-
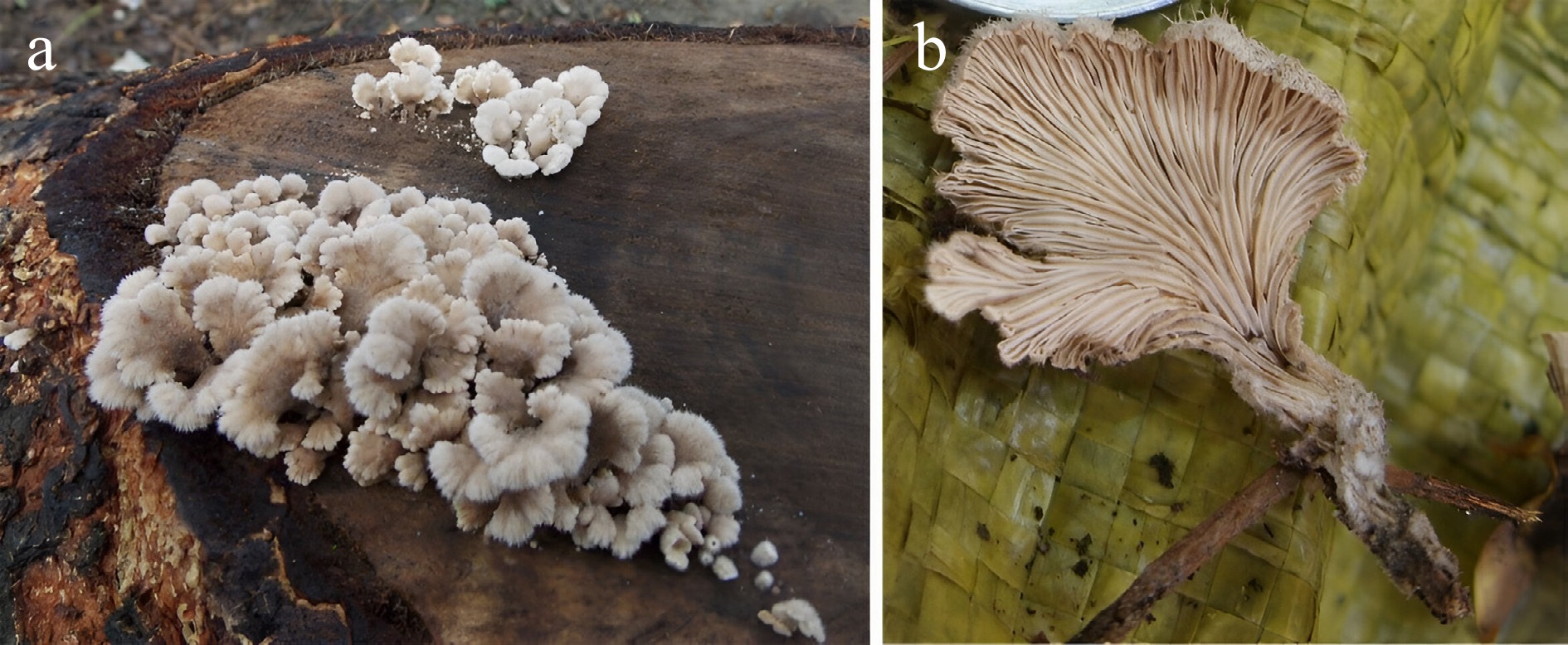

Figure 1.
(a) Habitat photographs of S. commune (split gill fungus); (b) Ventral surface of the fruiting