-
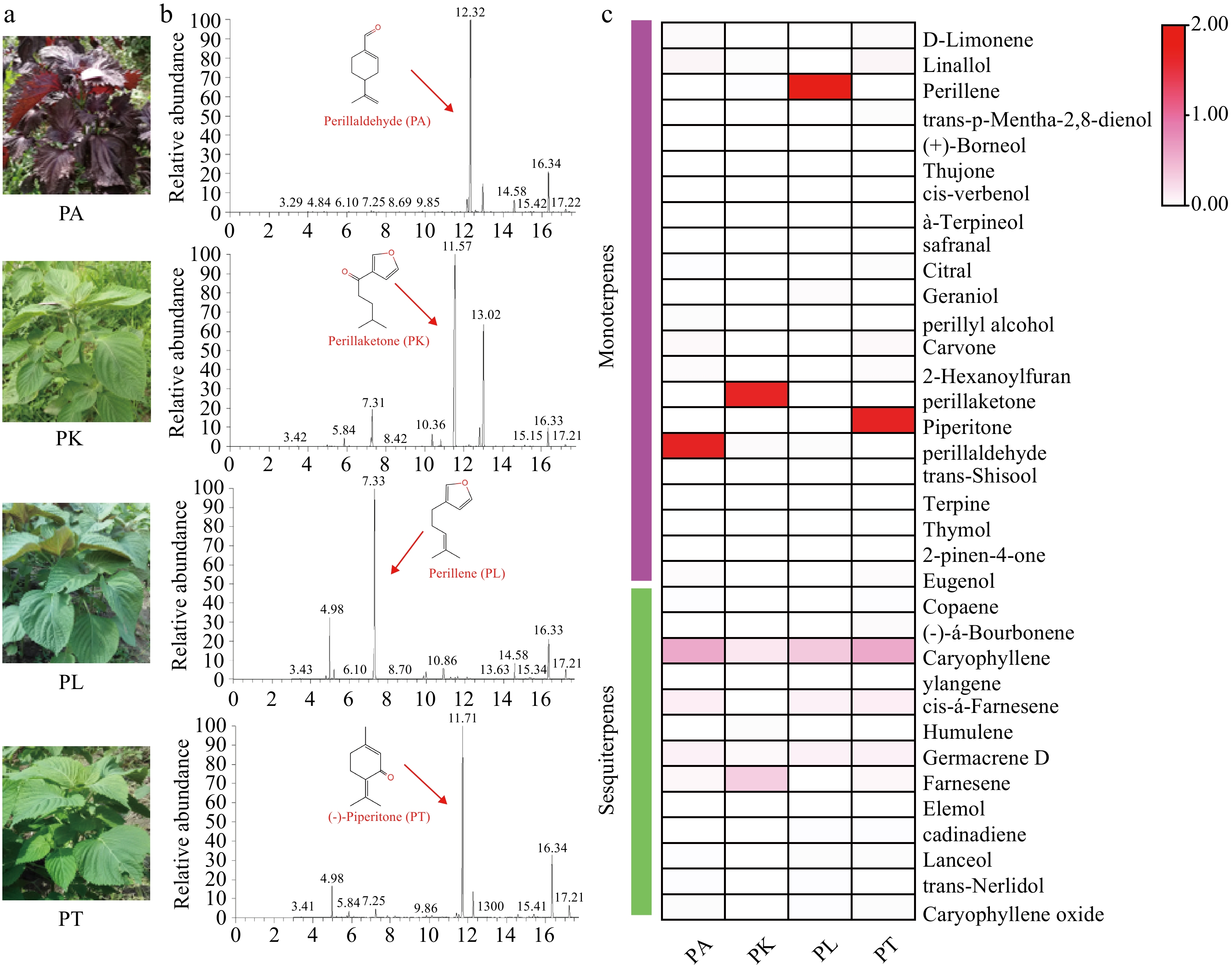
Figure 1.
The analysis of volatile components in four Perilla cultivars. (a) Phenotype of four chemical types of Perilla; (b) GC-MS analysis of volatile essential components from four Perilla leaves; (c) Heatmap of metabolite contents in four Perilla leaves.
