-
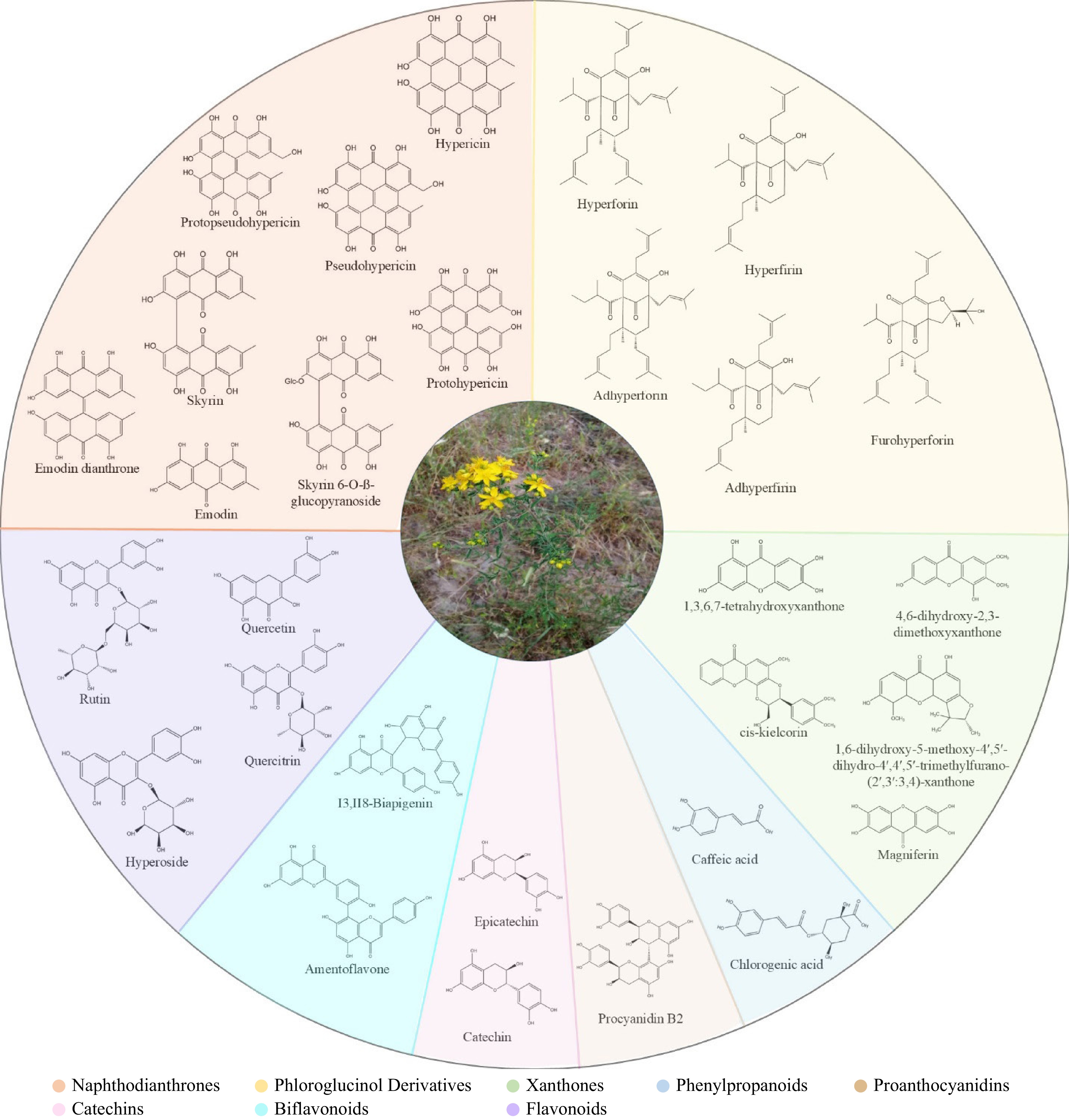
Figure 1.
Key chemical constituents of Hypericum perforatum. Different colors represent chemical classes: Naphthodianthrones, Phloroglucinol Derivatives, Xanthones, Phenylpropanoids, Proanthocyanidins, Catechins, Biflavonoids, Flavonoids.
