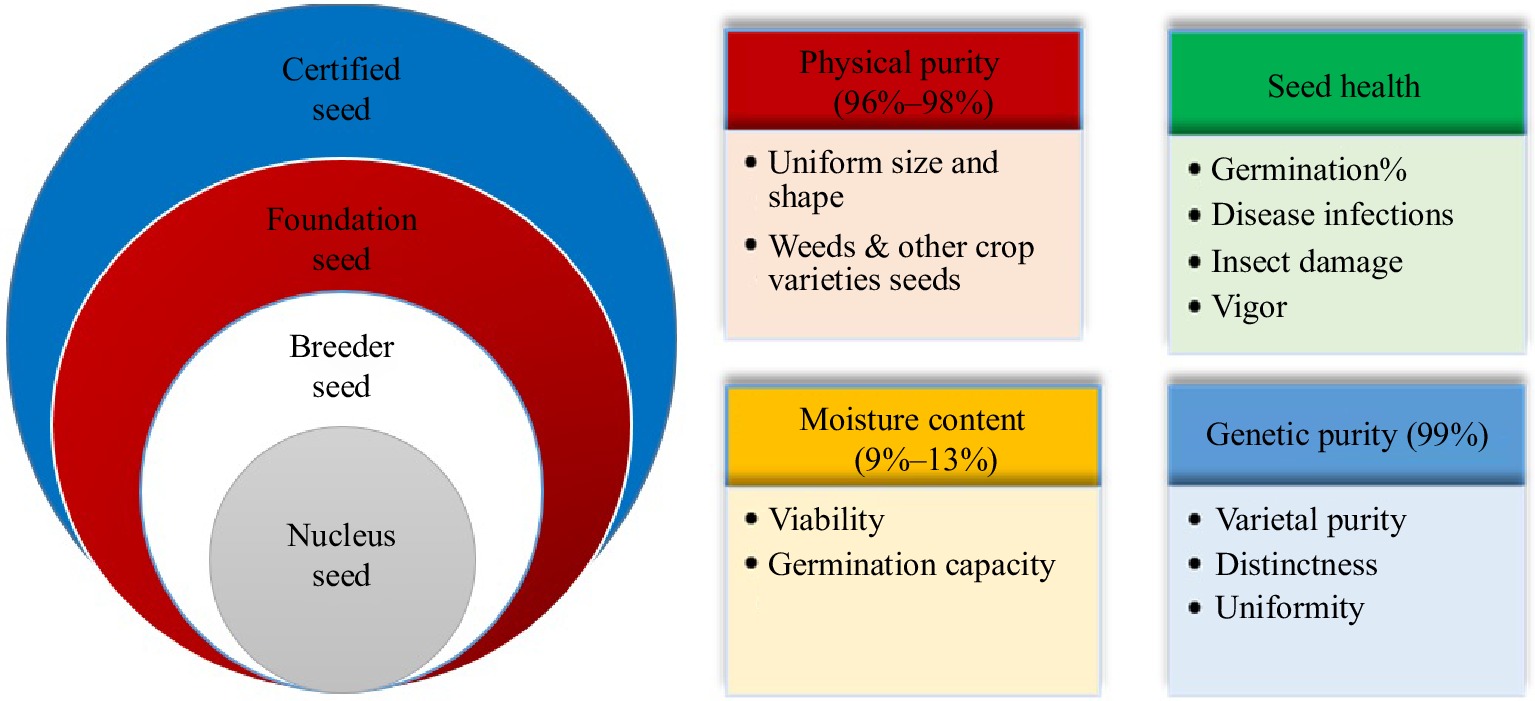
Figure 1.
The characteristics that are evaluated in different seed classes during seed certification process.
