-
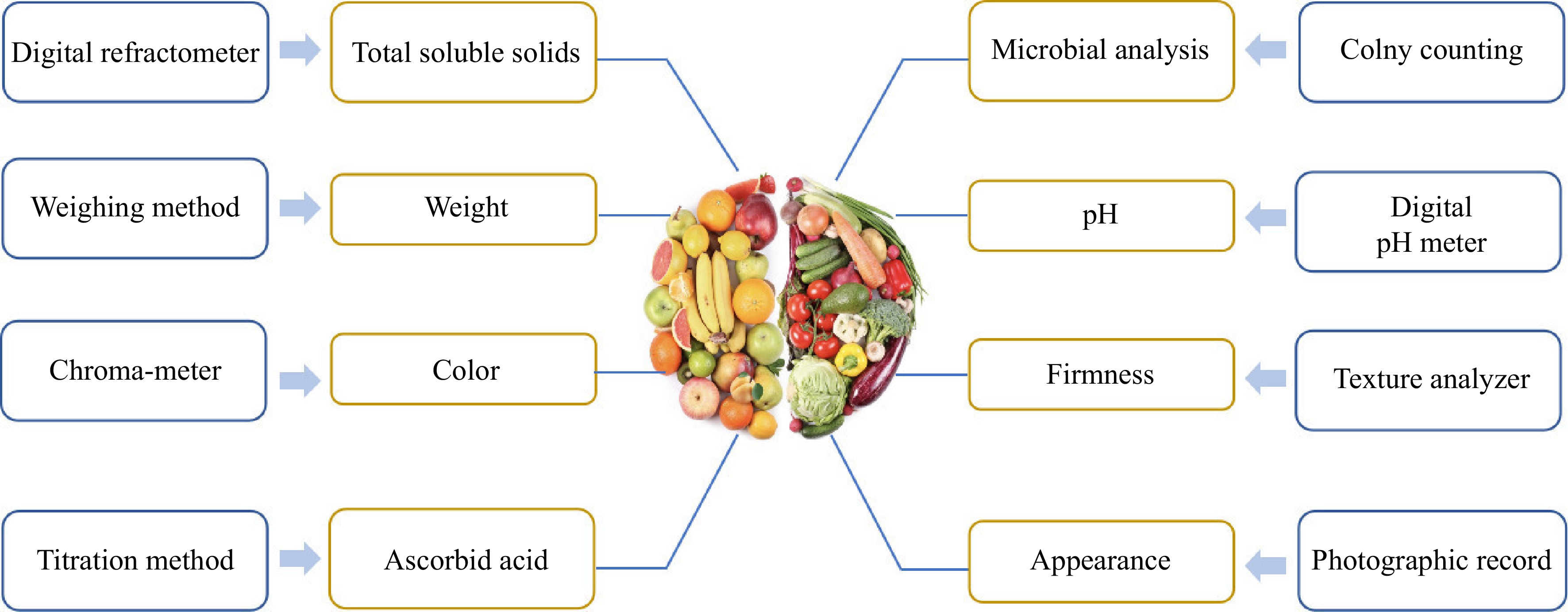
Figure 1.
Quality indicators of fruits and vegetables and their detection methods or instruments.
-
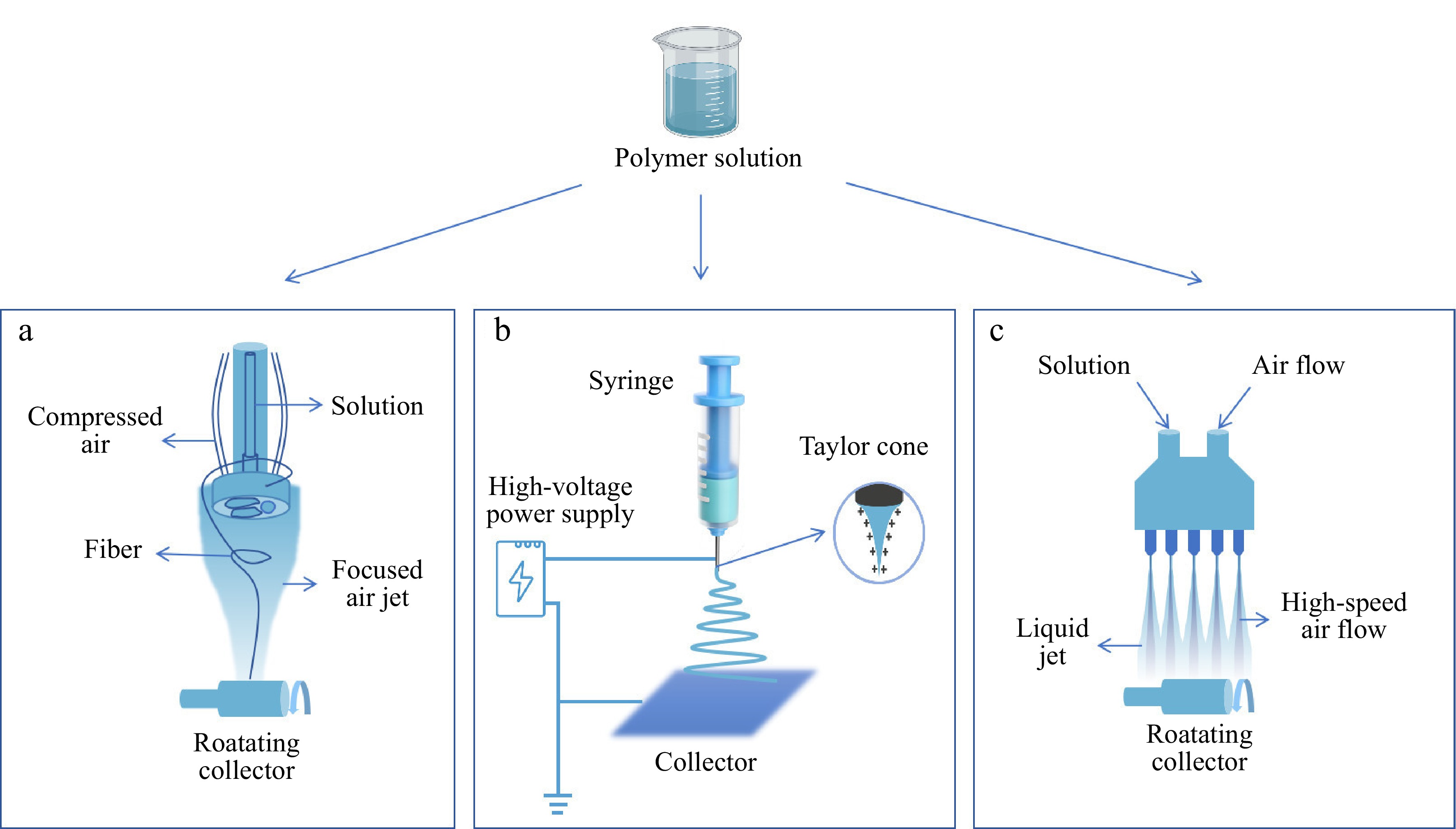
Figure 2.
Formation of different spinning film: (a) rotary jet spinning; (b) electrospinning; (c) solution blow spinning.
-

Figure 3.
Microspheres made using the emulsify-crosslinking method and their antibacterial effect.
-
Constituent substance Fabrication method Food system Ref. Cactus mucilage, gelatin, plasticizer (glycerol/sorbitol), probiotic Casting Fresh-cut apple [27] Sargassum pallidum polysaccharide nanoparticles, chitosan Casting Cherry [28] Corn/cassava starch, glycerol, eugenol, gelatin microspheres Casting Fresh-cut apple [29] Zein, sodium alginate, glycerol Casting Chili peppers [30] Guar gum, candelilla wax, glycerol Casting Strawberry [31] Aloe vera gel, chitosan Casting Fresh fig fruits [32] Levan, pullulan, chitosan, ε-polylysine Casting Strawberry [33] Chitosan, cellulose nanocrystals, beta-cyclodextrin Casting Cherry [21] Pomegranate peel extract, jackfruit seed starch Casting White grapes [34] Succinylated corn starch, glycerol Extrusion Mango [18] Starch, gelatin, natural waxes Extrusion / [35] Gelatin, native corn starch Extrusion with the casting Mango [36] Cassava starch, wheat, oat bran Extrusion / [37] Zanthoxylum bungeanum essential oil, polyvinyl alcohol, β-Cyclodextrin Electrospinning Strawberry and sweet cherry [38] Baicalinliposomes, alcohol-chitosan Electrospinning Mushrooms [39] Zein, gelatin-proanthocyanidins-zinc oxide nanoparticles Electrospinning