-
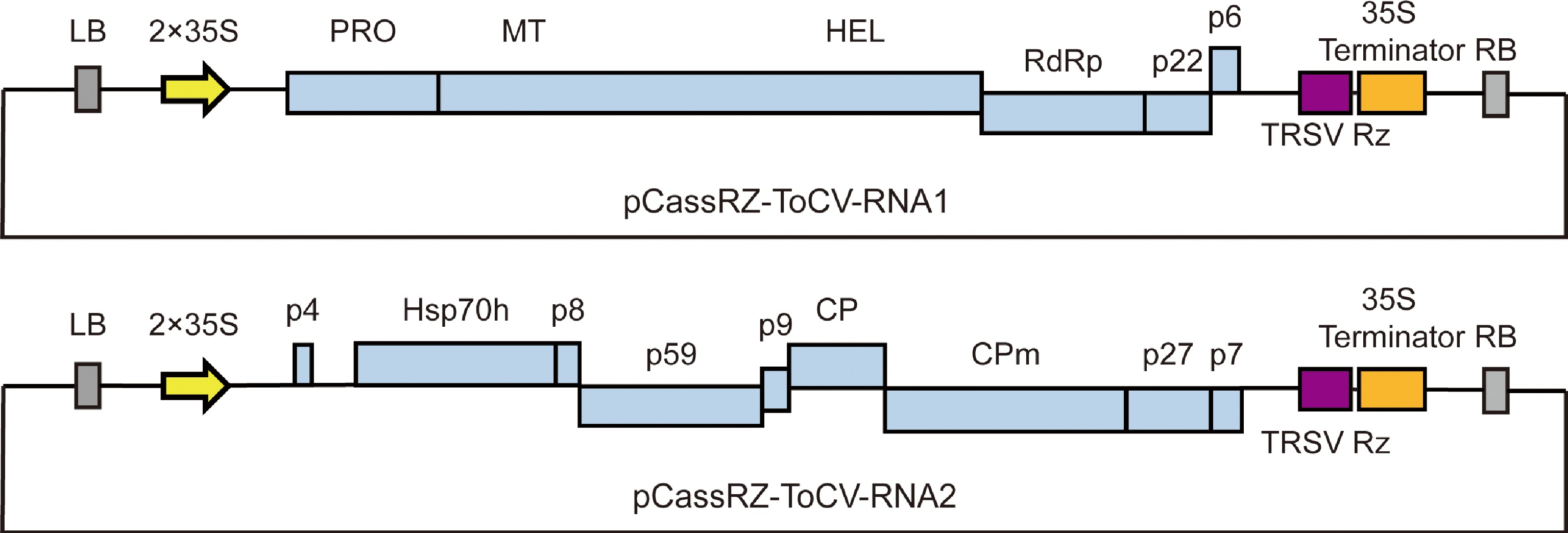
Figure 1.
Structure map of ToCV-infectious clones. LB: left border repeat of T-DNA; 2 × 35S: two tandem cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter; TRSV Rz: the cis-cleaving ribozyme sequence of tobacco ringspot virus; 35S Terminator: CaMV 35S terminator; RB: right border repeat of T-DNA. PRO: papain proteinase; MT: methyltransferase; HEL: helicase; RdRp: RNA dependent RNA polymerase; Hsp70h: heat shock protein 70 homolog; CP: coat protein; CPm: minor coat protein; p4, p6, p7, p8, p9, p22, p27, and p59 represent proteins of 4 kilodaltons (kDa), 6 kDa, 7 kDa, 8 kDa, 9 kDa, 22 kDa, 27 kDa and 59 kDa, respectively.
