-
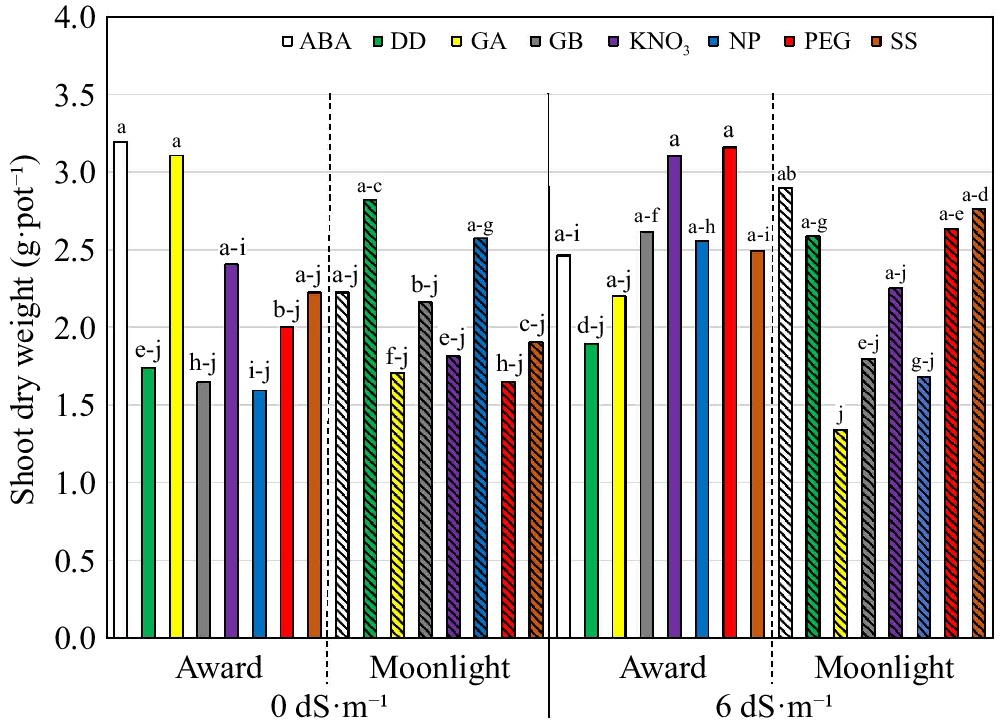
Figure 1.
Shoot dry weight (g·pot−1) of 'Award' and 'Moonlight' (hashed) Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by the cultivar × growing condition × priming interaction. The priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05).
-
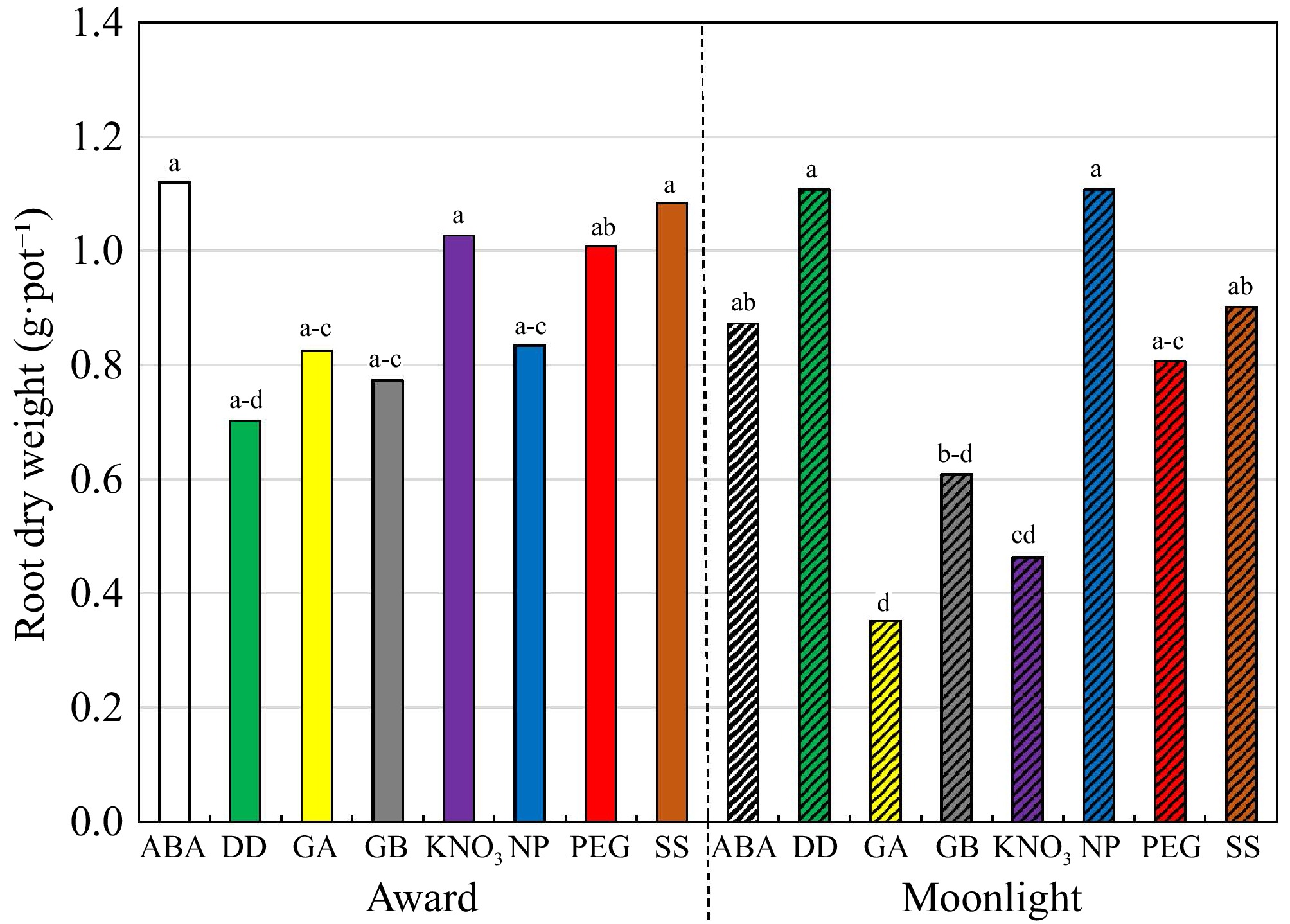
Figure 2.
Root dry weight (g·pot−1) of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by the cultivar × priming interaction when data were pooled across salinity. The priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05).
-
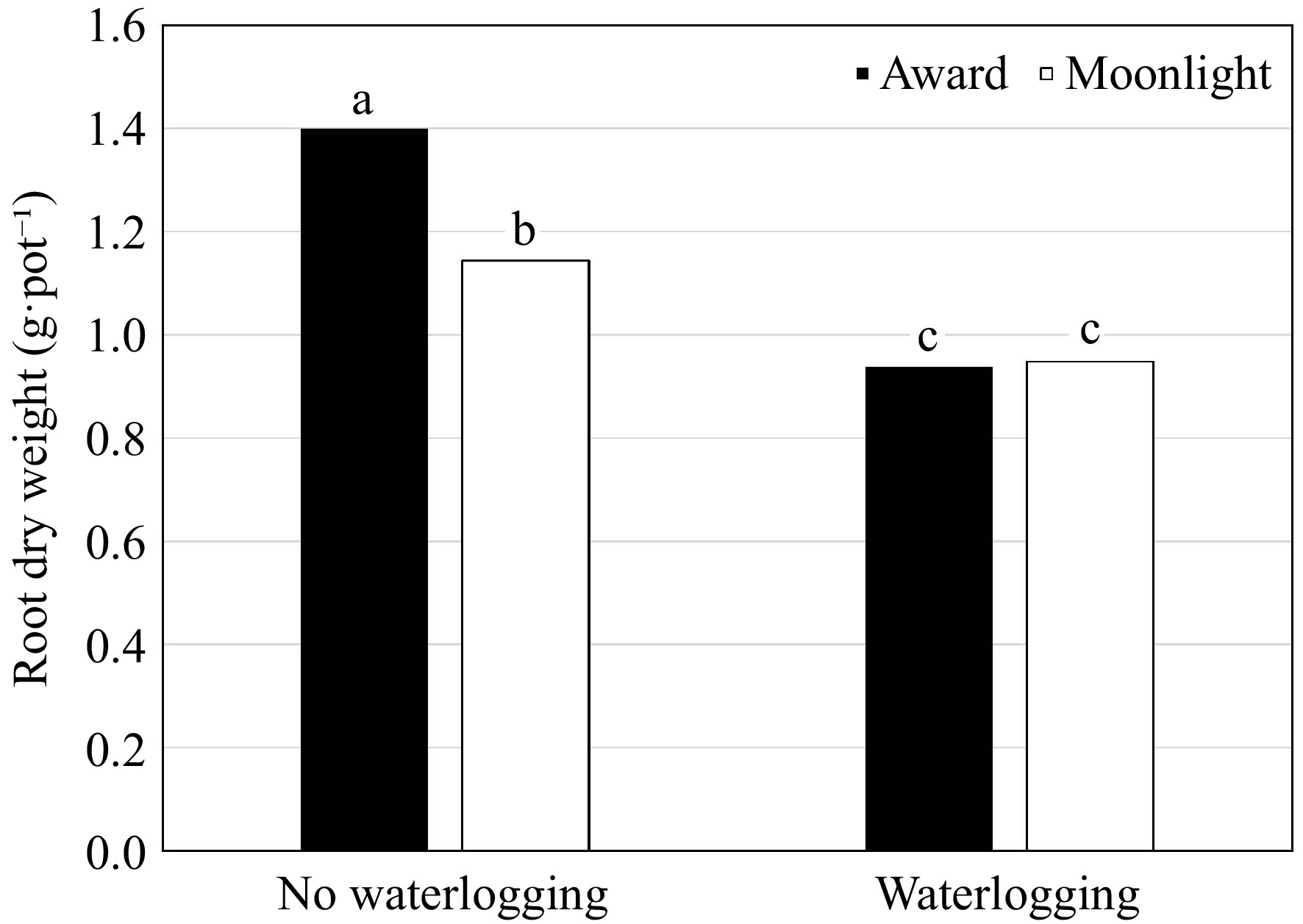
Figure 3.
Root dry weight (g·pot−1) of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by the cultivar × waterlogging interaction when data were pooled across priming treatments. Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05).
