-
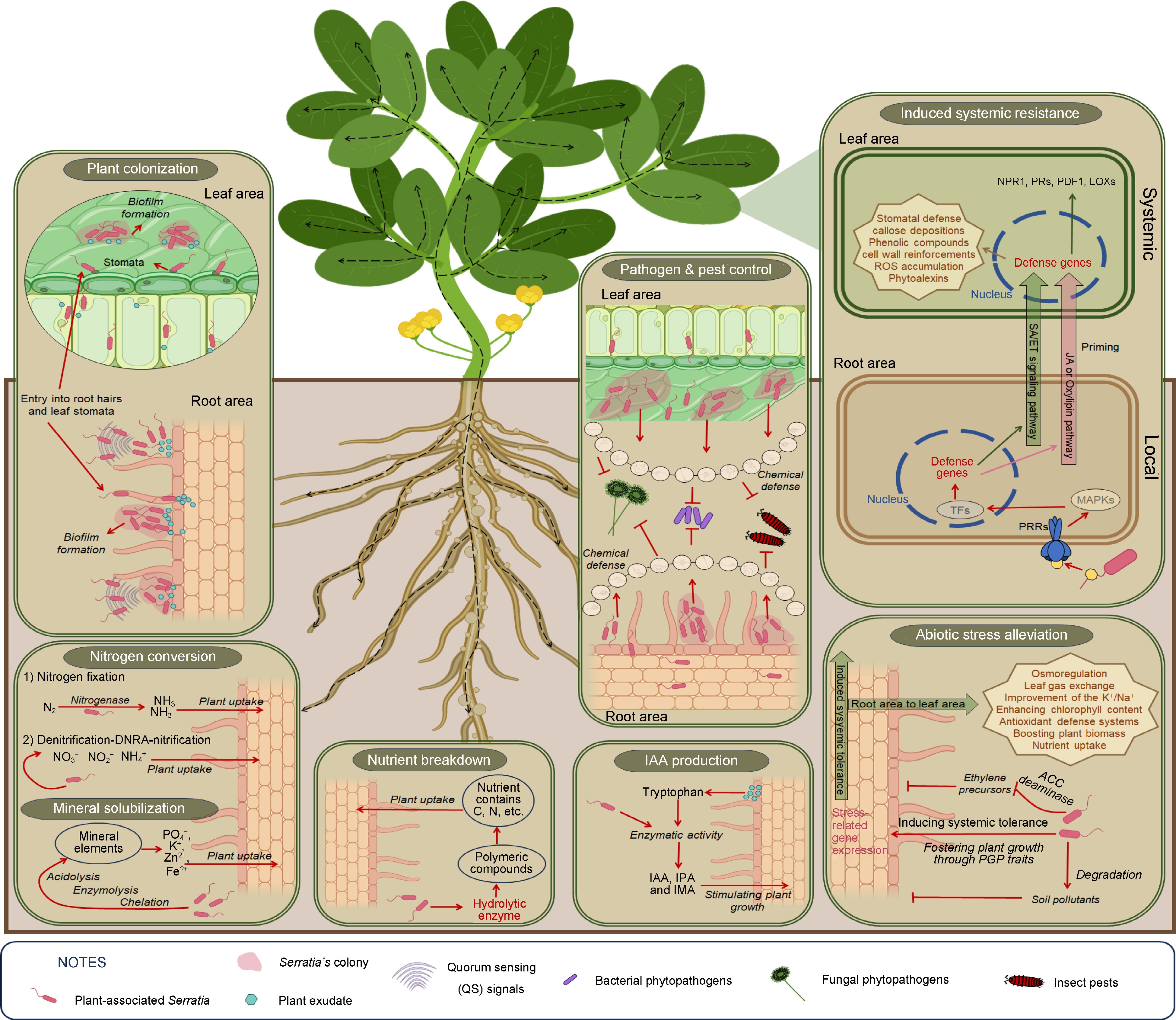
Figure 1.
Benefits of Serratia species to host-plants.
-
No. Plant growth-promoting traits Mechanisms Serratia species Ref. 1 Colonization Biofilm formation S. marcescens
S. plymuthica
S. fonticola
S. oryzae
Serratia spp.[2,36−39,44,46−50,53] Chemotaxis Entry into root hairs and leaf stomata 2 IAA production Trp-dependent pathway S. marcescens
S. liquefaciens,
S. plymuthica
S. Rubidaea S. glossinae
S. nematodiphila
Serratia spp.[5,8,26,38,48,57−59,90] 3 Nitrogen conversion Nitrogen fixation S. marcescens
S. nematodiphila
Serratia spp.[2,26,58,63,64] Denitrification-DNRA-nitrification 4 Minerial solubilization Organic acid production S. marcescens
S. nematodiphila
S. plymuthica
Serratia spp.[26,44,58,65,67−69,71,74,123] H+ extrusion Exopolysaccharide production Siderophores producion Solubilizing enzyme production 5 Nutrient breakdown Extracellular hydrolytic enzyme
productionS. marcescens
Serratia spp.[53,64] 6 Abiotic stress alleviation ACC deaminase production S. marcescens
S. liquefaciens
S. proteamaculans
Serratia spp.[5,6,44,58] Induced systemic tolerance PGP traits stimulation Cadmium (Cd) detoxification Pyrene degradation 7 Induced systemic resistance Elicited by AHLs,
bacterial flagellin (flg22), translation elongation factor Tu (elf18), and
2,3-butanediolS. marcescens
S. liquefaciens
S. rhizosphaerae
Serratia spp.[17,39,82,83] Table 1.
Plant growth promoting traits of Serratia species.
