-
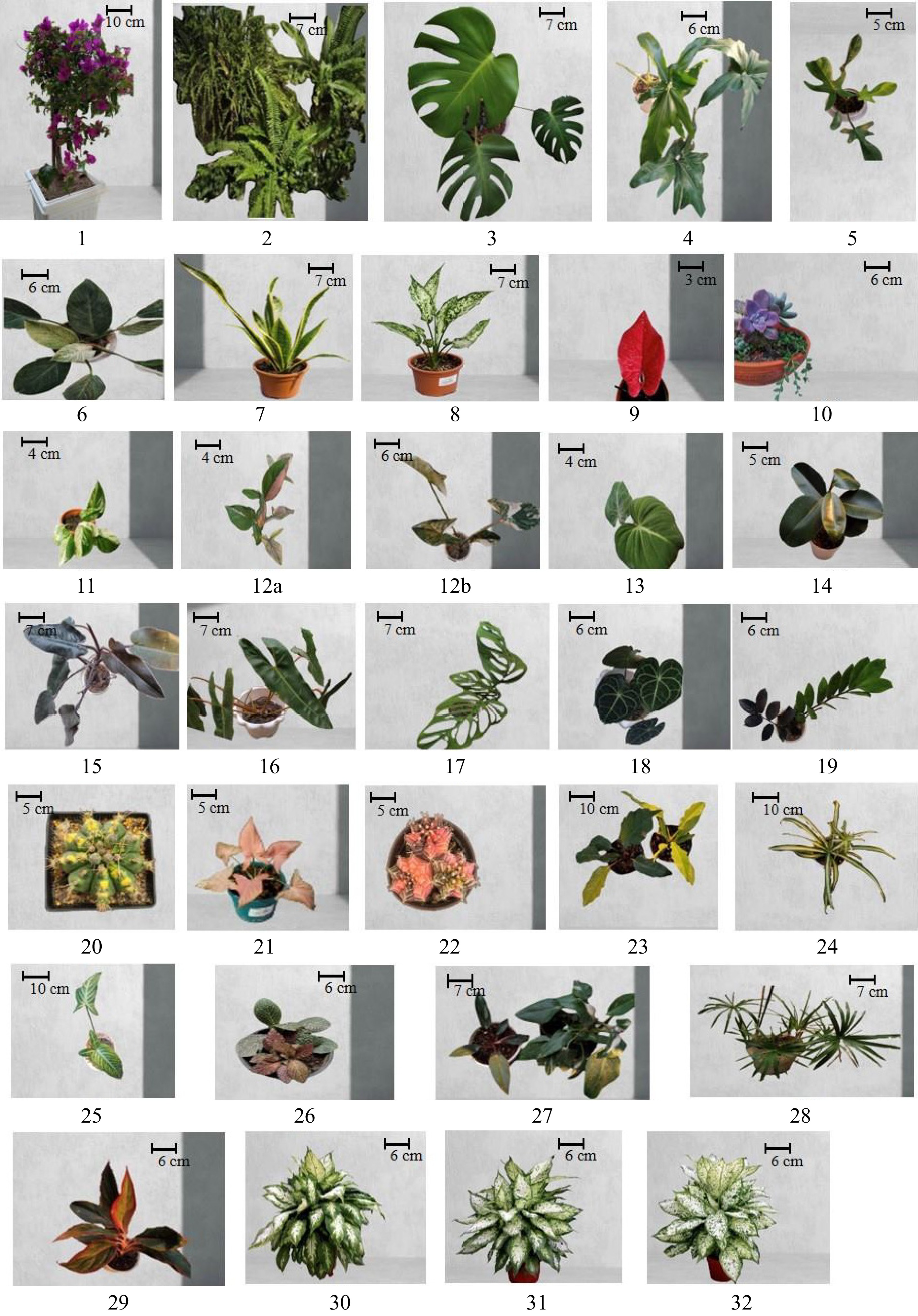

Figure 1.