body. (Photographs captured by Chakraborty N, unpublished).
-
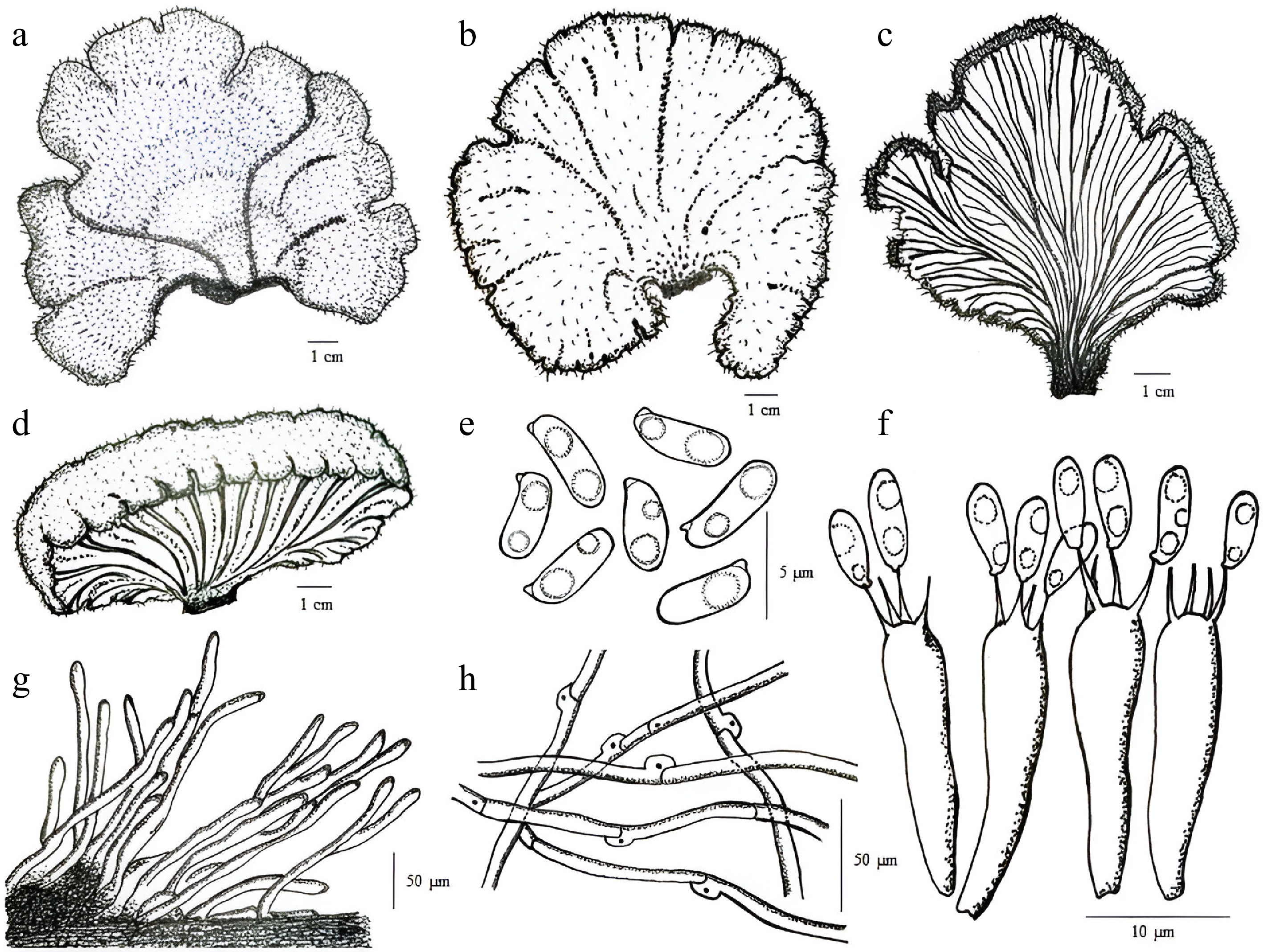
-
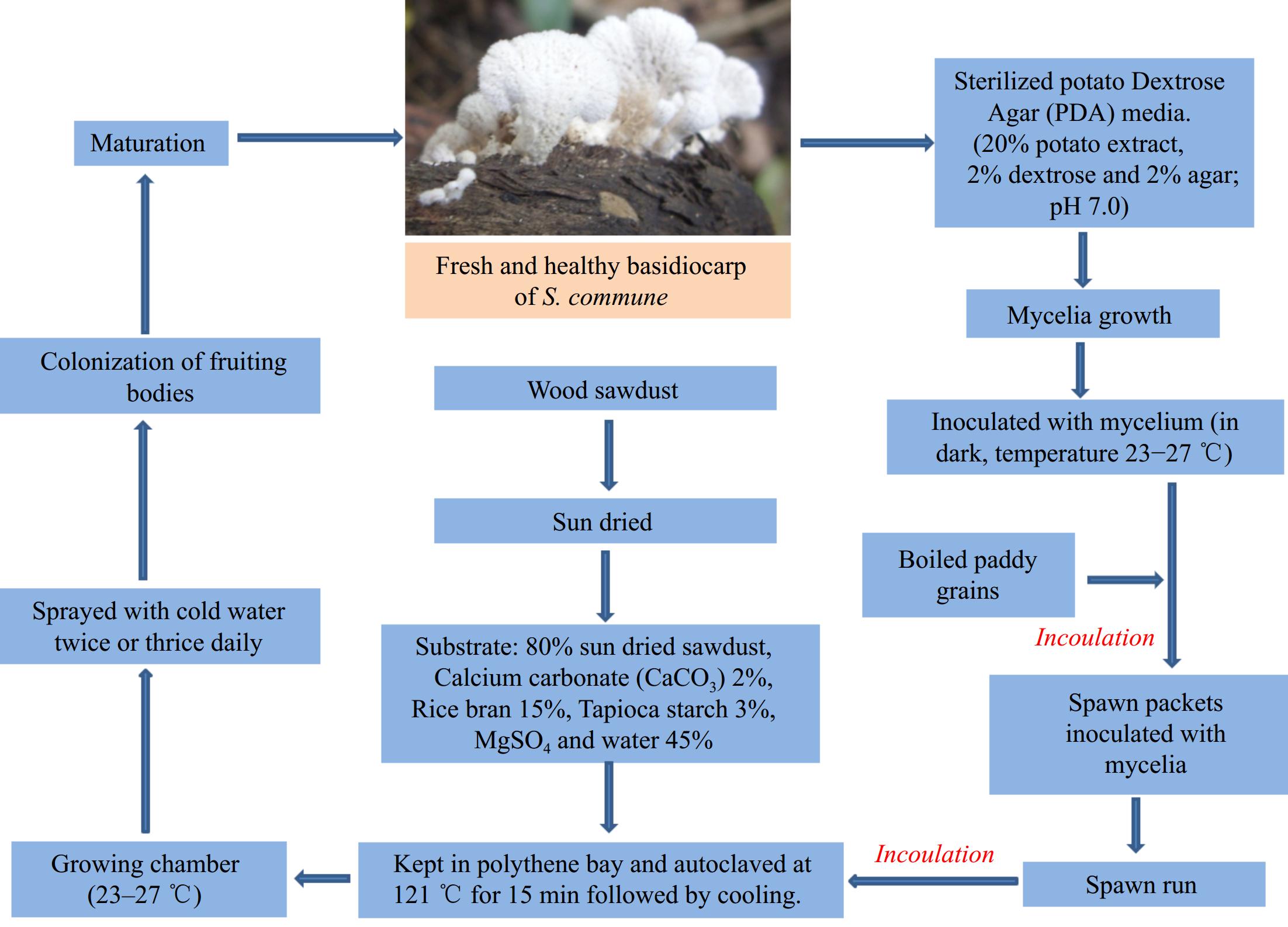
Figure 3.