-
No. Compounds produced by
Serratia spp.Analyzed biosynthetic genes Mechanisms of action Ref. 1 Protease yfgC Degrading the cell walls of most of fungi and the insect's midgut [8,22,47,48,76,89,90,111] 2 Chitinase chiA,B, C Degrading the cell walls of most of fungi
Degrading the insect exoskeletons3 β-1,3 glucanase Gene encoding β-1,3-glucanase
in glycoside hydrolase familyDegrading the cell walls of most of fungi 4 Lipase lipA,B,C,D Degrading the insect's mitgut [140] 5 Phospholipase phlA Degrading the peritrophic membrane lining the midgut [109] 6 Serralysin
(alkaline metalloprotease)prtA1-prtA4 Promoting hemolymph bleeding in insect pests [22,114−116] 7 Prodigiosin
Tripyrrole alkaloidpig gene cluster (pig A-N) Inhibiting spore germination and growth of hyphae
Inhibiting immune system enzymes protease phosphatase, acid phosphatase, and acetylcholine esterase
Reducing pH in the insect's midgut[7−9,57,91,117−121] 8 Pyrrolnitrin - tryptophan-derived secondary metabolite prnABCD Damaging the cell membrane in combination with phospholipids
Inhibiting fungal growth by inhibiting the respiratory electron transport system[8,37,48,90,93−95] 9 Oocydin A - chlorinated macrocyclic lactone ooc gene cluster Anti-oomycete activity [4,141] 10 Biosurfactants
Serrawettin W1, Serrawettin W2swrW, swrA Swarming activity of Serratia spp.
Biosurfactant activity disturbing the cell membrane of phytopathogenic cells[21,96,97] 11 Serratiochelin A, B, C, D
Bis catecholate siderophoressch gene cluster Iron competition with phytopathogenic cells [48,90,139,142] 12 Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Sodorifen
DMDS
acetic acid, methylthiolacetate
Terpene synthase gene (Q5A_011535)
mdeA
Methyltransferase gene (Q5A_011540)Inhibition of fungal growth [99−101] Table 2.
Common compounds produced by Serratia for the control of plant diseases and insect pests.
-
No. Strains Hosts Applications Ref. 1 S. marcescens IRBG500 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Improving plant biomass [2] 2 S. marcescens OK482790 Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Improving plant biomass [64] 3 S. nematodiphila EU-PW75 Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Reducing plant abiotic stress
Improving plant biomass[123] 4 S. proteamaculans M35 Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Reducing plant abiotic stress
Improving plant biomass[77] 5 S. plymuthica MBSA-MJ1 Petunia (Petunia × hybrida), impatiens (Impatiens walleriana), and pansy
(Viola × wittrockiana)Reducing plant abiotic stress
Improving plant biomass under[124] 6 Serratia sp. Wed4 Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Reducing plant abiotic stress
Improving plant biomass[58] 7 Serratia CP-13 Maize (Zea mays L.) Reducing plant abiotic stress
Improving plant biomass[79] 8 S. nematodiphila (code SN01) Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Biocontrol of Rice blast caused by
Magnaporthe oryzae Improving grain yield[127] 9 S. nematodiphila RGK Turmeric rhizome (Curcuma longa L.) Biocontrol of Pythium aphanidermatum
Improving plant biomass and bioactive compounds[26] 10 Serratia liquefaciens, S. plymuthica and S. rubidaea Oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) Biocontrol of Verticillillm dahliae , Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerntinia sclerotiorum [8] 11 S.liquefaciens CL80 Dutch white cabbage
(Brassica oleracea L.)Biocontrol of B. cinerea [125] 12 S. plymuthica HRO-C48 (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) Biocontrol of Verticillium dahliae and
Phytophthora cactorum[47] 13 Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), bean (Phaeseolus vulgaris L.),and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Biocontrol of Pythium apahnidermatum and
Botrytis cinerea[37] 14 Oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) Biocontrol of Verticillium wilt [48] 15 S. nematodiphila CT-78 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Biocontrol of leaf blight disease [25] 17 S. marcescens Dolichos bean (Lablab purpureus L.) Biocontrol of Anthracnose disease caused by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum [132] 18 Serratia sp. G3 Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Biocontrol of Botrytis cinerea, Cryphonectria parasitica, Rhizoctonia cerealis and Valsa sordida [90] 20 S. marcescens NPKC3_2_2 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Reducing the damages from rice stem borer attacks (Scirpophaga innotata) in rice crops [108] 21 S. marcescens HJ-01 The red palm weevil (RPW), Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) Reducing the red palm weevil (RPW), Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) larvae [111] 22 S. marcescens B2 Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Eliciting plant ISR against rice blast caused by Pyricularia oryzae [85] 23 S. liquefaciens MG1 Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Inducing systemic resistance against Alternaria alternata infection [83] 24 S. marcescens Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) Inducing systemic resistance against against root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita [126] 25 S. marcescens 90-166 Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Inducing systemic resistance against Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci and cucumber mosaic virus [39] 26 S. rhizosphaerae KUDC3025 Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Inducing systemic resistance against soft-rot disease caused by P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum SCC1 [17] 27 S. marcescens GPS5 Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Inducing systemic resistance against late leaf spot disease [130] 28 S. marcescens N4-5 (extract) Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Control of cucumber damping-off caused by
Pythium ultimum[128] 29 S. marcescens SE1 and SE2 (extracts) Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Control of yellow mold disease caused by A. flavus [129] 30 S. plymuthica AED38
(extract)Avocado (Persea americana L.) Control of root rot caused by by Phytophthora cinnamomi [139] 31 Serratia sp. ARP5.1 (extract) Avocado (Persea americana L.) Control of fruit
body rot (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)
and root rot (Phytophthora Cinnamomi)[138] Table 3.
Application of Serratia species for enhancing plant growth and plant protection.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(3)