Pictures of common houseplants. 1. Bougainvillea glabra, 2. Nephrolepis cordifolia, 3. Monstera deliciosa, 4. Philodendron angela, 5. Philodendron Florida, 6. Philodendron Birkin, 7. Dracaena trifasciata, 8. Aglaonema commutatum, 9. Caladium bicolor, 10. Echeveria gibbiflora, 11. Epipremnum aureum, 12a. Syngonium podophyllum (pink), 12b. Syngonium podophyllum (white), 13. Philodendron melanochrysum, 14. Ficus elastic, 15. Philodendron Majesty, 16. Philodendron domesticum, 17. Monstera adansonii, 18. Anthurium crystallinum, 19. Zamioculcas zamiifolia, 20. Gymnocalycium damsii variegata, 21. Syngonium podophyllum, 22. Gymnocalycium mihanovichii, 23. Philodendron wendlandii, 24. Chlorophytum comosum, 25. Caladium lindenii, 26. Fittonia albivenis, 27. Philodendron erubescens, 28. Cyperus alternifolius, 29. Aglaonema Schott, 30. Carina, 31, Rebecca, 32. Sarah. Images 1−29 were collected from local nurseries located in 24°22'26" N, 88°36'04" E and images 30−32 were adopted from Chen et al.[1].
-
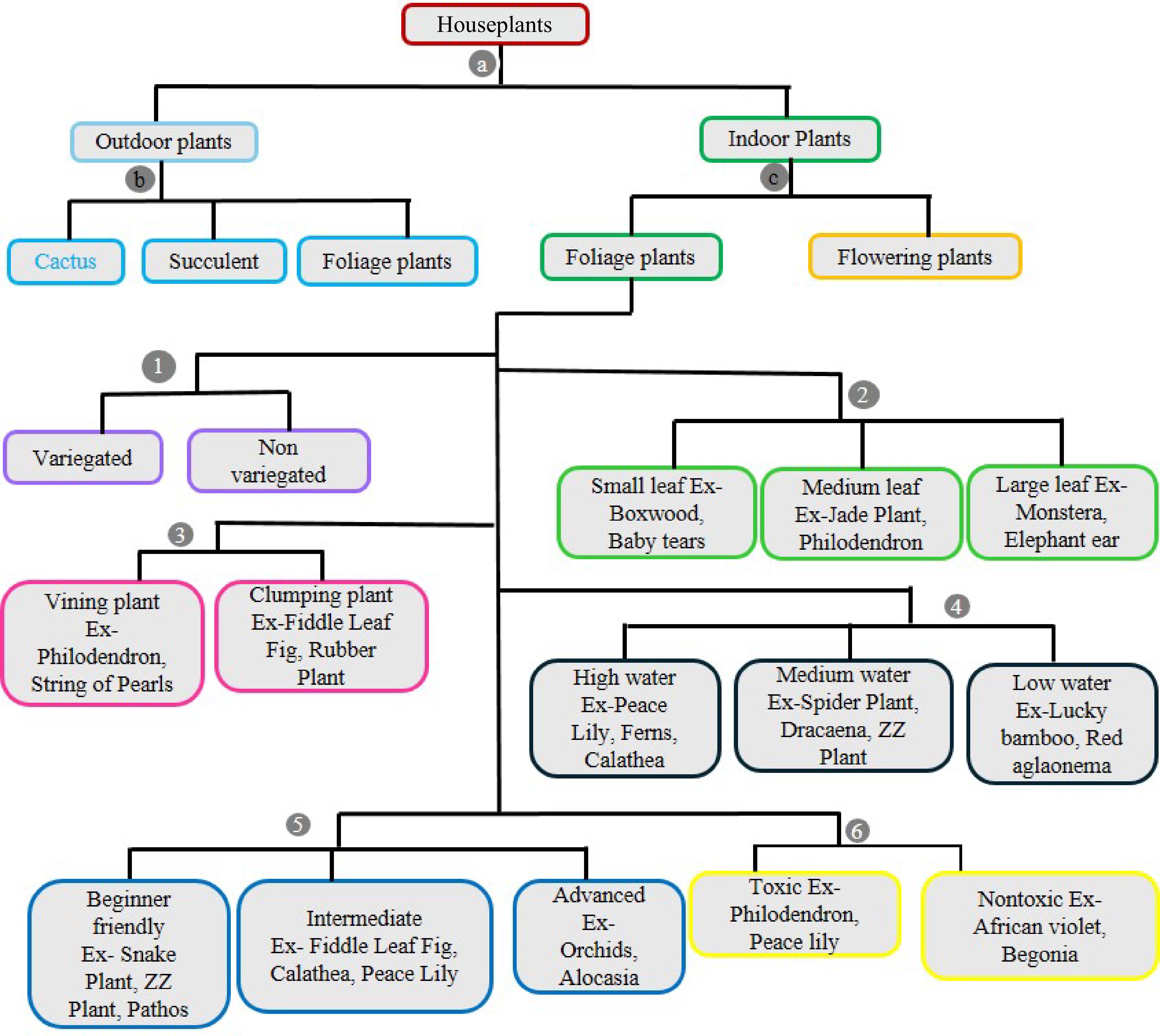
Figure 2.