Cultivation techniques of split gill fungus[31].
-
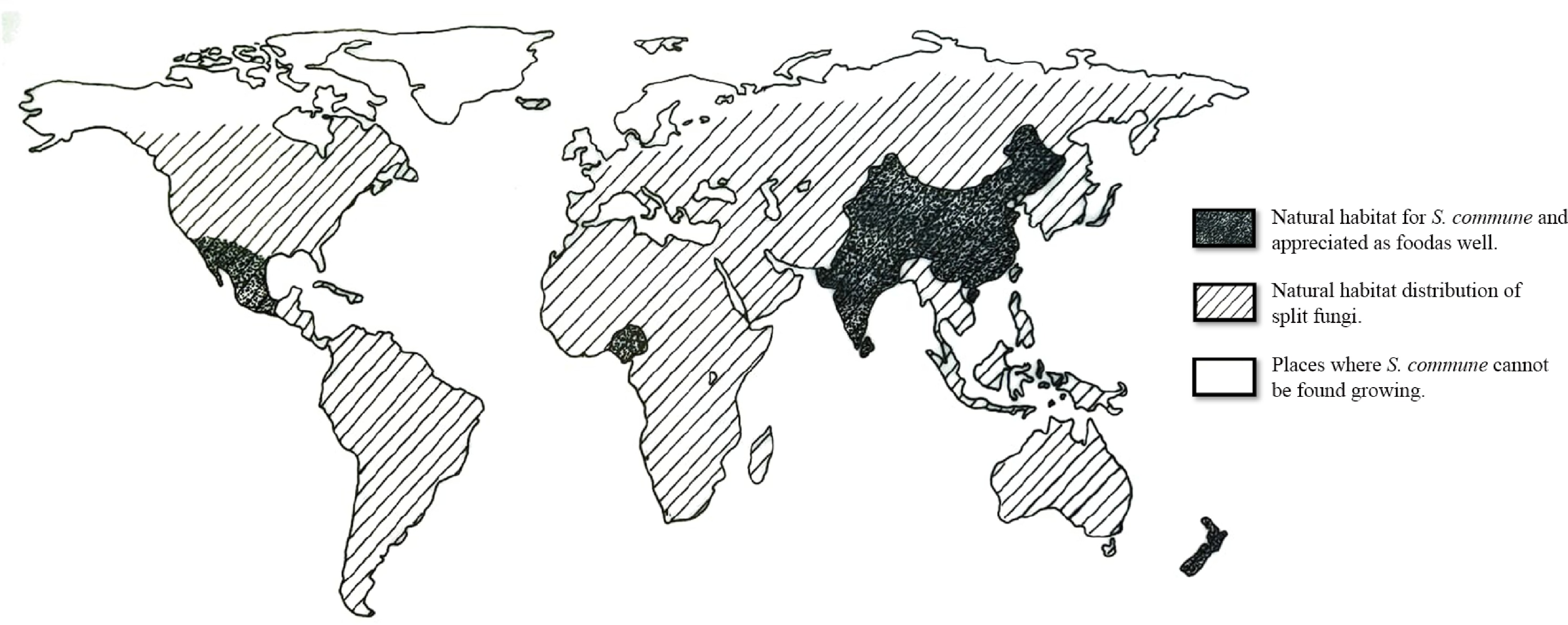
Figure 4.
Geographical distribution and culinary interest of Schizophyllum commune.
