-
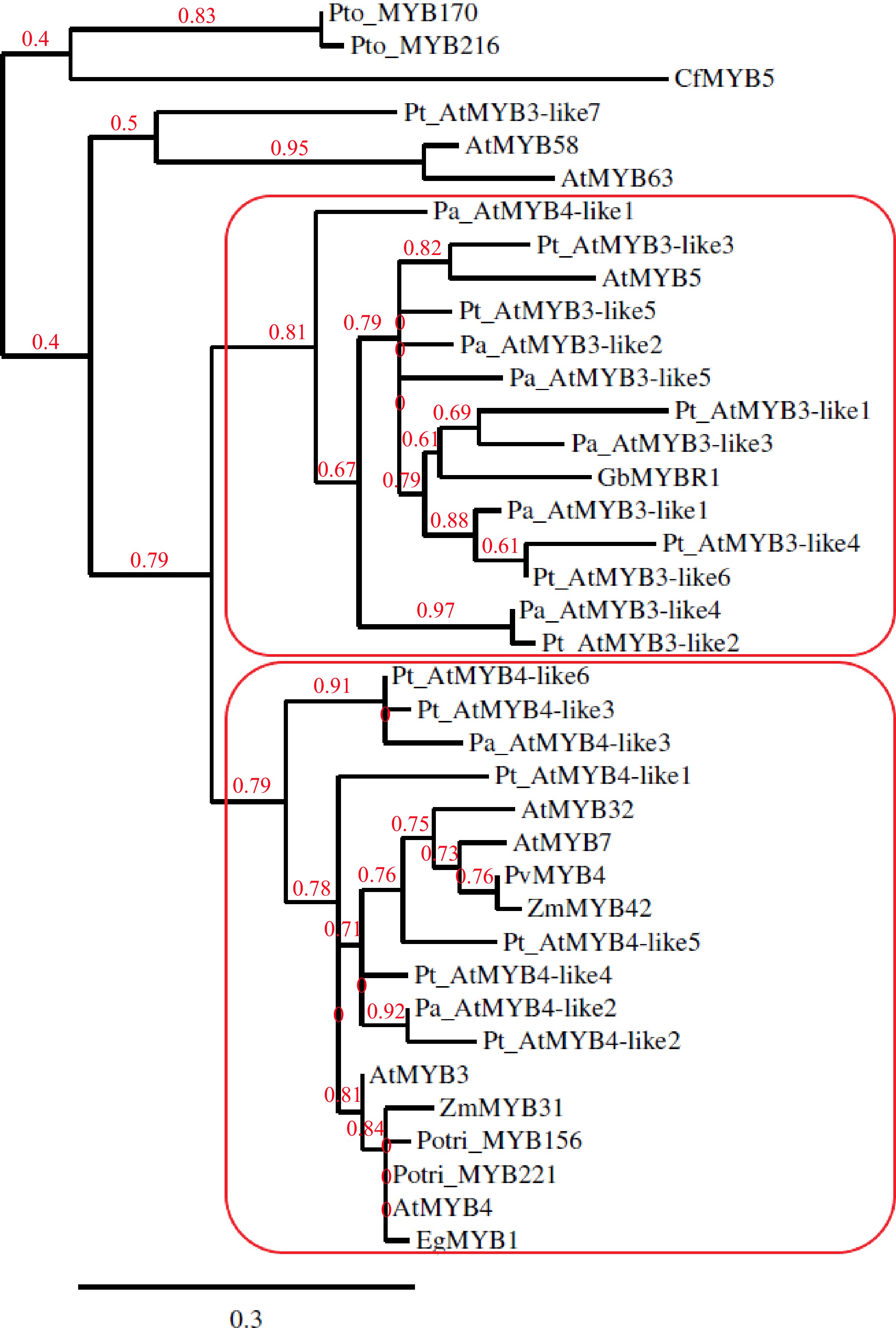
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree constructed with copies of MYB3-like and MYB4-like from Picea abies (Pa) and Pinus taeda (Pt) along with GbMYBR1 from Ginkgo biloba (Gb); CfMYB5 from Cryptomeria fortune (Cf); MYB3, MYB4, MYB5, MYB7, MYB32, MYB58 and MYB63 from Arabidopsis thaliana (At); MYB156 and MYB221 from Populus trichocarpa (Potri); MYB170 and MYB216 from Populus tomentosa (Pto); EgMYB1 from Eucalyptus gunnii (Eg); ZmMYB31 and ZmMYB42 from Zea mays (Zm) and, PvMYB4 from Panicum virgatum (Pv).
-

Figure 2.
Alignment of N-terminal regions of the lignin repressor MYB members from gymnosperms and angiosperms showing the conserved R2, R3, and bHLH domains: MYB3-like and MYB4-like copies from Picea abies (Pa) and Pinus taeda (Pt) along with GbMYBR1 from Ginkgo biloba (Gb); CfMYB5 from Cryptomeria fortune (Cf); MYB3, MYB4, MYB7, and MYB32 from Arabidopsis thaliana (At); MYB156 and MYB221 from Populus trichocarpa (Potri); EgMYB1 from Eucalyptus gunnii (Eg); ZmMYB31 and ZmMYB42 from Zea mays (Zm) and PvMYB4 from Panicum virgatum (Pv).
