-
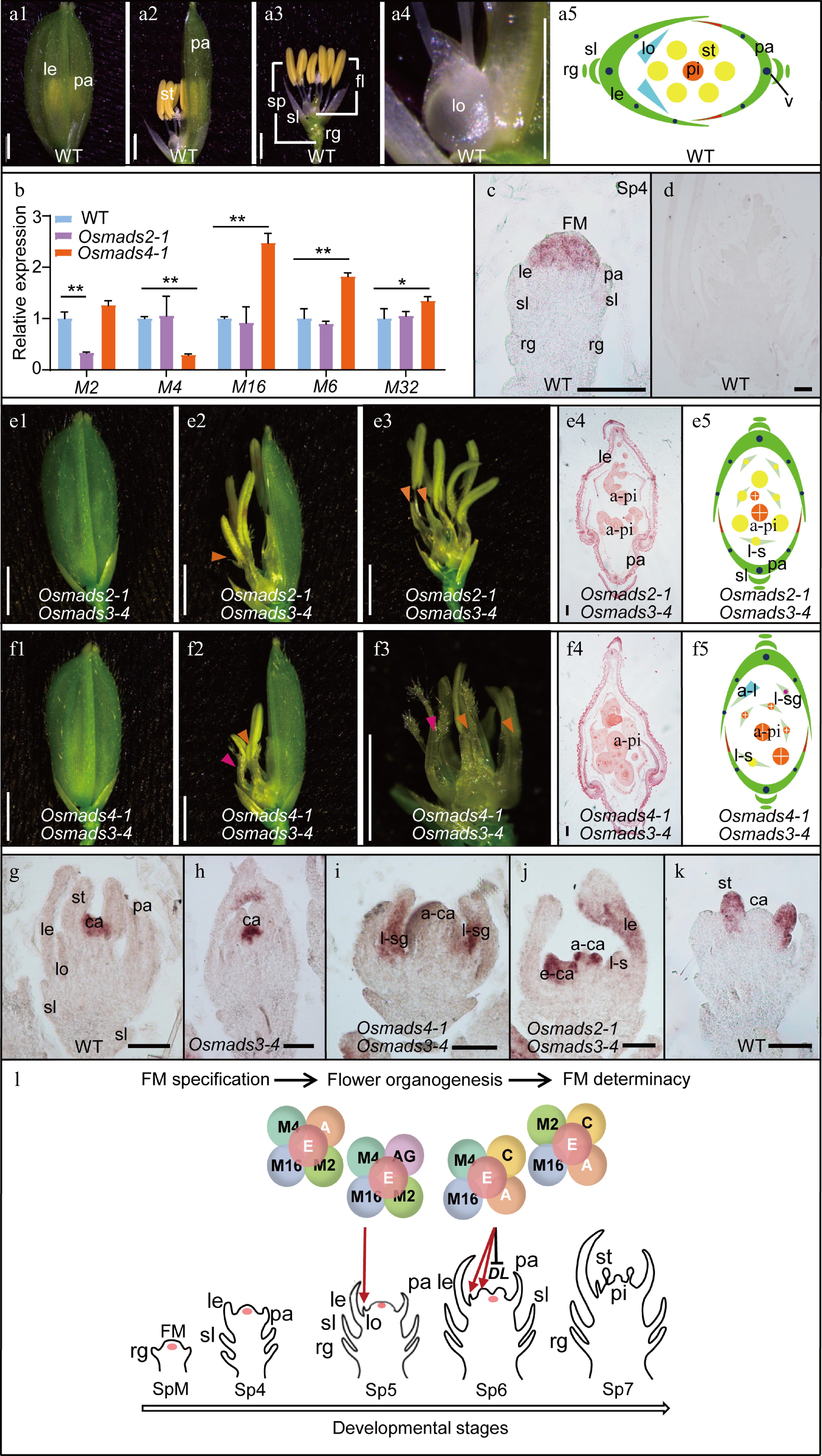
Figure 1.
OsMADS2 and OsMADS4 play partially distinct roles in lodicule and stamen specification. (a) Spikelet morphology (a1−a4) and cartoon diagram (a5) of Wild Type (WT). (b) Expression level of the B-class genes (OsMADS2, OsMADS4 and OsMADS16), OsMADS6 and OsMADS32 in the 2-mm inflorescence of WT, Osmads2-1 and Osmads4-1. Results are shown as mean ± SD. Error bars indicate SD for three biological replicates. ** indicates p-values < 0.01, * indicates P-values between 0.05 to 0.01, analyzed by Student-t test. (c), (d) In-situ hybridization analysis of OsMADS4. In the WT, signals for the anti-sense probe were detected in FM (c), whereas no signals for the sense probe were detected (d). Spikelet morphology (1−3), transverse section (4) and cartoon diagram (5) of the (e) Osmads2-1 Osmads3-4 and (f) Osmads4-1 Osmads3-4 double mutants. (g)−(j) In-situ hybridization analysis of DL in WT, Osmads3-4, Osmads4-1 Osmads3-4 and Osmads2-1 Osmads3-4, respectively. (k) In-situ hybridization analysis of OsMADS4 in WT. (l) A working model of the function of OsMADS2 and OsMADS4 in regulating rice flower development. OsMADS2 and OsMADS4 may engage with different protein complexes in specifying lodicule and stamen identity and morphogenesis. To specify lodicule identity, OsMADS2 and OsMADS4 play partially redundant roles in forming a complex with OsMADS16, the A-class proteins, AGL6-like proteins, and/or E-class proteins. OsMADS2 plays an additional role in regulating lodicule morphogenesis. On the other hand, OsMADS4 may form a protein complex with OsMADS16, and C-, A- and E-class proteins to determine stamen identity. OsMADS4 has a specific role in inhibiting the expression of DL in the lodicule and stamen to specify their identity and morphogenesis. Orange arrowheads in (e) and (f) indicate lodicule-stamen mosaic organs; Rose arrowheads in (e) indicate lodicule-stigma mosaic organ. a-ca, abnormal carpel; a-pi, abnormal pistil; e-ca, ectopic carpel; fl, floret; FM, floral meristem; le, lemma; lo, lodicule; l-s, lodicule-stamen mosaic organ; l-sg, lodicule-stigma mosaic organ; pa, palea; pi, pistil; rg, rudimentary glume; sl, sterile lemma; sp, spikelet; st, stamen. Scale bars = 2 mm in a1 to a4, e1 to e3 and f1 to f3; scale bars = 100 μm in e4 and f4; and scale bars = 50 μm in g to k. Red arrows in l indicate positive regulation in flower organ identity specification. The black bar in l indicates negative regulation. A, A-class proteins; AG, AGL6-like proteins; C, C-class protein; E, E-class proteins; SpM, spikelet meristem. M is the abbreviation of OsMADS; DL, DROOPING LEAF. Sp refers to a developmental stage of rice spikelet.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(0)