-
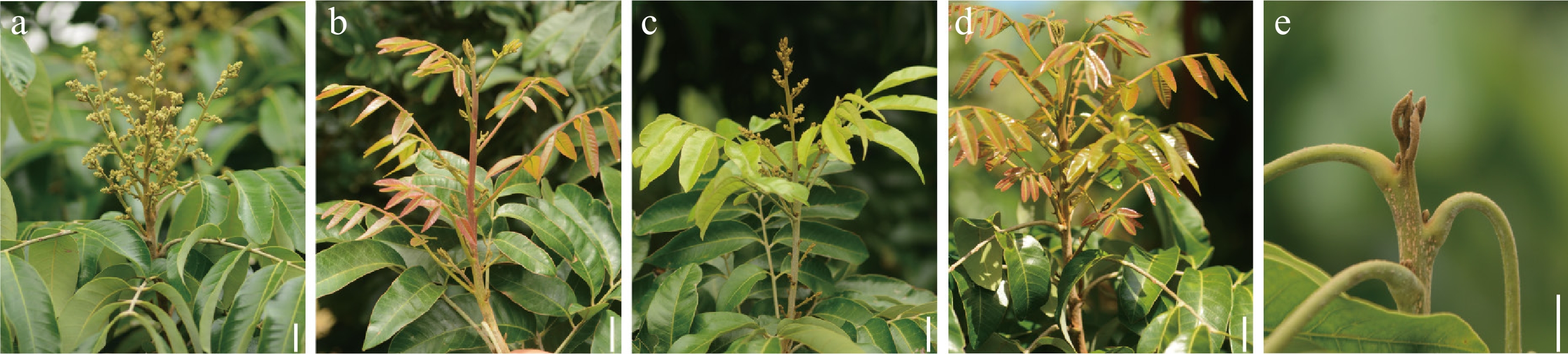

Figure 1.
Phenotypic variation of branches induced by KClO3 in off-season flowering of longan. (a) buds exhibiting shoot-like morphology that undergo direct floral bud differentiation; compound leaves show inhibited growth or abscission. (b) initial shoot elongation followed by bud transition and morphological differentiation during the red leaf stage. (c) shoots exhibiting floral transition demonstrate a "flower with leaf" phenotype. (d) vegetative shoots develop without entering floral transition. (e) dormant buds that do not produce flowers or new shoot growth. Scale bars = 2 cm.
-
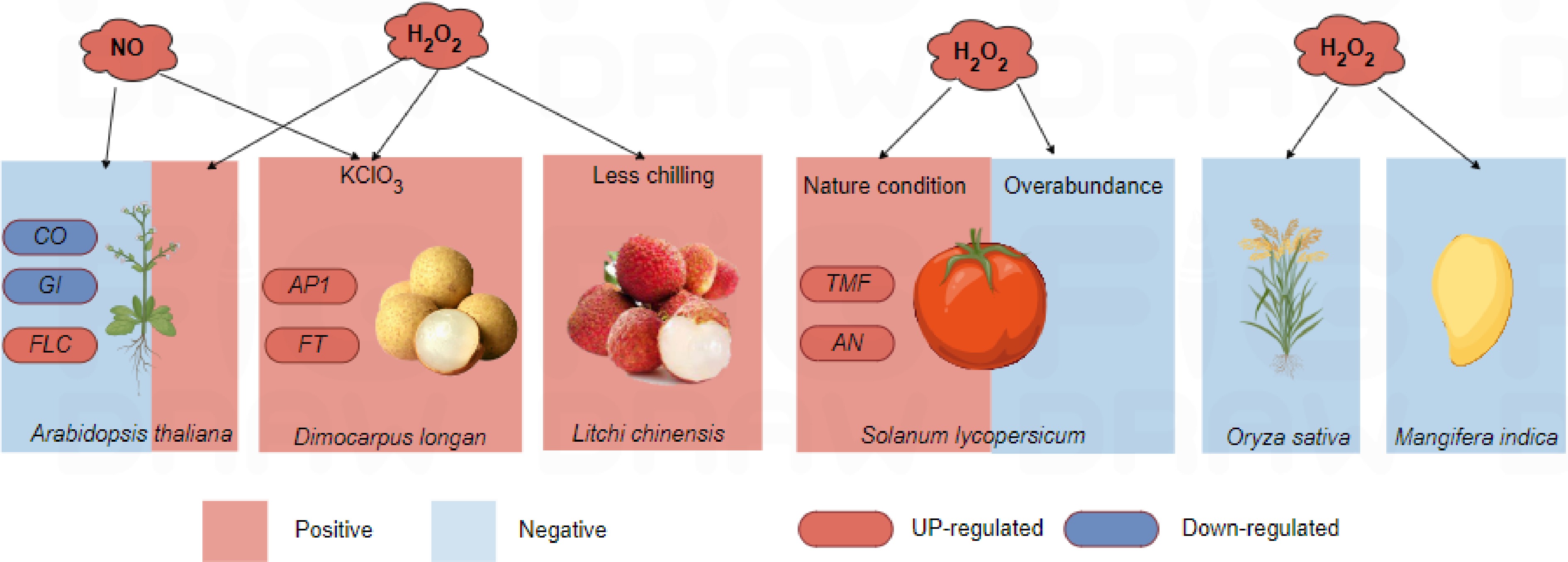
Figure 2.
