-
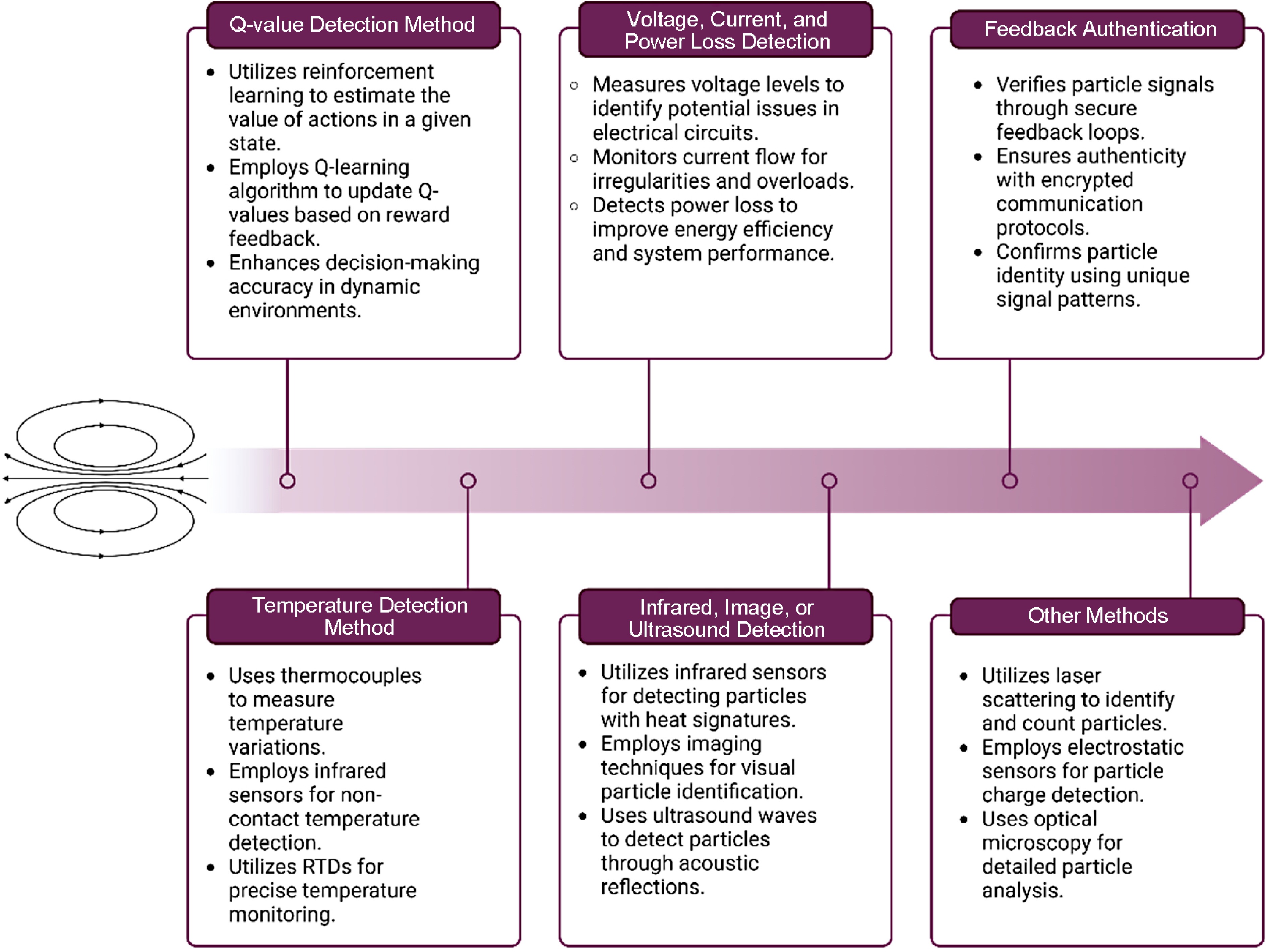
Figure 1.
Different metal detection methods used in wireless power transfer.