-
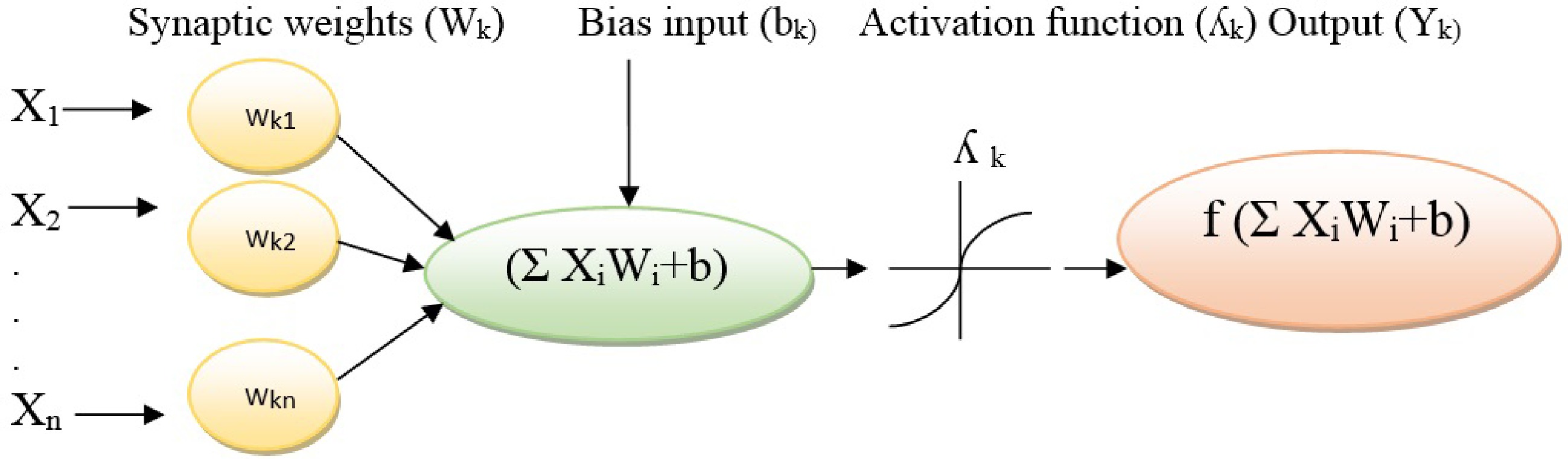
Figure 2.
A schematic illustration of an artificial neuron.
-
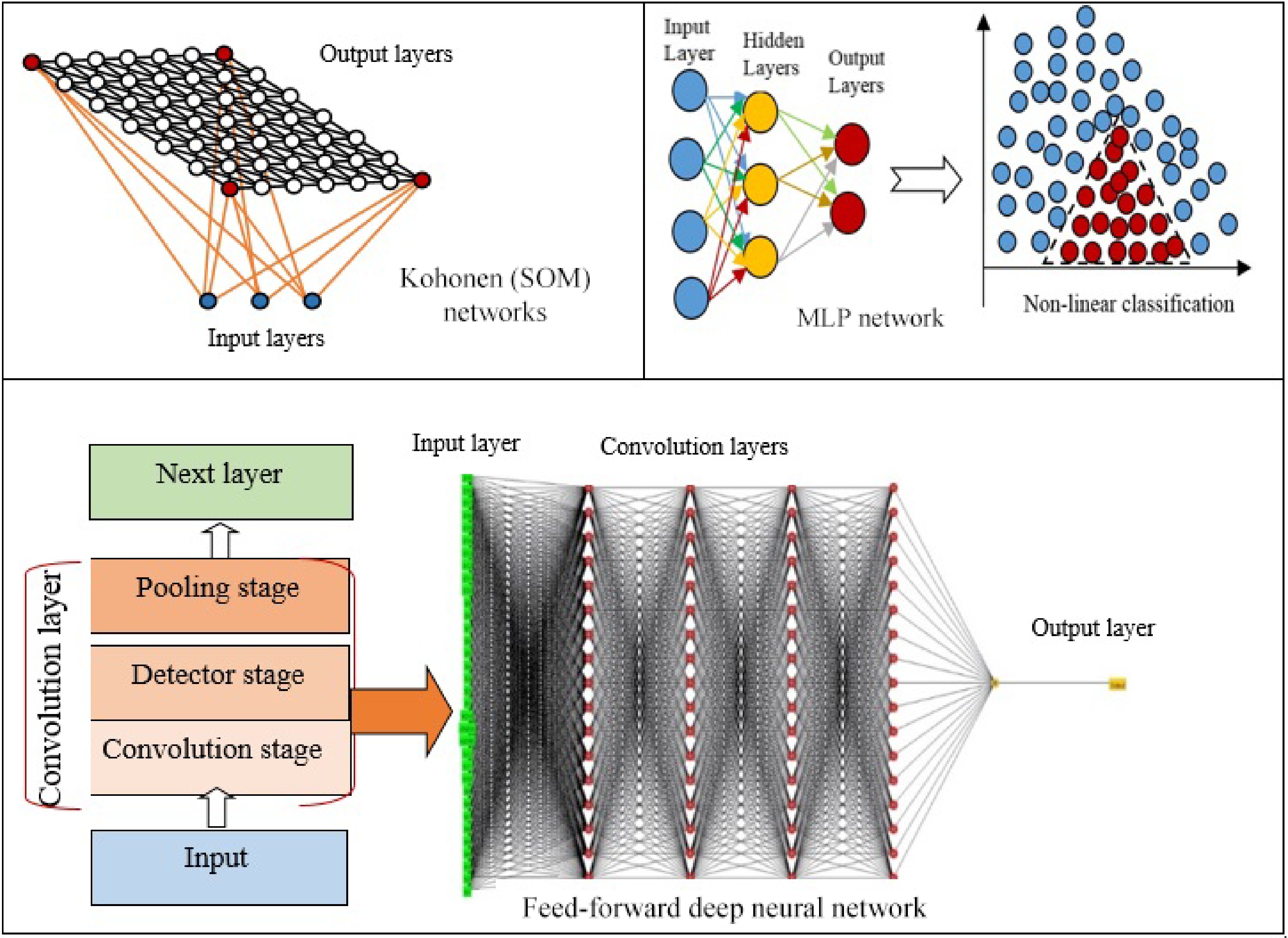