The influence of ROS on plant flowering. NO, nitric oxide; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; CO, CONSTANS; GI, GIGANTEA; FLC, FLOWERING LOCUS C; AP1, APETALA1; FT, FLOWERING LOCUS T; TMF, TERMINATING FLOWER; AN, ANANTHA. Red marked NO, H2O2 and genes meant their increasement in content and gene expression level, and the red box indicated that they promoted flowering of the corresponding plants, while the blue box indicated that the gene expression level was down-regulated, and the blue box indicated that plants were inhibited flowering.
-
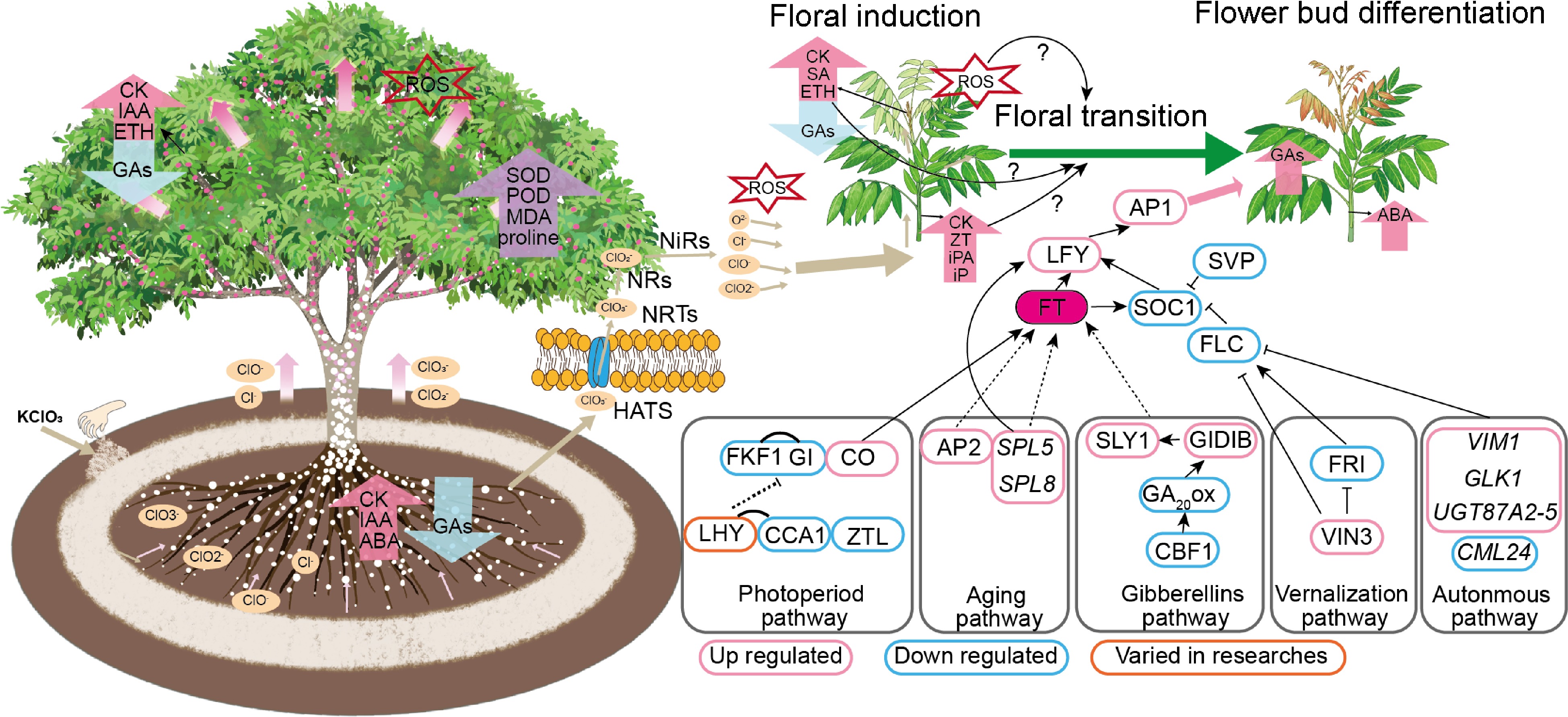
Figure 3.
Hypothetical model for KClO3-induced flowering in longan. Note: Cl-, chloride ion; ClO-, hypochlorite ion; ClO2-, chlorite ion; ClO3-, chlorate ion; CKs, Cytokinin; GAs, Gibberellins; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NR, Nitrate Reductase; NiR, Nitrite Reductase; NRT1, Nitrate Transporter 1; HATS, High-Affinity Transport System; FKF1, Flavin-Binding, Kelch Repeat, F Box 1; CO, CONSTANS; GI, GIGANTEA; CCA1, CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1; LHY, LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL; ZTL, ZEITLUPE; SPL, SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE; AP2, APETALA 2; GID1B, GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1B; GA1, GA REQUIRING 1; FLC, FLOWERING LOCUS C; VIN3, VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3; FRI, FRIGIDA; VIM, VARIANT IN METHYLATION; FY, WDR33; MYB30, MYB domain protein 30; AP1, APETALA1; FT, FLOWERING