-
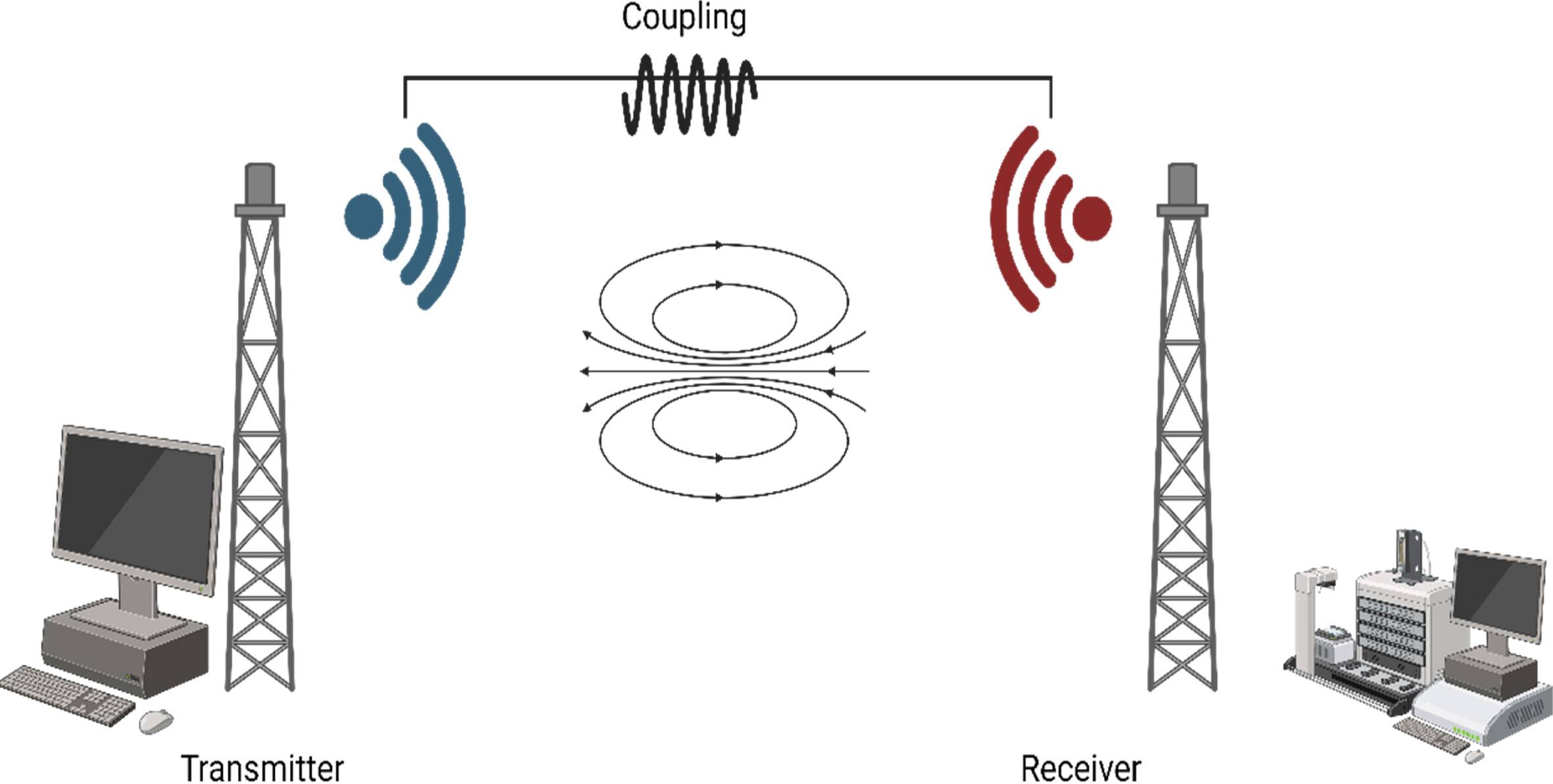
Figure 2.
Block diagram of wireless power transmission technology.
