-
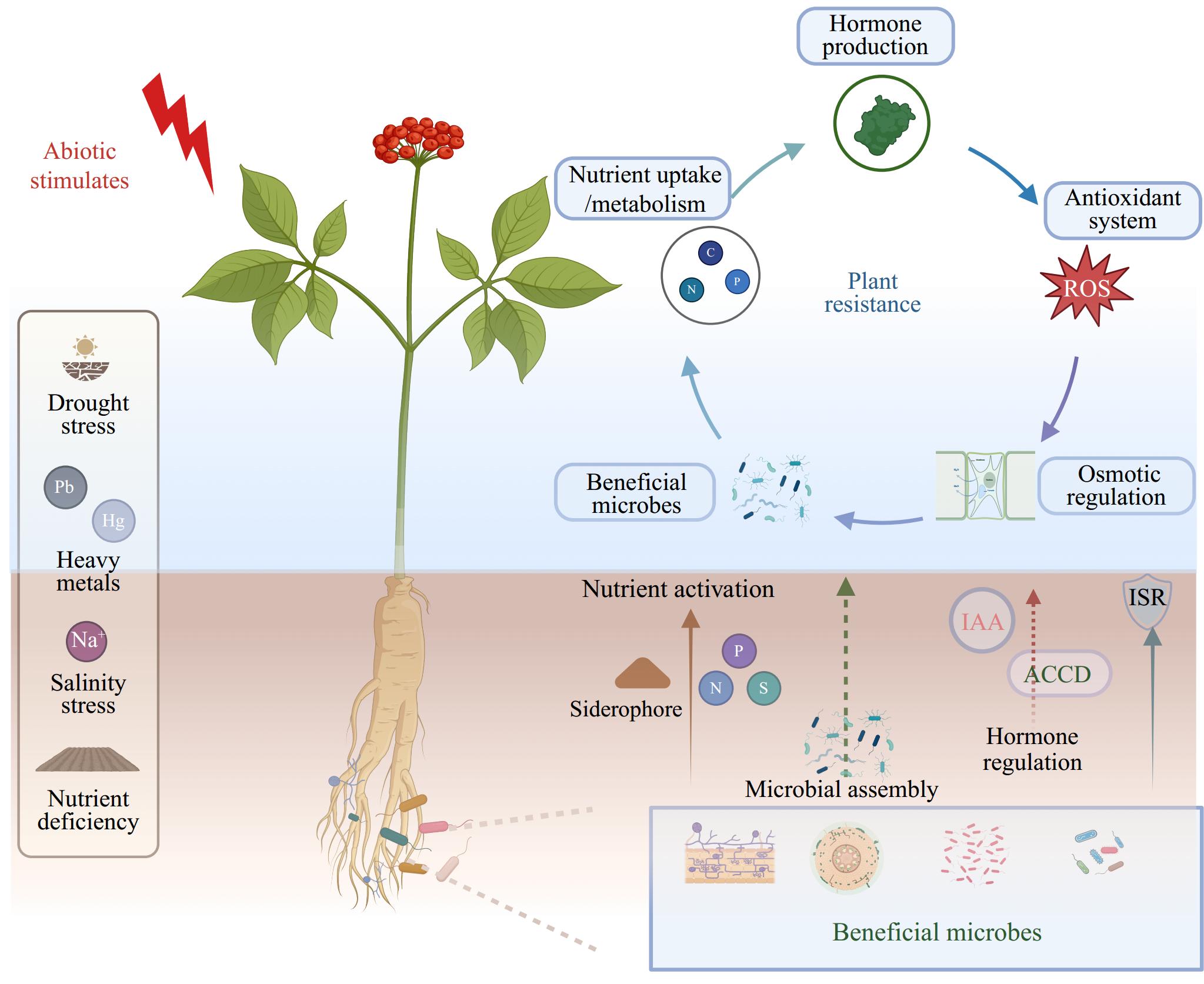
Figure 1.