-
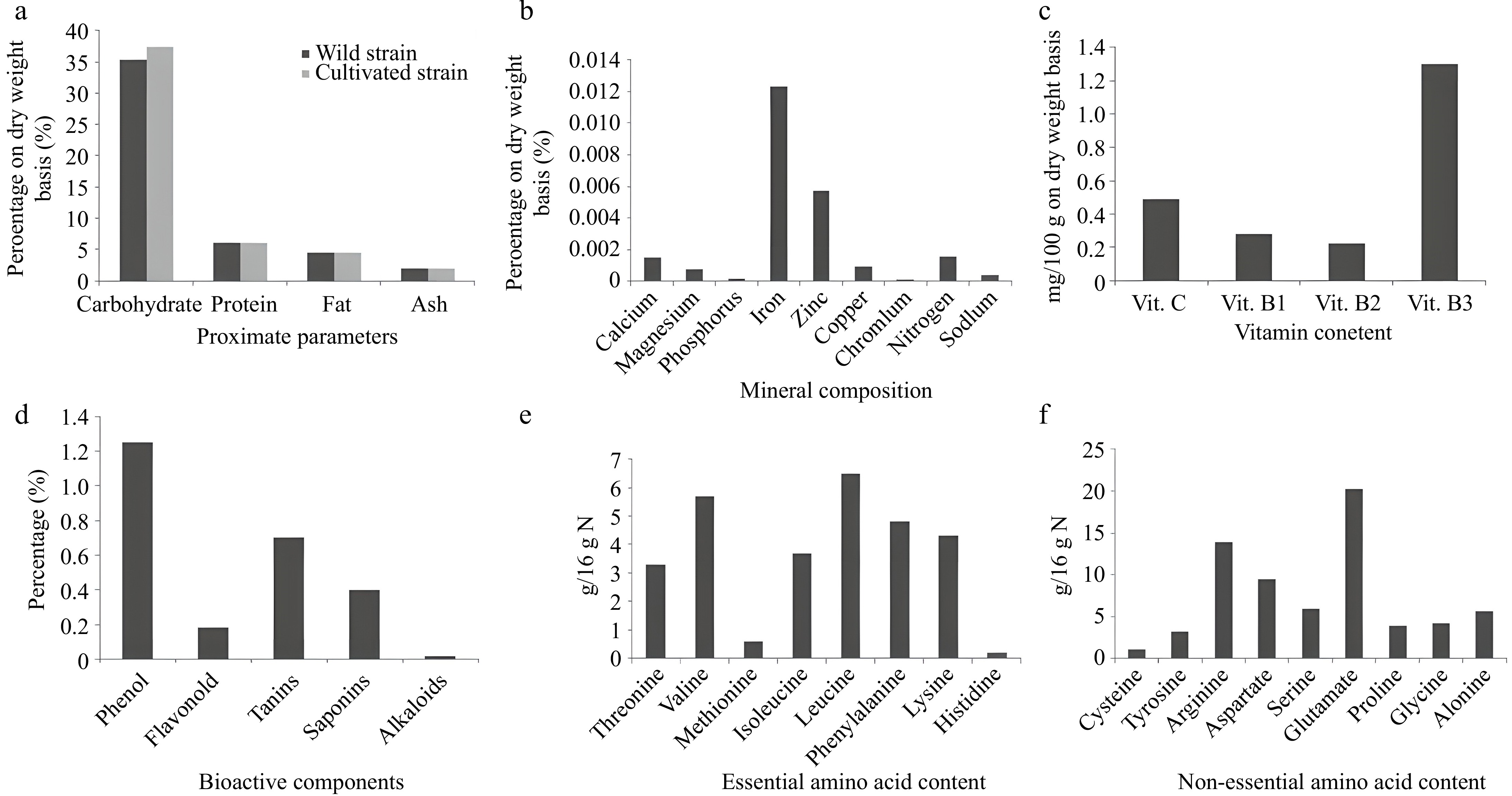
Figure 5.
(a) Comparative analysis of the proximate composition of wild vs cultivated strains of S. commune. (b) Mineral composition. (c) Vitamin concentration. (d) Bioactive component composition. (e) Essential amino acid composition. (f) Non-essential amino acid composition of S. commune[32,51−54].
