-
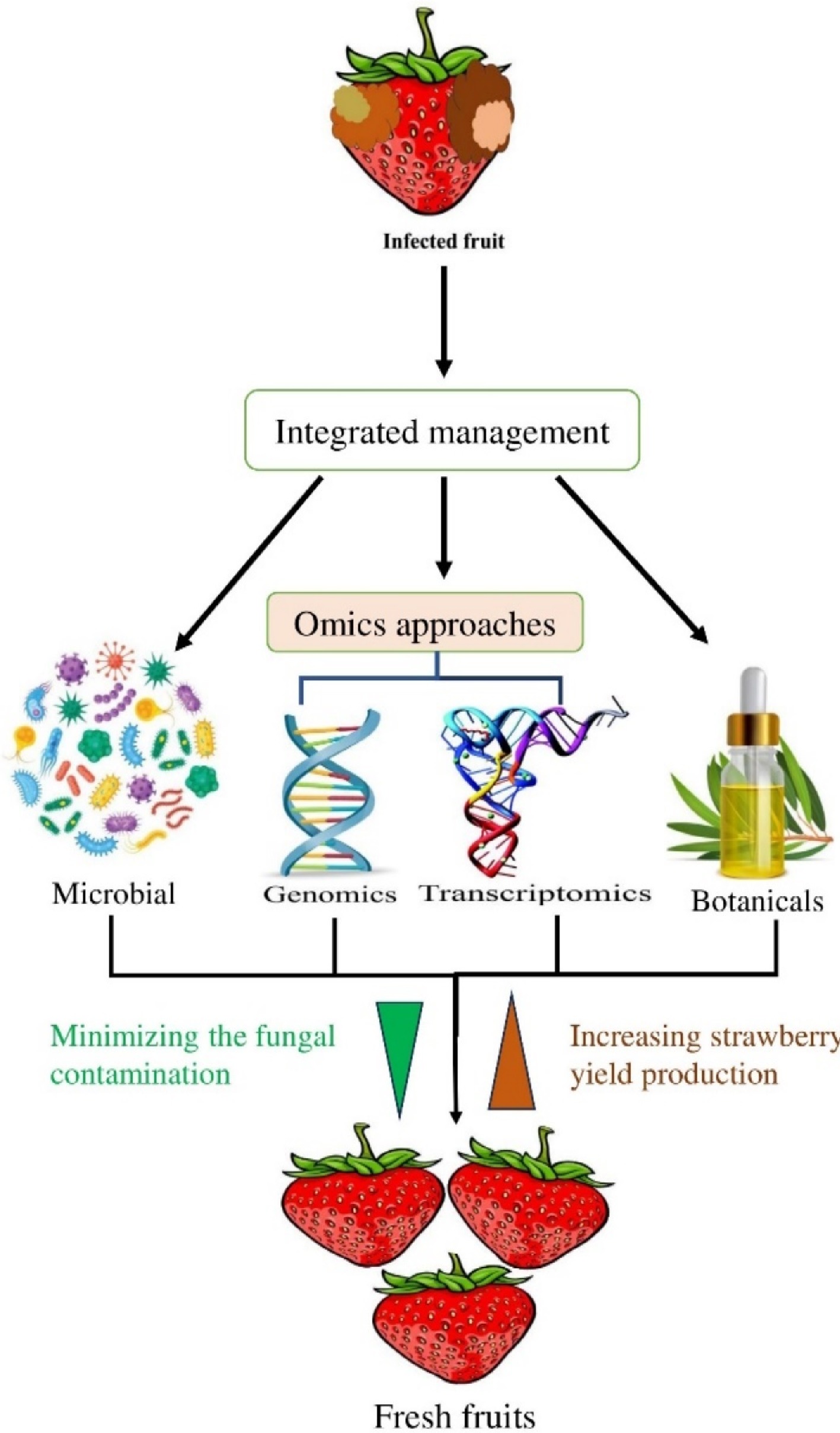
Figure 1.
Illustration showing integrated approaches for managing strawberry fruit rot diseases.