LOCUS T; AGL24, AGAMOUS-like 24; LFY, LEAFY; FUL, FRUITFULL; SOC1, SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CO 1. The expression of genes was based on the comprehensive analysis of the results of references, down and up-regulated meant that these genes were commonly down or up-regulated in several references.
-
Other cultivars 'Sijimi' Integrators FT1: positive*[21,22,32] SVP: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] FT2: negative*[21,22,32] TFL1-1: negative[24] TFL1-2: negative[24] Photoperiod
pathwayGI: positive[27] COL: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] FKF1: positive[27] APRRs: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] ELF4-1/2: negative[28] GI: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] FKF1: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] EFL: positiveRNA-seq[10,29] LFY: negativeRNA-seq[10,29] Flower meristem identity LFY: positive[10] − Others − WRKYs: positiveRNA-seq[30] WRKYs: positiveRNA-seq[30] *'positive' and 'negative' referred to the results of molecular function verification. 'positive' genes were those that, when overexpressed in other plant species, accelerated flowering time, whereas 'negative' genes delayed flowering. In the absence of experimental verification, classification was based on RNA-seq or RT-qPCR data, with 'positive' genes showing upregulation and 'negative' genes showing downregulation in flower buds compared to leaf buds.RNA-seq Represented the results based on RNA-seq. Table 1.