-
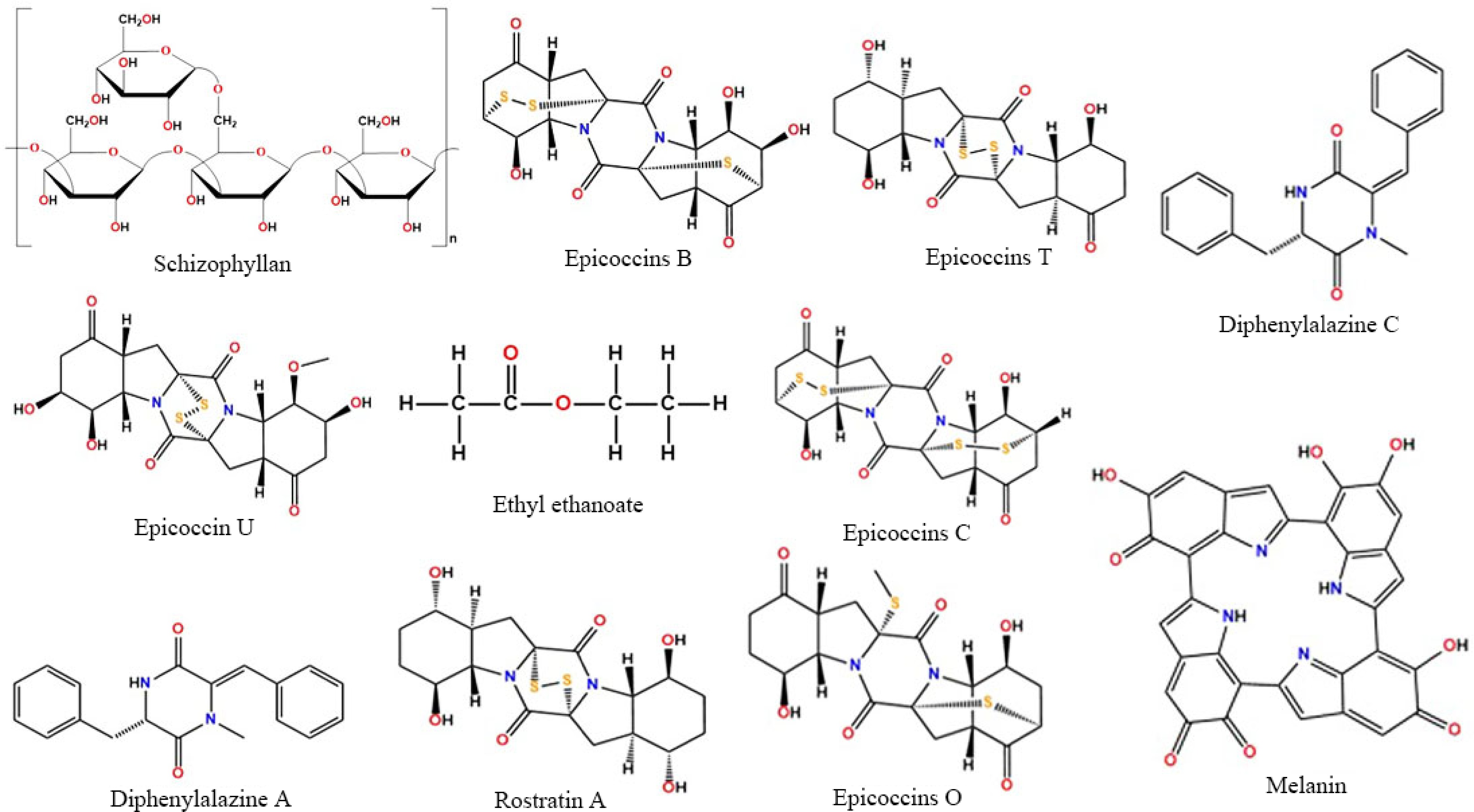
Figure 6.
Chemical structure of some bio-active constituents obtained from S. commune.
-
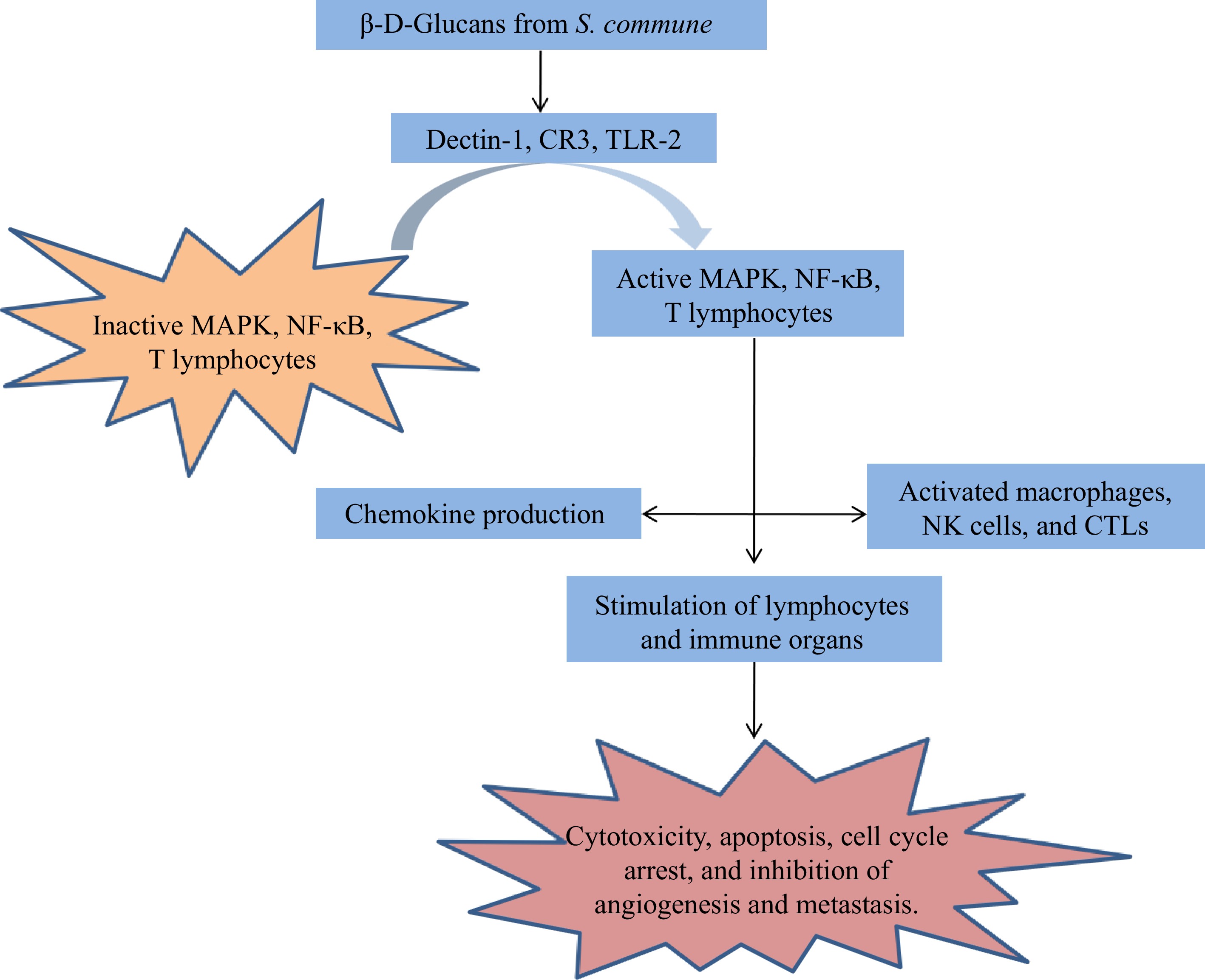
Figure 7.
