-
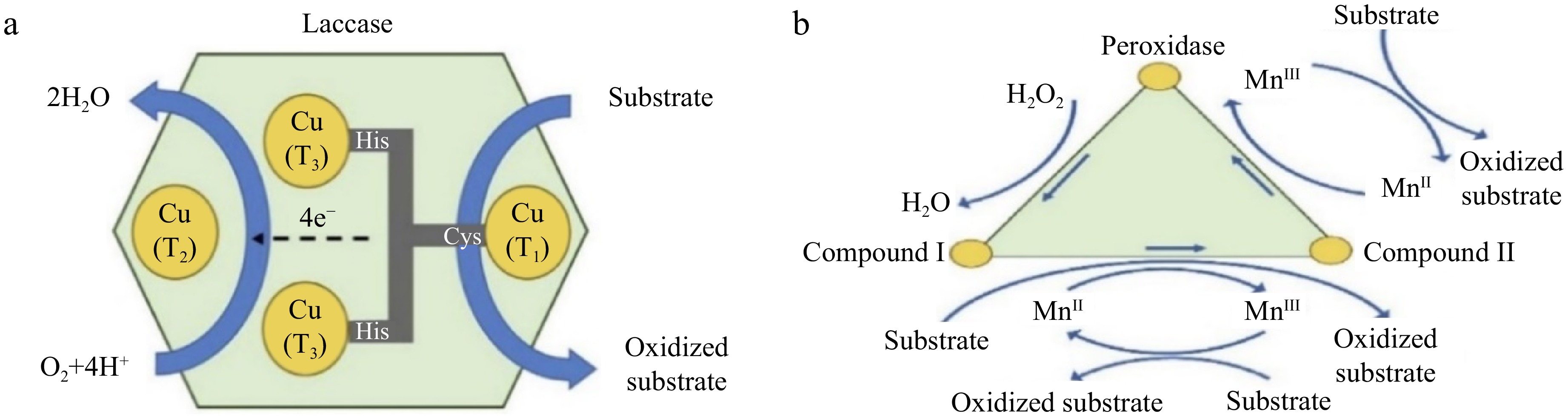
Figure 1.
Oxidation mechanism of compounds: (a) using laccase enzyme, and (b) using peroxidase enzyme[8].
-
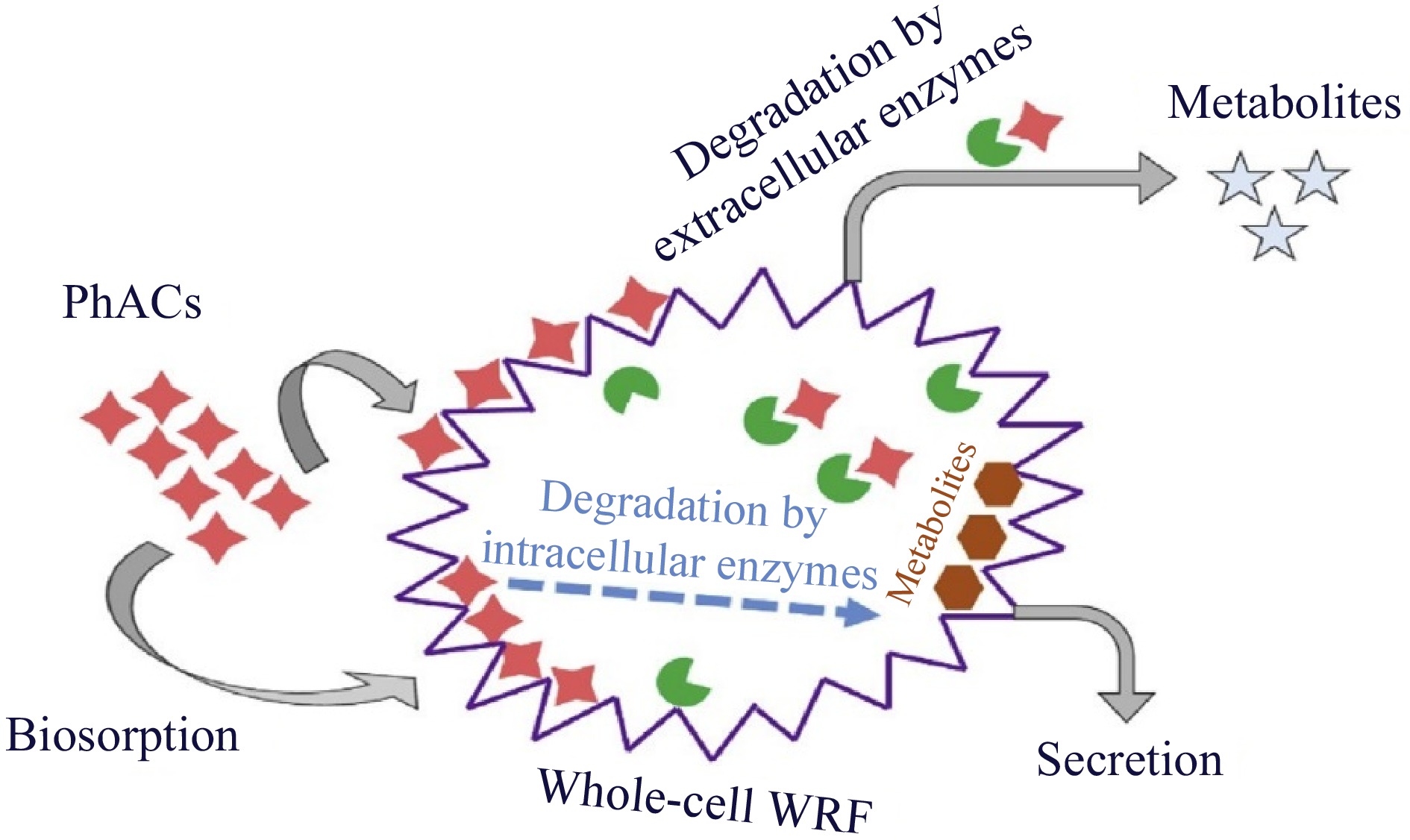