-
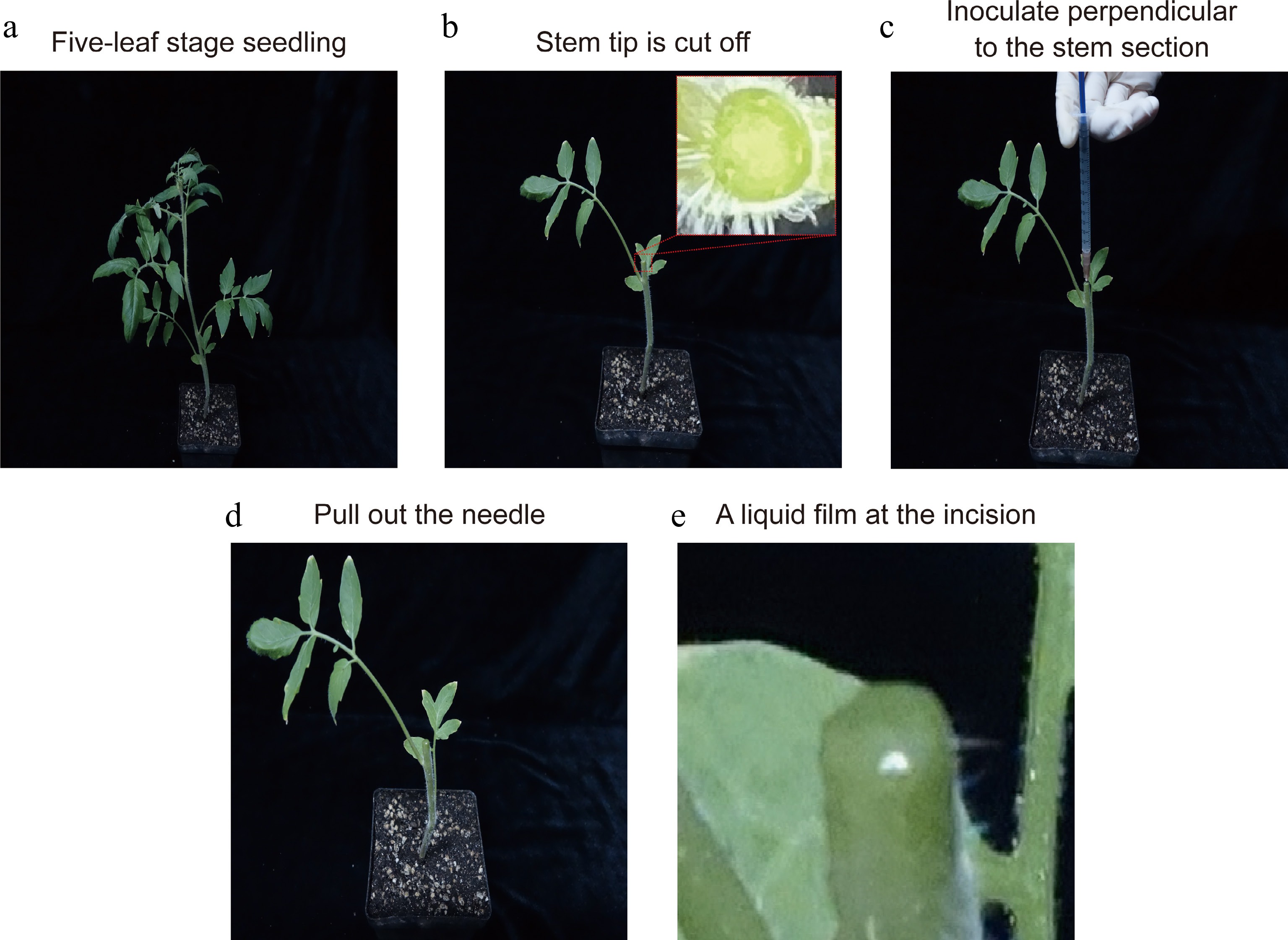

Figure 2.
The operation flow of the improved stem-inoculated method. (a) Preparing five-leaf-old tomato seedlings. (b) The stem tips of seedlings were excised with a sterile scalpel blade, retaining two basal leaves. The incision of stem segment is flat and can distinguish phloem and xylem clearly. (c) About 0.5−1 mL ToCV-inoculated buffer was absorbed with a sterile syringe. Then, a small amount of ToCV-inoculated buffer was injected multiple times until the incision tissue is visibly infiltrated. (d), (e) Slowly pull out the needle, and the ToCV-inoculated buffer will naturally form a liquid film at the incision.