Figure 3.
ANNs algorithms from old to new versions.
-
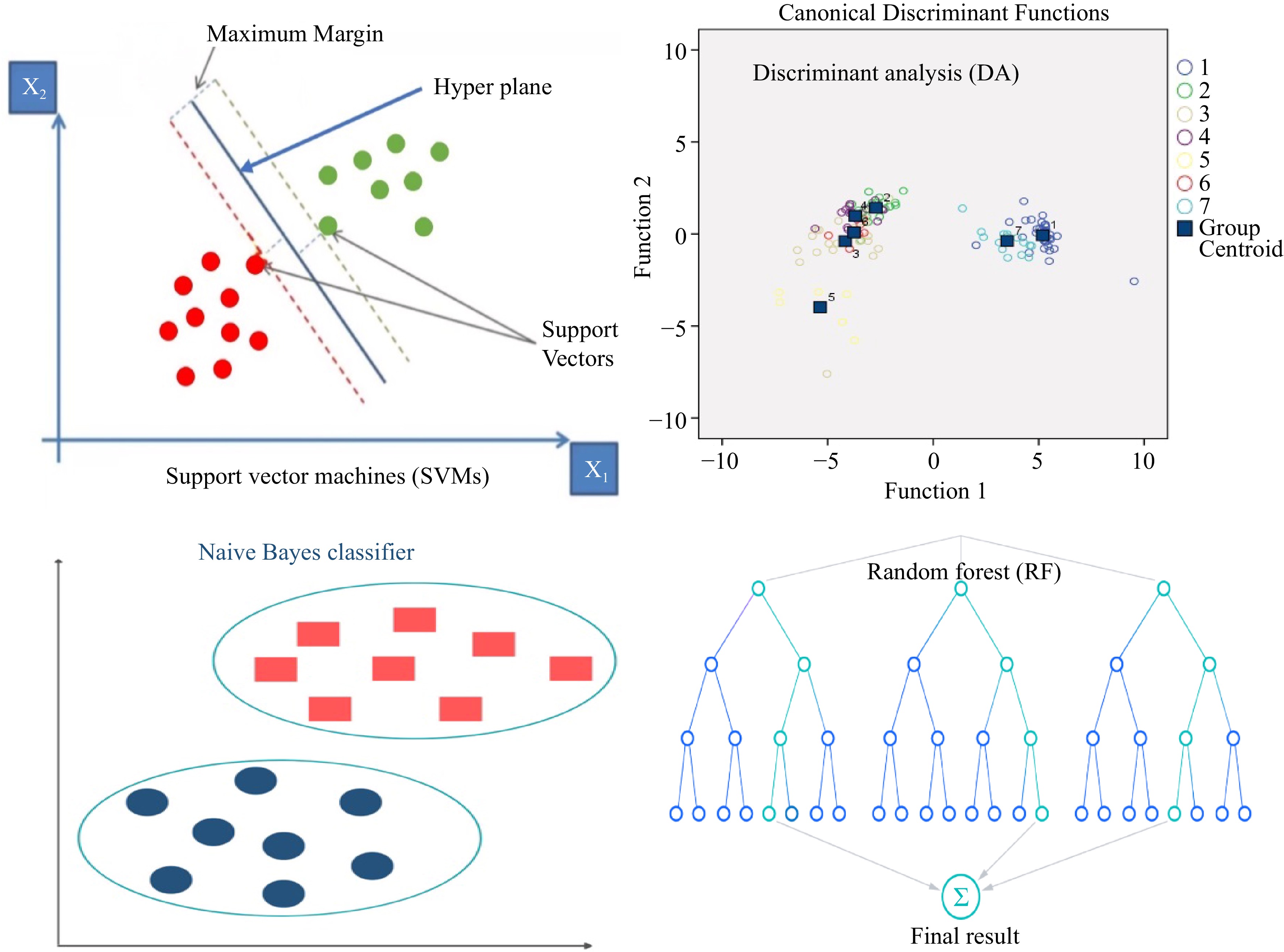
Figure 4.