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of pollutant removal using white-rot fungi[8].
-
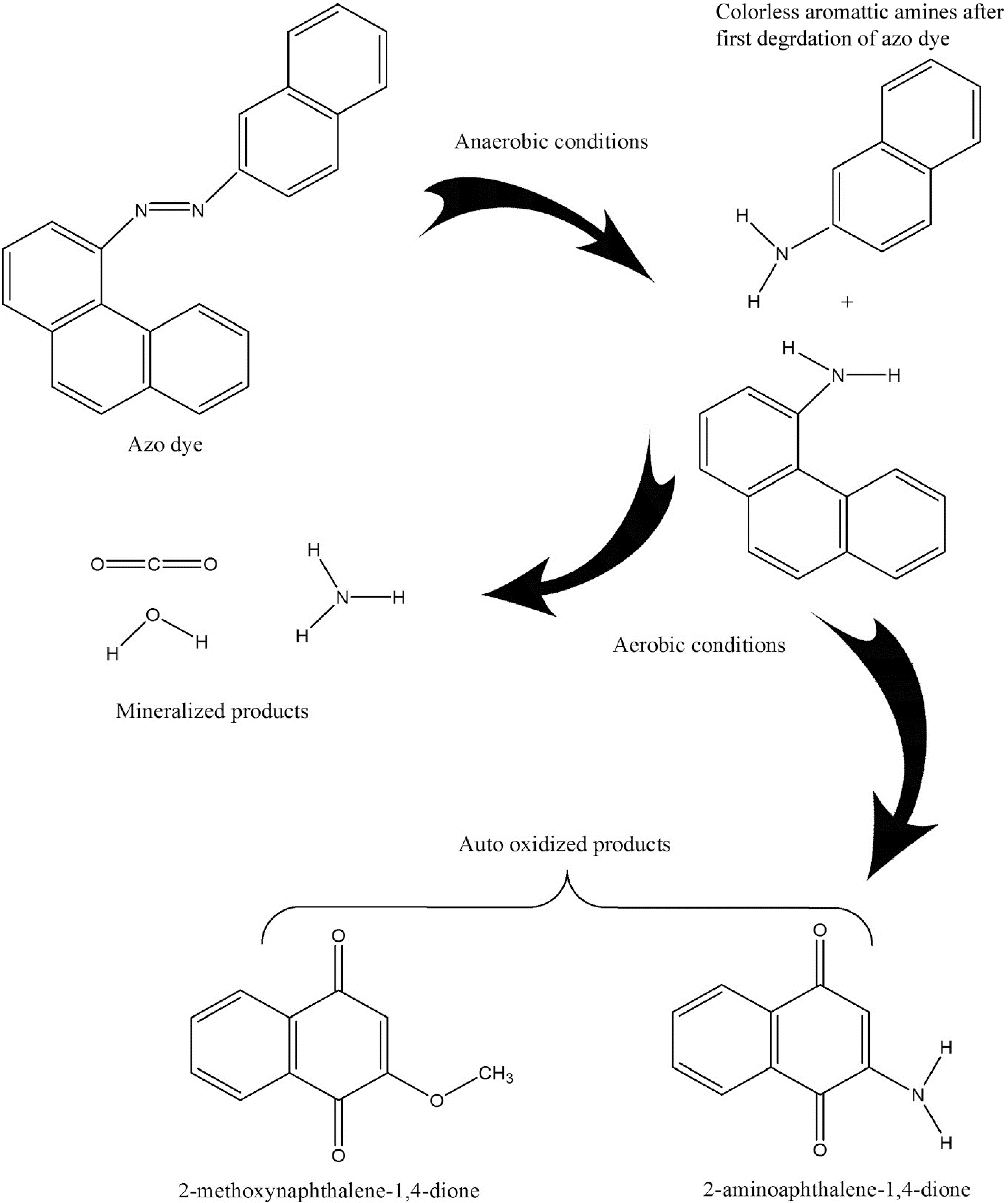
Figure 3.
