-
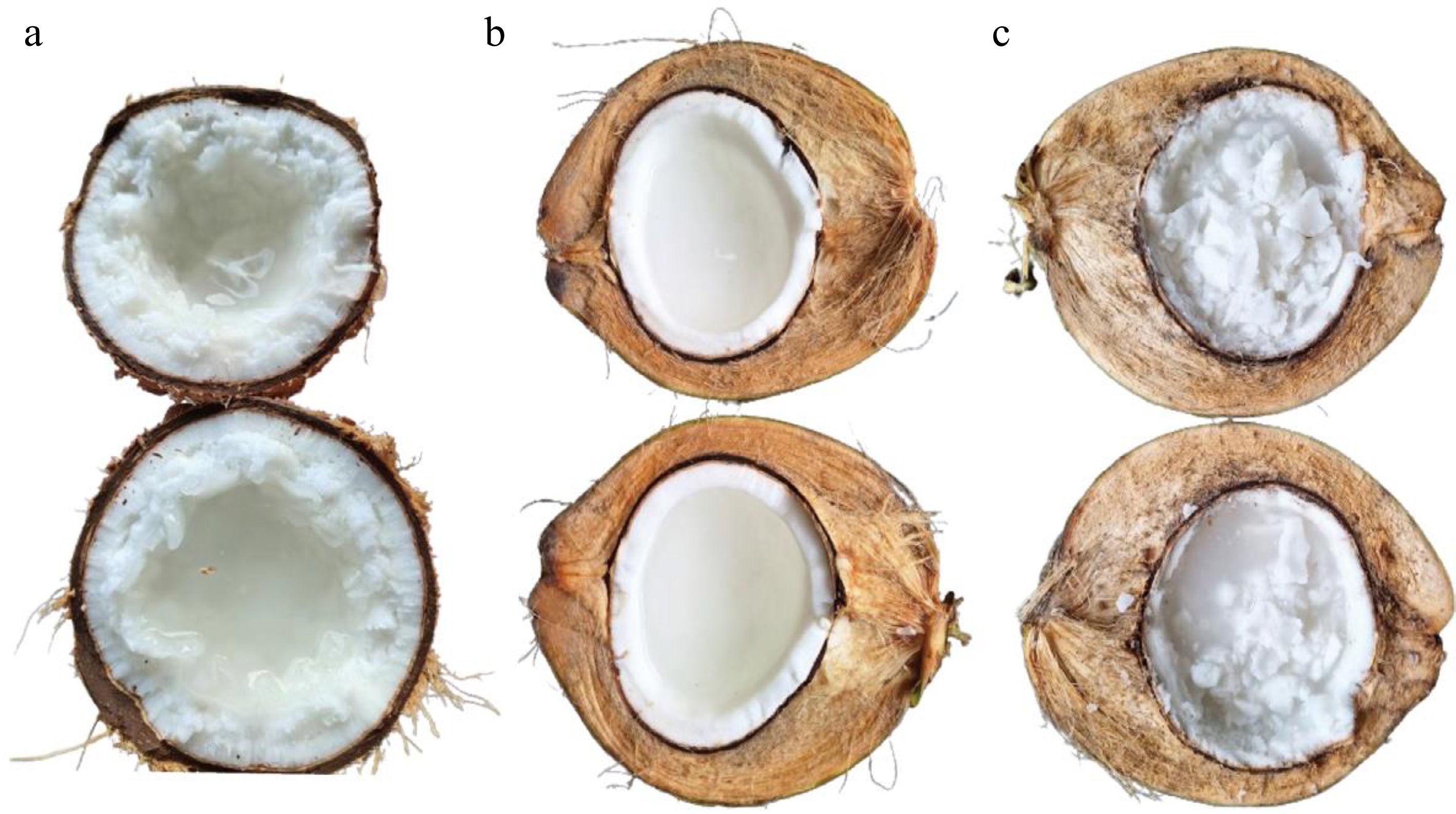

Figure 1.
The comparison between normal coconut and makapuno coconut. (a) Fruit of Thai makapuno coconut with jelly-like liquid endosperm, (b) fruit from normal tall coconut variety, (c) special makapuno variety from Indonesia called kopyor.