-
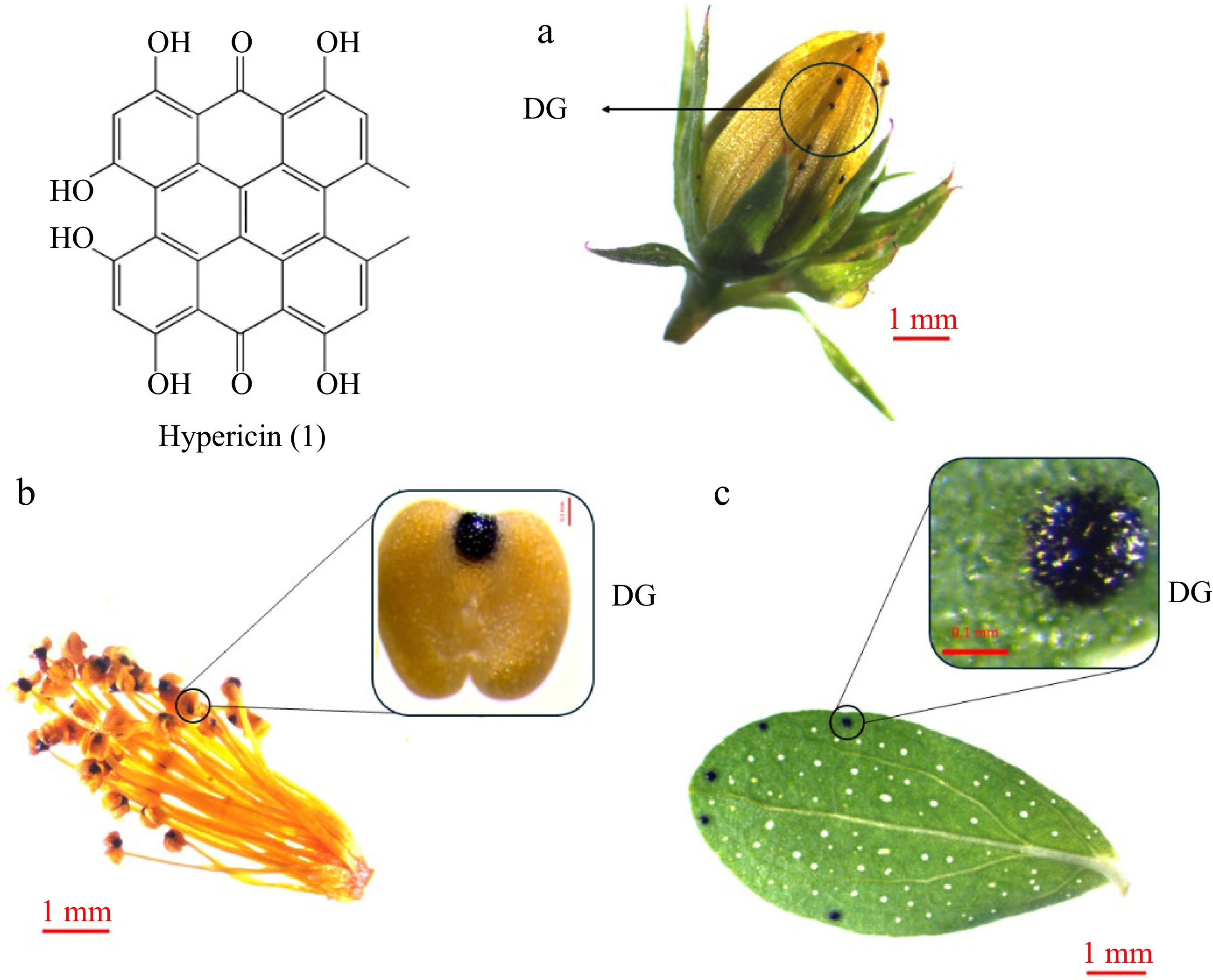
Figure 2.
Hypericin accumulation in Hypericum perforatum organs: (a) bud, (b) stamens, (c) leaf. Hypericin (1) is accumulated in Dark Glands (DGs) of the aerial parts of the plants like (a) sepals and petals, (b) stamens, and (c) leaves.
