-
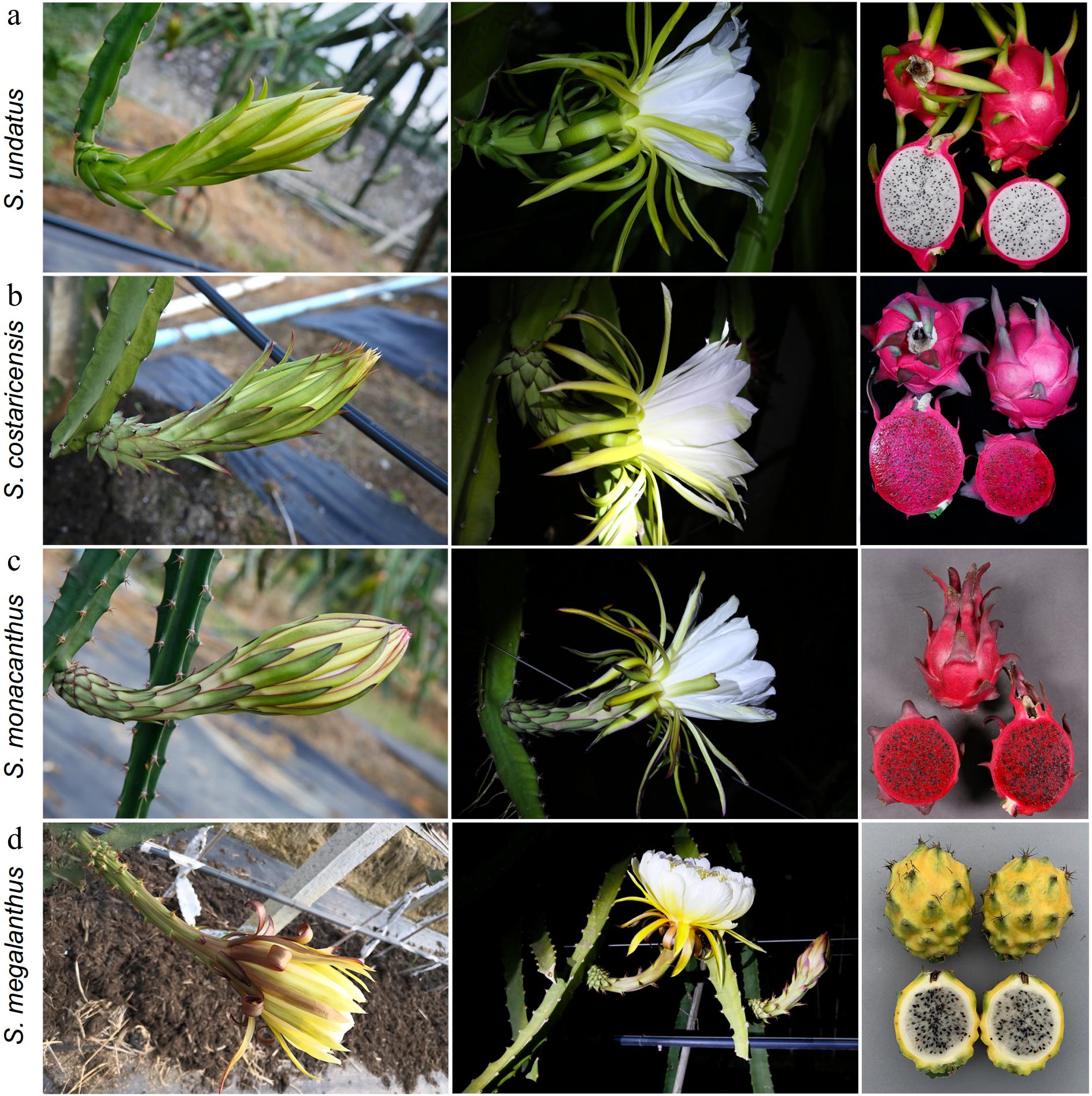

Figure 1.
The phenotype of bud, flower and fruit of four main commercial dragon fruits. (a) S. undatus has green buds; big, funnel-shaped, and white nocturnal flowers; and oblong fruits with pink peel, and white flesh and covered with green, long, and hard scales. (b) S. costaricensis has green buds along with lighter red edges on the outer perianth; big, funnel-shaped and white nocturnal flowers; and ovoid fruit with dark magenta peel and violet-red flesh, and covered with red, soft and short scales. (c) S. monacanthus has green buds along with bright red edges on the outer perianth; big funnel-shaped and white nocturnal flowers; and ovoid fruit with crimson peel and flesh covered with red, soft and short scales. (d) S. megalanthus has green buds along with dark brown outer perianth; big funnel-shaped (rounder than other species) and white (a little yellow) nocturnal flowers; and ovoid fruit with yellow peel and white (transparent) flesh covered with thorns on tuberculate skin instead of scales.