Probable mode of action of β-D-Glucan against cancer[84].
-
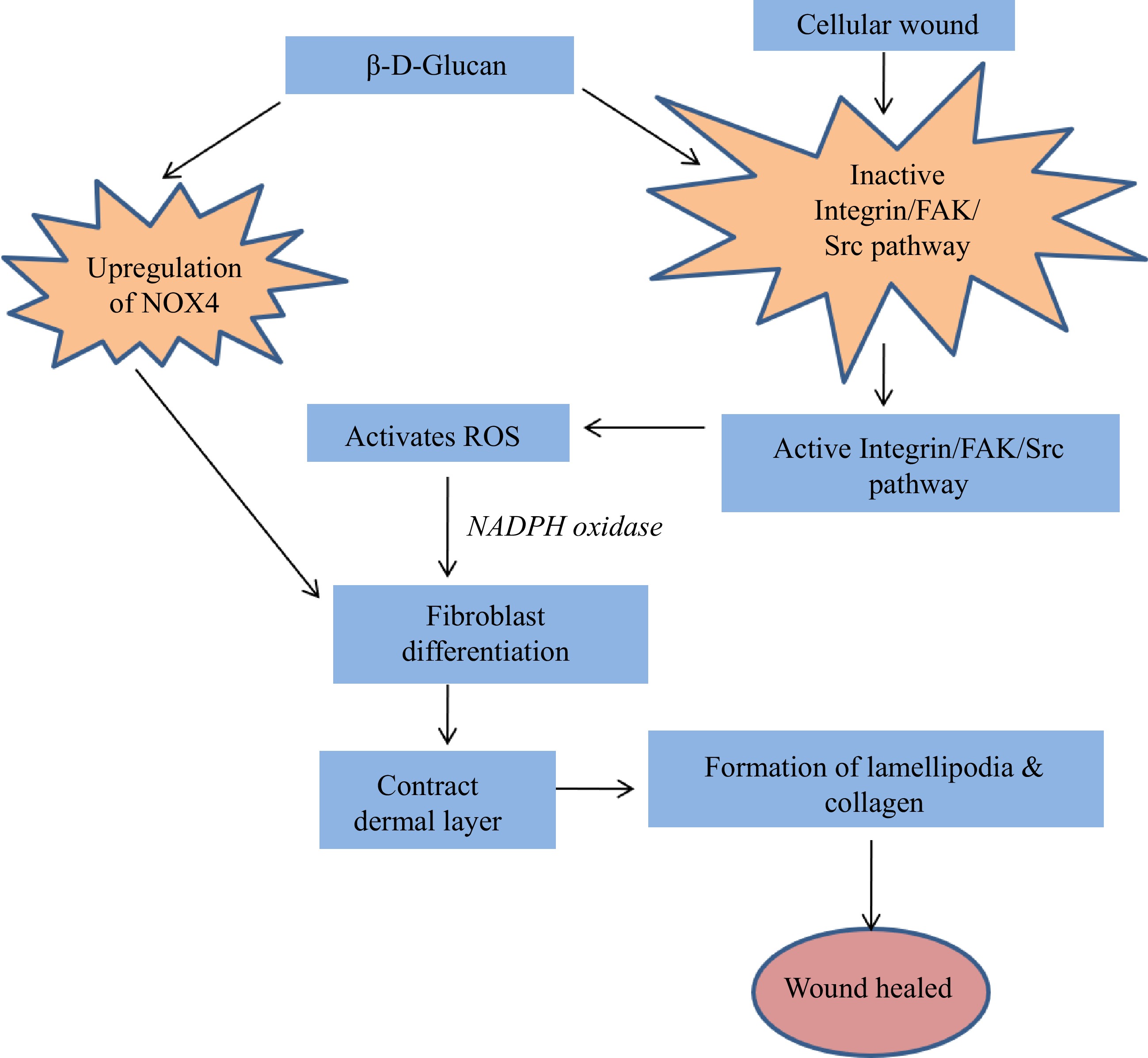
Figure 8.