Azo dye degradation mechanism in the presence of isolated enzymes[17].
-
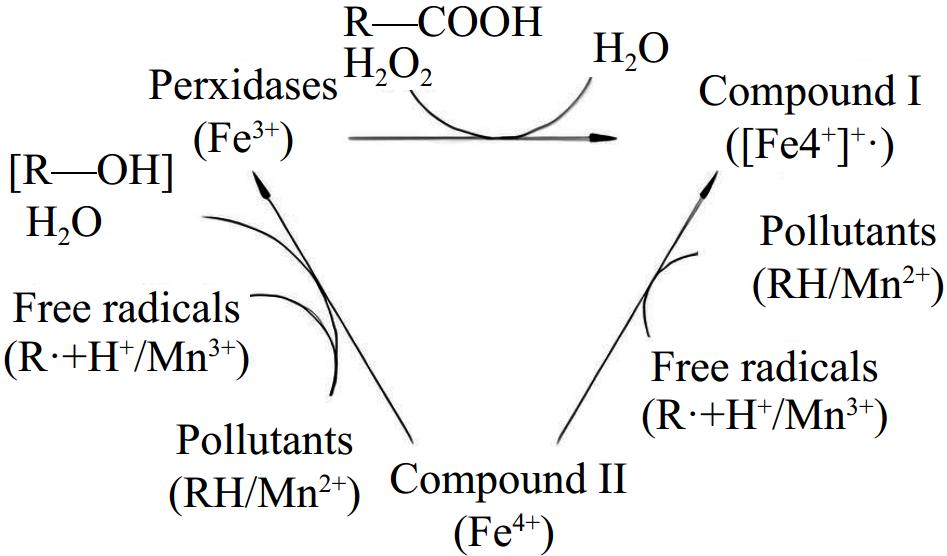
Figure 4.
Generic scheme of the catalytic cycle of peroxidases[30].