Cherry [40] Pullulan, citric acid, thyme oil Rotary jet spinning Avocados [41] Thymol, 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, chitosan, polycaprolactone Solution blow spinning Tomato [42] Pullulan, Water-in-oil emulsions Solution blow spinning Fresh-cut apple [43] Corn starch, gelatin, hawthorn berries extract 3D printing / [44] Gelatin, glycerol, Garcinia atroviridis extract 3D printing / [45] /, not provided. Table 1.
Fabrication method of edible film for fruits and vegetables preservation applications.
-
Additives Concentration Water content Water vapor permeability Water solubility Ref. Pectin 5% 30.79%−21.07% 13.39−29.25 × 10−3 g·m/h·pa 76.77%−83.32% [79] Whey protein isolate / 40.21%−21.85% 15.28−23.32 g/m2·day 34.71%−36.46% [80] Cellulose nanocrystals 75% 9.6236%−12.9845% 1.75−2.34 × 10−9 g/s·Pa·m / [81] Oxidized poly- (2-hydroxyethyl acrylate) 10% 17.01%−25.7% / 41.7%−56.9% [82] Tangerine oil, tween 80 0.10% 26.05%−20.25% 0.613−0.233 g·mm/m2·h·kPa 50.19%−45.94% [83] Arrowroot powder, refined wheat flour, corn starch 3.5%, 2%, 2% 13.69%−6.76% 0.0019−0.0106 g·mm/m2·day·mmHg 33.33%−24.35% [84] Black pepper essential oil 0.15% 31.79%−39.25% 0.315−0.420 g·mm/m2·h·kPa 24.00%−22.35% [85] Modified potato starch, glycerol 9%, 1% / 18.1−6.1 × 10−3 g·mm/h·m2·Pa 62.238%−45.639% [86] Sunnhemp protein isolate, potato starch 50%, 50% 18.31%−12.89% / 74.26%−52.77% [16] Orange oil 2.50% 16.12%−9.55% 2.71−2.25 × 10−12 g·cm/cm2·s·Pa 74%−29% [87] /, not provided. Table 2.
Effects of different additives on the barrier properties of edible films.
Figures
(3)
Tables
(2)