-
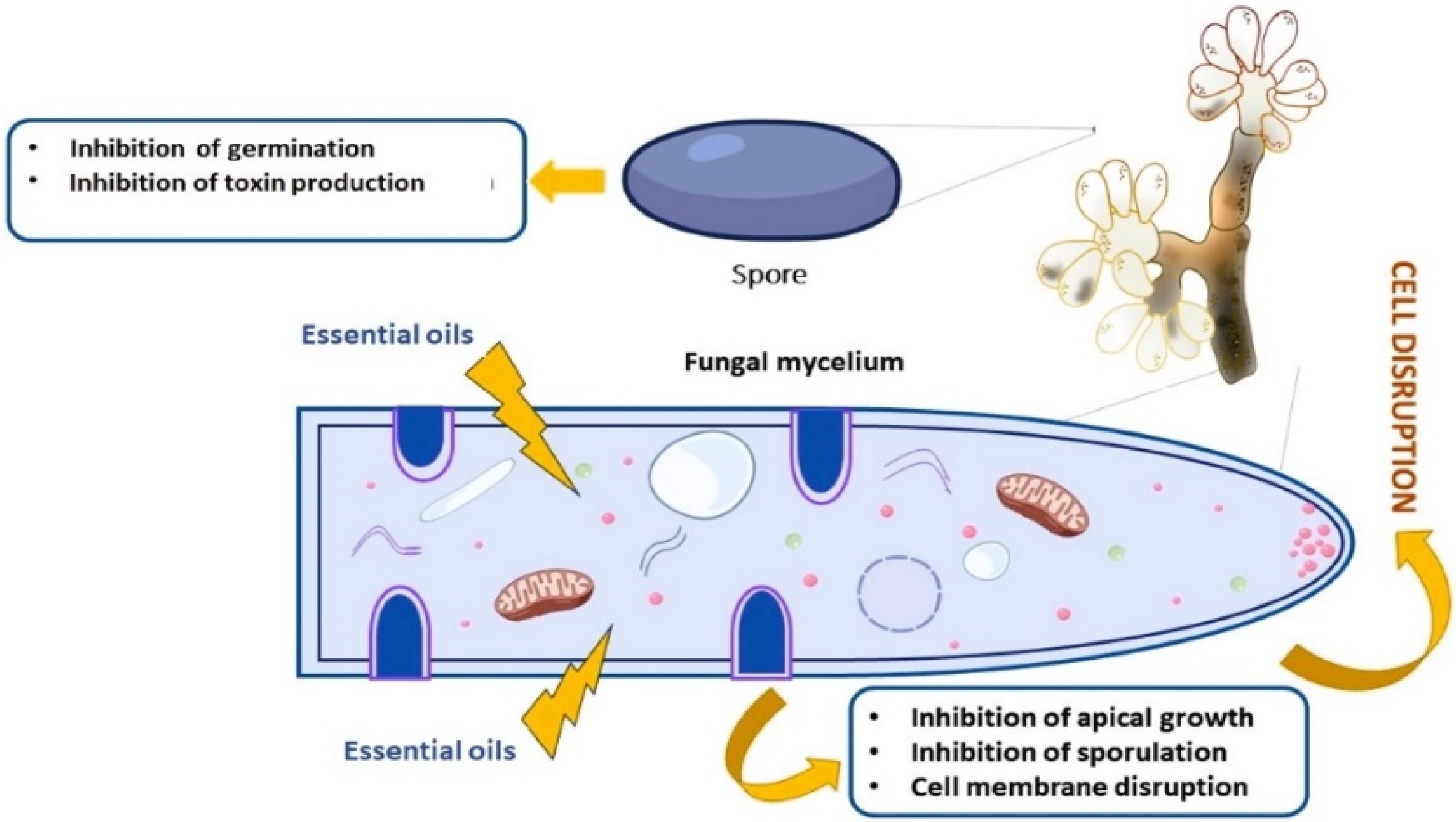
Figure 2.
Illustration showing the mode of action of essential oils against fungal pathogens.
-
Diseases Pathogens Symptoms Countries Ref. Anthracnose Colletotrichum acutatum Dark and sunken spots appeared on both green and ripe fruit, which can enlarge and become hard, dry, and shriveled, eventually forming mummified fruits. USA [11] Colletotrichum siamense China [12] Gray mold Botrytis cinerea Soft light brown lesions, often starting at the stem end or other diseased parts or where the fruit contacts with soil, eventually turning into a mummified, gray, powdery mass. China [12] Botrytis fabiopsis China [12] Botrytis fragariae USA [13] Leather rot Phytophthora cactorum Infected green fruit develop dark-brown, firm spots that can expand and cover the entire berry. The infected areas become tough and leathery. Florida [14] Phytophthora nicoteanae Phytophthora citricola Poland [15] Black rot/Leak rot/
Rhizopus rotRhizopus stolonifera Water-soaked, discolored spots that rapidly enlarge, causing the fruit to become limp, brown, and leak its contents, often covered with a white mycelium with black sporangia. Italy [16] Rhizopus nigricans China [17] Penicillium fruit rot Penicillium citrinum A soft, watery rot with a sharp boundary between healthy and disease tissue, sometimes showing blue-green spore masses and an earthy, musty odor. Egypt [18] Penicillium digitatum China [19] Aspergillus fruit rot Aspergillus flavus Fruits become discolored, water-soaked spots that become tan to dark brown and may eventually mummify and become black. Egypt [19] Aspergillus niger Strawberry fruit rot Calonectria fragariae Lesions may be surrounded by pale-orange colored spore masses. Brazil [20] Sour rot Geotrichum candidum Water-soaked, soft rot, a sour smell, and white mycelium on the fruit surface. China [21] Strawberry fruit rot Neopestalotiopsis iranensis sunken, tan lesions with abundant black spores appear on the fruit surface. Iran [22] Neopestalotiopsis mesopotamica Alternaria fruit rot Alternaria alternata Sunken, dark lesion appears near the calyx end of the fruit. These lesions are covered by a dark green velvety growth. Infected fruit becomes soft and
shriveled.Oman [23] India [24] China [12] Alternaria tenuissima China [12] Blossom blight Cladosporium cladosporioides Infections first appear as soft, sunken, water-soaked lesions on the fruit, later a grayish, fuzzy coating or web produced by the fungus; infected fruit can shrivel and become dry and mummified. Korea [25] Cladosporium tenuissimum Fusarium fruit rot Fusarium graminearum Fusarium wilt primarily affects the plant and not the fruit directly, but infected plants may have reduced fruit production. Infected berry eventually desiccate, turning hard and black. China [12] Fusarium incarnatum Fusarium ipomoeae Fusarium proliferatum Table 1.