Genes in regulating the natural flowering of longan
-
Cultivar Region Treatment method Type and dosage * Cultivation pattern and tree age/year Processing time Flower bud emergency/d Flowering rate of trees/% Flowering rate of branches% References Shixia Guangxi province, China Dissolved in water and then applied to soil −; 100 g/m2 Plantation; 20 Early Jun. 40 100% 43.50% [67] Shixia Danzhou city, Hainan province, China −; 0.75 kg/tree Plantation; 7 Jul. 9th 45 − − [68] Shixia Lujiang Town, Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan province, China −; 0.5 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 100% 35% [69] Shixia −; 0.75 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 33% 48% Shixia −; 1.0 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 100% 45% Shixia Hainan province, China Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 0.5 kg/m Plantation; 8 After three times of branches 28 [70] Shixia Guangdong province, China Injection −; 8 g/tree Plantation; 4 − 30 − − [71] Shixia Ditched and then broadcast over the soil 90% purity; 1 kg/tree Plantation; 7 Oct. 28th − − − [72] Shixia Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 1.0~1.5 kg /tree Plantation; - Dec. 3th − 100% 46.25% [73] Shixia Foliar spraying applied twice AR; 830 mg/L Plantation; - Dec. 10th − 100% 78.38% [73] Shixia Guangxi province, China Dissolved in water and then applied to soil + foliar spraying TG; 0.5 kg/tree Plantation; 30 Early Dec. 47 − 91.78% [45] Shixia − −; 7.5 g/tree Plantation; 12 Oct. 1th − − 52.25% [74] Chuliang Lujiang Town, Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan province, China Dissolved in water and then applied to soil −; 0.75 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 100% 35% [69] Chuliang −; 0.5 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 66% 32% [69] Chuliang −; 1.0 kg/tree Plantation; 5 Aug. 7th − 33% 33% [69] Chuliang Guangxi province, China Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 7.5 g/tree Plantation; 12 Oct. 1th 23 d advance − 29.79% [74] Chuliang Guangdong province, China Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 1.0~1.5 kg/tree Plantation; - Dec. 3th − 50% 3.59% [73] Chuliang Foliar spraying applied twice AR; 830 mg/L −; - Dec. 1th − 100% 4.61% [73] Fenglisui Xiamen city, Fujian province, China Ditched and then broadcast over the soil AR, 99.5% purity; 5 g/tree −; 5 Sep. 21th 40 100% 74.50% [47] Fenglisui AR, 99.5% purity; 5 g/tree + girdling −; 5 Sep. 21th 40 100% 86.8% [47] Fenglisui AR, 99.5% purity; 5 g/tree + branch pulling −; 5 Sep. 21th 40 100% 90.2% [47] Fenglisui Xiamen city, Fujian province, China Dissolved in water and then applied to soil 99% purity; 5 g/tree −; 3 Sep. 21th 38 100% 94.80% [46] Fenglisui 99% purity; 15 g/tree −; 3 Sep. 21th 38 75% 86.20% [46] Fenglisui 99% purity; 25 g/tree −; 3 Sep. 21th 38 50% 75.30% [46] Songfengben 99% purity; 70 g/tree Plantation; 6 Aug. 29th 43 94% 92.80% [48] Songfengben −; 5 g/tree Pot experiment; 3 Nov. 25th 45 100% 60% [48] Songfengben −; 10 g/tree Pot experiment; 3 Nov. 25th − 0 0 [48] Guixiang Guangxi province, China − −; 7.5 g/tree Plantation; 12 Oct. 1th − 32.63% [74] Fuyan Fujian province, China Broadcasting −; 700 g/tree Street tree; - Middle of Jun. − 75.50% − [58] Fenker Taiwan province, China Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 80 g/tree Plantation; 14 Oct. 24th 43.8 − 69% [75] Fenker −; 80 g/tree+ girdling Plantation; 14 Oct. 24th 46.4 − 73% [75] E-Daw Ban Pong district, Ratchaburi province, Thailand − −; 300 g/tree Plantation; 8~10 − 27 100% − [76] Daw Thailand − −; 10 g/tree −; 2 − 35 − 91% [77] E-Daw Chiang Mai city, Thailand Broadcasting −; 8 g/tree Plantation; 4-6 21 − 100% [41] E-Daw Chiang Mai city, Thailand Foliar spraying −; 1 g/L Plantation; 4-6 Hot season − − 12.50% [41] E-Daw Rainy season − − 61.70% [41] E-Daw Cool season − − 96.70% [41] E-Daw Chiang Mai city, Thailand Dissolved in water and then applied to soil −; 4 g/m2 Plantation; 4 Aug.