-
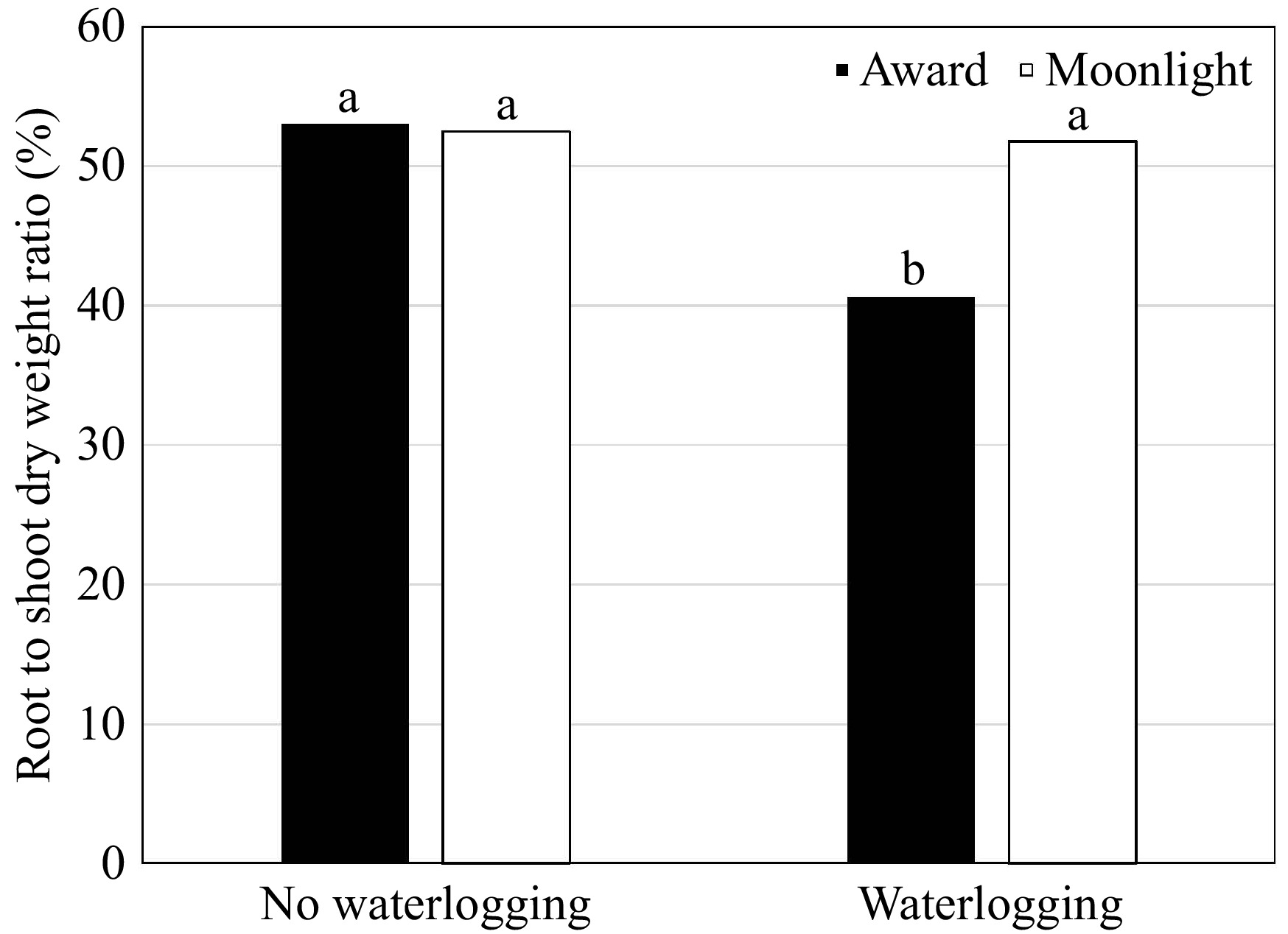
Figure 4.
Root to shoot dry weight ratio (%) of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by the cultivar × waterlogging interaction when data were pooled across priming treatments. Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05).
-
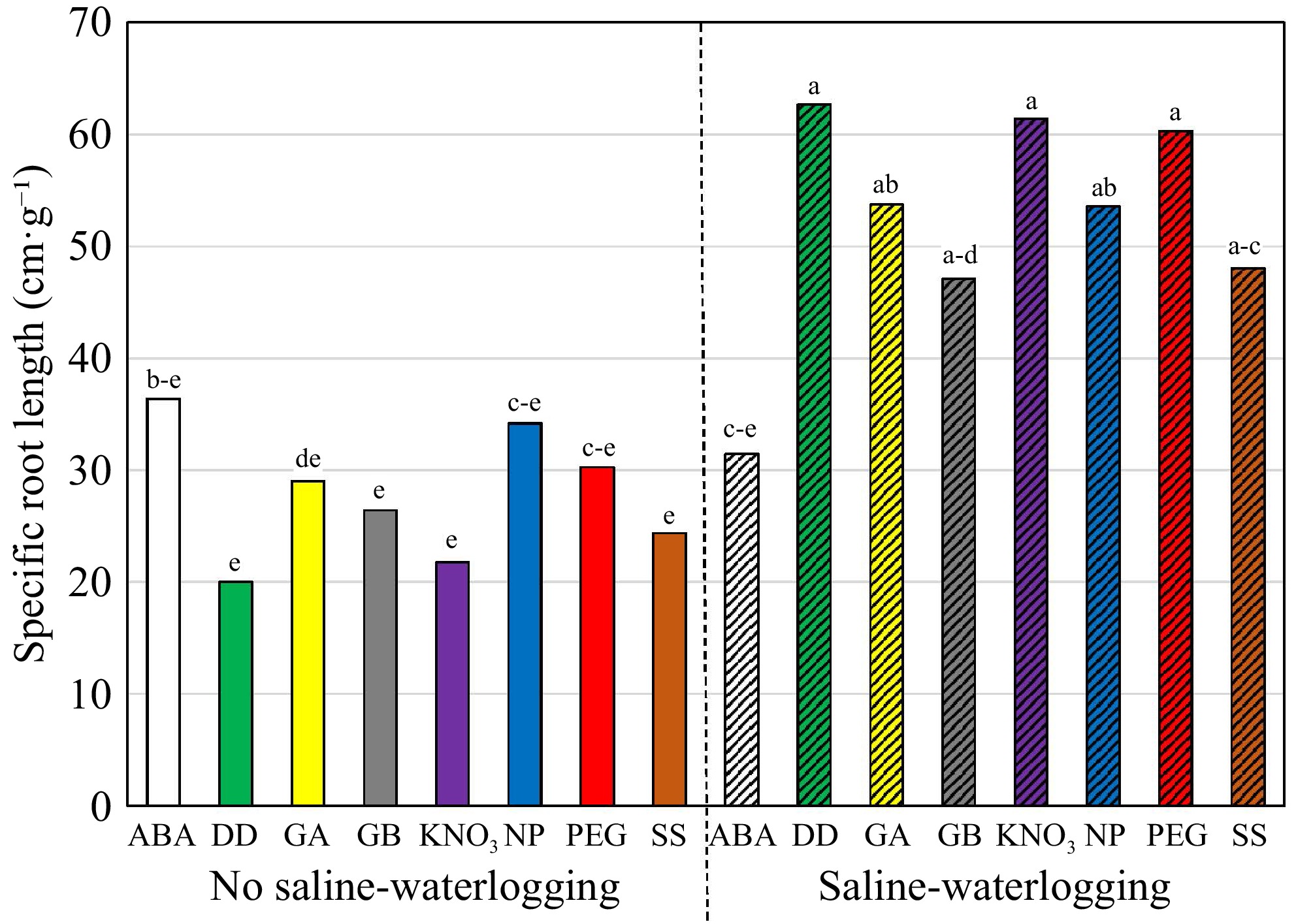
Figure 5.
Specific root length (cm·g−1) of Kentucky bluegrass seedling as affected by the growing condition × priming interaction when data were pooled across cultivars. The priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05).
-