Classification of houseplants. 1. Based on variegation, 2. based on leaf size, 3. based on growing structure, 4. based on water requirement, 5. based on care requirements, 6. based on toxicity.
-
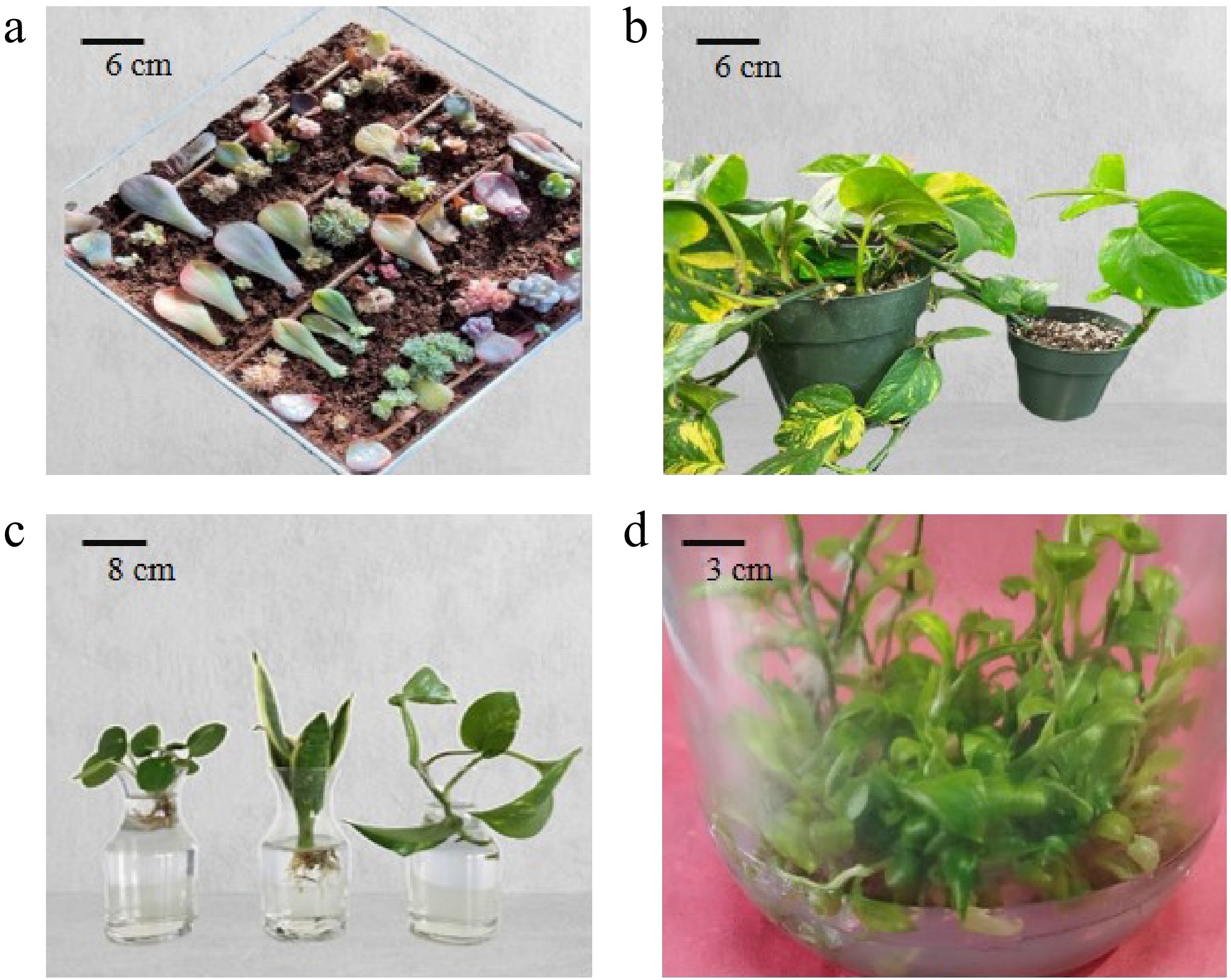

Figure 3.