-
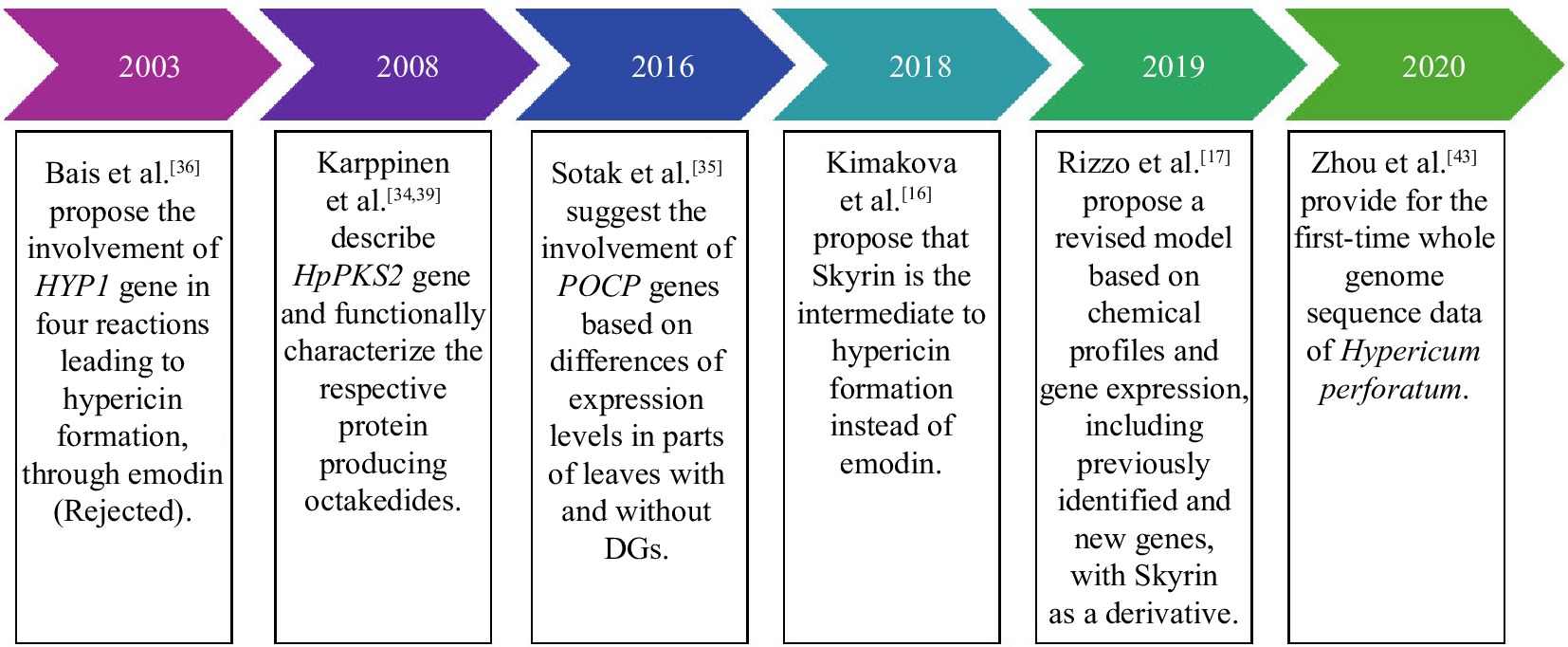
Figure 3.
Key points to hypericin biosynthesis research.