-
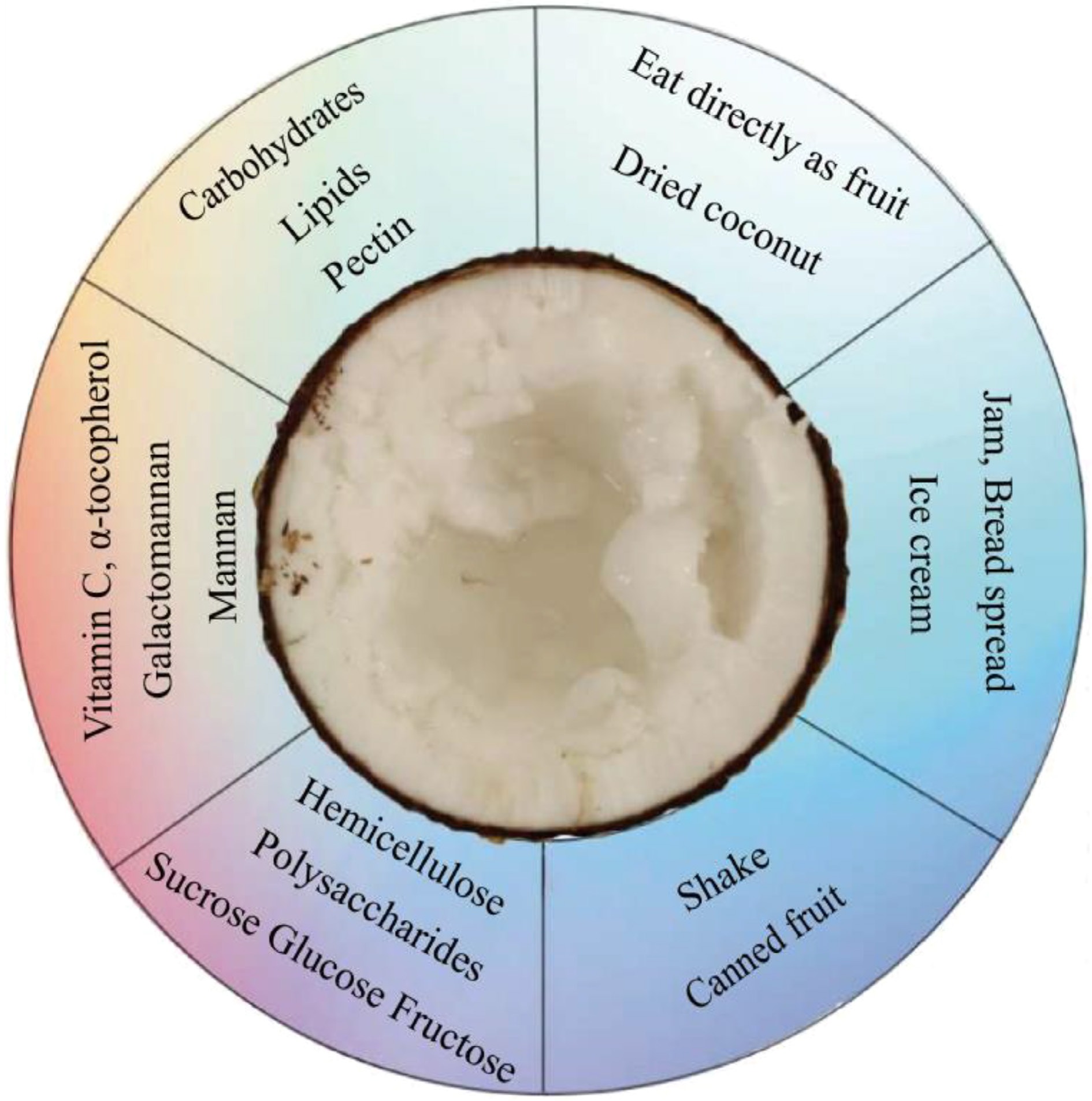
Figure 2.
Nutritional value of makapuno coconut.