Propagation techniques of houseplants. (a) Cutting propagation, (b) layering, (c) water propagation, (d) micropropagation.
-
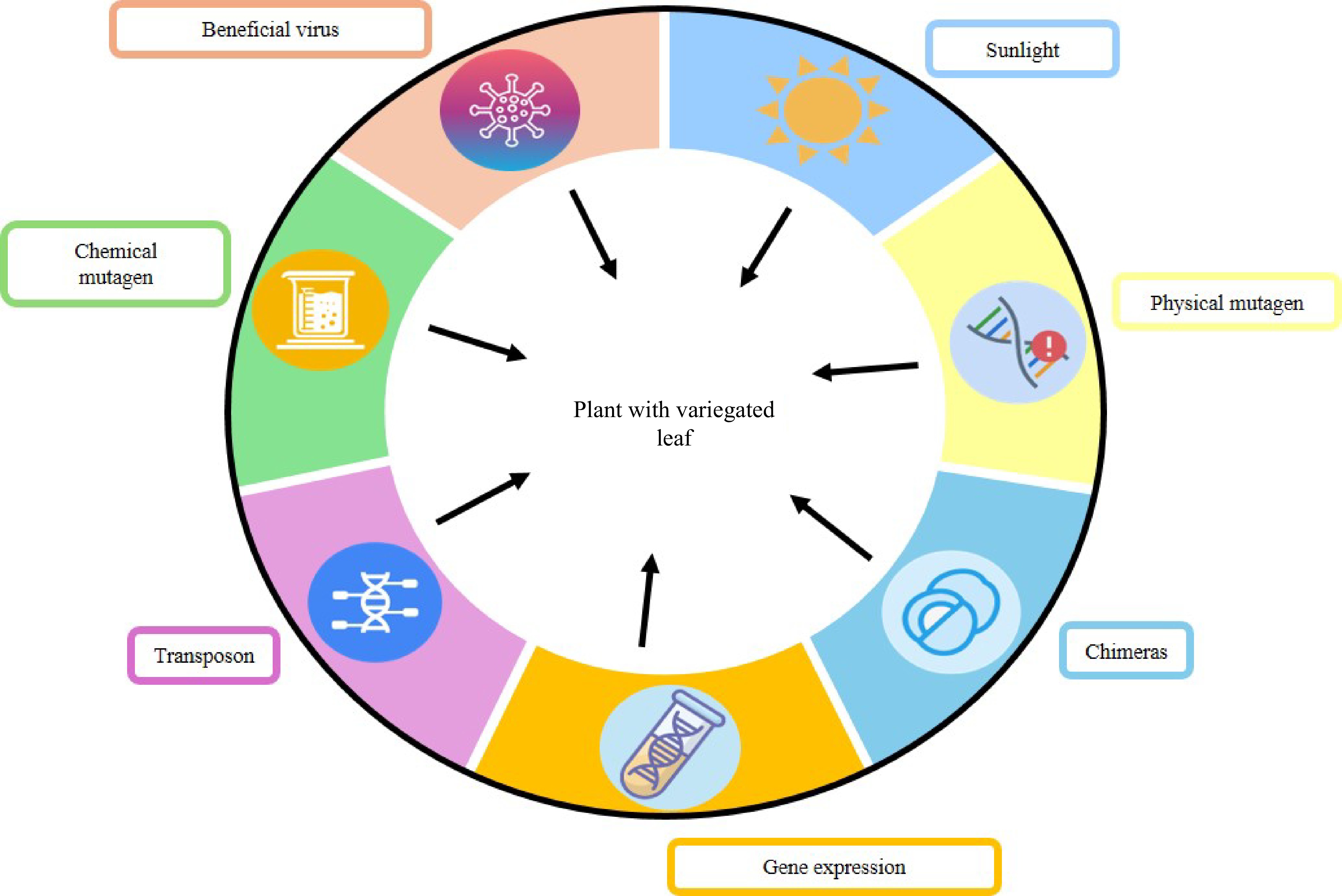
Figure 4.