Mechanistic insights into how beneficial microbes enhance medicinal plant resilience to abiotic stress.
-
Stress type Strain/microbes Medicinal plant Mechanistic function Ref. Drought AMF Pelargonium graveolens, Glycyrrhiza uralensis; Camellia sinensis Activation of antioxidant systems Xie et al.[54]; Amiri et al.[55]; Wang et al.[56] Poncirus trifoliate; Osmotic regulation Wu et al.[57] Nicotiana tabacum;
Cinnamomum migaoActivation of antioxidant systems;
osmotic regulationBegum et al.[58];
Yan et al.[59]Ephedra foliata Boiss Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulating IAA, GA and ABA levels Al-Arjani et al.[60] Poncirus trifoliate; Regulating root development;
regulating IAA and ABA levelsLiu et al.[61];
Zhang et al.[62]Glycyrrhiza uralensis Regulating aquaporin expression; regulating ABA level Xie et al.[63] DES Lycium ruthenicum, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Regulating root development, nutrient uptake and regulating soil microbiome assembly He et al.[20]; He et al.[64]; He et al.[65] Glycyrrhiza uralensis Regulating IAA production and ACCD activity Ahmed et al.[66] DSE+ Trichoderma viride Astragalus mongholicus Regulating soil microbial assembly He et al.[67] Bacillus sp. Glycyrrhiza uralensis; Activation of antioxidant systems Xie et al.[68] Bacillus sp. Trigonella foenum-graecum Enhancing ACCD activity;
beneficial microbial colonizationBarnawal et al.[69] Bacterial combination/
syncomsAstragalus mongholicus Activation of antioxidant systems Lin et al.[70] Mentha piperita; Hyoscyamus niger Activation of antioxidant systems Chiappero et al.[71]; Ghorbanpour et al.[72] Mentha pulegium Activation of antioxidant systems;
regulation of ABA and flavonoid levelsAsghari et al.[73] Ociumum basilicm Osmotic regulation Heidari et al.[74] AM fungi and PGPB Lavandula dentata Regulation of IAA levels and ACCD activity Armada et al.[75] Trigonella foenum-graecum Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulation of JA levels Yue et al.[76] Echinacea purpurea Regulation of nutrient uptake Attarzadeh et al.[77] Glycyrrhiza Regulation of nutrient uptake; beneficial microbial colonization Hao et al.[78] Myrtus communis Regulation of nutrient uptake; antioxidant system activation Azizi et al.[79] Salt stress AMF Chrysanthemum morifolium Regulation of nitrogen uptake Wang et al.[80] Ocimum basilicum Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio Abd-Allah and Egamberdieva[81] Trifoliate orange Enhanced aquaporin expression Cheng et al.[82] Ocimum basilicum Activation of antioxidant systems Yilmaz et al.[83] DES Artemisia ordosica Activation of antioxidant systems; IAA production; regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio Hou et al.[84] Trichoderma asperellum; Priestia endophytica Lycium chinense;
Trigonella foenum-graecumRegulating nitrogen uptake and assimilation Yan et al.[85];
Sharma et al.[86]Streptomyces sp. Glycyrrhiza uralensis Activation of antioxidant systems Li et al.[87] Glutamicibacter sp. Limonium sinense Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio; promotion of flavonoid synthesis Qin et al.[88] Bacillus sp.;
Streptomyces sp.; Azotobacter sp.Limonium sinense; Glycyrrhiza glabra; Iranian Licorice Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio Xiong et al.[39];
Qin et al.[89];
Mousavi et al.[90];
Mousavi et al.[91]Paenibacillus sp. Panax ginseng Activation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation; regulation of ABA level Sukweenadhi et al.[92] Achromobacter sp. Catharanthus roseus Activation of antioxidant systems;