Wound healing efficacy of β-D-Glucan obtained from S. commune[95].
-
Fatty acids Structures Percentage (%)
based on
btotal fatPalmitic acid (16C) CH3-(CH2)14-COOH 20.8 Stearic acid (18C) CH3-(CH2)16-COOH 2.5 Arachidic acid (20C) CH3-(CH2)18-COOH 0.2 Oleic acid (18:1) CH3-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH 10.4 Linoleic acid (18:2) CH3-(CH2)3-(CH2-CH=CH)2-( CH2)7-COOH 61.3 Linolenic acid (18:3) CH3-(CH2-CH=CH)3-(CH2)7-COOH 4.8 Table 1.
Depiction of the fatty acid content of split fungus[51].
-
Sl. No. Crude extracts Pharmaceutical properties Mechanism of action Ref. a) Ethanolic extract Antioxidant Largest exposed tissue system to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the skin which is very much susceptible to biological stress caused by ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species), and this will promote early aging and overproduction of melanin. Here comes the role of antioxidants. Ethanol extracted from S. commune exhibit antioxidant property which can delay senescence and inhibit excess melanin formation. [68] Anti-tyrosinase Phenol oxidase or Tyrosinase is the precursor for melanin production, and overproduction leads to hyperpigmentation. Kojic acid is known to be the most efficient tyrosinase inhibitor. Split gill fungi also possess a certain amount of ethanol, which is also effective against phenol oxidase to some extent. [68,69] Anti-acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase (AchE) is an Alzheimer's disease (AD) promoting agent. The ethanol (EtOH) and polysaccharide (PSH) extracted from S. commune can efficiently inhibit the formation of AchE and reduce the chance of developing Alzheimer's disease. [70] b) Methanolic extract Antidiabetic Patients with diabetes may suffer from an array of clinical disorders, such as coronary, renal, cardiovascular, and peripheral vascular diseases. In recent days, methanol extract from split fungi has been demonstrated to have anti-diabetic activity with phytochemical validation. Accordingly, it could be a great natural alternative to synthetic anti-diabetic drugs. [38] c) Methanol, Ethyl acetate and Dichloromethane Anti-microbial Extracts of split gill fungi, i.e., Methanol, Ethyl acetate, and Dichloromethene, showed impressive results against the growth of numerous common pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli, Shigella flexneri, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus subtilis) and fungi (Yeast, Candida parapsilosis). However, Dichloro-methane showed the best results against microbial growth, whereas the other showed moderate activity. [60] d) Exopolysaccharide Anti-inflammatory The anti-inflammatory effect of exopolysaccharide obtained from split gill fungus was determined by its helical structure and molecular weight. It was reported that high—and medium-molecular-weight exopolysaccharide is effective against intestinal inflammations. [71] e) Ethanol (EtOH) and Polysaccharide (PSH) Anti-Alzheimer Both EtOH and PSH extracted from S. commune showed preventive effect against Alzheimer's disease (AD) through the production of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors. However, the activity of PSH extraction showed comparatively greater efficiency. [70] f) Dichloromethane Anti-bacterial Crude extract of S. commune containing Dichloromethane showed excellent efficacy against certain gram (+) bacteria like Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus aureus. Thus, the mycelia of this mushroom have antibacterial drug-yielding potential. [72] g) Ethyl acetate or ethyl ethanoate(C4H8O2) Anti-diabetic Ethyl acetate extracted from S. commune has potential inhibitory activity against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in Wistar rats. Ethyl Ethanoate can cause a significant decrease in the blood sugar level and an increase in body weight in just 14 d after application. [73] Table 2.
Representation of a few crude extracts obtained from split gill fungus along with their working mechanism.