Natural and chemical inducers of variegated houseplants.
-
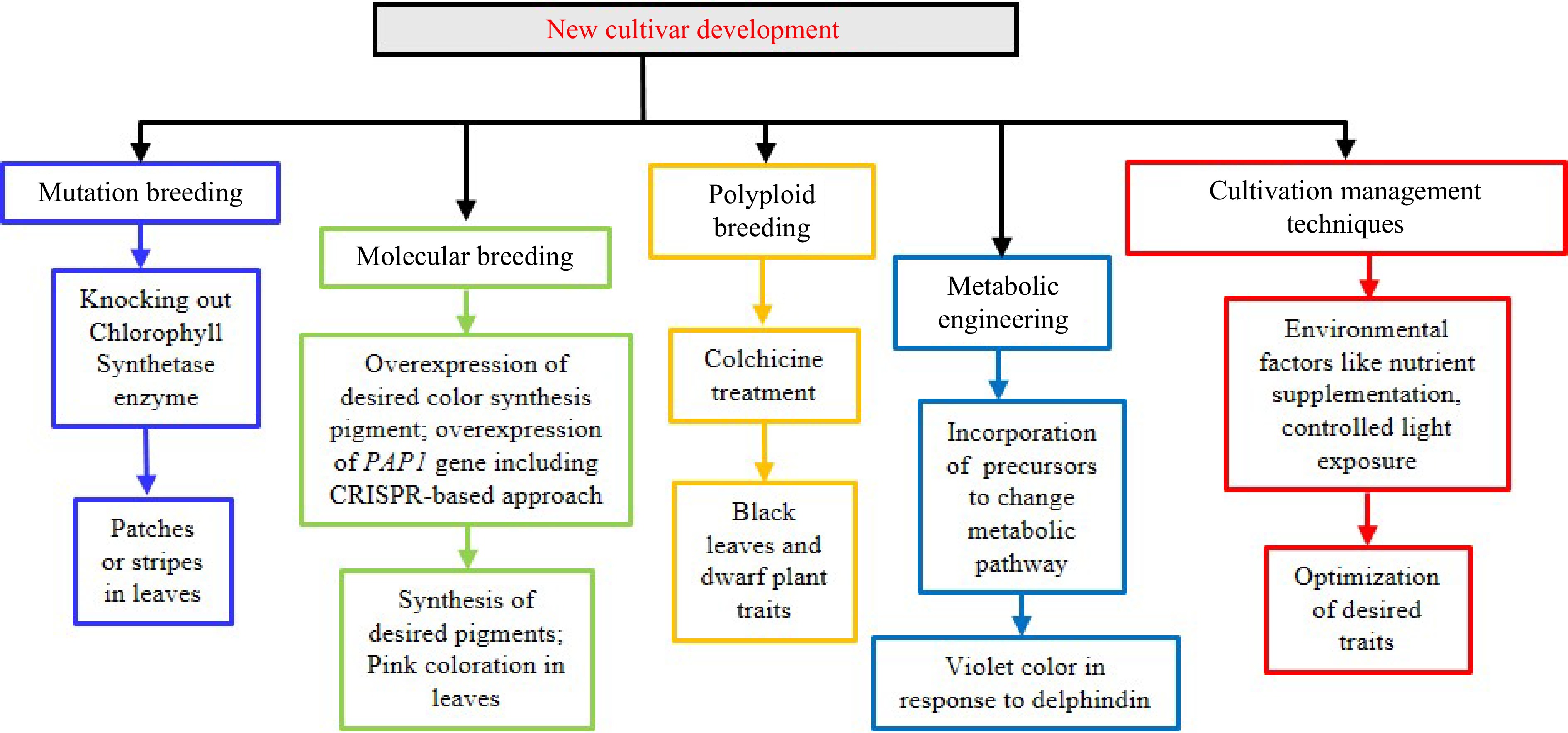
Figure 5.
Proposed approach for developing new cultivars of houseplants.