-
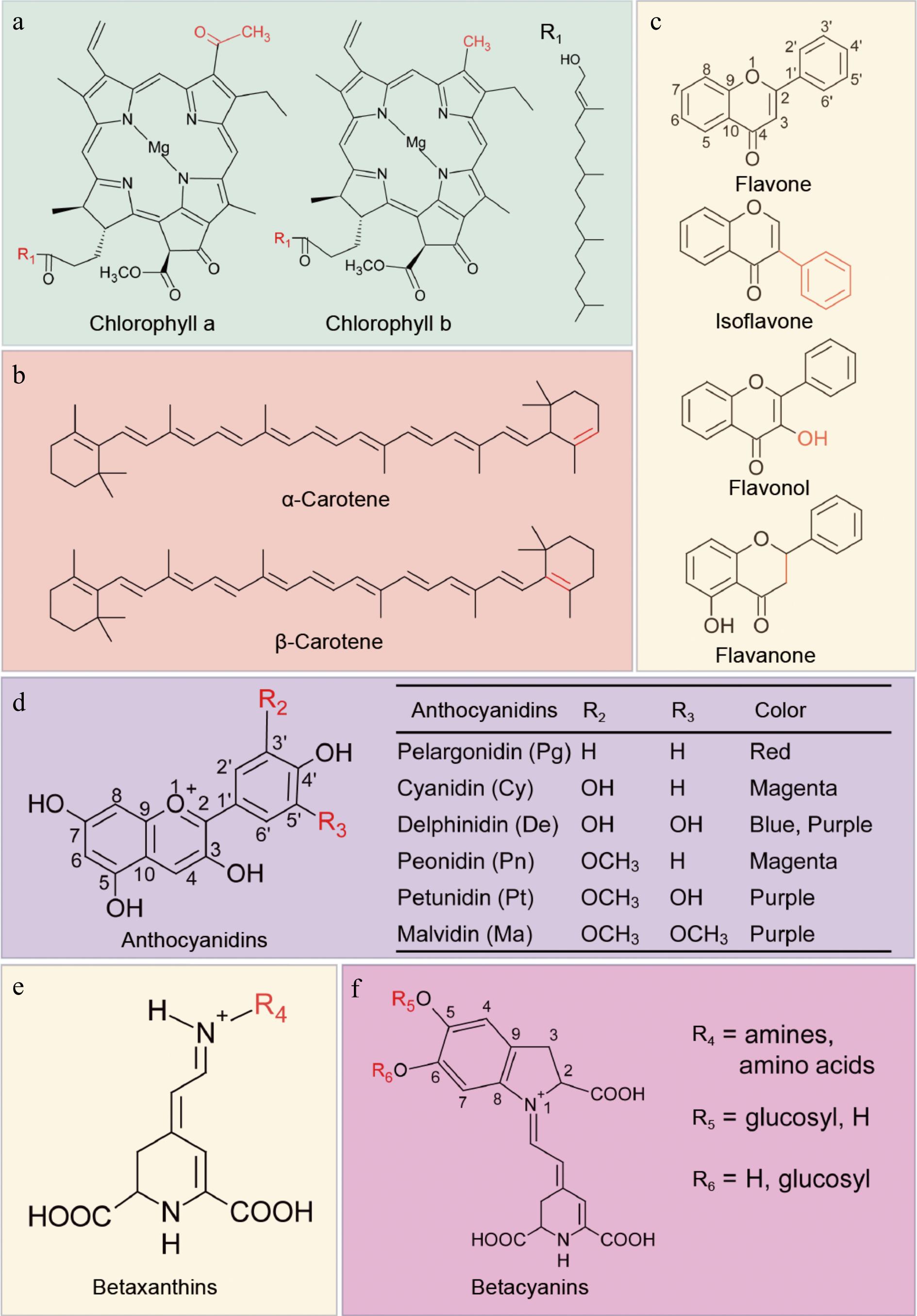
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of four natural plant pigments. (a) Chemical structures of chlorophyll a and b (green). Residue R1 is shown on the right. (b) Chemical structures of carotenes (orange). (c) Chemical structures of flavones and flavonols (yellow), flavone is the core structure for this class of substances. (d) Chemical structures of anthocyanidins. Residues R2, R3 and corresponding color for different type anthocyanidins are listed in the table. (e), (f) Chemical structures of betalains. Composition of residues R4, R5, R6 will produce kinds of betalains. Red groups in (a) − (c) represent the differences of pigments with similar structures.