-
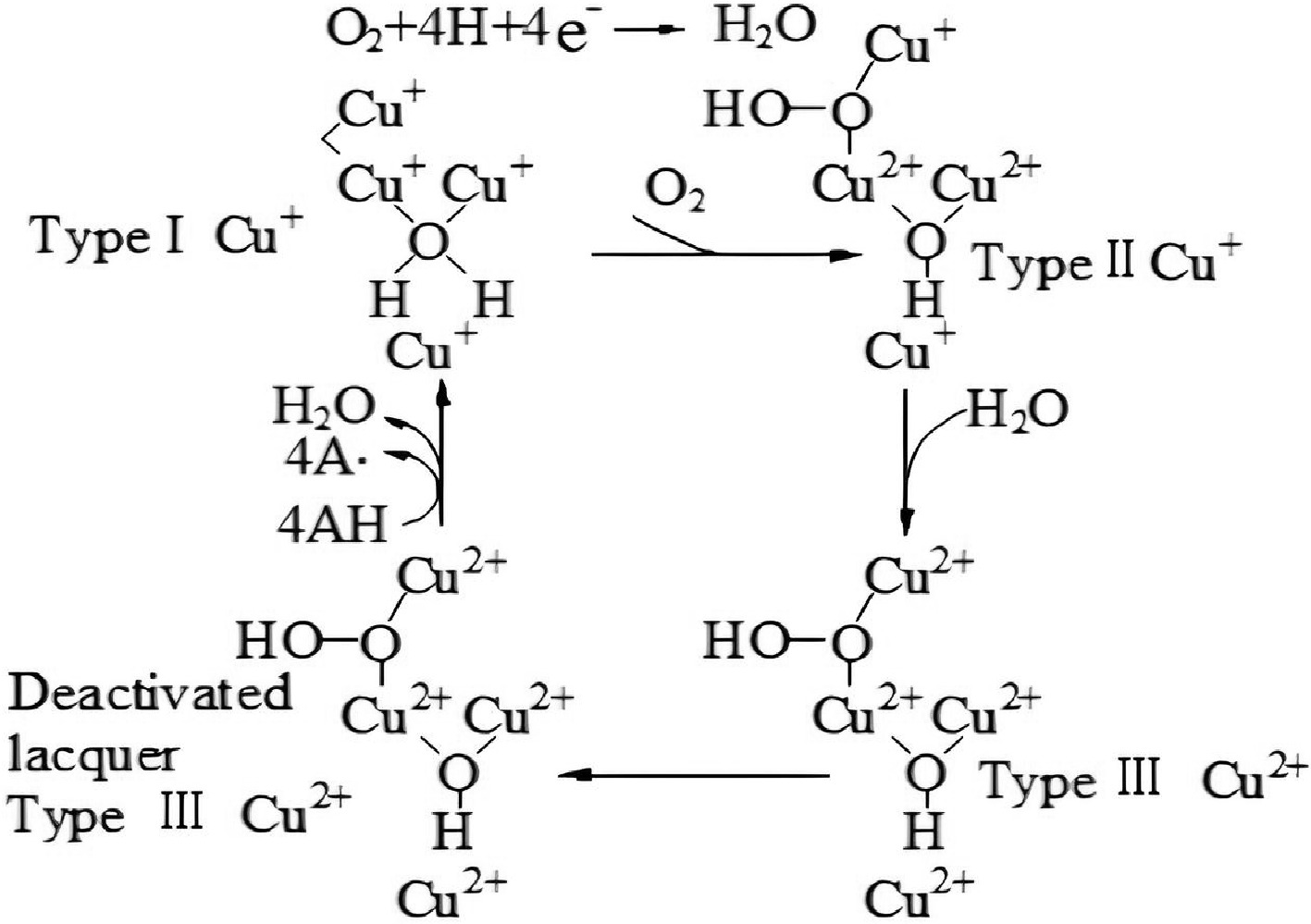
Figure 5.
The catalytic cycle of laccases[30].