-
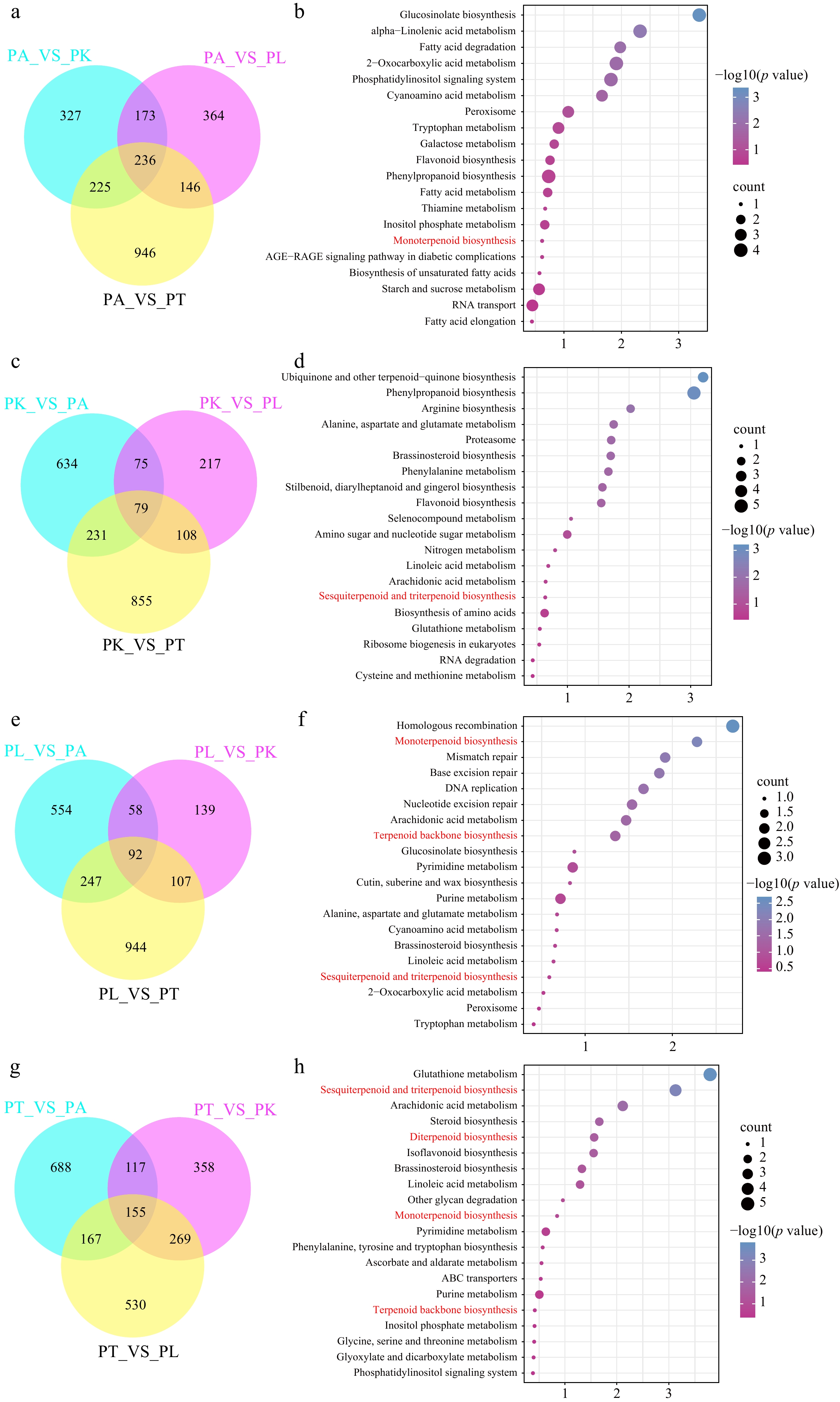
Figure 2.
Different expression genes and KEGG enrichment analysis of four Perilla cultivars. (a), (c), (e), (g) The intersection of PA, PL, PK, PT4 chemotypes with the other three chemotypes are indicated in the Venn diagrams. (b), (d), (f), (h) KEGG enrichment analysis of special up-expressed genes in PA, PL, PK, PT-type, respectively.