-
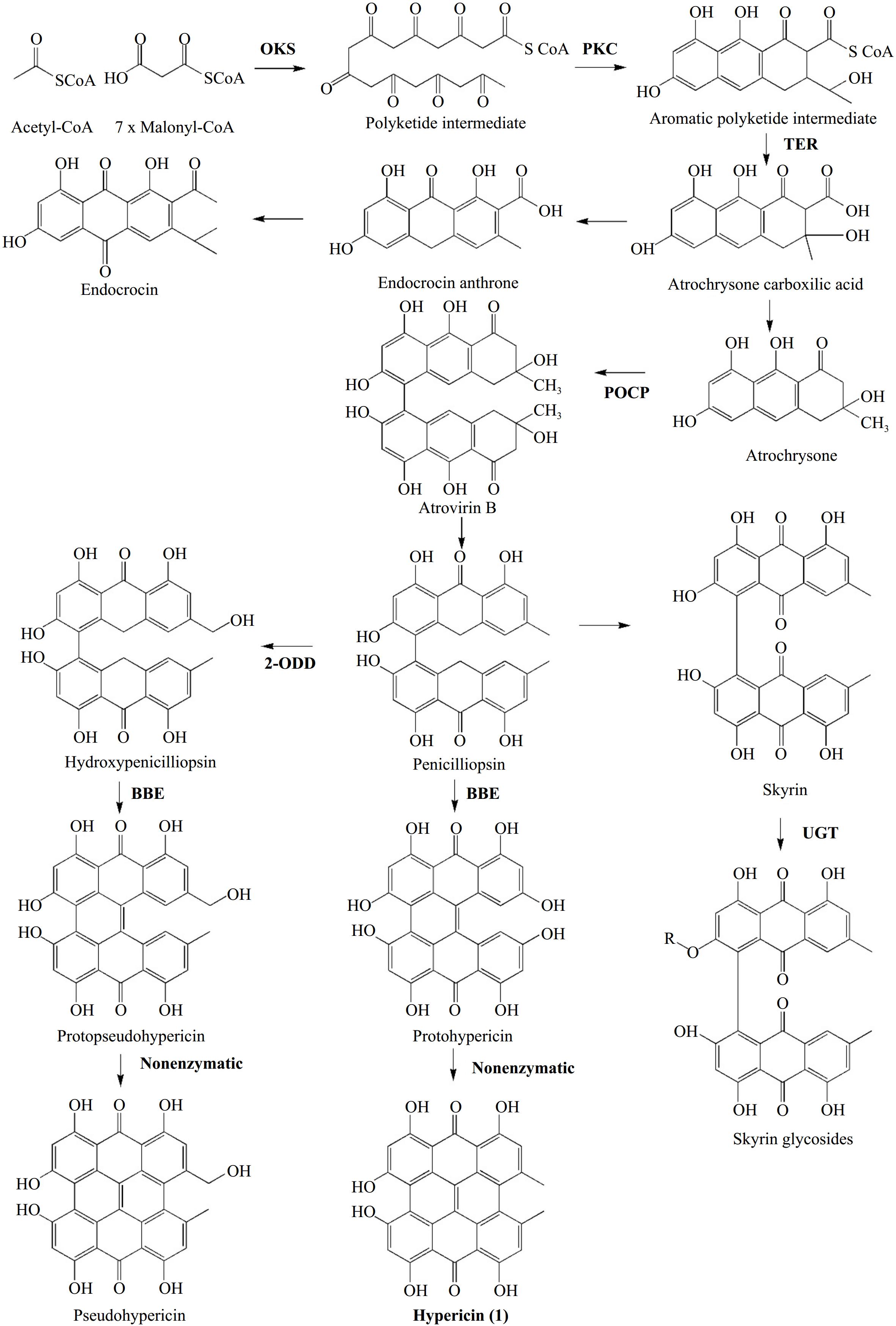
Figure 4.
Hypericin biosynthesis as presented by Rizzo et al.[17]. In bold: enzymes involved in reactions' catalysis. Abbreviations: OKS: Oktaketide Synthase, PKC: Polyketide Cyclase, TER: Thioesterase, POCP: Phenolic Oxidative Coupling Protein, BBE: Berberine Bridge Enzyme, 2-ODD: 2-oxoglutarate and Fe(II)-dependent oxygenase, UGT: UDP-glucosyltransferase.