-
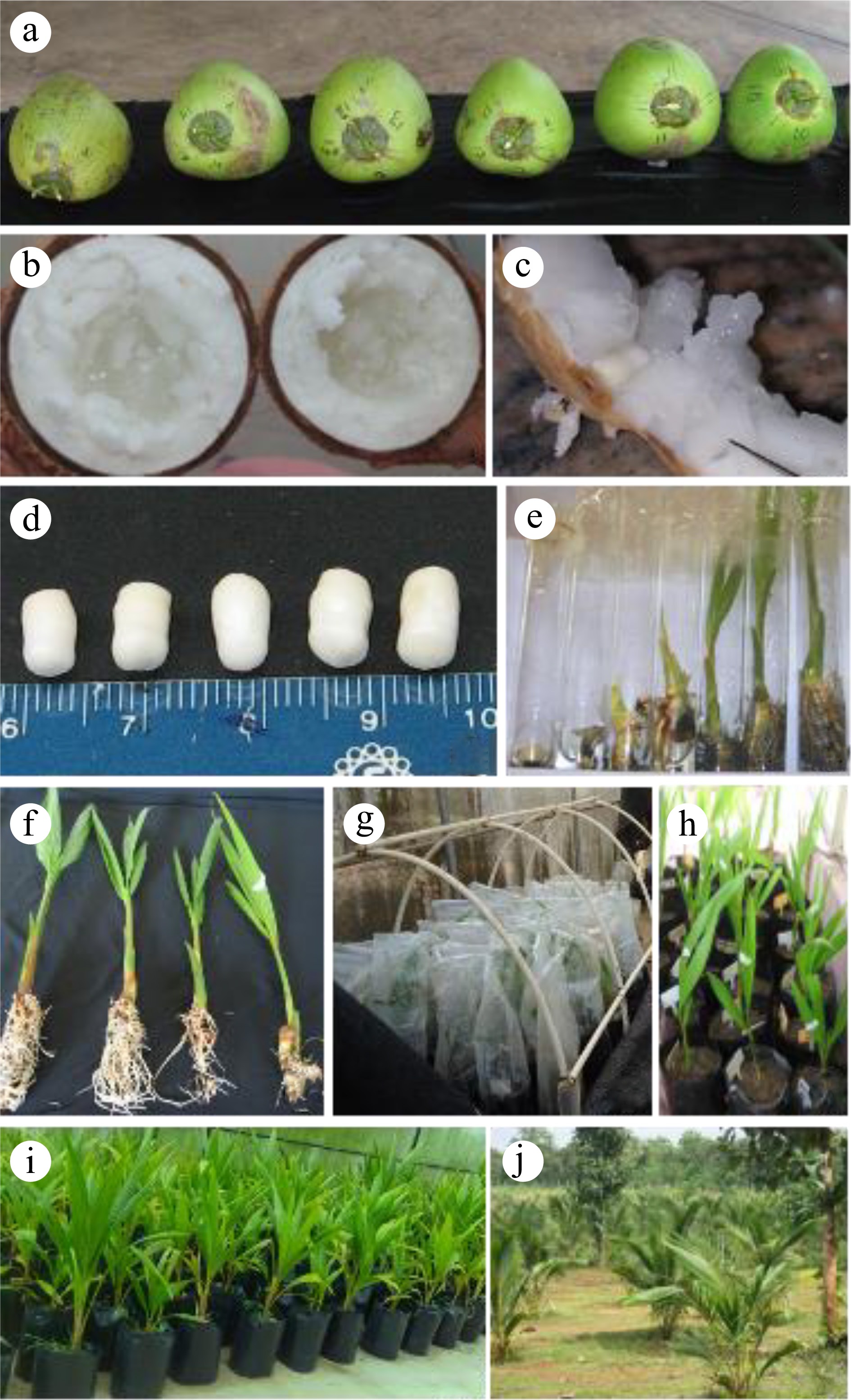

Figure 3.
Makapuno coconut propagation methods (Sri Lanka). (a) Mature dikiri nuts at 11−12 months postpollination, (b) dikiri kernel, (c) extraction of dikiri embryo, (d) dikiri embryos taken from kernel, (e) dikiri plantlets from embryo culture at different stages, (f) plantlets at growth stages 7−8-month in vitro period, (g) initial acclimatization in polybags, (h) potted plants, (i) fully acclimatized plants ready for selling, (j) field establishment of dikiri plants in Coconut Research Institute, Sri Lanka.