Priming solution Stress Ref, Deionized, distilled water (DD) Saline, drought, low temperature [12,14] KNO3 (500 ppm) Saline, drought [12] Polyethylene glycol-6000 (PEG, 20%) Drought [15] Glycinebetaine (GB, 100 mM) Saline, drought [8] Abscisic acid (ABA, 50 ppm) Drought [16] Gibberellic acid (GA, 100 ppm) Drought [16] Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (SS, 1:1, w:w,
3 dS·m−1)Table 1.
Priming solutions showed enhanced stress tolerance in previous research.
-
Expt 1 – salinity Expt 2 – waterlogging Expt 3 – saline-waterlogging Control Salinityz Control Waterloggingz Control Saline-waterloggingz Soil ECe (dS·m−1) 1.38 2.31 1.34 1.27 1.35 2.47 Soil pH 8.02 8.13 8.20 8.04 8.13 8.05 zSalinity stress was induced by salt irritation (a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 mixture, 1:1, w:w) at 6 dS·m−1; waterlogging was induced by keeping excessive tap water (~0.5 cm above soil surface) in experimental pots; saline-waterlogging was induced by keeping excessive salt solution (a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 mixture, 1:1, w:w, 6 dS·m−1) (~0.5 cm above soil surface) in experimental pots. Table 2.
Soil salinity (electrical conductivity from saturated soil paste, ECe) and pH of each experiment.
-
Treatment Shoot dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root to shoot ratio (%) Root length (cm) Specific root length
(cm·g−1)Salinity (S, dS·m−1) 0 2.20ay 0.86a 37.3a 20.6a 42.1a 6 2.40a 0.84a 33.6a 18.6b 39.6a p-value nsx ns ns * ns Cultivar (C) Award 2.43a 0.92a 36.4a 20.1a 40.5a Moonlight 2.18b 0.78a 34.5a 19.2a 41.1a p-value * ns ns ns ns Primingz (P) ABA 2.80a 1.00a 36.7a-c 19.2a 23.9a GB 2.05a 0.69bc 33.1bd 19.8a 37.0a NP 2.10a 0.97ab 43.0a 20.8a 30.4a DD 2.26a 0.90ab 37.4a-c 20.1a 40.4a GA 2.09a 0.59c 26.2d 17.6a 74.6a KNO3 2.39a 0.74a-c 28.6cd 19.9a 53.8a PEG 2.36a 0.91ab 37.9ab 21.0a 29.1a SS 2.35a 0.99a 40.6ab 18.6a 37.5a p-value ns * * ns ns C × P * * ns ns ns C × S ns ns ns ns ns P × S * ns ns ns ns C × P × S * ns ns ns ns zThe priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). yMeans in a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05). xns and * mean no significant differences and significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, respectively. Table 3.