-
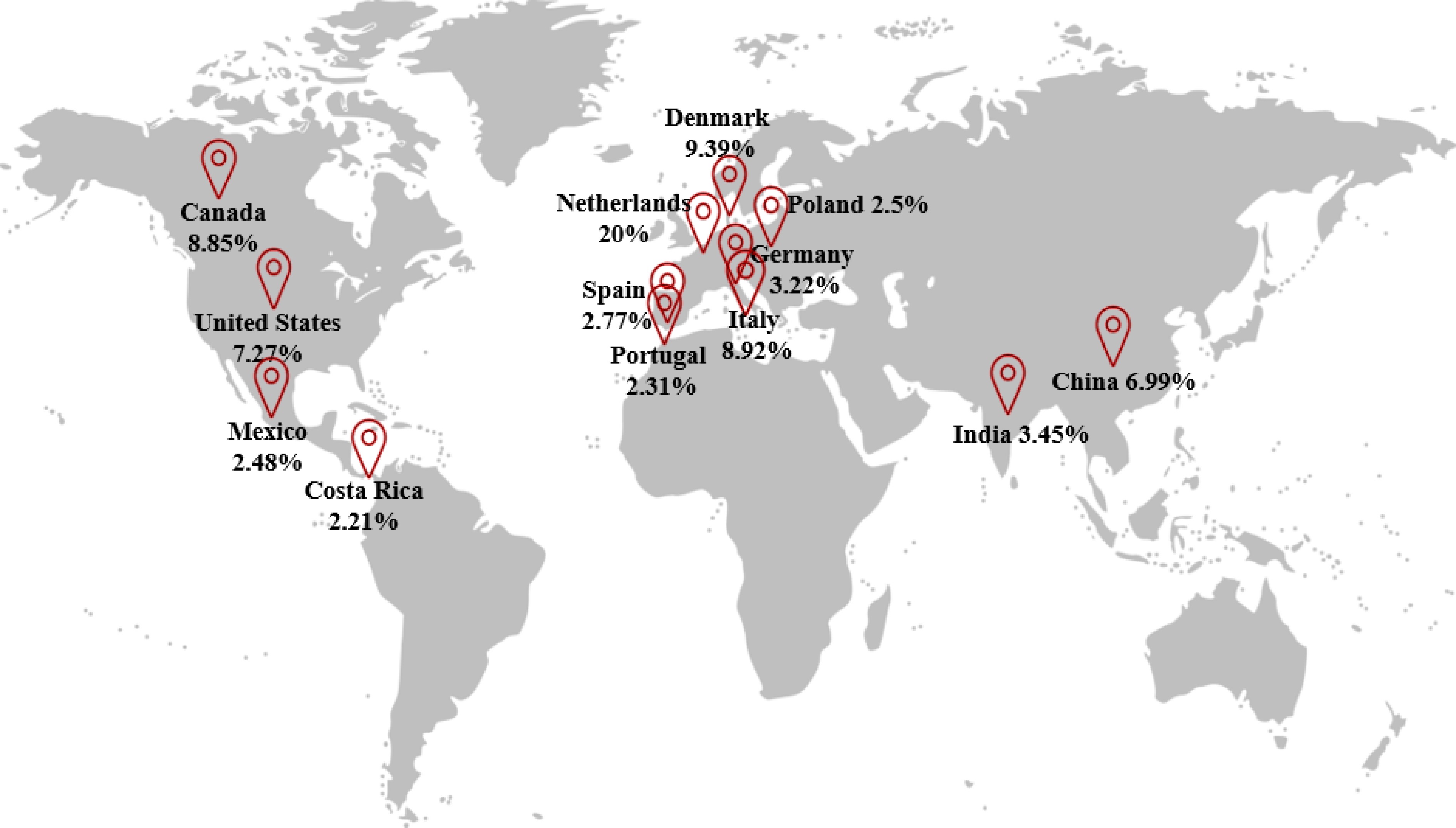
Figure 6.
Major houseplant exporter countries worldwide.