Schematic views of SVMs, DA, NB and RF algorithms.
-
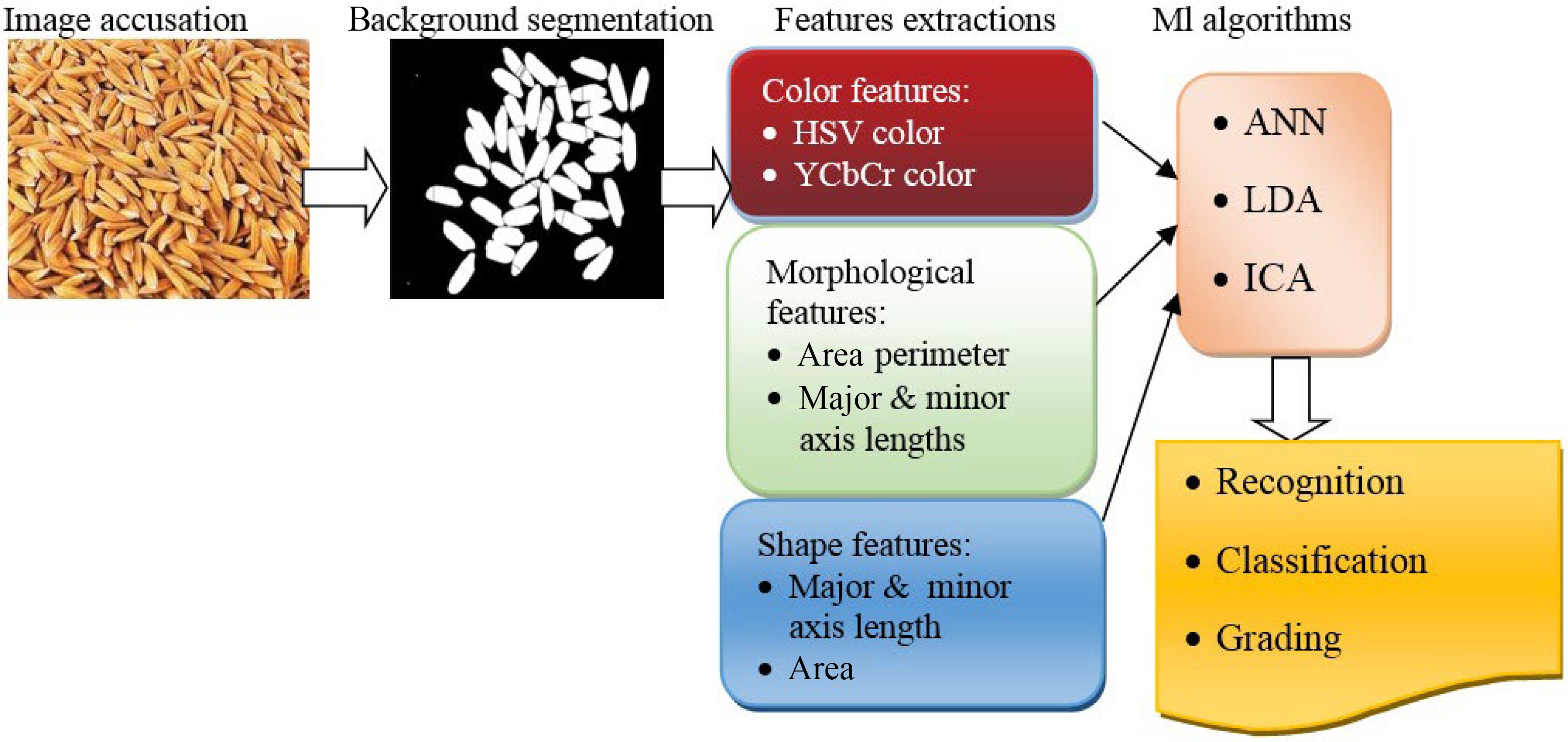
Figure 5.
Schematic views of ML applications in seed