-
Sl. No. Immuno-
modulatorvx dfsTreated for/ pharmaceutical properties Mechanism of action Ref. a) Sizofilan (SPG)/
Sizofiran/
SchizophyllanHead and neck cancer Therapeutic effect of Sziofilan (SPG) can increase the recovery rate of cellular immunity, hazarded by radiation, surgical methods and chemotherapy. Mainly effective against neck and head cancer. [74] Ovarian adenocarcinoma and carcinoma, SPG can decrease the growth rate of tumors in combination with cisplatin, when given prior to photodynamic therapy, in ovarian adenocarcinoma of rats and carcinoma in mice. [75,76] fibrosarcoma, and bladder cancer The reduction of growth rate and metastatic foci in squamous-cells and an increase in survival time could be observed by the activity of SPG against bladder cancer and fibrosarcoma in mice. [77,78] Anti-tumor Two cytokines i.e., Interferon- γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin 2 (IL 2) produced by Scizophyllan are found to be increased in the culture medium of phytohemagglutin (PHA)- or concanavalin A (Con A)- stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were measured by radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This evidence suggests the anti-tumor activity of Schizophyllan. [79] Anti-hepatotoxicity The beneficial role of Schizophyllan against chronic Hepatites B could be observed due to its increased immunological responsiveness to the virus, specifically in IFN-γ production. [80] Cervical carcinoma Sizofiran activity can increase the survival rate of human cervical carcinoma when combined with 5-fluorouracin after radiotherapy. Sizofiran is an immunotherapeutic agent for cervical carcinoma because it stimulates a rapid recovery of the immunogenic parameters by radiotherapy. [81] Protective against chemotherapy and radiation After treating the bone marrow with chemotherapy or radiation, Sizofiran can reinstate cell mitosis and lower the sister chromatid exchange in mice. [82] Sizofiran can partially protect mice's bone marrow's Natural Killer (NK) activity after treatment with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). [83] b) Lectin Cytotoxic activity A glycoprotein, viz., lectin obtained from S. commune (SCL), showed high cytotoxic activity against epidermal carcinoma in humans. [62] Mitogenic activity Lectin also possesses mitogenic activity against mouse splenocytes, and its inhibition was maximum at a concentration of 4 μM. [13] c) Schizocommunin Anti-lymphoma Schizocommunin is an indole derivative extracted from a liquid culture of split gill fungi. It has established strong cytotoxic activity against murine lymphoma cells. [63] d) Diphenylalazine C
and Epicoccin UCytotoxic activity The cytotoxic activities of these two biopolymers were assayed by the MTT method against human gastric cancer, human leukaemia, and human myelogenous leukaemia. The results were positive, as they possess mild cytotoxicity against these cell lines. [67] d) β-D-Glucans Anti- cancerous β-D-Glucans extracted from split gill fungi are known to fight against cancers by modulating both innate (nonspecific) and adaptive (specific) immune systems. [84] e) Extracellular melanin Antioxidant Comparatively, a lower concentration of extracellular melanin shows a high free radical scavenging activity of DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl), which indicates the presence of antioxidant properties in S. commune. [85] Epidermoid larynx carcinoma Melanin also shows visible positive impact on inhibition of cellular proliferation of human epidermoid larynx carcinoma cell line (HEP-2). [85] Table 3.
Representation of some immuno-modulators along with their working principle.
-
Sl. No. Bio-active
compoundsPharmaceutical properties Mechanism of action Ref. a) Sizofilan (SPG)/
Sizofiran/
SchizophyllanAnti-viral Sendai virus infection and Kuruma shrimp with Penaeus japonicas virus infection in mice showed high survival rates and phagocytic activity when treated with SPG. It has visible positive effect against certain viral diseases. [86,87] Anti-inflammatory SPG shows a positive inhibitory effect against inflammation in murine macrophages. This property makes SPG useful for treating some periodontal issues. [88] Anti-fungal Schizophyllan can control the activity of Candida albicans (candida static activity), an allergic fungus, in mice. [89] UV photo-protectant and anti-aging Schizophyllan is well known for its protective activity against UV radiation, anti-inflammatory effect on the skin, and anti-aging properties. [90] prebiotic The growth and development of gut microbiota and its associated metabolic functions are influenced by the prebiotic activity of 1,3-β-D-Glucan. Dietary interference with prebiotic activity will also increase total bacterial abundance and metabolisms related to host immune strengthening. [91] b) Lectin Anti-viral Lectin can inhibit certain pathogenic viruses. It can target multiple stages of the viral life cycle, such as viral penetration, attachment to the host cell, and replication inside the host. [92] The inhibitory activity of lectin has already been proven. However, it also possesses inhibitory activity against HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. As a result, lectin can be used for the treatment of HIV in the future. [13] c) Flavonoid Anti-hyperlipidemic Flavonoid from S. commune has an inhibitory effect on hyperlipidemia. A significant change in lipid profile marker parameters (Total cholesterol, Triglycerides, LDL, HDL cholesterol) level was observed when hyperlipidemic rats with high-fat diet (HFD) were treated with flavonoid extract of split fungi. [93] Anti-hypothyroidism Induced hypothyroidism in rats by applying 0.1% Aminotriazole can be controlled by applying flavanoid extract of S. commune. Though there was no change in T3 level, a significant increase in T4 and TSH levels could be observed after treatment, which indicates a positive impact on hypothyroidism. d) Sesquiterpenes Anti-fungal and anti-bacterial Sesquiterpene, a volatile substance extracted from split gill fungi, can inhibit bacterial and fungal growth and is effective against wood-decaying fungi and bacteria. [94] e) Epicoccin U and Diphenylalazine C Antimicrobial Epicoccin U and Diphenylalazine C can significantly show their antifungal and antibacterial effects. Though it is considered to be a weak inhibitor, it is still effective against Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus. [67] f) β-D-Glucan Wound healing activity One of the main constituents of the cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and cereals is β-D-Glucan. As we already know, S. commune can produce β-D-Glucan, which has a significant role in wound healing through the migration of keratinocytes or fibroblasts. [95] g) Extracellular melanin Anti-microbial At a high concentration, melanin can act as an antimicrobial component. It showed a significant inhibitory effect against E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Psuedomonas flurescens. Melanin is also effective against pathogenic fungi, such as Trichophyton simiii and T. rubrum. [85] Table 4.
Overview of bioactive components obtained from S. commune and their medicinal properties and working mechanism.
Figures
(8)
Tables
(4)