-
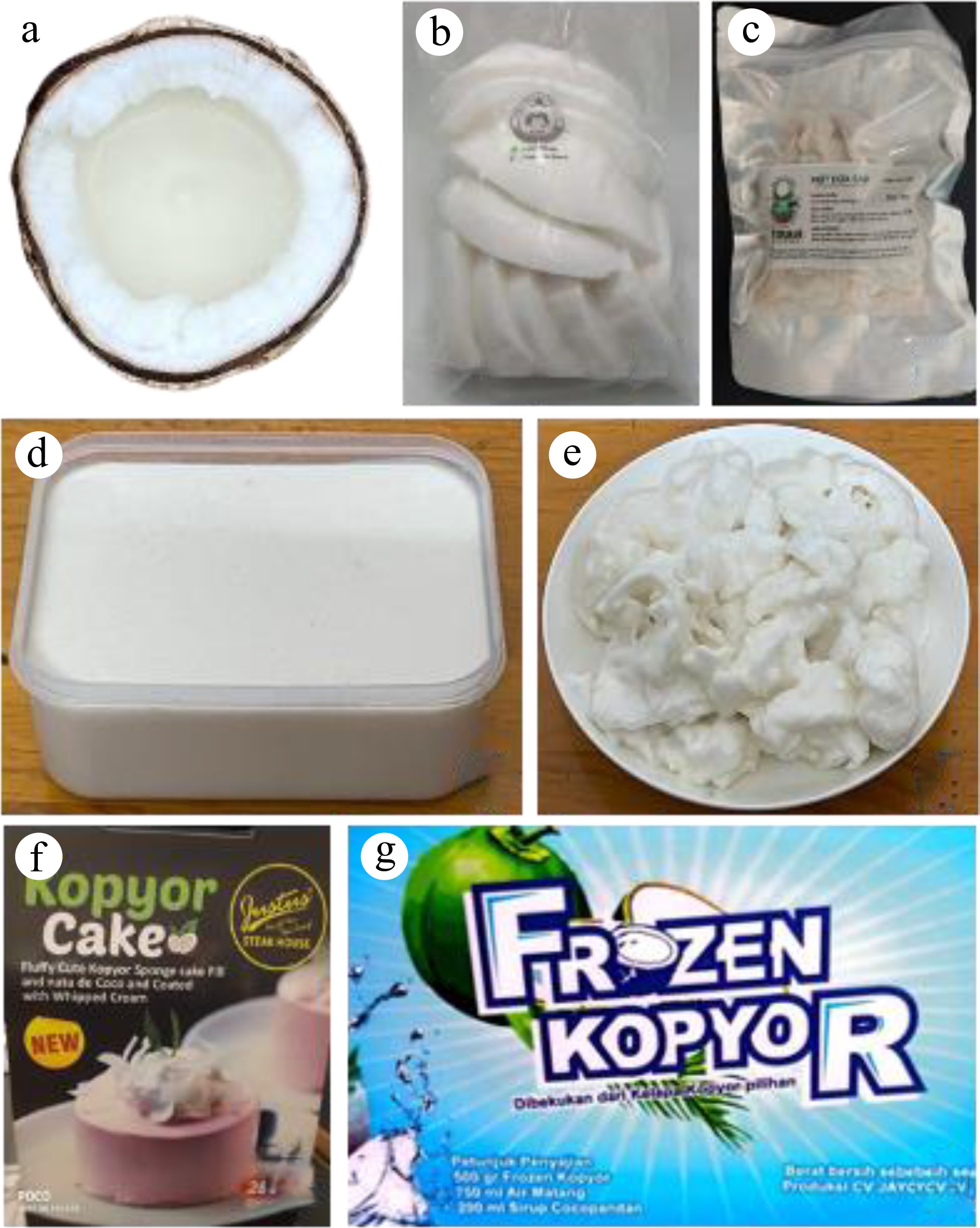

Figure 4.