-Rainy season 31 − 50.90% [41] E-Daw Sep.- Rainy season 24 − 11.90% [41] E-Daw Oct.-Cool season 20 − 88.60% [41] E-Daw Nov.- Cool season 26.3 − 80.00% [41] E-Daw Dec.- Cool season 39.5 − 88.80% [41] E-Daw Mar.- Rainy season 27 − 77.50% [41] E-Daw Apr.- Rainy season 24.3 − 87.50% [41] E-Daw May- Rainy season 31.5 − 50.00% [41] E-Daw Jun.- Rainy season 21.5 − 36.30% [41] E-Daw Jul.- Rainy season 25 − 51.30% [41] E-Daw Lampang province, Thailand Dissolved in water and then applied to soil −; 5 g/m2 10-12 Nov. 30th 38 − 98.7% [78] Si-Chompoo Chiang Mai, Thailand Broadcasting −; 1 g/tree Plantation; - Apr. 6th 21 − 100.00% [41] Si-Chompoo Chiang Mai, Thailand Injection −; 0.25 mg/cm branch Plantation; - Apr. 6th 49 − 90.00% [41] Si-Chompoo Dissolved in water and then applied to soil −; 1 g/m2 Plantation; 4-6 Nov. 5th 21 − 100.00% [41] Si-Chompoo −; 2 g/m2 Plantation; 4-6 Nov. 5th 21 − 100.00% [41] Si-Chompoo −; 4 g/m2 Plantation; 4-6 Nov. 5th 21 − 100.00% [41] XCV Mekong Delta provinces, Vietnam Ditched and then broadcast over the soil −; 24-36 g/m + girdling (2-3 mm width) Plantation; - − − − − [79] TDB 20-40 g/m + girdling (0.5-1.0 mm width) Plantation; - − − − − [79] E-Daw 40-60 g/m Plantation; - − − − − [79] Biew Kiew State of Hawaii, USA Broadcasting 300 g/tree Plantation; 7 Apr. 5th 49 − [80] Biew Kiew Plantation; 4 Sep. 15th − − 97.80% [81] AR, analytical reagent; TG, technical grade; * m refers to the canopy diameter, and m2 refers to the canopy projection area. Due to the different units in each article and the lack of information on canopy diameter, this statistical table retained the data and units mentioned in the references. Table 2.
Statistics of literature information on the treatment methods and flowering rates of KClO3-induced flower for longan
-
Pathway Genes Positive* Negative* Integrators FT1*[22]; FT[71] FT2*[22]; FT3[22]; SVP[20]; SOC1[20,71]; FLC[20,94] Photoperiod Pathway LHY[71]; CO[94] LHY[94]; CO[71]; GI[71]; FKF1[71]; CCA1[71]; ZTL[71] Vernalization VIN3[71] Hormone GID1, SLY1[71]; ARF3[32] ABI5[71]; GA2ox[94]; CBF1[94] Aging pathway AP2[32]; SPL8[32]; SPL5[94] Autonomous Pathway GLK1, UGT87A2-5, VIM1[94] CML24[94] Flower meristem identity AP1[20,71,94,96]; LFY[71,94]; MADS98, AG[71,94], SEP1/2/3/4, AP3-1/2, PI, AG, AGL6[20,94] AG[32]; AGL42[32]; MADS111, MADS82[20,94] Others MYB23/33/9/116[95]
Early stage:
3 C3Hs; 2 HMGs; 3 MYBs; 1 bHLH; 1 CPP[71]
Middle stage:
3 AP2-EREBPs; 2 C2-like; 1 CCAAT-like; 1 MYB; 1CPP[71]
Last stage:
10 MADSs; 4 HBs; 1 LEAFY; 3 AP2-EREBP-like[71]Early stage:
1 C3Hs; 1 CCAAT-like[71]
Middle stage:
1 EIL; 4 b-ZIPs; 2 TRAFs; 1 C2-like; 1 bHLH[71]
Last stage:
2 C3Hs; 1 GRAS; 1 C2-like; 1 bHLH; 2 MADSs; 1 MYB[71]*This table was organized based on the results of RNA-seq from reference, with 'positive' genes showing upregulation and 'negative' genes showing downregulation in flower buds compared to leaf buds. Table 3.
Genes in regulating the KClO3 induced flowering of longan
Figures
(3)
Tables
(3)