-
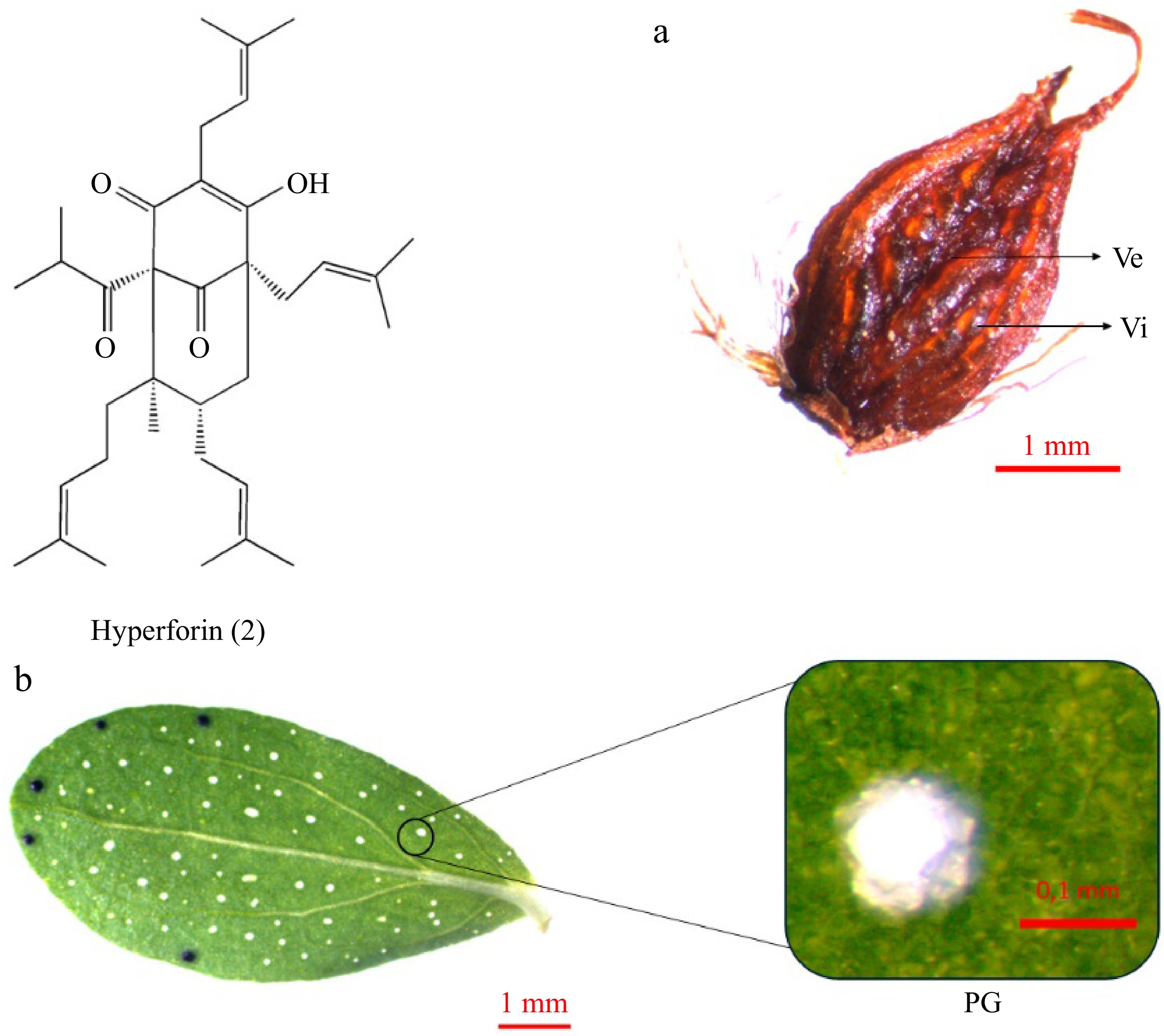
Figure 5.
Hyperforin accumulation in Hypericum perforatum organs: (a) fruit, (b) leaf. Hyperforin (2) is accumulated in formations like vittae (Vi) and vesicles (Ve) on the (a) fruit capsule, and in the (b) Pale Glands (PGs) of the leaves.