-
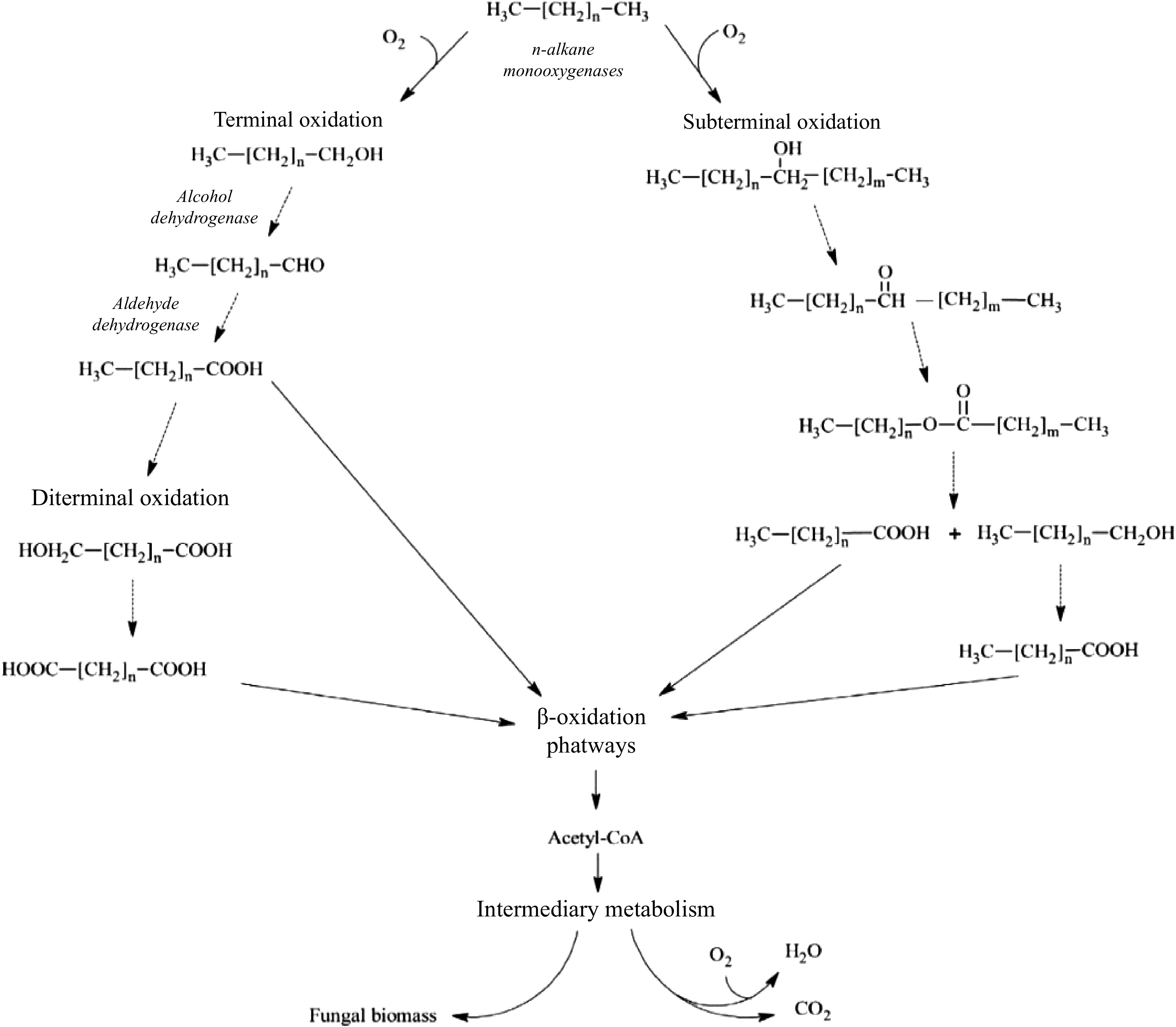
Figure 6.
Aerobic degradation of aliphatic hydrocarbons by fungi. The figure shows the terminal, diterminal and subterminal possible pathways for the degradation of n-alkanes (modified from Prenafeta-Boldú et al.[52]).