recognition, classification and grading.
-
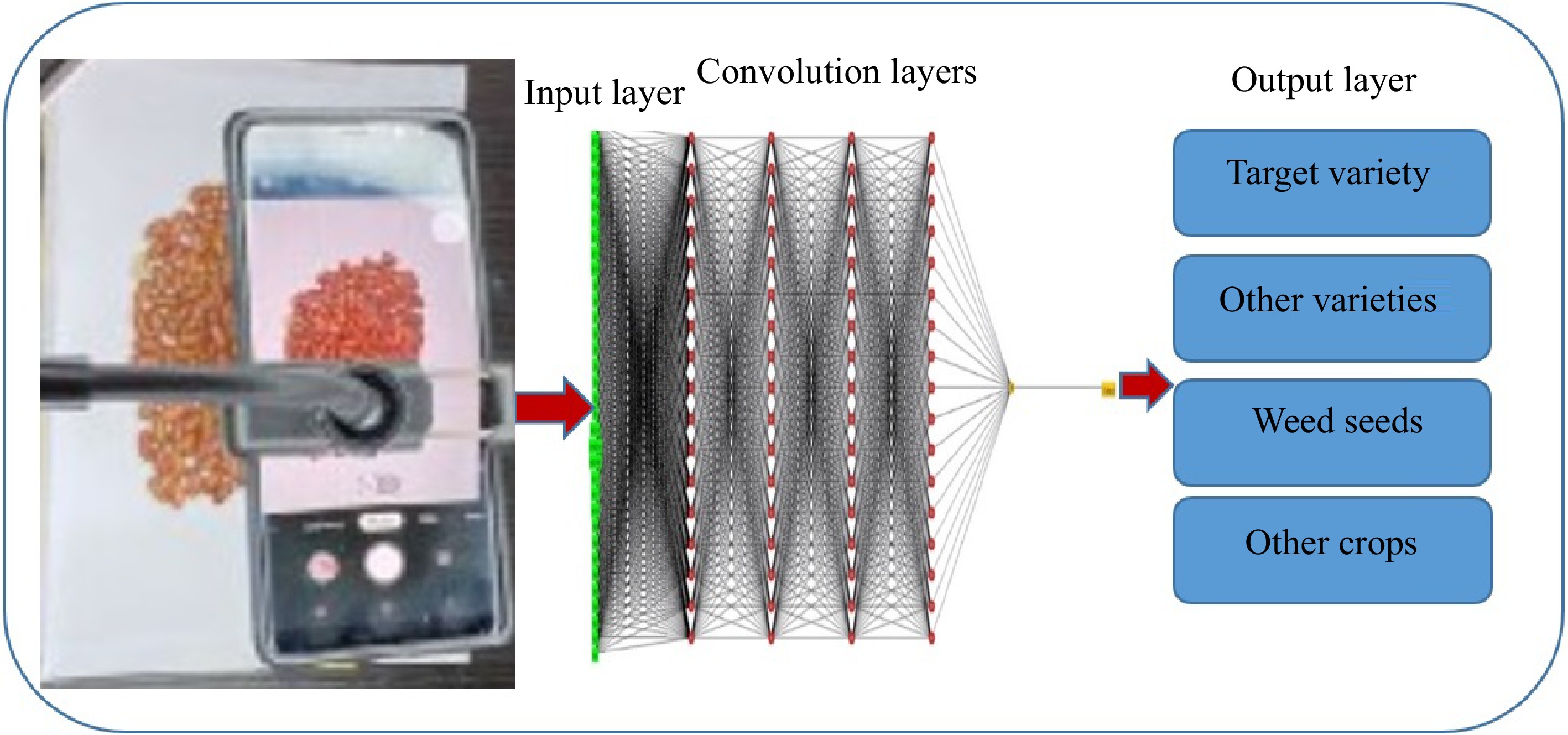
Figure 6.
Schematic illustration of weed seeds