-
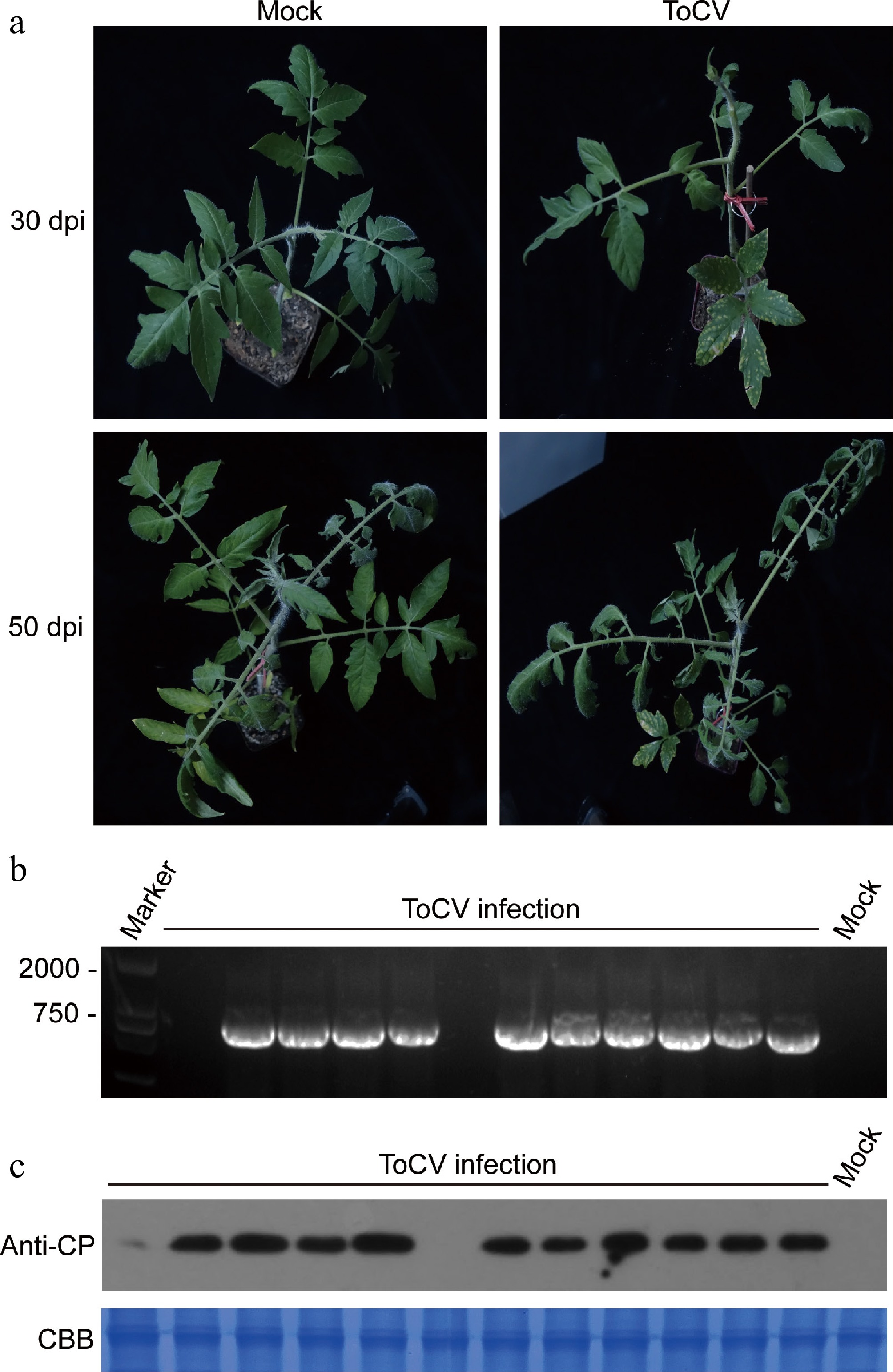

Figure 3.
(a) The phenotype of tomato ToCV disease at 30 and 50 dpi. (b) ToCV CP gene identification of inoculated plants at 30 dpi. (c) ToCV CP protein identification of inoculated plants at 30 dpi.
-
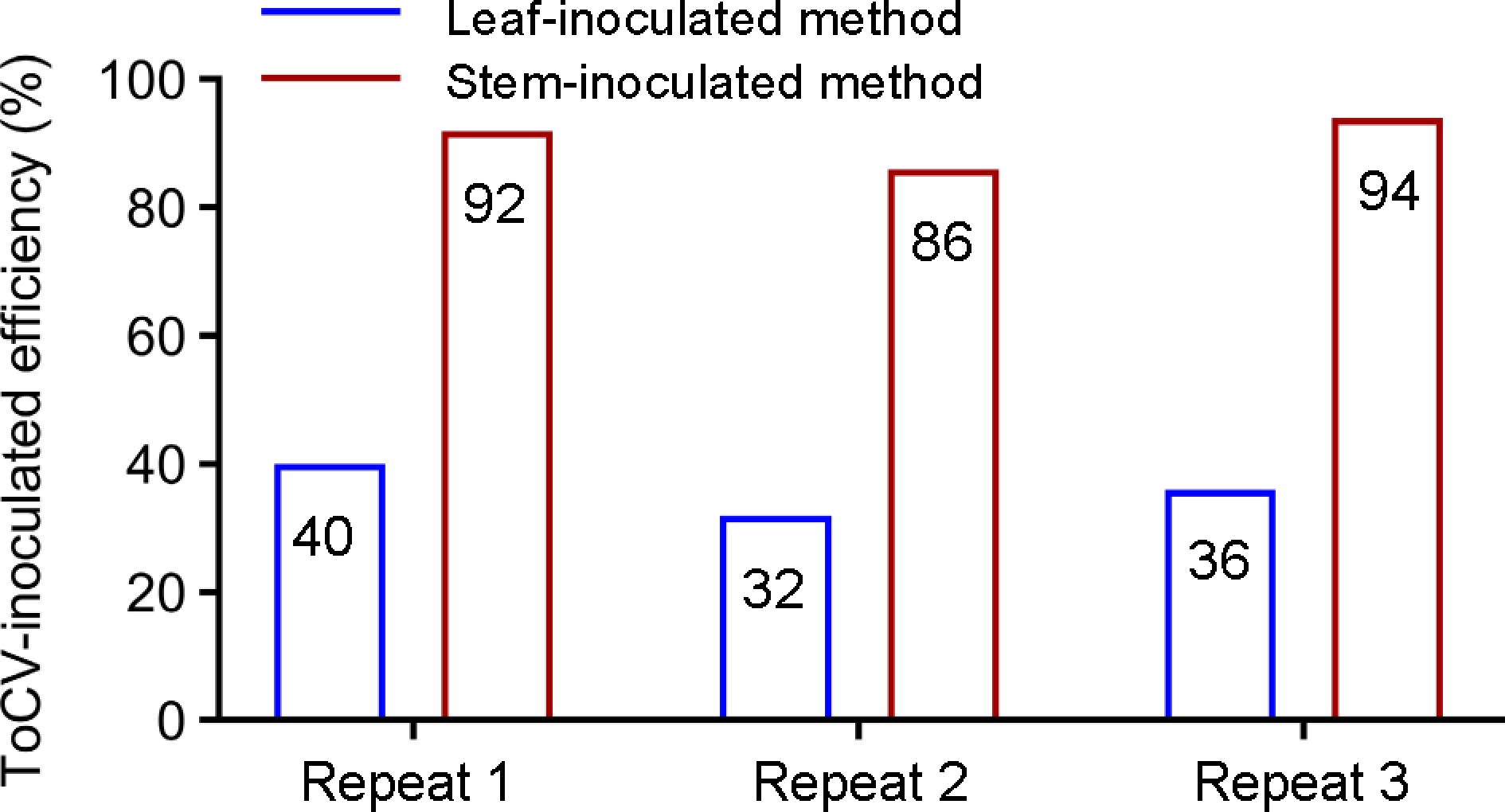
Figure 4.
Comparing the inoculation efficiency of traditional leaf-inoculated method and improved stem-inoculated method. Three independent inoculation experiments with AC plants were performed. Each testing contains 50 plants per treatment.
-
Number Tomato varieties Source DI DR 1 Ailsa Craig TGRC (LA2838A) 96 HS 2 Fireball TGRC (LA3024) 62 S 3 Momor TGRC (LA2828) 45 MR 4 Red River TGRC (LA4350) 71 S 5 Nagcarlang TGRC (LA2661) 82 HS 6 New Yorker TGRC (LA2009) 44 MR 7 Moneymaker TGRC (LA2706) 75 S 8 Heinz 1706-BG TGRC (LA4345) 98 HS 9 M-82 TGRC (LA3475) 71 S 10 Shan Nong Tian Fen Yi Hao Our Lab. 26 R 11 Shan Nong Tian Fen Er Hao Our Lab. 82 HS 12 Lu Xiao Fan Yi Hao Our Lab. 20 R 13 Qing Lian Yi Hao Our Lab. 80 HS 14 Zhu Yu Our Lab. 58 S 15 Jin Peng Yi Hao Commercial 67 S 16 Bei Ying Commercial 85 HS 17 Tao Tai Lang Commercial 46 MR 18 Shang Hai Da Hong Commercial 70 S 19 Zhong Shu Si Hao Commercial 79 HS 20 Zhong Shu Wu Hao Commercial 71 S 21 Zhong Shu Liu Hao Commercial 62 S 22 Lu Fen Yi Hao Commercial 83 HS 23 Fu Shan 88 Commercial 28 R 24 Qian Xi Commercial 60 S 25 Bei Bei Commercial 58 S Table 1.
Information, disease index (DI), and disease resistance (DR) of tomato varieties.
-
Disease
level (d)Symptom description 0 No visible symptoms. 1 Several chlorotic yellow spots appear on local leaves of plant base. Plant is not dwarf. 2 Intervein yellowing and chlorosis appear on leaves of 1/3 base of the plant. Plant is not dwarf. 3 Half of the leaves of the plant are seriously yellowed. Leaves become brittle and hard. Plant is obviously dwarfed, the plant height is reduced by 10%−30% when compared to control. 4 Leaves of the whole plant are seriously yellowed and curled. Plant is obviously dwarfed, the plant height is reduced more than 50% when compared to control. No further planting value. Table 2.
Symptom description and classification of tomato ToCV disease.
Figures
(4)
Tables
(2)