Exhibited strawberry fruit rot diseases with causal agents reported in various countries.
-
Disease Pathogens Essential oils Plant part use Effective dose Ref. Grey mold Botrytis cinerea Origanum onites L. Leaves 1.00 mL·L−1 [66] Ziziphora clinopodioides L. Leaves and flowers 2.00 mL·L−1 Thymus vulgaris Leaves and flowers 0.021% [67] Mentha longifolia Leaves 0.021% Mentha spicata Leaves 10% [68] Cymbopogon martini Leaves and flowers 10% Origanum heracleoticum Leaves and flowers 100 μL·L−1 [69] Thymus vulgraris Leaves and flowers 100 μL·L−1 Syzygium aromaticum Dried flower buds 92.56 μL·L−1 [70] Brassica nigra Seeds 15.42 μL·L−1 Solidago canadensis Inflorescence 0.1 mL·L−1 [71] Zataria multiflora Leaves 1,500 ppm [72] Leak mold Rhizopus stolonifera Mentha spicata Leaves 10% [68] Cymbopogon martini Leaves and flowers 10% Pelargonium graveolens Leaves 625 μL·L−1 [73] Cymbopogon citratus Leaves 500 μL·L−1 Foeniculum vulgare Seeds 800 μL·L−1 [74] Nigella sativa Seeds 800 μL·L−1 Pimpinella anisum Seeds 800 μL·L−1 Anthracnose Colletotrichum spp. Mentha longifolia Leaves and shoots − [75] Allium sativum Bulbs 1,700 μL·L−1 [65] Rosmarinus officinalis Leaves and flowers 700 μL·L−1 Cinnamon zeylanicum Inner bark 301.152 μL·L−1 [76] Satureja khuzestanica Leaves and flowers 550.803 μL·L−1 Aloysia citriodora Leaves − [77] Lippia alba Leaves − Ocimum americanum Leaves − Table 2.
Showing beneficial plant volatiles against fungal pathogens of strawberry fruit.
-
Disease Pathogens Plant extract Plant part use Effective dose Ref. Gray mold Botrytis cinerea Coriandrum sativum Seeds 0.0312 g·mL−1 [82] Cinnamon zeylanicum Inner bark 800 μL·L−1 [85] Azadirachta indica Leaves 15% w/v [86] Syzygium aromaticum Dried flower buds 600 μL·L−1 [87] Silene uniflora Leaves and flowers 1500 μg·mL−1 [88] Allium sativum Bulb 20% [89] Origanum majorana Leaves and flowers 20% Thymus vulgaris Leaves and flowers 20% Leak rot Rhizopus stolonifer Laminaria digitata Dry thallus 30 g·L−1 [90] Euphorbia tirucalli Latex and stem bark − [91] Citrus sinensis Peels − [92] Crocus sativum Petals 235.15 μL·L−1 [93] Eucalyptus Leaves 30% [67] Anthracnose Colletotrichum spp. Piper betle Leaves 100% [94] Azadirachta indica Leaves 10,000 μL·L−1 [95] Cinnamomun zeylanicum Inner bark − [96] Melissa officinalis Leaves 20% w/v [97] Origanum vulgare Leaves and flowers 20% w/v Datura stramonium Whole plant 25% w/v [98] Allium sativum Bulb 25% w/v Lawsonia inermis Leaves 25% w/v Table 3.
Effective plant extracts against fungal pathogens of strawberry fruit rot.
Figures
(2)
Tables
(3)