-
Scientific name Common name Scientific name Common name Aglaonema commutatum Chinese evergreen Chlorphytum comosum Spider plant Alocasia azlanii Jewel alocasia Cissus rhombifolia Grape ivy Aloe barbadensis Aloe Codiaeum variegatum Croton Anthurium andraeanum Lace leaf Cordyline terminalis Ti plant Aphelandra squarrosa Zebra plant Crassula argentea Jade plant Araucaria heterophylla Norfolk island pine Cycas revolute Sago palm Araucaria heterophylla House pine Cyclamen persicum Florist's cyclamen Asparagus densiflora Asparagus fern Dieffenbachia seguine Dumb cane Aspidistra elatior Cast iron plant Dizygotheca elegantissima False aralia Asplenium nidus Bird's nest fern Dracaena marginata Dragon tree Beaucarnea recurvata Ponytail palm Dracaena sanderiana Lucky bamboo Brassaia actinophylla Umbrella plant Dracaena trifasciata Snake plant Chamaedorea elegans Parlor plant Epipremnum aureum Pathos Euphorbia milli Crown of thorns Philodendron erubescens Pink princess Ficus benjamina Weeping fig Philodendron scandens Heart leaf philodendron Ficus elastic Rubber plant Pittosporum tobira Pittosporum Ficus lyrata Fiddle-leaf fig Platycerium bifurcatum Staghorn fern Fiscus lyrata Fiddle leaf Pleomele reflexa Pleomele Gardenia augusta Gardenia Podocarpus macrophyllus Podocarpus Gynura aurantiaca Purple passion plant Saintpaulia ionantha African violet Hedera helix English ivy Schefflera actinophylla Umbrella plant Helxine soleirolii Baby tears Schefflera arboricola Hawaiian schefflera Hoya carnosa Wax plant Schlumbergera bridgesii Cuistmas cactus Maranta leuconeura Prayer plant Semperflorens Cultorum Begonia Monstera deliciosa (Albo borsigiana) Variegated monstera Soleirolia soleirolii Corsican creeper Monstera obliqua Broken heart plant Spathiphyllum wallisii Peace lily (white flag) Nephrolepsis exaltata Boston fern Syngonium podophyllum Nephthytis Peperomia obtusifolia Peperomia Tolmiea menziesii Piggyback plant Phalaenopsis amabilis Moon orchid Variegated Philodendron Minima Mini monstera Table 1.
Some popular houseplants and their scientific names.
-
Plant Sterilization steps Ref. Ficus elastica, Ruby 1. Young upper leaves were washed with soapy
water and washed again by tap water;
2. Washed with 1% KMnO4 for 25 min;
3. Washed with 70% C2H5OH for 1 min;
4. Washed with 2%−6% chloramine B containing 25%−29% active chlorine for 5, 10, 15 min or with Domestos for 25 min;
5. Washed three times with distilled water.[34] Spathiphyllum, Peace lily 1. Explants were washed under running tap water
for 1 h;
2. Washed with 70% ethanol for 30 min;
3. Washed with 15% sodium hypochlorite NaOH (Clorox + 0.01% Tween 20) for 7 min;
4. Rinsed with sterile water three times;
5. Dipped in 0.1% HgCl2 solution for 5 min;
6. Rinsed five times with sterile water.[35] Zamioculcas zamiifolia,
Black ZZ1. Leaves were washed with dishwashing liquid for
20 min;
2. Explants placed under running tap water for
30 min;
3. Treated with 10% sodium hypochlorite (active chloride) for 10 min;
4. Disinfected with 0.1 mg/L HgCl2 solution for 10 min;
5. Washed with ethanol 70% for 1 min;
6. Washed three times with sterile distilled water for
5 min.[36] Dracaena sanderiana,
Lucky bamboo1. Explants were rinsed 3–4 times with sterilized double distilled water.
2. Surfaces disinfected for 10 min in H2O2 (1%) solution.[29] Monstera deliciosa
Liebm, Thai constellation1. Washed in the sink with soap and water;
2. Surface sterilized using 2% sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) for 20 min;
3. Rinsed in dH2O;
4. Washed with 2% sodium hypochlorite for another 20 min;
5. Lastly rinsed three times with water.[37] Monstera deliciosa,
Liebm1. Immersed in fungicidal antioxidant solution for
3 min with vacuum pump agitation;
2. Double immersion in 1.25% NaClO + three drops
of Tween-20 for 15 min;
3. Immersion in 0.83% NaClO + three drops of
Tween-20 for 10 min;
4. Two washes between each NaClO immersion, three final washes with sterilized distilled water;
5. Final immersion in antioxidant solution.[32] Monstera acuminata, Koch 1. Immersed in fungicidal antioxidant solution for
3 min with vacuum pump agitation;
2. Double immersion in 1.25% NaClO + three drops
of Tween-20 for 15 min;
3. Immersion in 0.83% NaClO + three drops of
Tween-20 for 10 min;
4. Two washes between each NaClO immersion, three final washes with sterilized distilled water;
5. Final immersion in antioxidant solution.[32] Table 2.
Step-by-step protocols for surface sterilization.