-
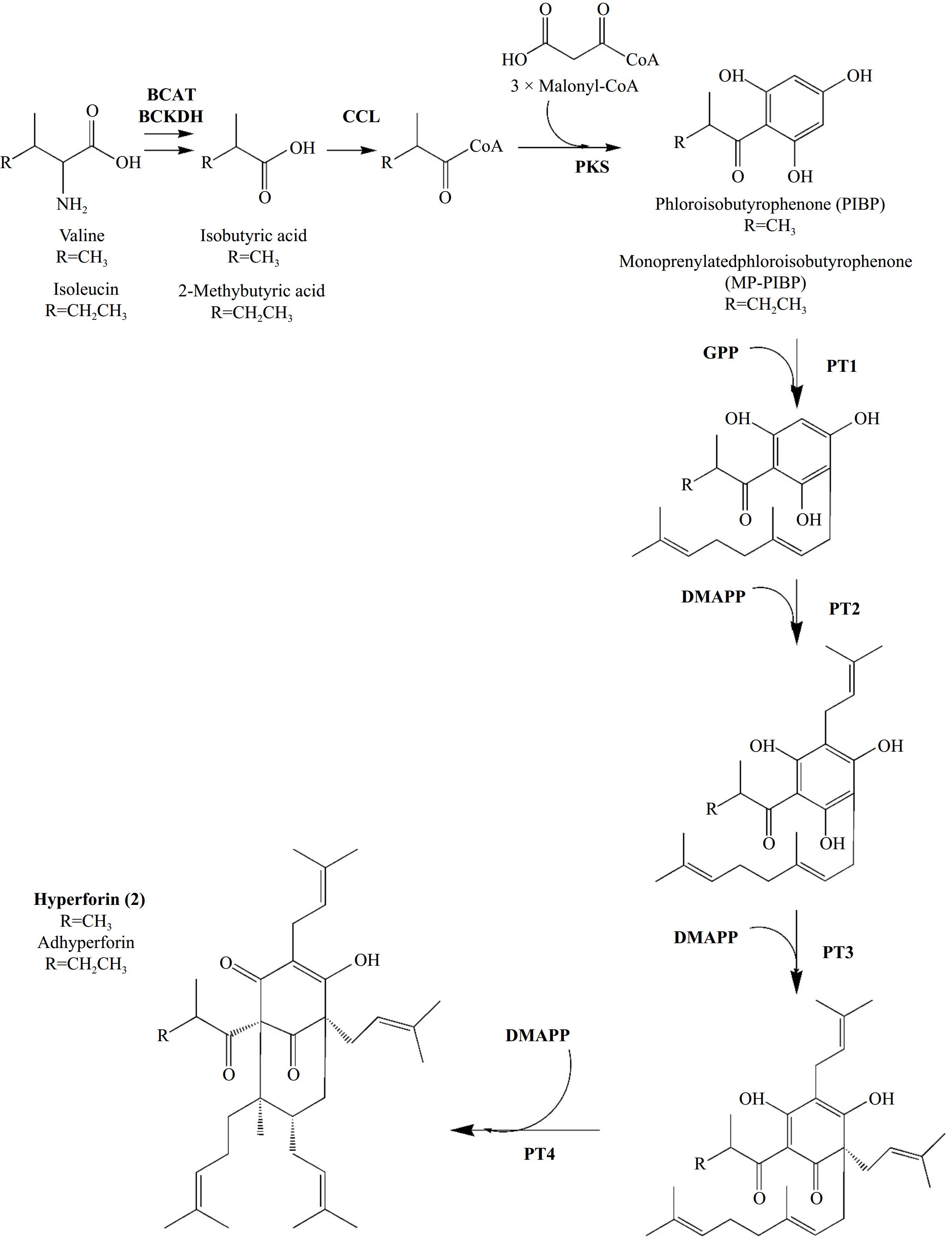
Figure 6.
Biosynthesis of Hyperforin (2) and its homologue Adhyperforin according to Wu et al.[37,38]. In bold: enzymes involved in reactions' catalysis and prenyl-groups. Abbreviations: BCAT: branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase, BCKDH: branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase, CCL: CoA ligase, PKS: Polyketide synthase, PT: Prenyltransferase, DMAPP: dimethylallyl-diphosphate, GPP: geranyl-diphosphate.