-
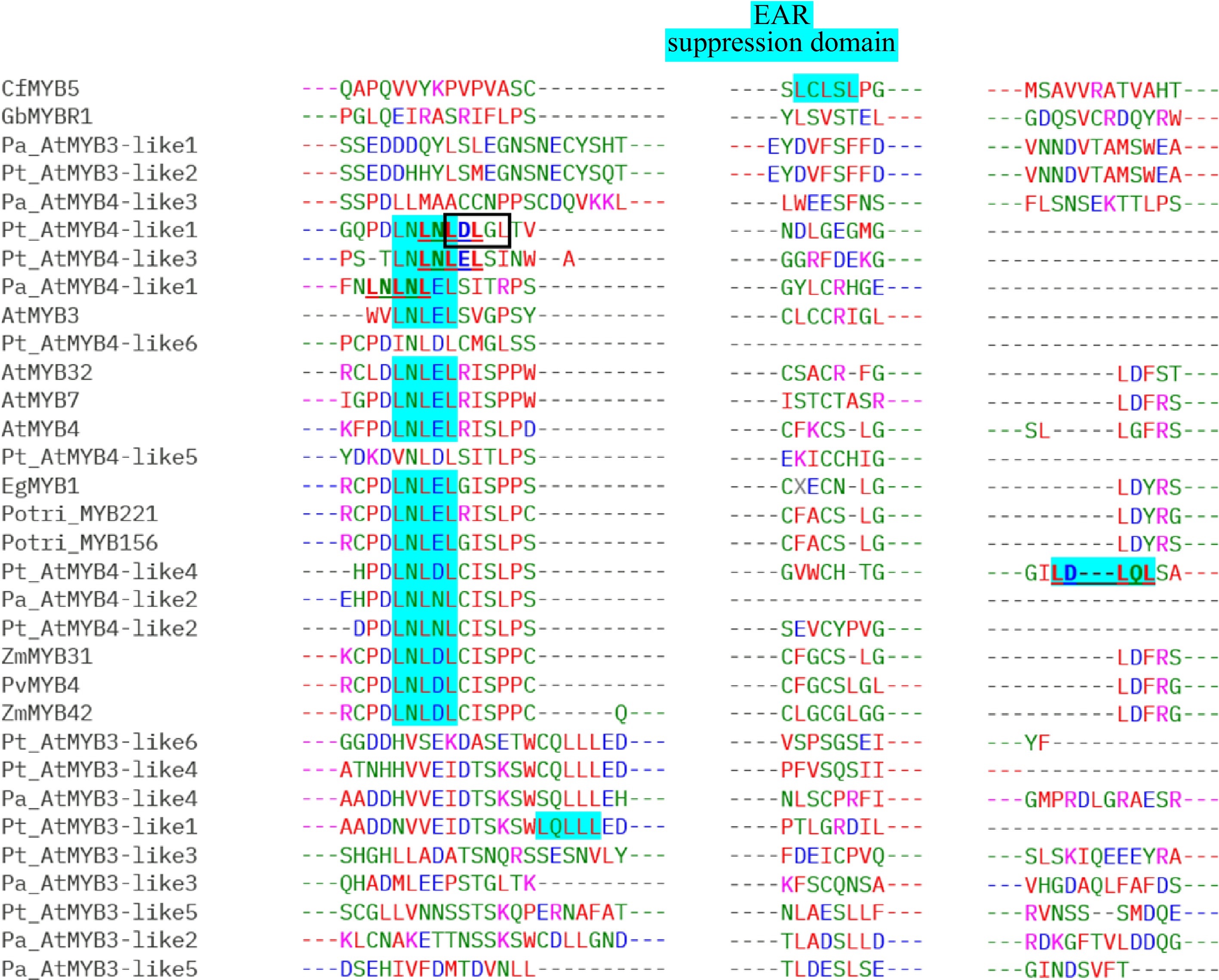
Figure 3.
Alignment of partial C-terminal regions of the lignin repressor MYB members from gymnosperms and angiosperms showing the conserved EAR domain (alternative EAR domains in Pt_AtMYB4-like1, Pt_AtMYB4-like3, Pt_AtMYB4-like4, and Pa_AtMYB4-like1 are marked with box and, bold and underlined): MYB3-like and MYB4-like copies from Picea abies (Pa) and Pinus taeda (Pt) along with GbMYBR1 from Ginkgo biloba (Gb); CfMYB5 from Cryptomeria fortune (Cf); MYB3, MYB4, MYB7, and MYB32 from Arabidopsis thaliana (At); MYB156 and MYB221 from Populus trichocarpa (Potri); EgMYB1 from Eucalyptus gunnii (Eg); ZmMYB31 and ZmMYB42 from Zea mays (Zm) and PvMYB4 from Panicum virgatum (Pv).
Figures
(3)
Tables
(0)