-
Plant Basic media Plant hormones and other nutrients Culture process Explant type Ref. Ficus elastica, Ruby MS media
pH 5.8−5.91.5 mg/L IAA and 0.5−4.0 mg/L BAP, 0.7% agar,
1 mg/L pyridine, 1 mg/L thiamine, 15 mg/L
ascorbic acid, 40 g/L sucroseIn vitro regeneration of the plantlets 2−3 months old upper young leaves [34] Spathiphyllum, Peace lily MS media,
pH 5.7−5.8BA 1.0−2.0 ppm, NAA 0.1−0.2 ppm, 0.8% agar, sucrose 25 g/L, Cu ion 2.5 ppm Embryogenic suspension culture and regeneration About 1.0 cm leaf blade from meristem [35] Zamioculcas zamiifolia, Black ZZ MS media,
pH 5.6−5.830g/L sucrose, 0.7% agar, 0.5 mg/L,
NAA and 2 mg/L BAIn vitro regeneration of the plantlets 15 mm ×15 mm leaf [36] Philodendron erubescens,
Pink princessMS media BAP 1.0 mg/L, 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) 0.5 mg/L, indole-3-butyric acid 3.0 mg/L (IBA), and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), Peat moss Ex vitro acclimatization of the plantlets 1.0–1.5 cm, 4–5 leaves,
and at least three roots[33] Dracaena sanderiana,
Lucky bambooMS media,
pH 5.6-5.86.78 μM 2,4-D, 46.5 μM CPA, 0.0–10.20
2,4-5-triacetic acids, 0.0–9.86 μM IBA,
0.0−10.73 μM NAA, 0.0−11.41 μM IAAIn vitro regeneration from nodal explants Node 1 cm, internodal stem 1 cm, leaf 1 cm, axillary buds 1 cm and roots 1 cm [29] Monstera deliciosa Liebm, Thai constellation MS media,
pH 5.6−5.8B5 vitamins supplemented with vitamin B5,
30 g/L sucrose, 2.5 g/L gellan gum, 7.5 mg/L
BAP (6-benzylaminopurine), and 0.5 mg/L
NAA, Bio stimulant IQ forte 3ml/LIn vitro clonal propagation Axillary buds [37] Monstera deliciosa Liebm MS media,
pH 5.6−5.8BAP 1 mg/L, 2,4-D 0.2 mg/L, PPM 1 mL/L In vitro propagation and organogenesis Mature leaves [32] Monstera acuminata, Koch MS media,
pH 5.6−5.8benomyl solution, cysteine, BAP 1 mg/L,
IAA 0.5 mg/L, NAA 0.1 mg/LIn vitro propagation and organogenesis Mature leaves [32] Table 3.
Tissue culture media.
-
Genera No. of cultivars Common cultivars derived
from somaclonal variantsRef. Aglaonema 13 Diamod Bay, Emerald Bay, Moonlight Bay [62,63] Alocasia 2 Polly, Purpley [63] Anthurium 5 Lady Carmen, Orange Hot, SmallTalk Red, SmallTalk purple. [63] Calathea 7 Angela, Cora, Dottie, Eclipse, Rosey Roseo Picta, Satum [64] Dieffenbachia 20 Camouflage, carina, Rebecca, Sarah [65] Ficus 1 Cleo [66] Musa 1 French Reversion [67] Philodendron 4 Baby Hope, Hope Compact, Hope2, Gold Queen [63] Spathiphyllum 5 Cristina, Domino, Gayle's Green, Hi Ho Silver, White lightening [63] Syngonium 23 Banana Allusion, Berry Allusion, Bob Allusion, Bold Allusion, Cream allusion, Pink allusion [63,68] Torenia 1 Uconn white [69,70] Table 4.
Number of houseplants released from the selection of somaclonal variants.
Figures
(6)
Tables
(4)