-
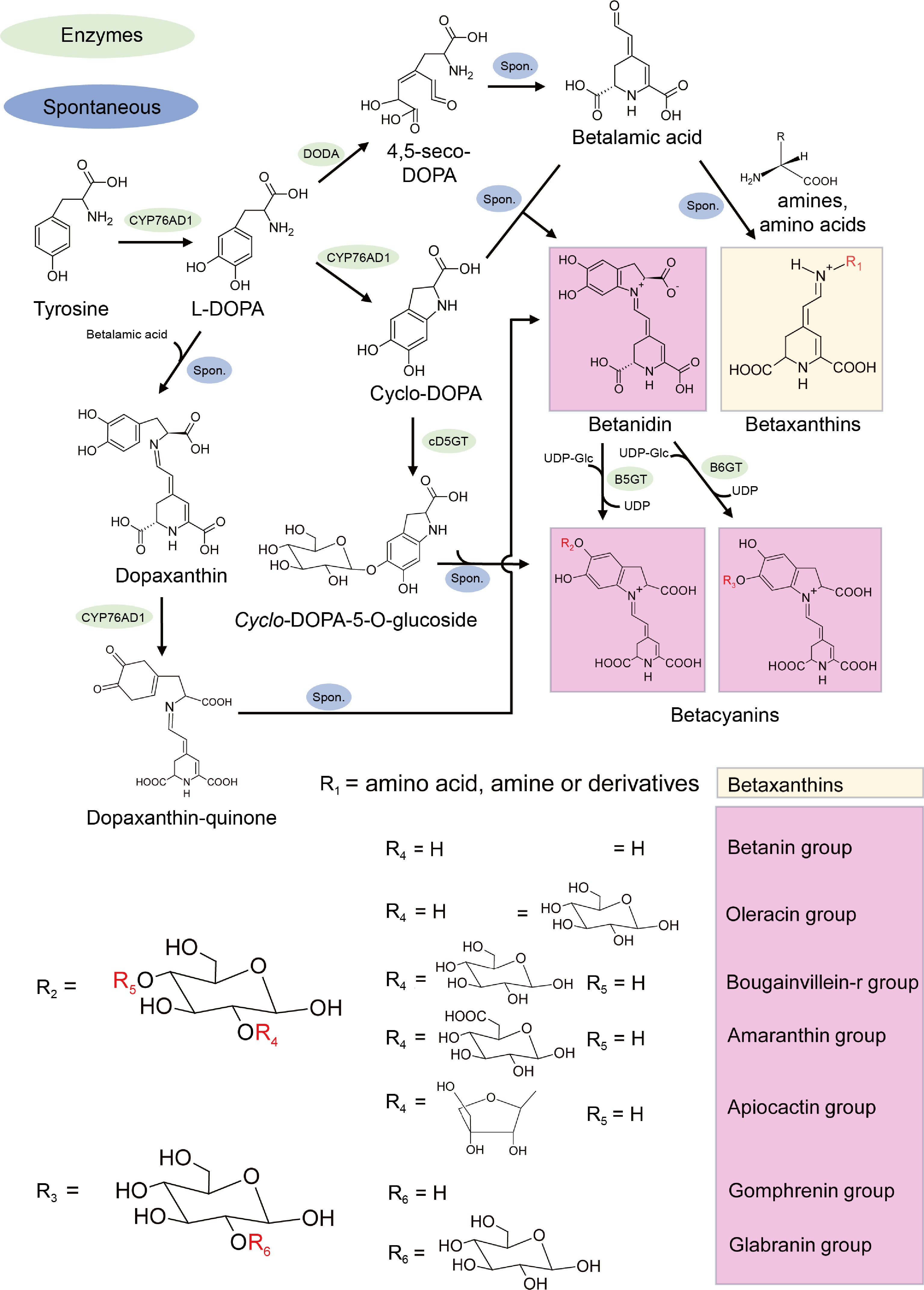
Figure 3.
Schematic pathway of betalains biosynthesis pathway. DODA, DOPA dioxygenase; cD5GT, cyclo-DOPA-5-O-glucosyltransferase; B5GT, betanidin-5-O-glucosyltransferase; B6GT, betanidin-6-Oglucosyltransferase; UDP, uridine-5'-diphosphate. Composition of residues R1-6 forms betaxanthins and seven type betacyanin pigments. The green color highlights the enzymes.
-
Gene name Gene Id Gene function Species Ref. HuADH1 HU03G02979.1 Arogenate dehydrogenases S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HuYP76AD1-1 HU03G00480.1 Cytochrome P450 enzyme S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HuDODA1 HU03G01342.1 4,5-DOPA extradiol dioxygenase S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HucDOPA5GT1 HU07G00239.1 cyclo-DOPA-5-glucosyltransferase S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HucDOPA5GT2 HU03G00240.1 cyclo-DOPA-5-glucosyltransferase S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HuMYB1 HU01G00040.1 MYB transcription factor, inhibiting the biosynthesis of betalains via suppressing the expression of HuADH1, HuCYP76AD1-1 and HuDODA1 S. undatus (H. undatus) [23] HubHLH159 HU11G01328.1 bHLH transcription factor, promoting betalains biosynthesis by activating the expression of HuADH1, HuCYP76AD1–1, and HuDODA1 S. undatus (H. undatus) [18] HpWRKY44 WRKY transcription factor, activates the expreesion of HpCytP450-like1, promoting the biosynthesis of betalains S. monacanthus
(Hylocereus polyrhizus)[86] HmoWRKY40 WRKY transcription factor, binding and activating the expression of HmoCYP76AD1 S. monacanthus
(Hylocereus monacanthus)[88] Table 1.
Reported genes involved in betalains biosynthesis.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(1)