-
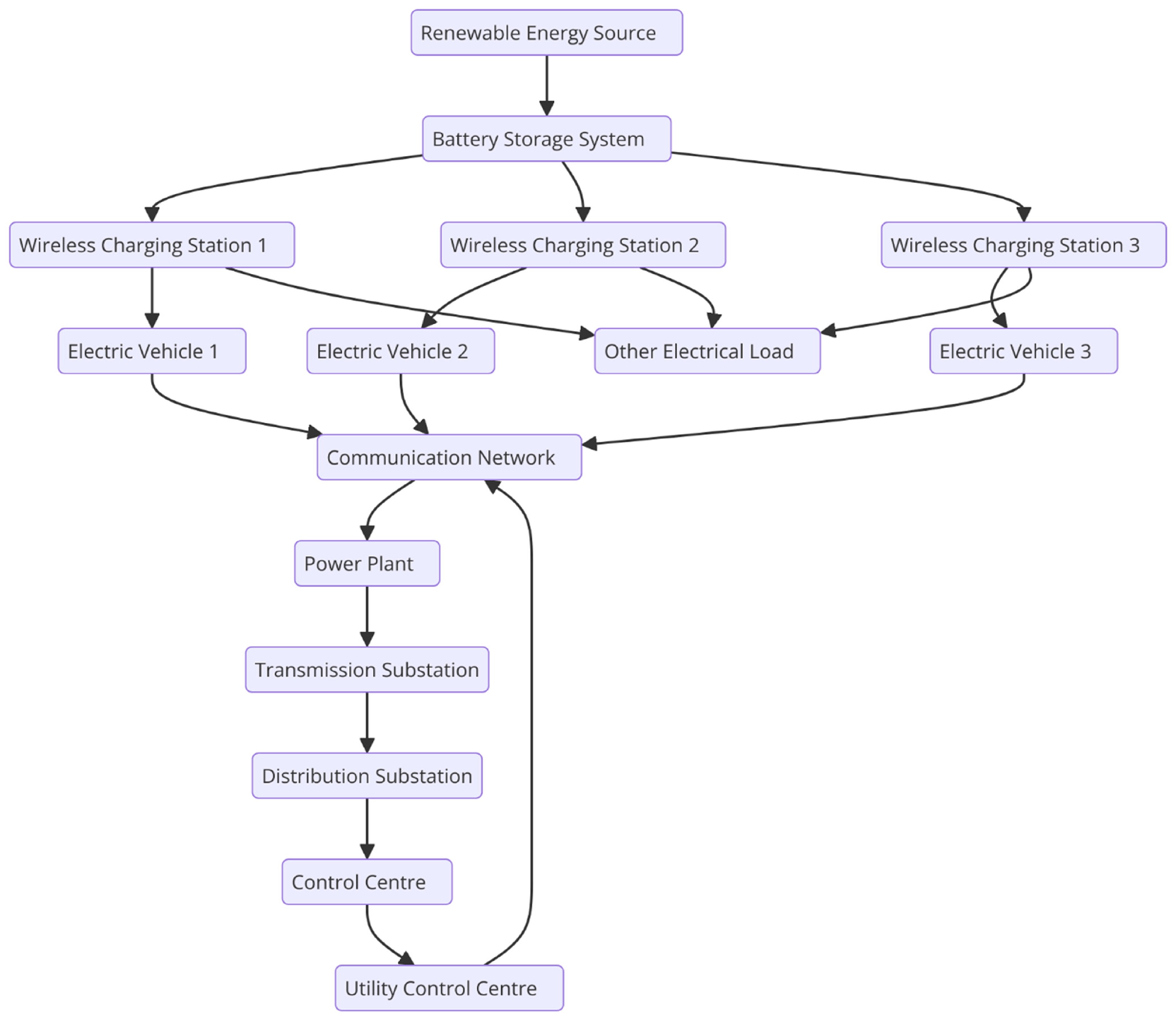
Figure 3.
Structure of the entire wireless charging industry chain.
-
Application field Key benefits Key challenges Efficiency Cost Examples of use Consumer electronics Convenience and mobility Limited range, slower charging Moderate Low to moderate Wireless charging pads for phones, tablets Electric eehicles Reduces the need for plug-in charging High infrastructure cost, efficiency loss Moderate to high High Static and dynamic wireless charging stations Medical eevices No wires, reducing infection risk Power transfer limitations, regulatory hurdles Low to moderate High Implants, wearable medical devices Industrial eutomation Flexibility, reduced wear on connectors Interference, high initial setup cost High High Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotics Military Reduced need for fuel transport Security risks, high-tech implementation Moderate Very high Remote charging of UAVs, field equipment Space exploration Enables long-distance energy transfer Extreme environmental conditions, tech reliability Low to moderate Very high Powering satellites, rovers Smart homes Enhanced user experience, convenience Interference with other devices, efficiency Low to moderate Low to moderate Wireless charging for smart home devices Wearable technology Improved user experience, flexibility Battery life limitations, power transfer efficiency Low to moderate Low to moderate Fitness trackers, smartwatches Table 1.
Comparative analysis of wireless power transmission technology in different application fields.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)