enhanced ACCD activityBarnawal et al.[93] Brachybacterium sp. Chlorophytum borivilianum Regulation of IAA level, ABA level and ACCD activity Barnawal et al.[94] Bacterial combination/ Syncoms Bacopa monnieri; Galega officinalis Regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio Pankaj et al.[95]; Egamberdieva et al.[96] Phyllanthus amarus;
Coriandrum sativumActivation of antioxidant system Joe et al.[97];
Al-Garni et al.[98]Bacopa monnieri; Salicornia sp.; Capsicum annuum Osmotic regulation Bharti et al.[99]; Razzaghi Komaresofla et al.[100];
Sziderics et al.[101]Coriandrum sativum Regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio;
activation of antioxidant systemsRabiei et al.[102] Glycyrrhiza uralensis Activation of antioxidant systems;
regulation of nutrient uptakeEgamberdieva et al.[103] Mentha arvensis Activation of antioxidant systems; regulation of nutrient uptake; regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio; regulation of ACCD activity and siderophore production Bharti et al.[104] Medicago sativa Regulation of the IAA level Saidi et al.[105] Pistacia vera Regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratio; regulating IAA level, ACCD activity and siderophore production Khalilpour et al.[106] Fungi and PGPB Ocimum sanctum Activation of antioxidant systems;
regulation of the ACCD activitySingh et al.[107] Acacia gerrardii Regulation of the nutrient uptake;
regulation of the K+/ Na+ ratioHashem et al.[108] Artemisia annuaitalic;
Sesamum indicumActivation of antioxidant systems; osmotic regulation Arora et al.[109]; Khademian et al.[110] Heavy metal stress Halomonas sp Ligusticum chuanxiong Reduction of the heavy-metal uptake and regulating rhizosphere microbial assembly Li et al.[111] Piriformospora sp. Piriformospora indica Improving tolerance; regulation of rhizosphere microbial assembly Rahman et al.[112] Rhizobia Robinia pseudoacacia Improving tolerance;
regulation of rhizosphere microbial assemblyFan et al.[113] Sphingomonas sp. Sedum alfredii Activation of antioxidant systems Pan et al.[114] Burkholderia sp. Sedum alfredii Regulating translocation ability Chen et al.[115] Leifsonia sp. Camellia sinensis Regulation of rhizosphere microbial assembly Jiang et al.[116] Pseudomonas sp. Solanum nigrum Regulation of nutrient uptake; recruiting beneficial bacteria Chi et al.[117] Microbial inoculant Panax quinquefolium;
Salvia miltiorrhizaReduction of heavy-metal uptake;
regulation of rhizosphere microbial assemblyCao et al.[118];
Wei et al.[119]Nutrient deficiency AMF Glycyrrhiza uralensis Regulation of P and K uptake; improving nutrient utilization Chen et al.[120] Bacillus sp. Mentha arvensis Improving P solubilization Prakash and Arora[121] Bacillus sp. Camellia sinensis Regulation of K utilization Pramanik et al.[122] Serratia sp. Achyranthes aspera Improving P solubilization, IAA level and siderophore production Devi et al.[123] Bacterial combination/syncoms Angelica dahurica Regulation of nutrient uptake Jiang et al.[40] Astragalus mongolicus Regulation of nutrient uptake; regulation of rhizosphere microbial assembly Shi et al.[124] Camellia sinensis Regulating root development;
Regulation of the N uptakeXin et al.[125] Glycyrrhiza uralensis Regulation of nutrient uptake, IAA level and siderophore production Li et al.[126] Heat stress Soil suspension Atractylodes lancea Recruiting specific endophytic bacterial Wang et al.[127] Chilling stress Fungi and PGPB Ocimum sanctum Regulation of nutrient uptake and the ACCD activity; osmotic regulation Singh et al.[128] Flooding stress Bacterial
combination/syncomsOcimum sanctum Regulation of the ACCD activity Barnawal et al.[93] Table 1.