-
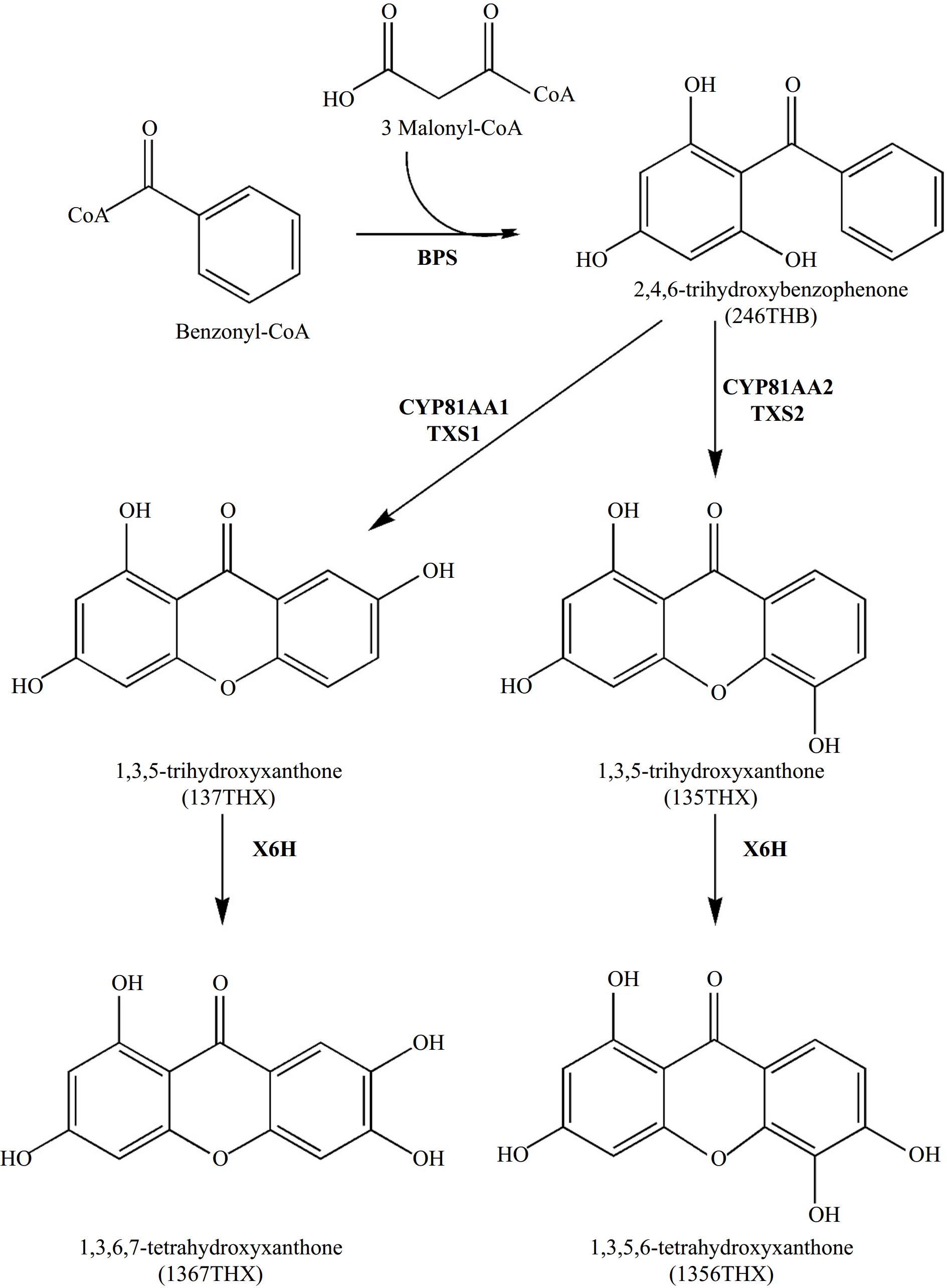
-
Class Substance Naphodianthrones (precussors and derivatives) Hypericin Pseudohypericin Protohypericin Protopseudohypericin Skyrin Skyrin-6-O-ß-glucopyranoside Emodin Emodin dianthrone Phloroglucinol derivatives Hyperforin Adhyperforin Hyperfirin Adhyperfirin Furohyperforin Xanthones 1,6-dihydroxy-5-methoxy-4′,5′-dihydro-4′,4′,5′-trimethylfurano-(2′,3′:3,4)-xanthone 4,6-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxyxanthone cis-kielcorin Magniferin 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone Phenylpropanoids Caffeic acid Chlorogenic acid Flavonoids Quercetin Quercitrin Hyperoside Rutin Biflavonoids I3,II8-Biapigenin Amentoflavone Proanthocyanidins Procyanidin B2 Catechins Catechin Epicatechin -
Genes involved in hypericin biosynthesis Genes involved in hyperforin biosynthesis Confirmed by the functional characterization of the respective protein HpPKS2[34] BCKDH[37] CLL[37] PKS[37] PT1-4[38] Hypothetical based on transcriptional data POCP1-4[35] TER[17] BBE[17] Rejected by experiments HYP1[36] HpPKS1[39] Table 2.
Genes suggested to participate in hypericin and hyperforin biosynthesis.
Figures
(7)
Tables
(2)