-
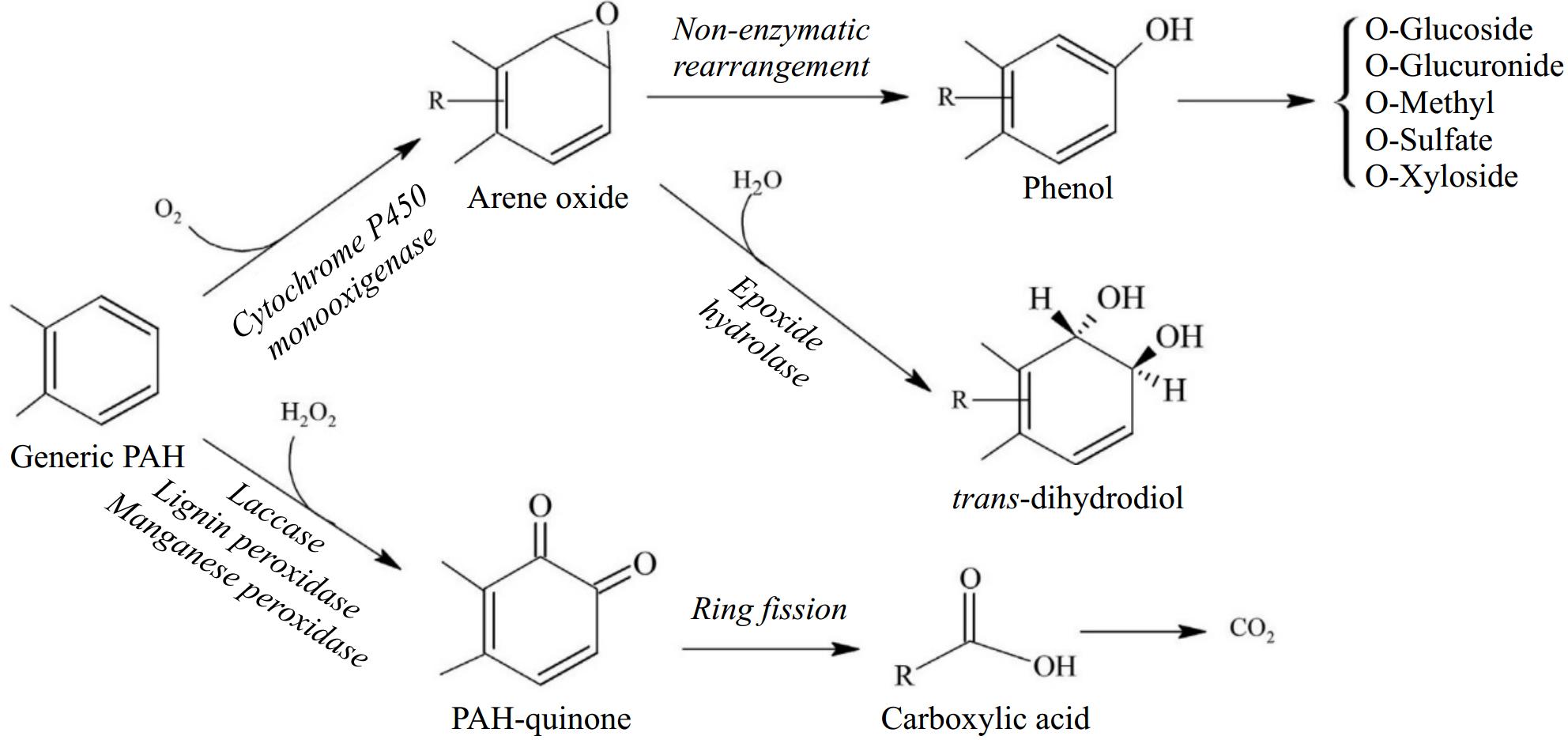
Figure 7.
Different pathways for the aerobic degradation of a generic PAH by fungi (modified from Kadri et al.[81]).
-
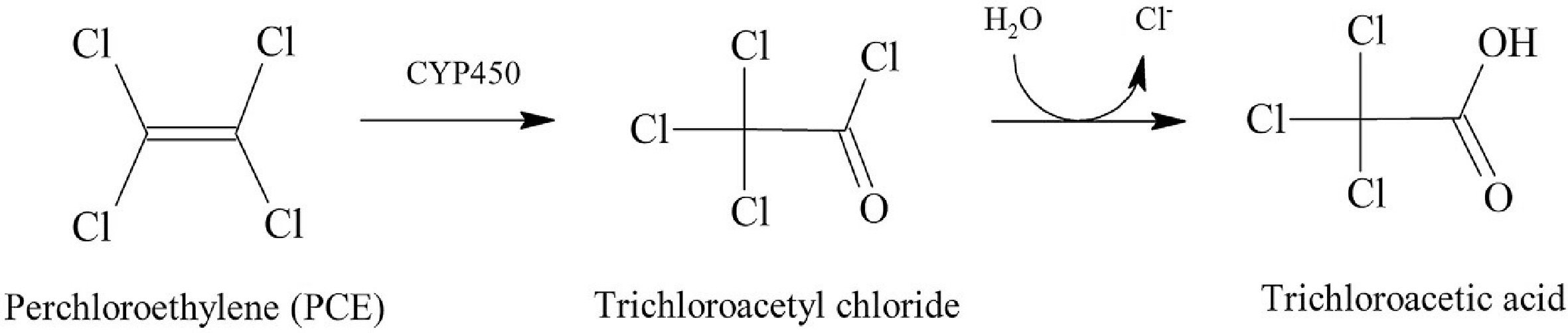
Figure 8.