Role of beneficial microorganisms in aiding host plant resisting abiotic stresses.
-
Stress type Strain/microbes Medicinal plant Contribution Ref. Drought AMF Glycyrrhiza uralensis Improving glycyrrhizin and liquiritin production;
up-regulation of the expression of key genes (e.g. squalene synthase (SQS1), β-amyrin synthase (β-AS)
and cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYP88D6
and CYP72A154)Orujei et al.[129];
Xie et al.[63]Nicotiana tabacum/ Pelargonium graveolens Enhancement of oil content; up-regulation of the expression of key genes Begum et al.[58]; Amiri et al.[55] DSE Glycyrrhiza uralensis Elevation of glycyrrhizin and glycyrrhizic acid content; regulation of the N and P content He et al.[147] Bacillus sp. Glycyrrhiza uralensis Enhancement of the total flavonoids, total polysaccharide and glycyrrhizic acid content; up-regulation of the expression of key enzymes (e.g. lipoxygenase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase); simulation of JA-synthesis Xie et al.[68];
Yue et al.[76]Bacterial combination/ Syncoms Astragalus mongholicus Enhancement of the astragaloside IV and calycosin-7-glucoside content Lin et al.[70] Mentha pulegium Improving phenolic, flavonoid and oxygenated monoterpenes production Asghari et al.[73] Hyoscyamus niger Improving tropane alkaloid production Ghorbanpour et al.[72] Salt AMF Glycyrrhiza glabra Elevation of the glycyrrhizin and terpenoid precursors production Amanifar et al.[148] Priestia endophytica Trigonella foenum-graecum Improving phenolic compounds and trigonelline synthesis and N fixation Sharma et al.[86] Azotobacter sp. Glycyrrhiza glabra Enhancement of the glycyrrhizic acid and glabridin production Mousavi et al.[91] Bacterial combination/ syncoms Artemisia annua Enhancement of the artemisinin production; improving N and P contents Arora et al.[109] Foeniculum vulgare Enhancement of the essential oil production Mishra et al.[149] Bacopa monnieri Enhancement of the bacoside A production Pankaj et al.[95] AM fungi and PGPB Sesamum indicum Improving phenolic, flavonoid, sesamin and sesamolin production Khademian et al.[110] Mentha arvensis Enhancement of essential oil content Bharti et al.[150] Heavy-metal stress Microbial inoculant Panax quinque folium Enhancement of the ginsenoside production; regulation of the rhizo-microbial structure and composition Cao et al.[118] Microbial inoculant Salvia miltiorrhiza Elevation of the total tanshinones content; recruiting beneficial microorganisms Wei et al.[119] N-deficiency Bacterial combination Angelica dahurica Enhancement of the furanocoumarin production Jiang et al.[40] Astragalus mongolicus Enhancement of the flavonoids, saponins, and polysaccharides contents Shi et al.[124] P-deficiency AMF Hypericum perforatum Enhancement of the glycyrrhizic acid, liquiritin, isoliquiritin, and isoliquiritigenin contents; regulation of the nutrient absorption Lazzara et al.[151] Polygonum cuspidatum Enhancement of the chrysophanol, emodin, polydatin, and resveratrol contents; regulation of the nutrient absorption Deng et al.[141] Nutrient-deficiency AMF Glycyrrhiza uralensis Elevation of the isoliquiritin and isoliquiritigenin content; enhancement of the P, K and microelements absorption Chen et al.[120] Heat stress Soil suspension Atractylodes lancea Enhancement of the hinesol, β-eudesmol, atractylon and atractylodin content, up-regulation of the expression of key genes (e.g. 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS), farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPPS), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme (HMGR)); enrichment of specific beneficial bacteria Wang et al.[127] Table 2.
Role of beneficial microorganisms in the contents of main medicinal compounds in medicinal plants subjecting to abiotic stresses.
Figures
(1)
Tables
(2)