Makapuno coconuts and the products derived from them. (a) Freshly cracked makapuno coconut, (b) packed makapuno flesh from Thailand, (c) makapuno sweetmeat from Vietnam, (d) jelly made from makapuno liquid endosperm, (e) homemade makapuno ice cream, (f) kopyor cake from Indonesia, (g) frozen kopyor endosperm from Indonesia.
-
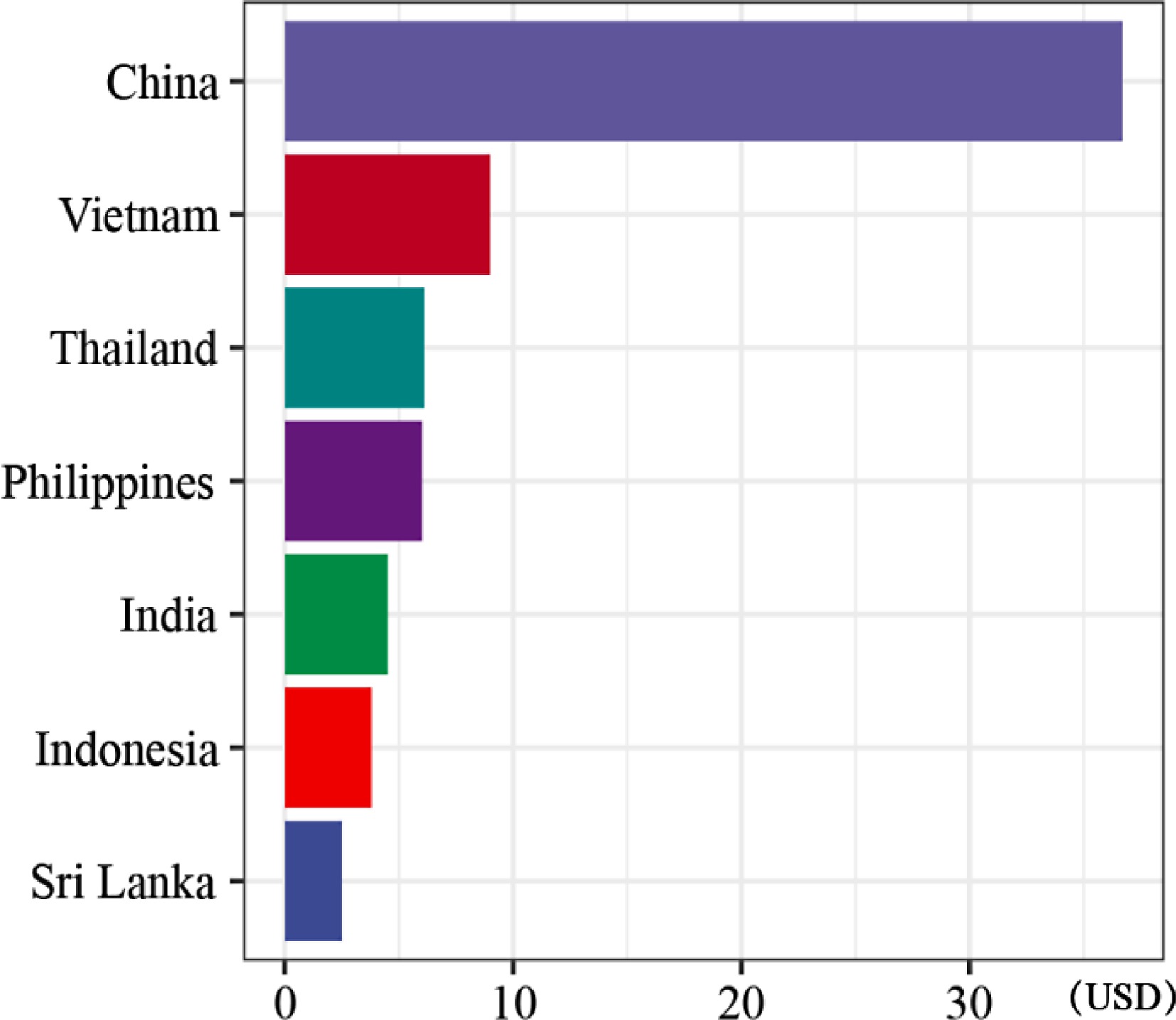
Figure 5.
The price of makapuno in different Asian countries.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(0)