Proposed pathway for partial enzymatic dehalogenation of PCE under aerobic conditions by T. versicolor[57].
-
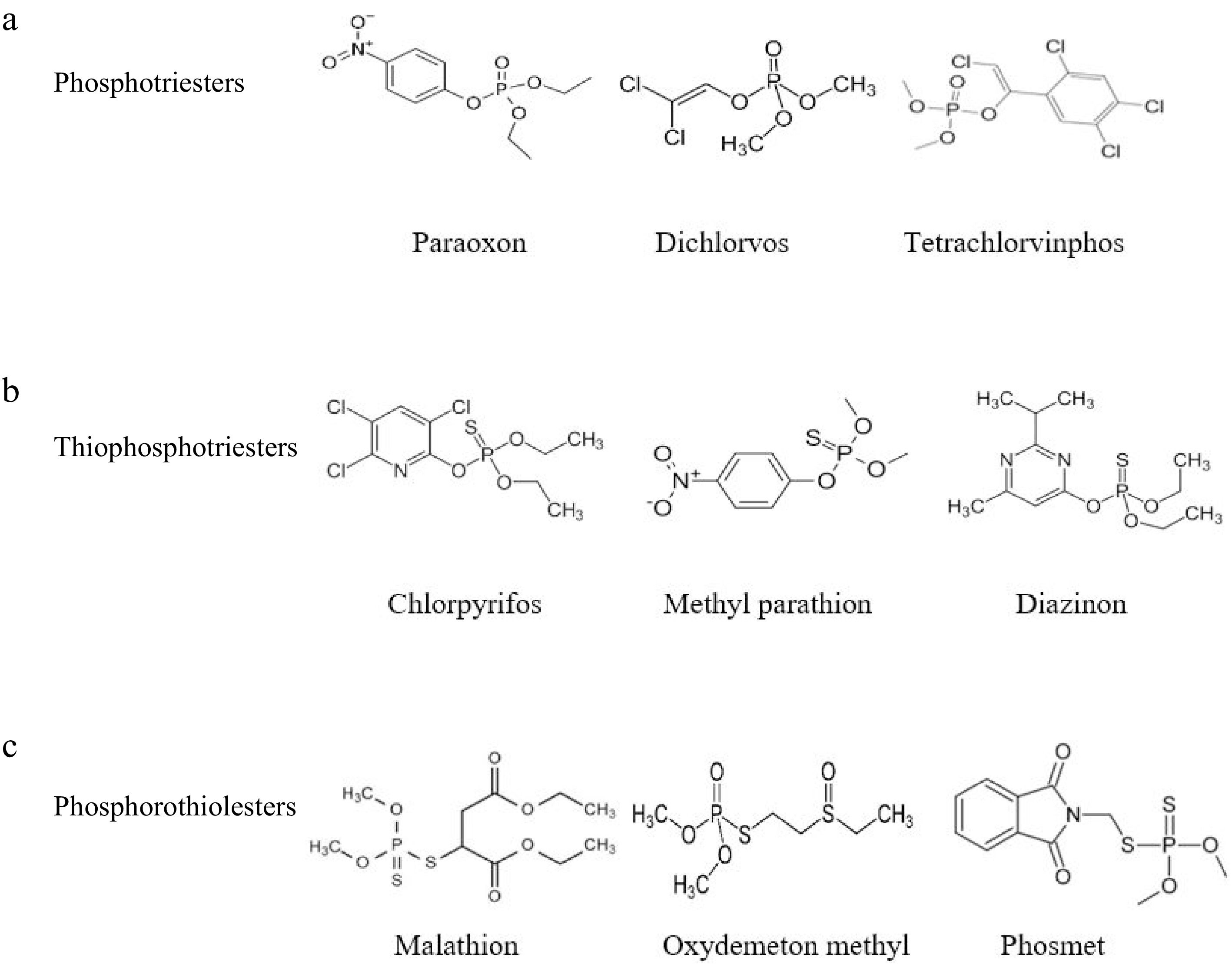
Figure 9.