Growth response of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by salinity [induced by a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 mixture (1:1, w:w)], cultivar, and priming solutions.
-
Treatment Shoot dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root to shoot ratio (%) Root length (cm) Specific root length (cm·g−1) Waterlogging (W) Non-waterlogged 2.41ay 1.28a 52.8a 22.0a 19.8b Waterlogged 2.16b 0.94b 46.2b 20.9a 26.2a p-value * * * nsx * Cultivar (C) Award 2.53a 1.17a 46.8b 21.4a 21.9a Moonlight 2.04b 1.05b 52.1a 21.5a 24.1a p-value * * * ns ns Primingz (P) ABA 2.33a 1.28a 54.8a 22.8a 22.4a GB 2.27a 1.12a 50.9a 22.3a 24.9a DD 2.57a 1.09a 44.6a 22.8a 24.3a GA 2.27a 1.08a 49.2a 21.6a 24.4a KNO3 2.46a 1.15a 49.0a 22.6a 20.9a NP 1.86a 0.90a 48.8a 19.8a 23.7a PEG 2.31a 1.15a 49.6a 20.5a 22.0a SS 2.21a 1.08a 49.0a 19.4a 21.5a p-value ns ns ns ns ns C × P ns ns ns ns ns C × W ns * * ns ns P × W ns ns ns ns ns C × P × W ns ns ns ns ns zThe priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). yMeans in a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05). xns and * mean no significant differences and significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, respectively. Table 4.
Growth response of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by waterlogging, cultivar, and priming solutions.
-
Treatment Shoot dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root dry weight
(g·pot−1)Root to shoot ratio (%) Root length (cm) Specific root length (cm·g−1) Saline-waterlogging (SW) Non-saline-waterlogged 1.86ay 0.81a 47.0a 19.8a 27.8b Saline-waterlogged 1.32b 0.43b 36.5b 18.8a 52.3a p-value * * * nsx * Cultivar (C) Award 1.87a 0.66a 38.0b 19.6a 37.1a Moonlight 1.31b 0.58b 45.5a 19.0a 43.0a p-value * * * ns ns Primingz (P) ABA 1.64ab 0.58a 37.5b 18.0a 33.9a GB 1.61a−c 0.70a 44.8a 19.2a 36.8a NP 1.76ab 0.61a 37.2b 19.4a 43.9a DD 1.41bc 0.68a 49.6a 20.4a 41.3a GA 1.17c 0.56a 47.5a 17.9a 41.4a KNO3 1.88a 0.59a 34.6b 18.5a 41.6a PEG 1.31bc 0.60a 47.7a 22.1a 45.3a SS 1.94a 0.63a 35.1b 18.9a 36.2a p-value * ns * ns ns C × P ns ns ns ns ns C × SW ns ns ns ns ns P × SW ns ns ns ns * C × P × SW ns ns ns ns ns zThe priming treatments are: abscisic acid at 50 ppm (ABA), glycinebetaine at 100 mM (GB), no priming (NP), deionized and distilled water (DD), gibberellic acid at 100 ppm (GA), KNO3 at 500 ppm (KNO3), polyethylene glycol-6,000 at 20% (PEG), and a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 (1:1, w:w) at 3 dS·m−1 (SS). yMeans in a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Fisher's protected least significant difference test (p ≤ 0.05). xns and * mean no significant differences and significant differences at p ≤ 0.05, respectively. Table 5.
Growth response of Kentucky bluegrass seedlings as affected by saline-waterlogging [induced by waterlog plants using a Na2SO4 + MgSO4 mixture (1:1, w:w, 6 dS·m−1)], cultivar, and priming solutions.
Figures
(5)
Tables
(5)