-
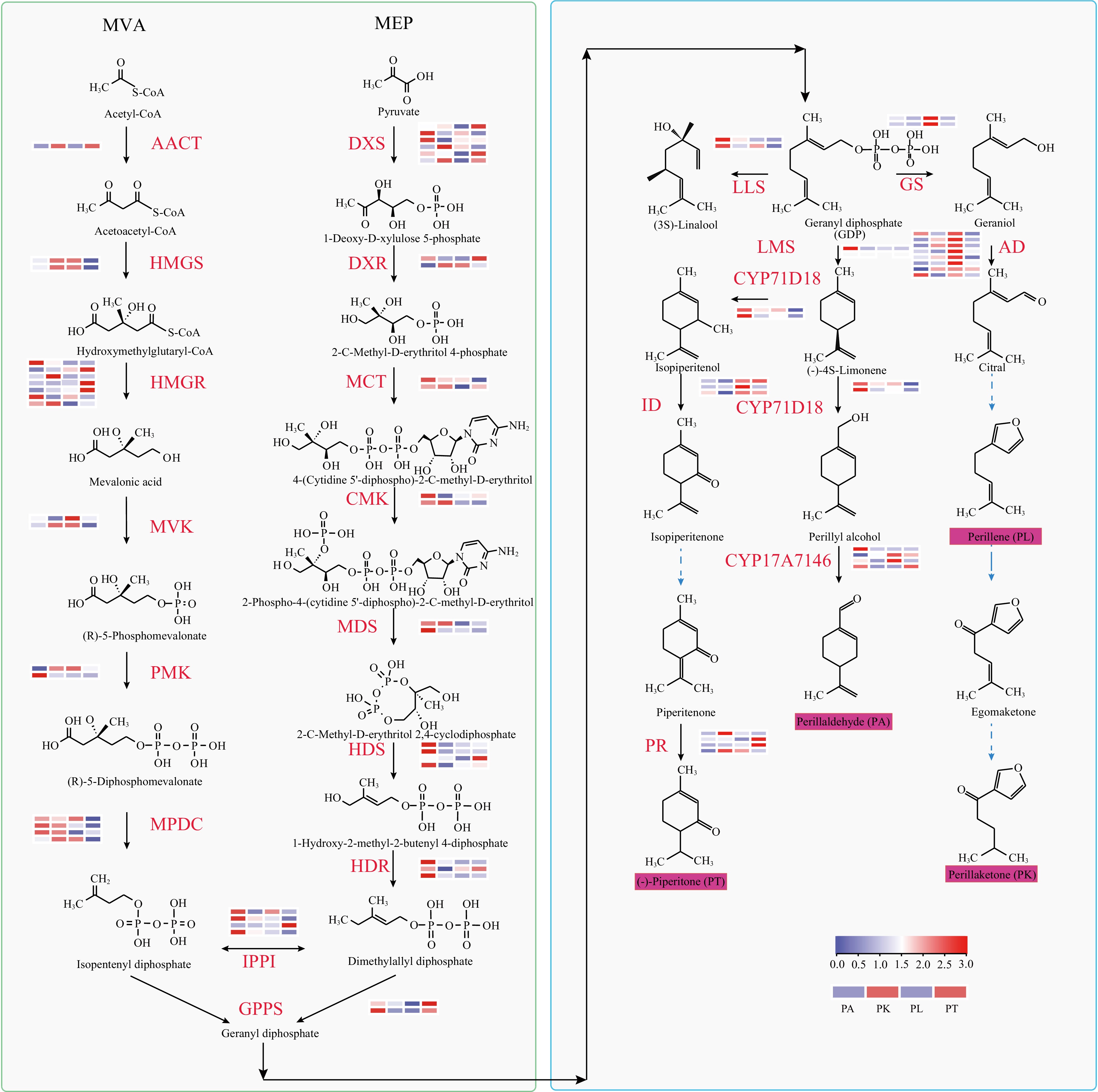
Figure 3.
Synthesis pathway and single thread synthesis pathway of P. frutescens isoprene. The MEP pathway: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS); 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR); 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (MCT); 4 diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase (CMK); 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (MDS/MECPS); (E)-4-hydroxy-3 methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate synthase (HDS); 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate reductase (HDR); The MVA pathway: acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase (AACT); hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase (HMGS); hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR); mevalonate kinase (MVK); phosphomevalonate kinase (PMK); diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase (MPDC); isopentenyl-diphosphate Delta-isomerase (IPPI); geranyl diphosphate synthase (GPPS); Linalool synthase (LLS); Geraniol synthase(GS); limonene synthase (LMS); alcohol dehydrogenase (AD); Cytochrome P450 proteins (CYP); isopiperitenol dehydrogenase (ID); pulegone reductase (PR).