identification in seed lots by ANN.
-
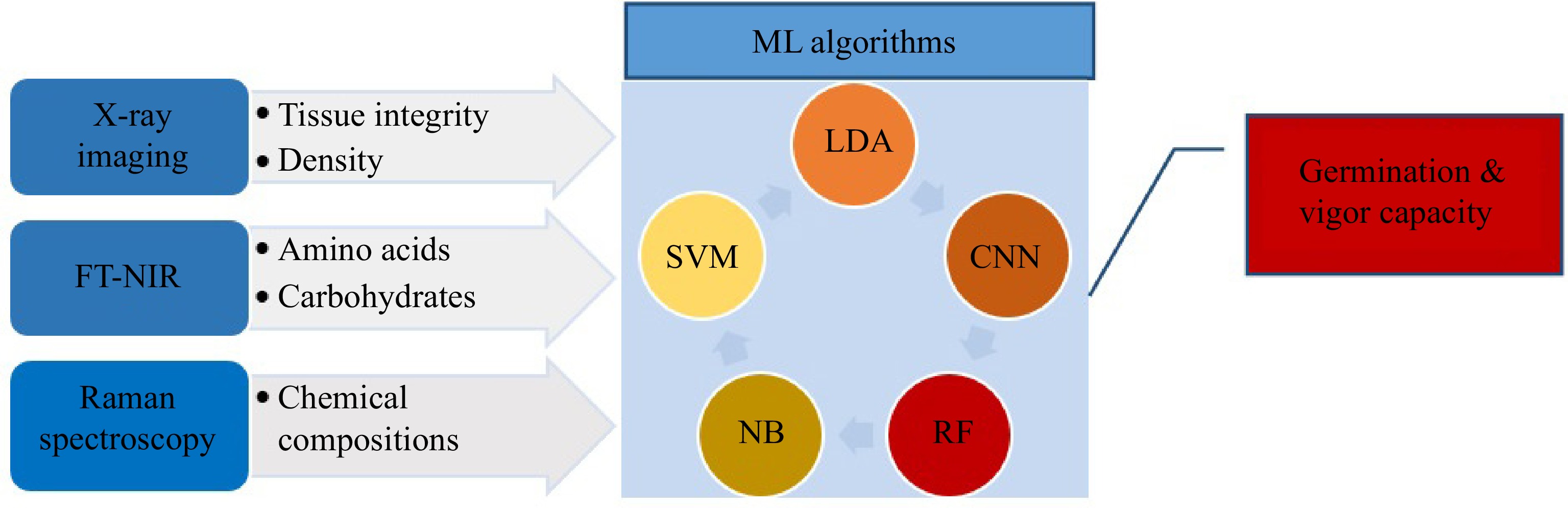
Figure 7.
application of ML models in seeds' viability.