Chemical structures of the main class of OPs. (a) Phosphotriesters; (b) Thiophosphotriesters; (c) Phosphorothio-lesters[18].
-
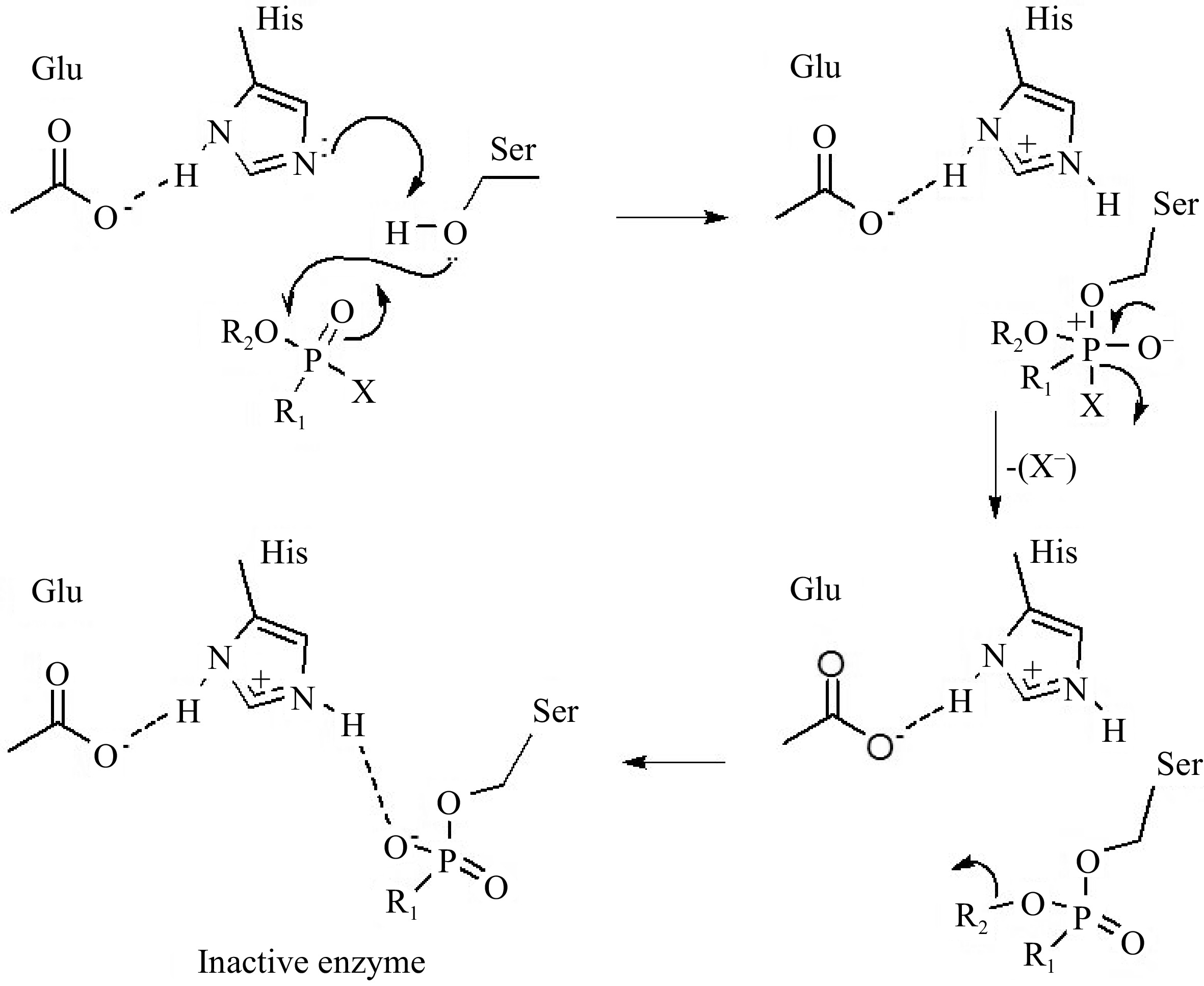
Figure 10.
Mechanisms of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by organophosphate pesticides[18].
Figures
(10)
Tables
(0)