-
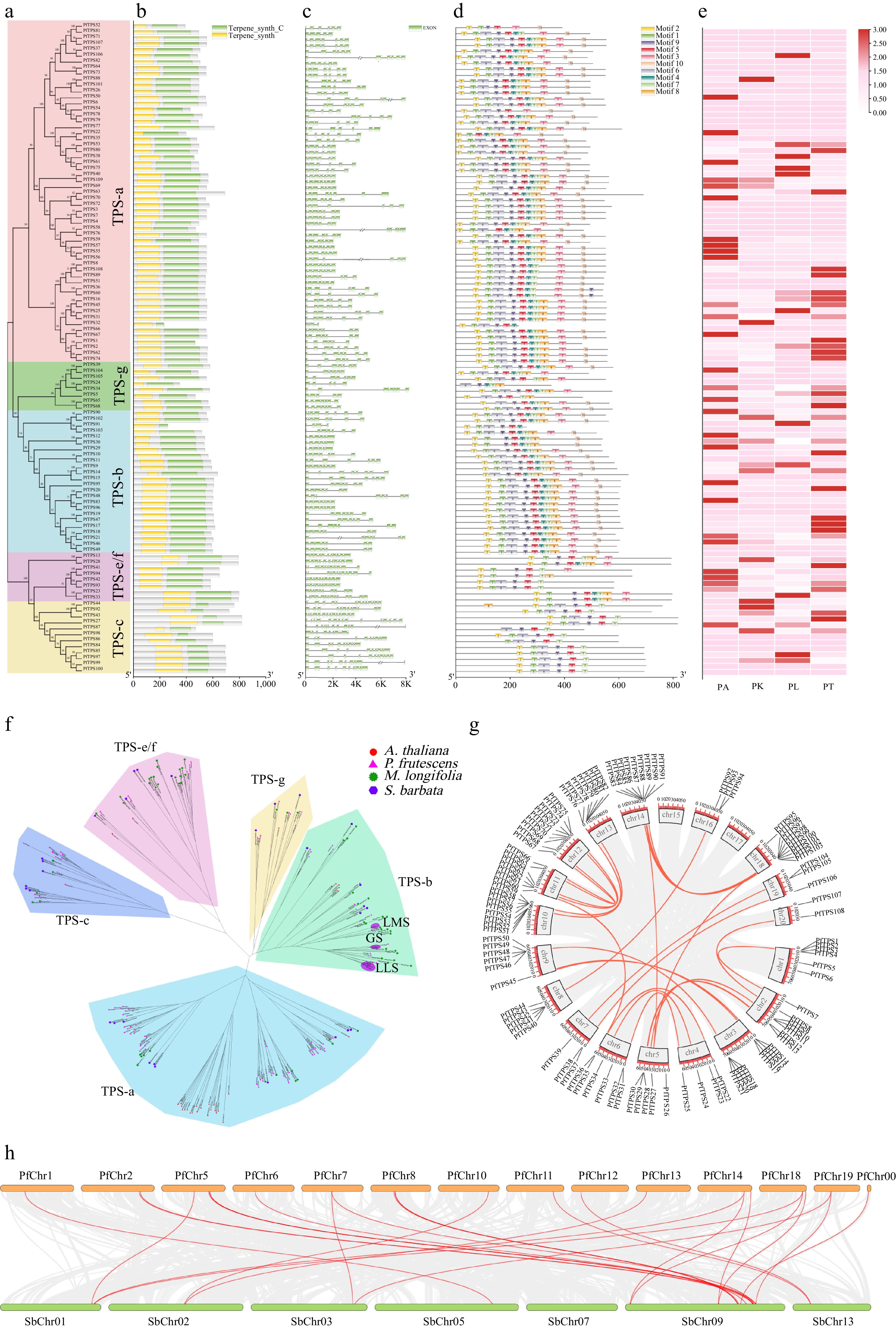
Figure 4.
The PfTPS Gene Family Characteristics in P. frutescens. (a)−(e) Phylogenetic evolutionary tree, conservative domain, gene structure, protein motifs and expression heatmap of PfTPS genes. (f) Subfamily classification of the PfTPS Family (LLS: linalool synthase; GS: geraniol synthase; LMS: limonene synthase). (g) Chromosomal localization and collinearity analysis of Perilla. (h) Collinearity analysis of TPS in Perilla and S. baicalensis.
-

Figure 5.
The co-expression analysis and verification of PfTPSs. (a)−(d) Co-expression analysis with core PfTPSs, including (a) PfTPS18, (b) PfTPS46, (c) PfTPS47 , (d) PfTPS49 and five other PfTPSs. (e) qRT-PCR verification of PfTPS genes and MVA pathway genes (qRT-PCR results (left, line) and transcription results (right, bar)).