-
ML algorithms SOM MLP DA SVMs RF NB CNNs Accuracy + +++ ++ ++++ +++++ +++ ++++++ Flexibility + ++ + +++ ++++ +++ ++++++ Advantages Fast Non-linear classification Quick, inexpensive Analyzing complex networks, diminishing the generalization error, using large number of hidden units Tolerant of
highly correlated predictorsSimplicity,
fast training, decreases the number of parametersAnalysis of massive
amounts of
unsupervised data, better classification
and predictionDisadvantages Unsupervised Time-consuming, few hidden neurons Unsupervised Algorithmic complexity, development of ideal classifiers for multi-class problems and unbalanced data sets Evaluation
of pairwise interactions is difficult, future predictions require the original dataOversensitive
to redundant
or irrelevant attributes, classification
biasIt needs further developments
for big data
analysisTable 1.
Comparisons among ML algorithms.
-
Plant species Type of machine learning Classifier Accuracy Features Purpose Ref. Corn Digital image MLP 98.83% Texture - spectrum hybrid Seed varietal purity [10] Wheat Digital image ANNs 85.72% Morphology Seed varietal purity [7] Wheat Digital image ICA-ANN hybrid 96.25% Color, morphology,
and textureSeed varietal purity [72] Wheat Digital bulk image LDA 98.15% Texture Seed varietal purity [37] Wheat Digital bulk image ANNs 97.62% Texture Seed varietal purity [73] Forage grass (Urochloabrizantha) FT-NIR spectroscopy & X-ray imaging RF 85% Spectrum-composition hybrid Seed germination & vigor [74] Corn FT-NIR spectroscopy PLS-DA 100% Chemical composition Seed germination & vigor [75] Pepper FT-NIR & Raman spectroscopy PLS-DA 99% Chemical composition Seed germination & vigor [76] 57 weed species Digital image NB & ANNs 99.5% Color, morphology,
and textureWeed identification [59] Wheat Video processing ANN - PSO hybrid 97.77% Shape, texture & color Physical purity & weed identification [77] Rice Digital image MLP 99.46% Morphology, texture & color Seed varieties classification [9] Rice Digital image ANNs − Morphology Seed grading [78] Rice Digital image DFA 96% Morphology Physical purity [79] Soybean Aerial imagery CNNs 65% Object detection Weed identification [80] Soybean Digital image CNNs 97% Color, texture and shape Seed deficiency [66] Soybean Digital image CNNs 86.2% Color, texture and shape Seed counting [70] Corn Digital image MLP 94.5% Color Physical purity [81] Soybean Flatbed scanner SVMs & RF 78% Color Seed grading [47] Bean Digital image RF 95.5% Color, texture and shape Seed varieties classification [16] Corn Hyperspectral image SVMs 98.2% Spectrum-texture – morphology hybrid Seed varieties classification [48] Corn Digital image SVMs 95.6% Color and texture Seed varieties classification [49] Corn Digital image GA–SVM hybrid 94.4% Color, texture and shape Seed varieties identification [50] Corn Digital image CNNs 95% Color, texture and shape Haploid and dioploid discrimination [82] Corn Digital image CNNs 95% Color, texture and shape Seed varieties identification [83] Barley Digital image DA & K-NN 99% Color, morphology & texture Seed varieties classification [8] Barley Digital image CNNs 93% Color, morphology & texture Seed varieties classification [84] MLP: Multilayer Perceptron, ICA: Imperialist Competitive Algorithm, ANNs: Artificial Neural Networks, LDA: linear discriminate analysis, FT-NIR: Fourier transform near-infrared, PLS-DA: partial least squares discriminant analysis, NB: naïve Bayes, PSO: partial swarm optimization, DFA: stepwise discriminant function analysis, CNNs: Convolutional neural networks, SVM: support vector machine, GA: genetic algorithm, DA: discriminant analysis, K-NN: K-nearest neighbors, SVMs: support vector machines. Table 2.
Examples of applied machine learning models in modern seed recognition and classification studies.
Figures
(7)
Tables
(2)