-
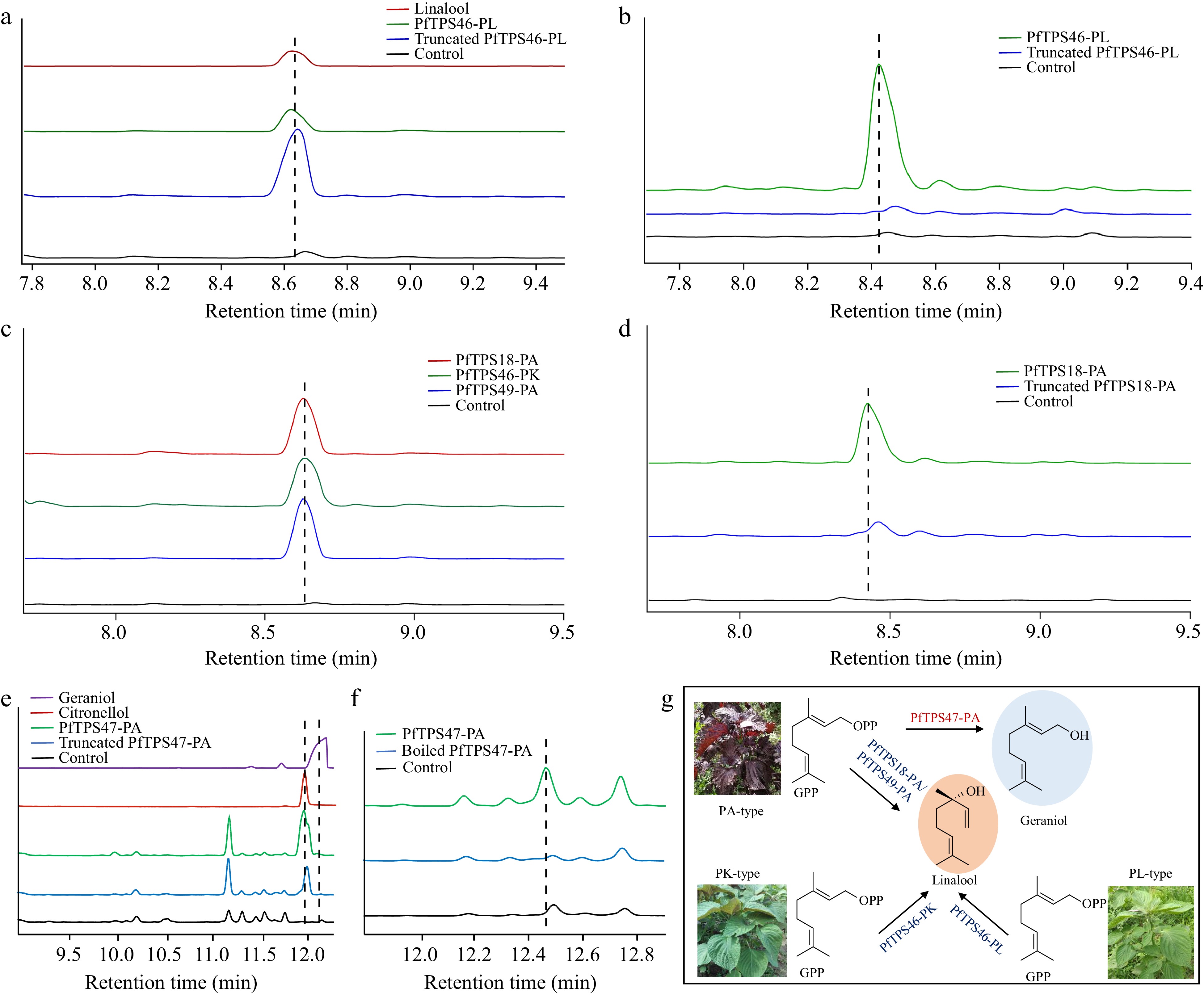
Figure 6.
Functional characterization of four PfTPSs. (a) Heterologous functional characterization of PfTPS46-PL and (b) the in vitro enzymatic reaction of PfTPS46-PL. (c) Heterologous functional characterization and (d) the in vitro enzymatic reaction of PfTPS46-PK, PfTPS18-PA, and PfTPS49-PA. (e) Heterologous functional characterization and (f) the in vitro enzymatic reaction of PfTPS47-PA. (g) Catalytic model of four PfTPSs.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(0)